Innovative SuDS Solutions for Urban Environments











Limited Footprint
Insufficient space in dense urban areas for below-ground systems
like tanks, crates, and ponds
Elevated groundwater can compromise the functionality of conventional SuDS
Existing infrastructure and topography can limit the feasibility of traditional SuDS approaches.



Shallow, vegetated depressions that temporarily store and slowly release stormwater.
Shallow, vegetated channels that convey and infiltrate surface runoff.
Porous paving and permeable surfaces that allow water to infiltrate into the ground.


1
2
Evaluate site constraints, soils, and groundwater levels to determine feasibility.
SuDS planters can be strategically placed along pathways, near building entrances, or in communal areas, serving as both decorative elements and stormwater management solutions.
Optimize for stormwater management, amenity, and environmental benefits.




Ensure regular mowing, pruning, and plant replacement for optimal performance.
Conduct regular inspections and address any structural or functional issues promptly
Periodically remove accumulated sediment to maintain storage capacity and infiltration.
Inform site users about the purpose and proper use of above-ground SuDS features





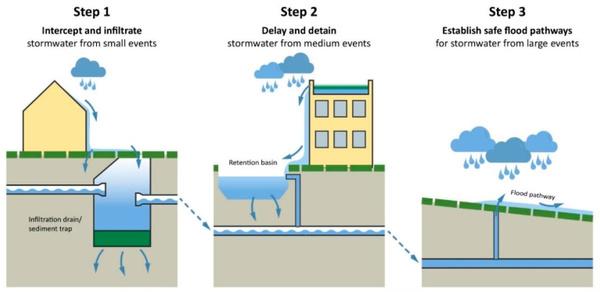
Stormwater Management
Effectively attenuate and infiltrate surface runoff, reducing flood risk

Ecological Enhancement
Provide habitat and support for native flora and fauna
Amenity Value
Integrate green infrastructure that enhances the aesthetic and recreational value of the site
Contribute to the overall sustainability and resilience of the urban environment.

Detention Basin
A shallow, vegetated depression that temporarily stores and infiltrates stormwater runoff.
Permeable Paving
Porous surfaces that allow water to infiltrate into the ground, reducing surface runoff
Shallow, vegetated channels that convey and infiltrate surface runoff, enhancing stormwater management




Integrated Approach
Multifunctional Design
Technological Innovations
Combining above-ground and below-ground SuDS systems for optimal performance.
Incorporating SuDS features that provide stormwater management, ecological, and amenity benefits.
Leveraging new materials, sensors, and data-driven tools to enhance SuDS effectiveness.
Collaborating with communities, policymakers, and experts to drive sustainable urban drainage solutions
Stakeholder Engagement


