




India is emerging as a global leader in digital transformation, driven by advancements in technology, a highly skilled workforce, and strong government support The rise of Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in India is central to this transformation, with businesses leveraging the country’s expertise in AI, cloud technologies, big data, and automation to stay competitive on the global stage.
A key factor in India’s success in the digital era is its ability to adopt both organic and open innovation models. By blending in-house development with external collaborations, Indian businesses can rapidly innovate, reduce costs, and accelerate time to market. Additionally, the growing importance of data in driving business outcomes has made cybersecurity and data management pivotal for GCCs, particularly in industries such as life sciences and healthcare.
For businesses seeking to establish successful GCCs, India offers a strategic advantage, with its talent pool, cost efficiency, and strong digital ecosystem The strategic framework for setting up GCCs involves careful planning around location, talent acquisition, and partnerships India's GCCs are playing an essential role in enhancing global business capabilities and driving digital innovation
In conclusion, India’s role in the global digital economy continues to expand, positioning the country as a key player in shaping the future of business through technology, innovation, and strategic collaborations

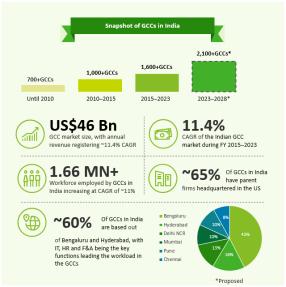
India’s emergence as a global hub for Global Capability Centers (GCCs) marks a significant shift in the global business landscape, driven by technological advancements and rapid digital transformation. With over 1,600 centers employing more than 1.5 million professionals, and a projected market valuation of $110 billion by 2030, India has become a critical pillar in global business innovation through its dynamic GCC ecosystem.
GCCs act as strategic hubs for international enterprises, enabling them to address diverse domestic and global markets while fostering leadership roles. India’s digital revolution, underpinned by a strong startup ecosystem and a highly skilled talent pool, has been integral to this growth. Moreover, initiatives such as "Make in India" and "Telangana’s 2030 Vision for Life Sciences" have further enhanced India’s attractiveness as a preferred destination for establishing GCCs
The Life Sciences and Healthcare (LSHC) sector, a significant contributor to the Indian GCC landscape, accounts for over 15% of the total workforce. Cities like Bengaluru and Hyderabad have emerged as prime locations for LSHC GCCs, with Hyderabad recognized as India’s “Healthcare Hub.” The city’s flourishing life sciences ecosystem, bolstered by governmentbacked initiatives like Genome Valley, Pharma Villages, T-Hub, and B-Hub, has fostered innovation through collaborative efforts. Consequently, Hyderabad’s life sciences sector has grown at an impressive rate of 23%, significantly surpassing the national average of 14%
Telangana is now home to over 214 FDA-approved manufacturing sites, contributing more than 35% of India’s pharmaceutical output The region’s skilled professional workforce, proficient in FDA processes and Good Clinical Practice (GxP), has driven this growth Additionally, Telangana boasts around 200 biotechnology firms and a robust healthcare infrastructure, including 12,000 hospital beds, 4,000 clinics, and more than 500 diagnostic centers This blend of life sciences and healthcare capabilities positions Hyderabad as an ideal destination for LSHC GCCs
While cost reduction remains a key factor in the establishment of GCCs, their role has evolved to include capability development, business value generation, and digital transformation This shift has transformed GCCs from transactional efficiency centers into hubs of innovation and market expansion Currently, more than 65% of organizations operate multiple functions within their GCCs, covering areas such as finance, HR, IT, and procurement, as well as strategic capabilities like sales, marketing, and R&D.
Beyond traditional business services, approximately 50% of GCCs are now integral to advancing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) objectives for their parent companies. Social responsibility and diversity are key focal points, with around 60% of GCCs actively supporting ESG initiatives through local partnerships and investments.
