BrainTumorSegmentationusinghybridofboth NetrosopicModifiedNonlocalFuzzyC-meanand ModifiedLevelsets
ShaimaElnazer1,MohamedMorsy2,MohyEldinA.Abo-Elsoud3
1LectureAssistant,Communicationdapartment, NileAcademy,Mans.univ,Mansoura,Egypt. Shaima_elnazer@yahoo.com
2Doctor,Communicationdapartment, Mans.univ,Mansoura,Egypt.
3Professor,Communicationdapartment, Mans.univ,Mansoura,Egypt.
Abstract:animprovedsegmentationapproachbasedonNeutrosophicsets(NS)andModifiedNonlocalFuzzyc-meanclustering (NLFCM)isproposed.ThebraintumorMRIimageistransformedintoNSdomain,whichisdescribedusingthreesubsetsnamely;the percentageoftruthinasubsetT%,thepercentageofindeterminacyinasubsetI%,andthepercentageoffalsityinasubsetF%.The entropyinNSisdefinedandemployedtoevaluatetheindeterminacy.NSimageisadaptedalsousingModifiedNonlocalFuzzyCmeanalgorithm(MNLFCM).Finally,MRIbraintumorimageissegmentedandtumorisselectedusingModifiedLevelSets(MLS). TheproposedapproachdenotedasNS-MNLFCM-MLSandcomparedwithanotherpaperusingJaccardIndexandDice Coefficient.TheexperimentalresultsdemonstratethattheproposedapproachislesssensitivetonoiseandperformsbetteronMRI brainimage.
Keywords:Magneticresonanceimaging,Netrosophic,Nonlocalfuzzycmean,Directionalα-meanoperation,modifiedlevelsets
1.Introduction
TheBraintumorsegmentationmethodscanbecome classifiedintothreeclassesinlinewiththelevelofrequired humanbeinginteractionasdescribedsimplybyFooetal. [1],Olabarrigaetal.[2],andYao[3]:manualsegmentation, semiautomaticsegmentation,andtotallyprogrammed segmentation.Braintumorsarehardtosegmentsincethey haveavarietyofpresenceandeffectonadjoiningstructures. Followingareseveralofthetypicalcharacteristicsofbrain tumors:(A)changegreatlyindimensionsandplacement,(B) varygreatlyinthewaytheybepresentinMRI,(C)might haveoverlappingintensitieswithnormaltissue,(D)canbe spaceoccupying(newtissuesthatmovesnormalstructure)or infiltrating(changingrealestateofexistingtissue),(E)may enhancefully,somewhat,ornotatevery,withcontrastagent.
Clusteringisknownasagenerallyusedmathematical procedurewhichinturnperformssegmentationprocessto distinguishthestructuresandmaternityshapespresentina greatinputimageordataset[4]Itcouldbecategorizedinto twogroups:hierarchicalanddividing[5].Theoutputof hierarchicalclusteringareliketreeandtheydon'tneedto specifythenumberoftheamountoftheclustersand independentofthefirstcondition.However,itmightfailto separateoverlappingclustersduetonotenoughinformation regardingthesizeofclustersoritsglobalcondition.Dividing clusteringalgorithmonfixthedisadvantageofhierarchical clusteringalgorithmpartitionsthedatasetintospecific numberofgroupings.Fuzzybasedclusteringallowspartition
aninputphotointoseveralhomogenousclassesorclusters, bywhichinturnidenticalconditionsaregroupedfoundina sameclassandnon-identicalitemsbelongtodifferent classes
Themajorityofthealgorithmsfoundinimageprocessing aresusceptibletoseveraluncertainties,pertainingto instance,graynessambiguity(uncertaintyinsidetheinput detailsitself).Thekeyaimofthisworkshouldbetolessen uncertaintywhileclustering.Generallytherearetwomain tacticsinclusteringtechniqueparticularlycrispandfuzzy clusteringtechnique.Duetodifferentsituations,forimages, problemslikesmallscaleofspatialresolution,poorlight, occurrenceofnoise,powerimbricationsleadscrisp segmentationahardtask.Betweennumerousclustering techniques,fuzzyc-means(FCM)[6]algorithmisusually moresignificantasaresultoftherobustness
Althoughitisdefinitelyrobustitworksjustontheimages withnonoise.Manyresearchersexperienceanalyzedbrain MRIsegmentationusingFSs,seeZhao[7]Agrawal[8].Yet thesealgorithmsstillincludeproblemsduetodifferent situations,forinstance,takingbrainimagesunderlowofthe illuminationmakeitunclear.Ingeneral,FCMcriteriahave greaterdatamanagingcapacityandhavebetteroperability afterdiversifiedinforange.Duetotheapplicationofpixel neighborhoodinformation,RFCMalgorithmhasniceoverall performanceofnoiserestraining,andgetsgoodsegmentation benefitscomparingwithstandardFCM.Yet,wefoundthat withalltheincreaseofnormaldeviationofnoise,theability ofnoisereductionsofFCMalgorithmmightbecomeweaken. V.P.Ananthi[9]useSegmentationofbraintumorbasedon
InternationalJournalofScienceandResearch(IJSR)
ISSN(Online):2319-7064
IndexCopernicusValue(2013):6.14|ImpactFactor(2014):5.611
interval-respectedintunisticfuzzysetsfeaturesDice coefficientequalzero.967.M.Zarinbal[10]workin astrocytomasextractiononlyusingtype2fuzzyandhavegot accuracyof89%.
Inrespecttothissituation,allofusputforwardclustering algorithmbasedinnon-localinformationNON-LOCAL unclearC-meansclustering,(NLFCM),agreaterweighted neighborhooddetailscanbeused,soitisdefinitelybetterto suppresssoundsthanthatofRFCMalgorithm.Non-local regularizationwasfirstformerlyusedforpicturedenoising, callednon-localindicatedenoising[11].Thealgorithm essentiallyusestheredundantinformationofnormal structure,franklyneighborhoodaboutapixelandaswell otherneighborpixelsfoundinthesamescenemaymatch witheachvariousother.TheNLFCMalgorithmidentifiesa weightedgraphofallpixelsintheimage,inwhichtheweight valueisreceivedbysimilaritycalculationoftwo neighborhoodpixels
Theconvergencerategetsaffectedifthenumberof clustersanditerationsaresubsequentlyincreased. Diminishingthenumberofiterationsandclusterstoobtain fasterconvergenceratehasanadverseeffectuponthe segmentationaccuracy.Toovercomethesekindsof hindrances,anovelsegmentationalgorithmwhichcombines Neutrosophystudiesthefoundation,characteristics,scopeof neutralities,andtheirinteractionswithdistinctideational spectra.Itisusuallyanewphilosophythatextendsfuzzy logicandisthebasisofneutrosophiclogic,neutrosophic likelihood,neutrosophicsettheory,andneutrosophic statistics.Becausetheworldisfilledwithindeterminacy,the imperfection of understanding that a human receives/observesfromtheexternaluniversealsocauses imprecision.Neutrosophyintroducesanewprinciple <Neut-A>,whichisdefinitelytherepresentationof indeterminacy.However,thistheorycanbemostlydiscussed inphysiologyandmathematics.Thus,applicationstoprove thistheorycanresolverealchallengesareneeded.Inthis kindofdissertation,Iapplyneutrosophytobraintumor segmentation.Inbraintumorsegmentation,neutrosophy helpsreducenoises.InMRIbraintumoursegmentation, neutrosophyintegratestwocontroversialopinionsabout noise.
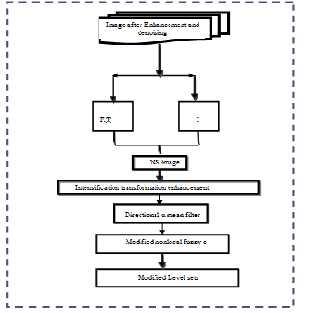
2.Proposedalgorithm
Ansuperiorsegmentationapproachbasedupon Neutrosophicsets(NS)andNonlocalFuzzyc-mean clustering(NLFCM)isrecommended.ThebraintumorMRI imageisbecomeNSdomain,whichisdefinedusingthree subsetsparticularly.TheentropyinNSisdefinedand employedtogaugetheindeterminacy.NSimageismodified usingMovingMeanOperation(MMO)andalsousing ModifiedNotlocalFuzzyC-meanalgorithm(MNLFCM). Finally,MRIbraingrowthimageissegmentedandtumoris selectedapplyingModifiedLevelSets(MLS).Theproposed approachdenotedasNS-MNLFCM-MLSandusing MaximaMorphologicalTransform(MMT)tofindaccurate tumorboundary.Wecomparedwithanothernewspaperusing




