No irrigation and sizeable water resources: Bordeaux is well supplied with water thanks to an oceanic climate that offers generous rainfall, an advantage to offset global warming and drought.
• 1st organic AOC vineyard in France in size
• 23% of the surface area of Bordeaux managed organically
• 25,300 hectares
• +27% increase in surface area in 1 year
• 2 391 hectares certified
In 2022, more than 75% of the Bordeaux vineyards are certified by an environmental approach HVE high environmental value
• 98 estates out of 192 certified in Europe
• 1st HVE department in France
• Approximately 50,000 hectares certified HVE
• Almost 50% of the surface area of Bordeaux
• +162% in the past 2 years




Paris
French national strategy
French national strategy
• - 20% of emissions by 2030 compared to 2015
• - 20% of emissions by 2030 compared to 2015

• - 46% of emissions by 2050 compared to 2015
• - 46% of emissions by 2050 compared to 2015
Glass and packaging Continue with glassmakers to reduce the impact of bottles (= 63% of the incoming materials), develop eco-design and new distribution models.
Freight Strengthen collective actions to reduce the impact of freight (=19% of the overall carbon footprint), especially downstream, through increased dialogue with carriers





fioul)
efficiency
Identify, test and deploy alternatives to reduce farm fuel consumption and input use. (Fuel oil = 70% of the energy)
and facilitate access to energy efficiency solutions
Avoiding emissions, storing carbon, producing renewable energy to generate new business and income





And has side effects on the reduction of GhG emissions by :
• reducing the number of interventions and passages in the vineyards
- reducing the use of pesticides


- sexual confusion
- project : introduction of disease resistant grape varieties (existing grape varieties and those of the Newvine project)
• store carbon
Biodiversity (fauna and flora) provides natural solutions: soil microbiology, regulation of vine pests, etc.


















- domestic bees / 1,000 species of wild pollinators - spiders, butterflies, beetles…

• Broad sense:
• The vine is hermaphroditic but the presence of insects is necessary for the balance of ecosystems.
• A sign of a healthy environment.

The natural regulation of vine pests
Helping to reduce the development of weeds by devouring their seeds
carabid beetles)
improvement
of organic matter
winegrowers modify their viticultural practices and technical itineraries
enhance diversity of species & the size of their community)

study to guide them :
project
plots studied since 2015
of biodiversity in vineyard landscapes
organic and conventional plots
the regulation of pests)

1 -Organic farming enhanced the proliferation of springtails & spider
2 - Organic farming had detrimental effects on soil microbial biomass & pollinator abundance



By destroying the flowers, the soil cultivation degrade the life conditions of pollinators
3 - Organic or conventional farming : no effect on the abundance of ground beetles or mites

2. Plant cover allows for a 2 to 3 times increase in the population of auxiliary nematodes
3. There is an antagonism between biodiversity and production but we can observe plots where wine practices and landscape conditions permit a synergy

1. No single answer: organic favours some species, conventional others




- 2017: studies in Bordeaux (INRAE - LPO - CIVB ) confirm that bats are predators of moths in the vineyards (study of bat guano and ultrasound recording)
- 2019-2020: studies to quantify the impact of bats (Counting of egg-laying and perforations of 100 bunches on 31 plots in the vineyard)

The profile of our bats (exclusively insectivores)
• Great diversity of bats that predate vine pests:
- 19 of the 22 species listed in Gironde are active in the vineyards
- About 10 species are very regular in the vineyard
• A bat eats between 500 and 1500 insects per night (more like 2000 for suckling bats)
Weak level of activity
Medium level of activity



High level of activity


Activities of the bats : clearly linked with the structure of the vineyards The presence of bats is more intense in grassy plots

• Bats have a significant effect on perforations: they reduce perforations by 14% on average, up to 50% on some plots
.
• Second effect: the presence of bats exerts a pressure/stress that limits the increase of pest population in the vineyard
Bats make it possible to keep pest populations low enough for winegrowers not to have to apply additional treatments.
Bats are wild and protected animals : can’t be raised or re-introduced but favorable measures can improve their presence.

• Through the implementation of agro ecological infrastructures : water point, grassy strip, trees and forests… and also old abandoned buildings

•Adapting viticultural practices (grassing)

On a more global scale (e.g. AOC level)
Organise so that bats can have sufficient food resources all year round (outside the "season" of the grape worm)











• What is it about ?
Provide free of GhG emission services: restored, healthy, fertile and living soil to produce quality grapes
• What are we talking about ?
Grass cover: spontaneous or seeding, in the row or under the row
Agroforestry: the trees (local species) :
- on the plot: in the row in place of vines or aligned between the rows of vines - on the borders of the plots: in hedges, in islands or isolated.




To adapt plant species, materials and technical itineraries to their agronomic problems while aiming for decarbonation
Good practices to be developed
1. To carry out spontaneous grassing and winter seeding together (by choosing plants that will meet the specific needs of the plot)
2. Promoting extensive cover management to increase the diversity of plants and facilitate the development of long-cycle annual species.
Annual plants reduce competition with the vines (their needs are not the same as those of the vines, so there is no competition for water and nutrients).
Annual plants store more carbon


3. To reduce mowing (1 to 2 per season, shorten, mow later, with the help of sheep if possible)
Reducing mowing encourages carbon sequestration in the soil and significantly increases organic matter content.






Many winegrowers mention an "additional freshness" in the plots cultivated with agroforestry.
To date, few studies have been carried out on the subject.
However, there is one study, VITI FOREST, carried out by INRAE which would tend to confirm this feeling.
Further studies need to be carried out to confirm this.








• the structuring and aesthetics of landscapes
• creates a positive image of a territory
• the tourist appeal of the Bordeaux vineyards

Although considered as a nonmarket value, biodiversity contributes to :
• These projects : another meaning to one's work, re-invent a new form of farming (reinforced since the COVID)
• Often, the environmental initiatives are one aspect of more global projects with social and societal dimensions (employment of disabled staff, gender equity, better reception of seasonal workers, etc.).
Development of CSR

• A balance to be found between ecological, societal and economic performance

Behind this philosophy : the men and women of Bordeaux, their convictions, motivation, commitment, passion and work


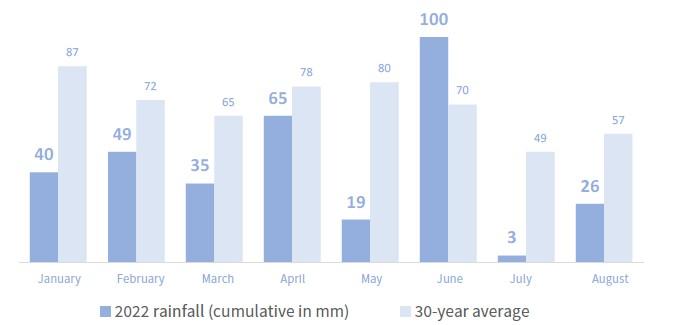
• A historic year for the climate. Harvesting started on August 16th: 15 to 20 days ahead of normal

• The heat and drought during the year favored the production of qualitative and healthy berries

• Strong impact of the water stress on berry size : the weight was 15 to 30% lower than the previous vintage : the overall yield of the 2022 vintage will be below the average for the last five years