GCCs leverage India’s talent and technology ecosystems through two innovation models: "Organic Innovation," which builds internal capabilities and a skilled workforce, and "Open Innovation," which fosters external collaborations with startups, academia, and other ecosystem partners. These models enable companies to access cutting-edge innovation and expertise beyond their traditional boundaries.
This white paper provides a detailed analysis of India’s evolving GCC landscape, with a particular focus on the factors driving Hyderabad’s rise as a leading destination for LSHC GCCs It explores various GCC models and their strategic benefits, offering actionable insights for organizations looking to define their vision, operational strategies, and competitive positioning Additionally, the paper presents a "Strategic Choice Cascade" framework to guide companies in their decision-making processes, helping them determine "Where to Play," "How to Win," and the capabilities needed to succeed
India has quickly established itself as a leading global hub for Global Capability Centers (GCCs), capturing over 50% of the global market share With approximately 1,600 centers employing over 1.5 million professionals, the Indian GCC sector is projected to reach a market valuation of $110 billion by 2030, up from $46 billion in 2023.
Bengaluru, the country’s largest GCC hub, accounts for more than a third of multinational corporations (MNCs) that have set up GCCs over the past 10 to15 years Meanwhile, Hyderabad has emerged as a formidable competitor, particularly in the life sciences sector, driven by its governmentsupported business ecosystem The life sciences sector in Telangana has grown by 23% in recent years, significantly surpassing the national average of 14% This growth has positioned Hyderabad as a key destination for life sciences and healthcare (LSHC) companies looking to establish their GCCs
Source:https://ansr.com/
Source:https://ansr.com/
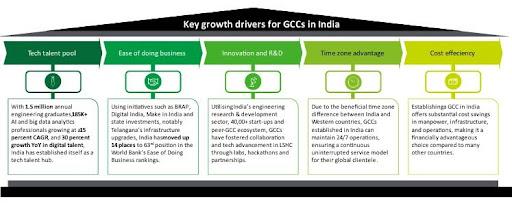
India is home to a vast talent pool, producing over 1 5 million engineering graduates annually, providingGCCs a strong foundation of technically skilled professionals. In 2019, the country saw a remarkable growth rate of 30% in digitally skilled graduates, reaching approximately 85,000. As industries increasingly embrace technology, including traditionally non-tech sectors like healthcare and life sciences, investments are being channeled into cultivating expertise in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital technologies.
A key example is the Telangana AI Mission (T-AIM), launched in 2020, which aims to position the state as a global AI hub. The initiative includes the 'Revv Up Accelerator' program, providing mentorship to AI startups in Hyderabad, fostering collaboration between industry leaders, enterprises, and government bodies India’s workforce also includes 5 67 million Human Resources for Health (HRH) professionals, with 74% actively employed This vast talent base makes India a strategic location for GCCs focused on advanced research, development, and innovation As a result, more than three-quarters of GCCs have chosen India to leverage its superior talent pool GCCs focused on advanced research, development, and innovation As a result, more than three-quarters of GCCs have chosen India to leverage its superior talent pool
Business-FriendlyEnvironment:PolicySupportand InfrastructureDevelopment
India is home to a vast talent pool, producing over 1.5 million engineering graduates annually, providingGCCs a strong foundation of technically skilled professionals. In 2019, the country saw a remarkable growth rate of 30% in digitally skilled graduates, reaching approximately 85,000 As industries increasingly embrace technology, including traditionally non-tech sectors like healthcare and life sciences, investments are being channeled into cultivating expertise in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital technologies
A key example is the Telangana AI Mission (T-AIM), launched in 2020, which aims to position the state as a global AI hub The initiative includes the 'Revv Up Accelerator' program, providing mentorship to AI startups in Hyderabad, fostering collaboration between industry leaders, enterprises, and government bodies India’s workforce also includes 5 67 million Human Resources for Health (HRH) professionals, with 74% actively employed This vast talent base makes India a strategic location for GCCs focused on advanced research, development, and innovation As a result, more than three-quarters of GCCs have chosen India to leverage its superior talent pool GCCs focused on advanced research, development, and innovation As a result, more than three-quarters of GCCs have chosen India to leverage its superior talent pool