sensitivity,SpecificityandDiceCoefficient.Thetrialand errorresultsdemonstratethefactthatofferedapproachisless hypersensitivetonoiseandfunctionsbetteronMRIbrain image.Figure1showtheflowchartoftheproposedapproach.
2.1NeutrosophicMRIbraintumorImage
LetUgetanuniverseoftalk,andWbeasetincludedin Circumstance,whichiscomposedsimplybybrightpixels.A neutrosophicimagePisindicatedbythreesubsetTo,Iand F.ApixelPintheimageisidentifiedasP(T,Myspouseand i,F)andbelongstoWinthenextway:itist%trueinthe dazzlingpixelset,i%indeterminate,andf%bogus,wheret variesinTvariesI,andfvariesinN.ThepixelP(i,j)inthe imagewebsiteistransformedintoneutrosophicdomainP NS(i,j)=T(i,j),I(i,j),F(i,j).WhereT(i,j),I(i,j)andF(i, j)willbetheprobabilitiesbelongtobrightwhiteset, indeterminatesetandnon-whiteset,respectively[12],which aredescribedas:equationbelow:
ThepixelP(i,j)intheimagedomainistransformedinto NeutrosophicdomainPN
Volume5Issue2,February2016 www.ijsr.net LicensedUnderCreativeCommonsAttributionCCBY
InternationalJournalofScienceandResearch(IJSR)
ISSN(Online):2319-7064
IndexCopernicusValue(2013):6.14|ImpactFactor(2014):5.611
S(i,j)={T(i,j),I(i,j),F(i,j)}. WhereT(i,j),I(i,j)andF(i,j)aretheprobabilitiesbelong towhiteset,indeterminatesetandnon-white set, respectively,whicharedefinedinthefollowingequations.
PNS(i,j)={T(i,j),I(i,j),F(i,j)} (1)


