










 i'm sherlock holmeow a consulting detective at the night city
i'm sherlock holmeow a consulting detective at the night city








Born about AD 70
Died about AD 135
Theon was a Greek philosopher who described how prime numbers, geometrical numbers such as squares, progressions, music and astronomy are interrelated.
Theon's most important work is Expositio rerum mathematicarum ad legendum
Platonem utilium . This work is a handbook for philosophy students to show how prime numbers, geometrical numbers such as squares, progressions, music and astronomy are interrelated.
He was called 'the old Theon' by Theon of Alexandria and 'Theon the mathematician' by Ptolemy. The date of his birth is little better than a guess, but we do have some firm data about dates in his life. We know that he was making astronomical observations of Mercury and Venus between 127 and 132 since Ptolemy lists four observations which Theon made in 127, 129, 130 and 132. From these observations Theon made estimates of the greatest angular distance that Mercury and Venus can reach from the Sun. The style of his bust, dedicated by his son 'Theon the priest', gives us the date of his death to within 10 years and it is placed within the period 130-140 (hence our midpoint guess of 135).

Case No:1103
Date:14/4/3250
Report made by: Sherlock Holmes
Incident
Lucretius and Theon are debating whether the earth is round or flat.
The incident took place at the Agora of Athens near Monastiraki, a large number of people and scholars gathered Lucretius and Theon of Smyrna are debating whether the earth is round or flat. " Agora:Anopen-airmeetingplaceforcitizenstoengageinvarious activitiesinancientGreekcities,usuallylocatedinthecentreof thecityorneartheport,wherepeoplecan debatefreely."
Actions Taken:
Using the scientific method, define the problem: clearly define the problem to be answered. The question can be how to explain a natural phenomenon, or what is the nature of certain things or laws of nature.
Formulation of Hypothesis: Attempt to formulate a scientific hypothesis or theory to answer a question.
Inferring predictions: Deriving some predictions using a hypothesis or theory.
Experimental Validation: Designing and using experiments to verify the validity of hypothesis tests about observational predictions.
If the relevant "Observational Prediction" is true, then the relevant hypothesis is confirmed to a certain extent.



Ancient Greek philosophers believed that "what is truth?" "what is good?" "what is beauty?" are the three most basic questions in thinking. However, from the perspective of thinking methodology, they are actually not the most basic. Compared with the above three questions, "How to think correctly?" This question is actually more basic.
Distinguishing right from wrong is a central feature of critical thinking. We can illustrate it through the
Mean What + What Basis
+ What Possibilities
=Critical Thinking

For the purposes of this question, X can refer to a concept, sentence, or question.


Mean What + What Basis + What Possibilities
=Critical Thinking

X can refer to a rumor or a theory.

Mean What + What Basis
+ What Possibilities
=Critical Thinking
"What is the basis for X?"

Mean What + What Basis
+ What Possibilities
=Critical Thinking
"In terms of X, what other possibilities are worth considering?"

The first question focuses on clarifying the language used. To think correctly, we need to use the three questions above appropriately. Correct thinking must be clear and reasonable, so critical thinking focuses on the first two questions. Appropriate use of the above three questions is the key to independent thinking.
These three questions seem simple, but it is not easy to use them flexibly and accurately. For example, to judge whether a theory is valid, it may involve complex logic or scientific method.

Mean What + What Basis + What Possibilities
=Critical Thinking
Why are there so many rumors on the Internet now? Why are these rumors so powerful? It turns out that it all comes from the "truth illusion effect" relationship, now, let us understand and break the vicious rumors! Just like the proverb that “words have no feet but can travel thousands of miles”, rumors spread in an instant, and as rumors spread repeatedly, unconfirmed content is often accepted as true.
Psychologist Nicholas DiFonzo conducted an experiment with students from the Rochester Institute of Technology. The experimental plan was to spread various rumours in various places within six days and to make each rumour heard multiple times. As a result, the trust level when hearing the rumour for the first time was 40%, and after hearing the same rumour six times, the trust level increased to as much as 60%.That is to say, even if you don't believe it at first, after hearing it many times, you will become convinced of the rumours like the

idiom "No wind, no waves, no fire, no smoke, three people become tigers". Even if the authenticity is uncertain, it is believed to be true due to the effect of repeated exposure, which is called the "Illusion of truth effect". So, where did the power of unfounded rumours come from? Social psychologists Gordon Allport and Leo Postman's formula for collating rumours is as above.
If this formula is in plain language, it means that the more important the content conveyed by the rumour and the less certain the situation is, the stronger the strength of the rumour becomes. So the more restless we are, the more sensitive we become to rumours, and the more we believe what we want to believe. Therefore, in order to deal with vicious rumours, the most important thing is to refute them quickly.
“Why do people believe fake news It turns out that the “illusion of truth effect” is making trouble!”

Pfor Point, the first sentence starts with “advocacy”
The first sentence should be moderately intriguing to the listener, making one wonder why you are thinking that way. Please first express your central "thinking" or "advocacy" in a concise and clear "summary way".
for Reason, the second sentence says the "basis" to support the conclusion
Next, the other party will definitely ask you “why do you think so”, so you have to come up with enough “basis” to support your claim. However, not all reasons can be grounded, and unfounded claims will be reduced to personal impressions or impressions.


for Example, in the third sentence, please say "actual case"
On the surface, the logic sounds correct, but it lacks information such as "background", "cause and effect" or "source of information", which inevitably makes others feel vague and not easy to be persuaded. Specific examples, especially "data, data, personal examples" as an example, will be particularly objective. If the source of the information can be provided by the way, it can be highly convincing on almost any occasion.