India has fostered a dynamic innovation ecosystem, bolstered by a thriving IT services sector and the world’s third-largest startup ecosystem. The country is home to over 20,000 startups, with approximately 8,800 focusing on low-cost, transformative technology solutions. Cities such as Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune are hubs for IT parks and innovation centers, fostering collaboration and technological advancements.
India has become the premier destination for Engineering, Research, and Development (ER&D), with nearly 75% of GCCs supporting ER&D functions. Digital Engineering (DE), a growing segment within ER&D, contributes about 30% of total revenues and is increasingly prominent in sectors such as healthcare, where it drives customer-centric innovations.
India’s strategic time zone offers significant advantages for GCCs, bridging the operational gap between Western countries like the U.S. and Europe, and the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region. This positioning enables GCCs to offer round-the-clock services, ensuring timely and efficient delivery to global clients. Through staggered shifts, GCCs can maintain continuous operations, fostering cross-regional collaboration and knowledge-sharing that enhances both the quality and innovation of the solutions developed.
Although operational costs are rising in major metropolitan areas, India remains a highly cost-competitive destination, especially in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities These locations offer lower operational expenses, including salaries, real estate, and administrative costs, while still providing access to a skilled workforce Cities like Kolkata, Hyderabad, and Chennai are among the most cost-effective in the country, with Pune and Delhi also offering competitive pricing.
Office rental rates in India’s GCC hubs are significantly lower than those in other APAC cities, providing additional cost advantages. Moreover, other operational costs, such as transportation and utilities, are also notably more affordable.
India’s emergence as a global hub for GCCs underscores its adaptability and innovative capabilities in an ever-evolving business landscape. This growth not only benefits multinational corporations but also strengthens India’s economy, reinforcing its position as a global leader in digital transformation and business innovation.
Originally established to leverage cost efficiencies in tasks such as payroll processing, customer support, and basic IT services, India’s Global Capability Centers (GCCs) have undergone a significant transformation over the years These centers, once focused on routine operations, now manage sophisticated functions, including data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced research and development (R&D) Today, they serve as transformation hubs, driving innovation in areas such as generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), machine learning (ML), and advanced analytics Over 50% of GCCs have integrated automation, reporting, analytics, process excellence, end-to-end (E2E) process ownership, and business continuity planning capabilities
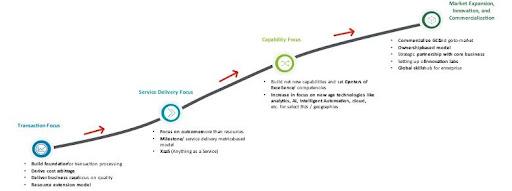
Indian GCCs have evolved from being viewed as “back offices” or “service providers” to becoming vital “value creators” within their parent organizations. Some GCCs now house global leadership positions, underscoring their growing importance. For instance, roles such as Global Delivery Technology Lead at AstraZeneca and Group Head of Network Transformation at Novartis highlight the strategic value these centers bring.
To cement their position as indispensable strategic partners, GCCs are expanding their capabilities and service offerings Currently, over 65% of GCCs manage multiple functions, leveraging cutting-edge technologies to deliver business value Function leaders increasingly turn to GCCs to improve efficiency, transparency, and automation through tools like AI, natural language processing (NLP), and intelligent automation
Beyond traditional enabling functions, GCCs are now prioritizing core functions that require innovation, domain expertise, and close collaboration with headquarters. While finance, HR, IT, and procurement continue to be fundamental to GCC operations, these centers are taking on roles in areas such as, sales and marketing, manufacturing, and R&D. This growing diversification highlights the shift of GCCs into strategic business partners.