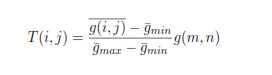

Ho(i,j)=abs(g(i,j)g(i,j)) (2) F(i,j)=1T(i,j) (3) (4) (5) (6)

Whereg(i,j)isthelocalmeanvalueoftheimage,Ho(i,j)is thehomogeneityvalueofTat(i,j)whichisdescribedby theabsolutevalueofdifferencebetweenintensityg(i,j) anditslocalmeanvalueg(i,j)Figureshowinputimageand ifoftheenhancedMRIimagethenNSImageareshownin fig(D)
2.2EnhancementofNSMRIbraintumorImage

TheMRIbraintumorpictureinNSdomainmightincreased usingintensificationtransformationenhancementtechnique (ITET)toincreasethetopqualityandemphasizescertain featuresofapicturetomakessegmentationeasierandmore effective[13].Figure3showresultofusing(ITET)
entropyisoptimum,theseveralintensitieshaveeven probabilityandthefeaturesdistributeuniformly.Ifthe entropyissmall,theintensitieshavedifferentpossibilities andtheirdistributionsareactuallynon-uniform.
Definition1(Neutrosophicimageentropy)NSpicture entropyisdefinedwhilethesummationoftheentropiesof threesubsection,subdivision,subgroup,subcategory, subclassF,TandI,whichisemployedtoevaluatethe distributioninthecomponentsinNSsite[14]:
EnT=−PT(i)lnPT(i) (9)
EnF=−PF(i)lnPF(i) (10) EnI=−PI(i)lnPI(i) (11) EnNS=EnT+EnI+EnF (12) WhereEnI,EnTandEnFaretheentropyofsubsetsT,Iand F,respectivelyasshowninfig4.
Fig4:GUIResultofentropycalculation
2.4Directionalα-meanoperation
In[14],anα-meanfunctioningwasdefinedona neutrosophicimage,andittakenoffnoiseefficiently However,itcouldblurringtheimageandlessenthecontrast, whichcanreducetheperformanceofthesegmentationto overcomethiskindofdrawback,directionalα-mean operationdenotedasDAMisusuallynewlyproposedto removethenoiseeffectandconservetheedgesatthesame time.ThefunctionofthedirectionalmeanfilterDAMis identifiedas[16]: WhereG(i,j)ThandG(i,j)TVarethenormofthe gradientat(,atthehorizontalandverticaldirection, respectively.