There are eight candies on the table, Kim says one of them is his, Kai says three of them are his, and George says seven of them are his;





Huh? How can it add up to more than eight? Looks like someone lied to get more candy...



King said, "George lied! "
Kai said, "Both Kim and George are lying!"
George said, "Kai lied!"

Hypothesis 1:

Kim did not lie, then George lied: "George said Kai lied" is a lie, so Kai did not lie, then what Kai said is correct, "Kim George lied", which conflicts with the assumption.


Hypothesis 2:
Kai did not lie, so Kim and George lied: "Kim said George lied" is a lie, so George did not lie, George said Kai lied, which conflicts with the hypothesis; if "George said Kai lied" is a lie, Kai did not lie, Although it does not conflict with the hypothesis, the reason for this hypothesis to be established is that the inference must be reasonable, and the inference of Kim's lie has conflicted.
George didn't lie, so Kai lied: "Kai said Kim and George lied" is a lie, there are three possibilities: Kim lied George did not lie; Kim did not lie George lied; Kim and George did not lie all can be established. If Kim lied and George did not lie, so "Kim said George lied" is a lie, so George did not lie, which is consistent; if Kim did not lie and George lied, which conflicts with the assumption; if Kim and George did not lie, but Kim said George lied, which conflicted with the premise.





It can be seen that Kim Kai lied, George did not lie, George said there were 7, Kim said that 1 was a lie, but there was one left, so one belonged to Kai, and Kim had 0.
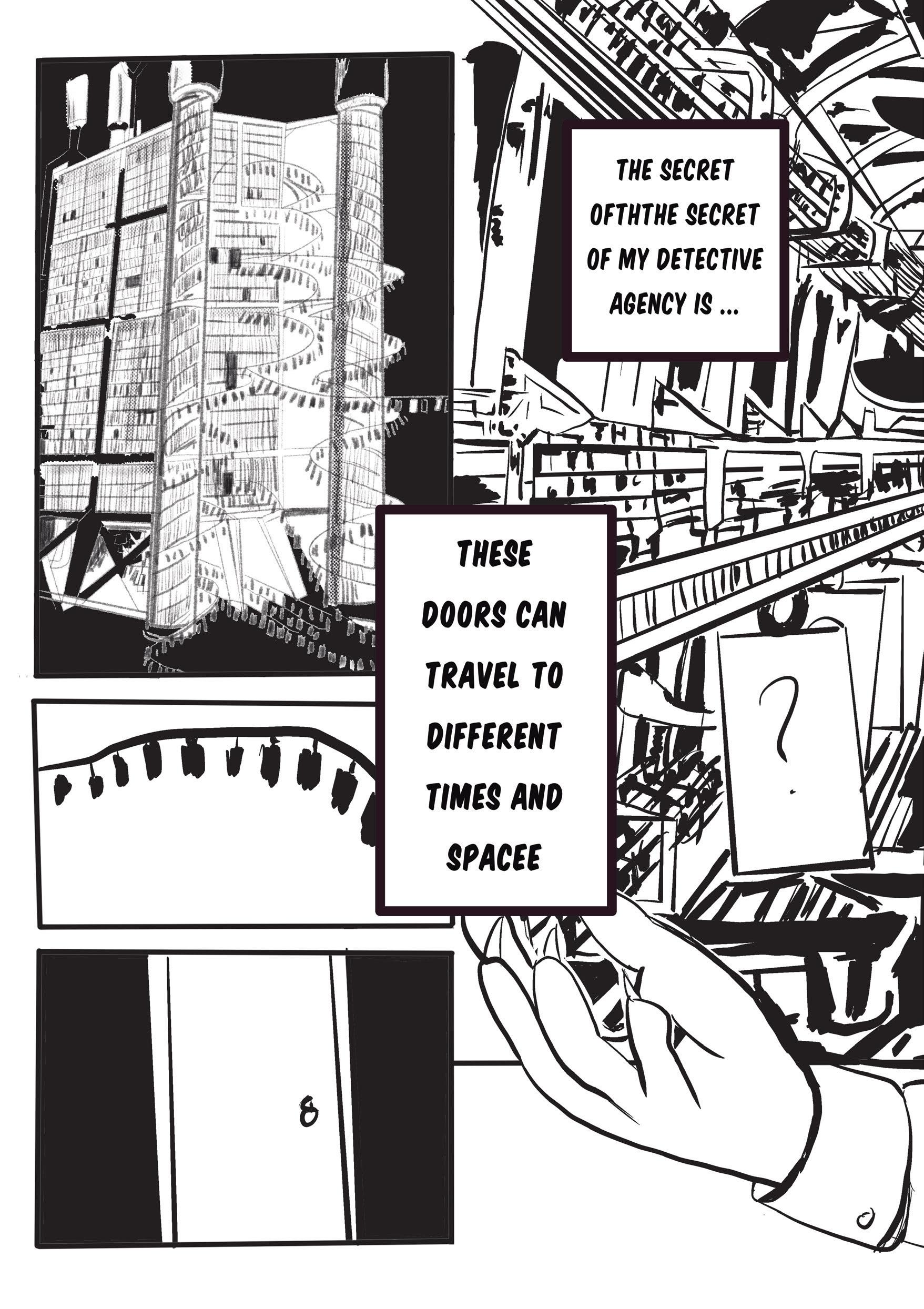
Sherlock Holmeow, who runs a detective agency, and this detective agency has a strange and mysterious...
“Nothing is so firmly believed as that which we least know.”



-Michel de Montaigne, The Complete Essays.