Additionally, around 50% of GCCs are actively contributing to their parent organizations' environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives These centers are integral to driving social responsibility and diversity, with about 60% supporting comprehensive ESG goals, including ESG reporting Furthermore, mature GCCs are increasingly expanding their expertise into legal, commercial, and risk and compliance functions
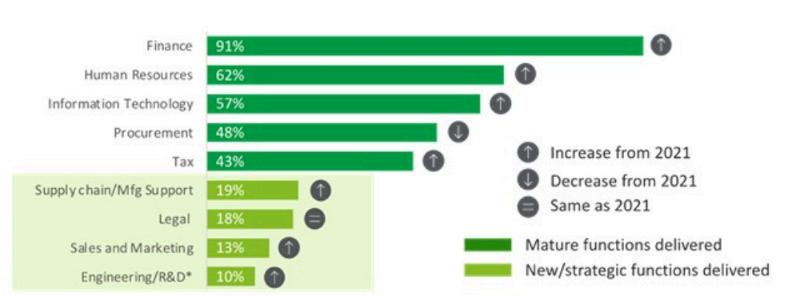
GCCs are embedding themselves more deeply into various business functions, becoming microcosms of their parent organizations. This integration is particularly noticeable in mature enabling functions, where GCCs provide advanced capabilities such as enterprise architecture design and IT strategy. In emerging core functions, such as commercial operations, GCCs focus on more foundational research and reporting. As they solidify their expertise in core offerings, GCCs are positioned to ascend the value chain, delivering highvalue processes across both core and enabling functions.
The life sciences and healthcare (LSHC) sector is witnessing the expanding influence of Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in shaping the strategic objectives of multinational corporations (MNCs). With over 280,000 professionals employed across these centers, LSHC GCCs account for more than 15% of the total GCC workforce in India. Notably, more than 55% of these centers are headquartered in the United States, underscoring the significant role India plays in supporting global operations
India is home to 95 LSHC GCCs, with Bengaluru hosting nearly one-third of them However, Hyderabad is quickly emerging as a key player The city's advanced technological infrastructure, coupled with a rich talent pool, has made it an attractive destination for LSHC companies. Additionally, the Telangana government's substantial investments in manufacturing and research and development (R&D) have contributed to the city's thriving pharmaceutical sector and accelerated growth in life sciences GCCs
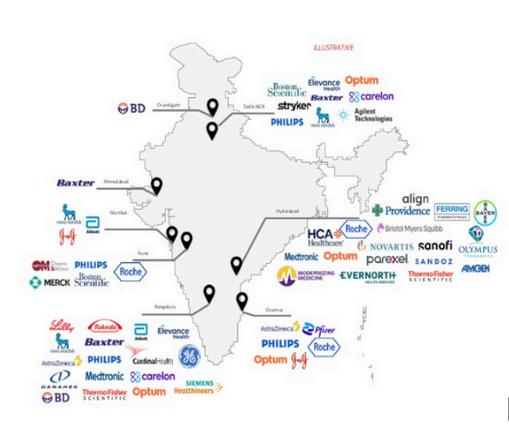
Hyderabad's growth in the healthcare GCC sector is equally remarkable. One example is the Hospital Corporation of America (HCA), a leading U.S. healthcare provider with international operations, including in the U.K. HCA recently announced plans to establish a GCC in Hyderabad, focused on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), data science, and analytics. In parallel, other healthcare GCCs, including Evernorth, are leveraging emerging technologies, including generative AI and process optimization, to spur innovation and drive efficiencies in healthcare operations
Consistent with trends across other industries, enabling functions such as finance, human resources (HR), and information technology (IT) are well-represented within LSHC GCCs. However, there is a growing emphasis on core functions. Life sciences GCCs are increasingly investing in R&D and commercialization processes, enhancing their role in drug discovery, development, and post-marketing activities. These centers are driving product innovation, advancing technologies, and leading digital transformation efforts that help parent companies achieve operational efficiency and deliver value across the healthcare spectrum Additionally, they play a critical role in analyzing vital aspects such as patient satisfaction, genomic research, and clinical outcomes in ambulatory care systems
Furthermore, LSHC GCCs are developing specialized capabilities in areas such as cybersecurity to enhance their value proposition, ensuring both operational integrity and innovation
In the past, life sciences GCCs were primarily involved in traditional tasks such as medical writing and regulatory documentation. However, their scope has evolved significantly, now encompassing critical functions such as drug discovery and development. This shift emphasizes their growing importance in bringing new therapies to market. A prime example is Bayer’s Data Science and Analytics Center in Hyderabad, which serves as the company’s Asia-Pacific hub. This center plays a vital role in the development of innovative therapies, particularly in Oncology Data Analytics (ODA), and employs industry-leading methodologies to drive advancements in cancer treatment.
Other GCCs are similarly advancing research in healthcare and MedTech, contributing to groundbreaking projects like MRI coil design, AI-based medical imaging, molecule testing, and fluorescence imaging.