2.3EntropyofNSbraintumorMRIImage

Entropyisutilizedtoassessthedistributionofdiversegray levelinmindtumorMRIimages.Intheeventthatthe



Volume5Issue2,February2016 www.ijsr.net LicensedUnderCreativeCommonsAttributionCCBY

InternationalJournalofScienceandResearch(IJSR)
ISSN(Online):2319-7064
IndexCopernicusValue(2013):6.14|ImpactFactor(2014):5.611
3.4ModifiedNonLocalFuzzyCmean:
Asshowninabove,NONlocalFCM(NLFCM)isextremely sensitivetotheoutliers.Themembershipfunctionofthe Nonlocalunclearismodifiedbylookingattheoutliers rejection;Frequency.(10)becomes:16
vicinityofapoorlydefinedborder,theborder-stopfunction (BSF)doesnotstopthecontour[22].
Thepartoftheexponentisdefinitelytolimitthepartially distributionwiththepointsbetweentwoneighboringclusters somewhatthantoallgroupings.Isdefinedas: ExactlywhereXmaxandTimesminarerespectively,the maximumandtheminimalintensityintheimageisbetween 1and2Ifthegraphichasabigintensityselectionthepartial distributionofthepixelsbetween2surroundingclustersis reduced.Notlikely,iftheimageincludesasmallintensity range,isusuallycloseto1andthepartialdistributionofthe pixelsisbasicallyamongtheadjacentgroupings.

ThemembershipfunctionofNLFCMismodifiedbysimply replacingtheoriginallengthfromequation8in[11]






ToovercomethelimitationwiththetraditionalBSFsin borderbasedactivecontourtypes,weproposeaconstruction toconstructagroupofrobustBSFsthatmakeuseof probabilityscoresratherthanthepredictedclassbrandsfrom aclassifier.Seeingthatthescoresfallin[0,1],thiskindof taskisjustlikefuzzysegmentation.Unlikethetechniquesof [23],[24],whichinturnrelyonlyoncategoryprobability usingBayes'guideline,ourframeworkisconsiderablymore flexiblesinceitutilizestheprobabilityscoresbyany classifier.Atthesametime,wemaintaingradientinformation toendcontourevolutionwhenpresentlytherearenofuzzy principlesduetodistinctlimitations.Theseideas differentiatetheworkfrom[25],whichreliesonenergyand isalsoconsideredaregion-basedlevelsettechnique.The traditionalBSFneedsreinititializationtoavoidirregularities duringitsevolution[20],[21].Asreinitializationoftenbrings aboutproblems,Lietal.[22]proposedthelengthregularized levelsetdevelopment(DRLSE)whichremovesthe advantagesofreinitialization.ThattheyappliedtheDRLSE toanedge-basedactivecurvemodelbyintroducingthe gradientflowasequation(19) WeusethefuzzyESF
CombiningNSbraintumorimagewithMNLFCMweget accurateplaceofbraintumorasshowninfigure6 a

2.5Modifiedlevelsets:
AfterusingnetrosophicwithModifiedNonlocalFuzzyC Mean(MNLFCM)wehavetomakeuseofboundarymethod togetaccuratetumor.InGeneral,picturesegmentation modelsusinglevelsetsmethod(LSM)canalwaysbe classifiedasedge-basedtypesorregion-basedmodels[17][18].Theformerutilizesedgedetails[19]althoughthelatter employsaregiondescriptortocontrolthedisplacementof theactivecontour[20],[21].Edge-basedtypesarenot sensitivetoinhomogeneityofimagefeatures.Butare sensitivetoobjectswithpoorlydescribedtumorsboundaries. Inimagesinwhichtheintensitieschangesteadilyinthe
WherePistheprobabilityscorefortheforeground Subsequently,thefuzzyESFisusedtoregularizefunctionin (4)toobtainwhichcanbesimplyexpressedby =
(17) (19)
ThefuzzyESF,willcompeltobenear0whenisnearzero despitethefactthatismuchhigherthan0,i.e.,whenthe pictureforcedropsbitbybit.Consequently,willbenear0 whichwillstopashapeatthefanciedlimit.Itisclearthat capacityassumesanimperativepartwhenaninadequately characterizedlimitisavailable.Itproducesabaseworth whenthescoresareatthechoicelimit.Besides,holdingthe inclinationdataishelpfulatclearlimitssubsequenttothere arenofluffyqualities.Capacityfusesbothofthesefavorable circumstancestogiveexactdivisionresults.What'smore,the proposedstructureisadaptable
Volume5Issue2,February2016 www.ijsr.net LicensedUnderCreativeCommonsAttributionCCBY
InternationalJournalofScienceandResearch(IJSR)
ISSN(Online):2319-7064
IndexCopernicusValue(2013):6.14|ImpactFactor(2014):5.611
2.6MaximatransformEnhancement
Forangraphicisdefinitelymadeusingmorphological operationssuchasiterateddilationsoftheimageandlaterit iscamouflaged.Kohetal[29]havedefinedHtransformas whereRI(I-h)istheretracedimagebydilatingIwith respecttoI-h.Thissortofrestrainsallpixelsinwhose powerrateislittlerthanthelimitifmaybetheworthisrather thantheirneighbors.Wellthenlocateallterritorialidealof pictureandindividualthepixelsofsuccessiveforce.Maxima strategyistakenoututilizingtheequationRegionalmaxima ofH-maximachangedgrouppicturehavingtumorcanbe utilizedtouprootneighborhoodpixelsofpowerunderneathh fromthecapabilities.UtilizingEq.(9),lastparticulartumor localeisunquestionablyseparatedwithoutedemaandother non-tumorarea.H-maximachangehappentobeshownin Fig.8.