Beyond R&D, life sciences GCCs are integral to commercial operations, supporting activities such as market research, sales operations, performance reporting, and analytics. Roche’s Global Analytics and Tech Center of Excellence (GATE) in Hyderabad exemplifies this role, providing commercial insights at scale in areas such as Real World Evidence (RWE), forecasting, automation, and market access. While these activities are wellestablished, there is increasing potential for GCCs to extend their impact into strategic domains such as channel strategy, product positioning, and sales planning. By combining deep domain expertise with analytical capabilities and digital technologies, GCCs are poised to influence the commercial success of life sciences products on a global scale.
This strategic evolution of LSHC GCCs reflects India’s transition from a service provider to a global innovation hub in life sciences and healthcare. By driving innovation, enhancing technological capabilities, and fostering collaboration, these centers are transforming the value they deliver to multinational parent organizations, positioning India as a pivotal player in the global life sciences and healthcare ecosystem.
The rapid advancement of technology, fueled by innovations like Generative AI (GenAI), is revolutionizing industries and creating new opportunities in automation, creativity, and problem-solving. These developments are reshaping the way we live and work. India, with its robust technology ecosystem and skilled workforce, stands at the forefront of this digital revolution, driving transformation across multiple sectors.
India’s strategic focus on long-term, sustainable growth is evident through substantial investments in engineering R&D, positioning the country as a global leader in innovative solutions The government’s initiatives and policies are actively promoting innovation, attracting foreign companies to establish operations and contribute to India’s growing digital landscape
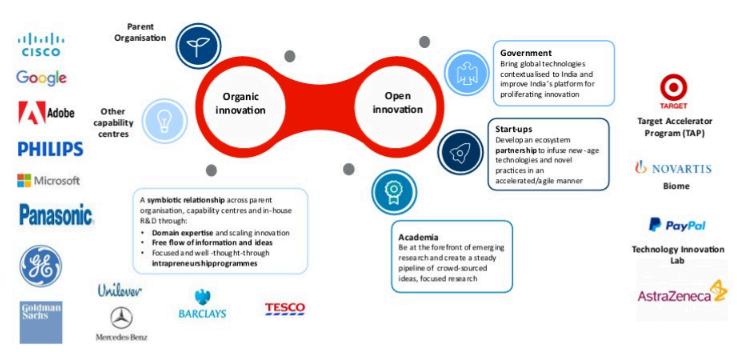
Given these developments, India is poised to lead a future defined by technological excellence. The country’s Global Capability Centres (GCCs) are uniquely positioned to drive digital transformation by leveraging India’s thriving tech ecosystem through both organic and open innovation models.
Within GCCs, innovation often occurs organically, either internally or in collaboration with the parent organization. Organic innovation involves nurturing a skilled workforce and developing technological capabilities through internal initiatives focused on emerging technologies like AI, cloud computing, blockchain, and data analytics. These efforts aim to forge transformative solutions for organizations
For example, Globalbiz Outlook’s Hyderabad-based GCC offers a comprehensive range of technological solutions, including cloud computing, cybersecurity, digital solutions, and data analytics The centre also pioneers next-generation technologies such as GenAI, all developed in-house The success of this initiative has been significant, with plans to double the workforce in India to meet the increasing demand for tech-driven, future-ready healthcare solutions
Open innovation allows GCCs to collaborate with a broader ecosystem of startups and academic institutions, enabling parent companies to access external innovations and new ideas. Large-scale transformational initiatives often begin as small pilots. GCCs identify high-value collaboration opportunities with external partners, aligning the parent organization’s strategic goals with the innovative capabilities of external contributors
In this model, the GCC provides the necessary context and functional expertise, while external partners contribute operational excellence, skilled talent, and cutting-edge technology. Successful collaborations are characterized by alignment between the parent organization’s objectives and the operational and cultural nuances of the GCC. Following the completion of successful pilots, initiatives can be scaled to meet organizational needs.
A notable example of open innovation is Globalbiz Outlook’s Biome India, launched in 2020 as its first digital innovation hub in Asia. Based in Hyderabad, Biome India fosters collaboration with Indian startups in the healthcare sector, enhancing access to advanced technology and expertise. Similarly, Carelon, Elevance Health’s 18,000employee GCC, with centres in Hyderabad and Bengaluru, collaborates with Telangana’s T-Hub, a leading startup incubator, to leverage the innovative solutions and expertise of startups.
By collaborating with startups, GCCs gain access to an innovative culture, agile methodologies, skilled talent, and a focus on solution-oriented thinking. Various engagement models can be adopted, depending on the needs of the GCC and the capabilities of the startups. While open innovation remains in its early stages for many GCCs, as the technological landscape evolves, further engagement with ecosystem players will be critical for driving growth and transformation.
The rapid growth of data across industries is reshaping decision-making and strategy development, providing companies with a competitive edge This shift is particularly impactful in the life sciences sector, where the ability to harness new data sources such as electronic medical records (EMR), health economics and outcomes research (HEOR), payer records, wearables, medical devices, and social media is driving transformative growth. As advanced technologies enable data-driven insights, life sciences GCCs in India are becoming crucial players in the global healthcare and life sciences ecosystem.
Life sciences GCCs in India are increasingly adopting advanced technologies like big data analytics, automation, and cloud services to maintain a competitive advantage. These technologies are already playing a key role across the drug development lifecycle. For instance, big data and analytics are enhancing target identification and predictive modeling for drug interactions. Automation is streamlining clinical trial management, and cloud services are offering scalable storage and computational power to integrate diverse data sources and facilitate global collaboration.
Cybersecurity is also critical within life sciences GCCs, ensuring the protection of sensitive data, compliance with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and safeguarding intellectual property. Additionally, evolving technologies such as AI, machine learning (ML), and Health IT (e.g., electronic health records) are contributing to advancements in drug discovery, development, commercialization, and care delivery.
Although the adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain technologies remains limited in the life sciences sector, GCCs are prioritizing more impactful technologies that deliver higher value to the business, helping them stay ahead of the competition.
India’s tech and digital revolution, driven by both organic and open innovation models, positions the country as a key player in the global technological landscape. With the adoption of cutting-edge technologies and the expansion of data-driven insights, GCCs in India are not only transforming industries but also redefining the future of global business operations. The evolving landscape of digital transformation promises even greater advancements, further solidifying India’s role as a leader in the tech-driven world.
In today's dynamic global business environment, Global Capability Centres (GCCs) have become essential drivers of strategic success for multinational corporations (MNCs)
Positioned across diverse geographic regions, these centres act as vital components within a company's global network, offering a range of strategic, operational, and financial benefits. However, building an effective GCC requires a structured approach to avoid common pitfalls. A series of interconnected decisions ranging from defining clear objectives to aligning operational choices can help organizations unlock new opportunities and test their decisions to ensure long-term success. A well-defined decision framework serves as a valuable tool to align business objectives with strategy.
Establishing a GCC must begin with a clear vision, shaped by the organization’s strategic priorities. While cost reduction and operational efficiency remain key drivers, emerging factors such as capability development, value creation, and digital transformation have increasingly influenced the adoption of the GCC model.
Cost arbitrage is one of the primary motivations for establishing GCCs. By operating in locations with lower labor and operational costs, companies can achieve significant savings. Many countries offer tax incentives, subsidies, and other financial advantages to attract foreign enterprises These financial efficiencies enable organizations to allocate resources more effectively, invest in growth initiatives, and maintain competitive pricing structures