ADSCestimationofzeroshowsnocover;anestimationof onedemonstratesperfectdivision.Highernumbersshow betterdivision,whichimpliesthatthedivisionresults coordinatethegroundtruthsuperiortoanythingresultswith lowerqualitiesDSCvalues.
Table1:Accuracyoftheproposedsegmentationapproach foreachsubjectusingdicesimilaritycoefficient(DSC(%)). &Accuracyoftheproposedsegmentationapproachforeach subjectusingthe98percentilemodifiedHausdorffdistance
Patient number DSC Hausdroff p.1 98.403 2.05 P.2 96.56 5.13 p.3 97.34 1.78 p.4 96.76 12.43 (20) (21)
Fig8:SegmentedtumorusingHtransform
2.7PerformanceEvaluationMetric:
Thedatasetsforexperimentalanalysiswereobtainedfrom MansouraHospitalUniversityMRIScan.Testsareexecuted onnumerousbrainMRimagedatasetshavingtumor.To evaluatethesegmentationaccuracy,weusedthreemetrics, namely,(i)theDiceSimilarityCoefficient(DSC),(ii)the98percentilemodifiedHausdorffdistance(H98)[30].The followingsubsectionswilldescribeeachusedmetricinmore detail.
A)DiceSimilarityCoefficientTheDicesimilaritycoefficient (DSC)measuressetagreementbetweentwosets(S,G),andis definedastheunionsizeofthetwosetsdividedbythe averagesizeofthetwosets
DSC(S,G)=(2|S∩G|/(S∩G+SG))×100 (22)
Insegmentationvalidation,theDSCisusuallyexpressedin termsoffalsepositive(FP),falsenegative(FN),true negative(TN),andtruepositive(TP)counts,whichwere obtainedbycomparingthesegmentationresultstotheground truth(goldstandard)(seeFigure31).Thesevaluescanbe usedtocalculatetheDSCasshownby[30]:
DSC=2TP/(2TP+FP+FN)×100 (23)
Fig9:Diagramillustratingthemeaningofsegmentationerrors,namely, truepositive(TP),falsepositive(FP),truenegative(TN),andfalsepositive (FP).Thesesegmentationerrors,obtainedbycomparingthesegmentedand thegroundtruthobjects,areusedtocalculatethedicesimilaritycoefficient (DSC).

B)ModifiedHausdorffDistance
Distancemeasuresareanothertypeofperformancemetric usedforevaluatingsegmentationmethods.TheEuclidean distanceisoftenutilized,butanothercommonmeasureisthe Hausdorffdistance(H).TheHvaluefromasetStoasetGis definedasthemaximumdistanceofthesetStothenearest pointinthesetG(seeFigure6[30]):
H(S,G)=maxsS{mingG{d(s,g)}}, (24)
wheresandgarepointsofsetsSandG,respectively,and d(s,g)isEuclideandistancebetweenthesepoints.The bidirectionalHausdorffdistance,denotedbyH(S,G), betweenthesegmentedregion(S)anditsgroundtruth(G)is definedas:
HBi(S,G)=max{H(S,G),H(G,S)}. (25)
Inthispaper,toeliminatetheeffectofsegmentationoutliers, the98-percentilemodifiedHausdorffdistance(MH)was usedtoassesstheproposedsegmentationframework accuracy.Metricswerecomputedbycomparingaground truthsegmentationtoresultsfromtheproposedsegmentation technique.Thedetailedsegmentationresultsforeachsubject aregiveninTables1
Volume5Issue2,February2016 www.ijsr.net
LicensedUnderCreativeCommonsAttributionCCBY
InternationalJournalofScienceandResearch(IJSR)
ISSN(Online):2319-7064
IndexCopernicusValue(2013):6.14|ImpactFactor(2014):5.611