GCCs also play a pivotal role in fostering innovation and building new capabilities. By serving as centres of excellence, these facilities develop specialized expertise that benefits the entire organization. Additionally, strategically located GCCs allow companies to leverage regional expertise and market insights, enhancing their ability to address global challenges.

Standardizing operations across different regions is another crucial factor driving GCC adoption. Centralizing operations helps streamline processes, reduce redundancies, and ensure consistency in quality and performance. This approach leads to cost savings, enhanced productivity, and improved market adaptability, which fosters organizational resilience

Originally designed to achieve transactional efficiencies, GCCs have evolved into hubs for innovation and market expansion. They now serve as vehicles for companies to diversify and enhance their service offerings across various functions.
GCCs are increasingly positioned as centres for digital transformation. By tapping into local ecosystems of innovation and research, these centres enable organizations to stay at the forefront of technological advancements and enhance their digital capabilities.


GCCs provide companies with access to a diverse and skilled talent pool. By establishing centres in regions with expertise in fields such as data science, cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity, organizations can enhance workforce quality and introduce new perspectives that drive innovation.
To ensure success, executives must define a clear vision for their GCC, establishing strategic objectives for the short, medium, and long term. This vision should clarify the primary role of the centre—whether focused on back-end operations or positioned as a strategic innovation hub.
The “Where to Play” decisions are critical for defining the strategic positioning of the GCC and ensuring it aligns with the broader goals of the organization B.WheretoPlay:StrategicLocationChoices
Selecting the optimal location for a GCC is one of the most significant decisions. Key factors include access to skilled talent, operational costs, competitive landscape, infrastructure quality, and the overall business environment Utilizing frameworks like the Critical Location Factor (CLF) can guide decision-makers in evaluating potential locations, helping them prioritize regions that align with business needs.

Companies can choose from various models for building GCC capabilities. Options include fully self-built centres, third-party-assisted builds, or hybrid models such as Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) The chosen model should align with both the business drivers and longterm strategic goals

Clearly defining roles within the GCC is essential for its success. For instance, organizations focused on cost efficiency may prioritize operational functions, while those establishing R&D centres may place greater emphasis on leadership roles that contribute to strategic decisions.

Once the strategic positioning is established, the next step is to define the operational framework This involves focusing on three key pillars: organizational structure, workforce planning, and external partnerships. C.HowtoWin:OperationalizingtheGCCStrategy
The internal structure of the GCC should align with the parent company’s framework, while also accounting for local nuances. A matrix structure, which integrates business lines and geographic or functional capabilities, can enhance collaboration and resource sharing across the organization.

In addition to internal operations, establishing strategic external alliances is vital. Collaborations with local governments, academic institutions, and startups can provide additional benefits, such as access to infrastructure, talent, and potential financial incentives, which strengthen the operational capacity of the GCC

Attracting and retaining top talent is crucial for the success of the GCC Offering competitive compensation, clear career progression paths, and continuous learning opportunities is essential for employee retention. Creating a supportive and inclusive culture focused on innovation and employee well-being will enhance overall satisfaction and longterm loyalty.

With strategic positioning and an operational framework in place, organizations must prioritize the development of strong processes and workflows. Standardized procedures should be balanced with the flexibility to adapt to local market conditions and cultural differences. Clear communication and collaboration mechanisms with the parent company should also be established to ensure alignment across regions.
Regular reporting, strategic reviews, and accountability structures are vital for maintaining alignment and promoting effective communication. Virtual meetings and workshops can foster collaboration and help ensure consistent alignment with organizational goals. Additionally, training programs that enhance both cultural competence and technical skills, such as data management and regulatory compliance, are essential to the GCC’s success
In recent years, Global Capability Centers (GCCs) have become crucial to India’s business ecosystem, driving innovation, digital transformation, and operational efficiency for multinational corporations. Formerly known as Global In-House Centers (GICs), these centers serve as vital hubs for high-value services, including IT, finance, R&D, and more. India’s strategic location, coupled with its extensive talent pool, has made it a highly attractive destination for these centers, which are integral to the global strategies of businesses worldwide.
In this article, we spotlight the top 10 GCCs in India that are reshaping the country’s business environment and significantly enhancing global operations.

Microsoft’s GCC in India stands as one of the most influential, focusing on product development, cloud computing, and AI-driven innovations With thousands of employees across cities like Bengaluru, the center plays a pivotal role in Microsoft’s global product development and digital transformation initiatives
Amazon’s GCC in India is a key player in ecommerce innovation, with multiple development centers spread across the country The center specializes in cloud solutions, artificial intelligence, and customer experience management, facilitating Amazon’s global operations for both its ecommerce and AWS platforms

Goldman Sachs established its GCC in Bengaluru to support global operations in financial services, risk management, and technological innovation. The center is crucial in enhancing banking processes worldwide, making India a key component of the firm’s global strategy.


JP Morgan’s Global Service Center (GSC) in India is at the forefront of fintech innovation, providing solutions for payment systems, digital banking, and AI-driven financial models. This center significantly impacts global financial markets and technologies

Deloitte’s GCC in India offers financial advisory, audit services, and consulting, with a strong focus on emerging technologies like automation and AI It is an essential part of Deloitte’s global projects, particularly in the areas of digital transformation and business efficiency
HSBC’s GCC in India plays a vital role in driving the bank’s technology innovations, including mobile apps and AI-powered cybersecurity solutions The center is integral to enhancing global banking experiences by leveraging India’s extensive talent pool


Walmart’s GCC in India develops solutions to optimize retail operations, supply chain management, and e-commerce, utilizing AI and data analytics. The center supports Walmart’s global retail innovation, especially in the omnichannel and digital sectors.
Shell’s GCC in India is focused on streamlining global operations in areas such as finance, procurement, and sustainability The center plays a critical role in Shell’s efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and improve energy efficiency through technological advancements

Citi’s GCC in India manages global operations in IT, data analytics, and customer experience, playing a pivotal role in the bank’s digital transformation and modernization efforts.

Bosch’s GCC in India specializes in developing advanced software solutions for automotive and industrial products The center drives research in IoT, automation, and smart mobility, supporting Bosch’s global product innovation strategy
The rise of GCCs has positioned India as a global hub for innovation, providing businesses with access to a vast talent pool and robust infrastructure. Here’s why GCCs are making a substantial impact:
Talent Utilization: India’s large pool of skilled professionals, particularly in IT, finance, and research, makes it an attractive destination for global companies seeking to expand their operations.
Cost Efficiency: GCCs in India offer significant cost advantages, enabling companies to innovate and scale more rapidly without the financial burden of their home countries
Innovation Hubs: Once considered just support centers, GCCs have now become integral to developing cutting-edge solutions that drive global business success, especially in digital transformation, AI, and automation
Sustainability and Compliance: Many GCCs focus on eco-friendly initiatives and corporate responsibility, contributing to global sustainability efforts and sustainable business practices.
The proliferation of GCCs in India is transforming the country into a hub for global innovation. These centers drive digital transformation, enhance business efficiency, and support multinational companies in staying competitive by leveraging India’s vast talent pool and resources.
For businesses aiming to enhance their brand positioning in this dynamic environment, Origami Creative, based in Bangalore and serving clients in India and Dubai, offers expert employer branding services and comprehensive internal and external communication solutions. Origami Creative ensures companies effectively communicate their brand values, attract and retain top talent, and bolster their market presence.