AsdemonstratedinTable1,theDSCforsegmentationofthe braintumorisgivesgoodresultusingourproposed algorithm.Performanceshowninfig(9)andintable2.
Conclusion:
Inthispaper,theproposedfullautomaticbraintumor segmentationtechniquehasbeendenotedasNS-MNLFCMMLSandusingMaximaMorphologicalTransform(MMT) tofindaccuratetumorboundary.Itisbasedonneutrosophic preprocessingmethodandModifiednonlocalfuzzycmea ClusteringmethodComparedwithanothernewpaperusing JaccardIndexandDiceCoefficient.Resultsdemonstratethe factthatofferedapproachislesshypersensitivetonoiseand functionsbetteronMRIbrainimageProposedalgorithm givehighaccuracyresultcomparedwithanothermethods. Theresultsoftheproposedmethodshowthatthe100% detectionrateinall34caseswithaverageofhighdice 99.37%,highspecificity99.26%andlowermissingrate 0.52,andmodifiedHausdroffdistance1.302.
[4]RafaelC.GonzalezandRichardE.Woods,DigitalImageProcessing, SecondEd..,PearsonEducationpublication,ISBN81–7808–629–8, pp.68–70.
[5]G.R.SinhaandBhagawatiCharanPatel,MedicalImageProcessing: ConceptsandApplications,PHIpublications,ISBN-978-81-203-4902-5, 2014.
[6]ZhouD,ZhouH,Amodifiedstrategyoffuzzyclusteringalgorithmfor imagesegmentation.2014.SoftComput,pp1–12.
[7]ZhaoF,JiaoL,LiuH(2013)Kernelgeneralizedfuzzyc-meansclusteringwithspatialinformationforimagesegmentation.DigitSignalProcess. 23:184–199
[8]AgrawalS,PandaR,DoraL(2014)Astudyonfuzzyclusteringfor magneticresonancebrainimagesegmentationusingsoftcomputing approaches.ApplSoftComput24:522–533
[9]V.P.Ananthi,Anewfuzzyclusteringalgorithmforthesegmentationof braintumorSpringer-VerlagBerlinHeidelberg2015
[10]M.Zarinbal,Intervaltype-2fuzzyimageprocessingexpertsystemfor diagnosingbraintumors.M.Zarinbal;Dept.ofInd.Eng.,AmirkabirUniv. ofTechnol.,Tehran,IranNorbertWienerinthe21stCentury(21CW),2014 IEEEConference
[11]AFUZZYC-MEANSCLUSTERINGSCHEMEINCORPORATINGNON-LOCAL SPATIALCONSTRAINTFORBRAINMAGNETICRESONANCEIMAGE
SEGMENTATION
Cong,Wang;Song,Jianhua;Wang,Lei;Liang,Hong;Li,JinJournalof MedicalImagingandHealthInformatics,Volume5,Number8,December 2015,pp.1821-1825(5)
[12].Mohan,J.,Krishnaveni,V.,Guo,Y.,Kanchana,J.:MRIdenoising basedonneutrosophicwienerfiltering.In:IEEEInternationalConference onImagingSystemsandTechniques(IST),pp.327–331(2012)
[13].Zhang,M.,Zhang,L.,Cheng,H.D.:Aneutrosophicapproachto imagesegmentationbasedonwatershedmethod.SignalProcessing90, 1510–1517(2010)
[14]Guo,Y.,Cheng,H.D.,Zhang,Y.,Zhao,W.:Anewneutrosophic appraochtoimagethresholding.In:Proceedingsofthe11thJoint ConferenceonInformationSciences,pp.1–6.AtlantisPress(2008)
[15]Y.GuoandH.D.Cheng,"Newneutrosophicapproachto imagesegmentation,"PatternRecognition,vol.42,pp.587595, [16]Y.Guo,H.D.Cheng,J.TianandY.Zhang.Anovel approachtospecklereductioninultrasoundimaging.Ultrasoundin Medicine&Biology,vol.35,2009.
[17]C.Li,R.Huang,Z.Ding,J.Gatenby,D.N.Metaxas,andJ.C.Gore,“Alevelset methodforimagesegmentationinthepresenceofintensityinhomogeneities withapplicationtomri,”IEEETrans.ImageProcess.,vol.20,no.7,pp. 2007–2016,2011.
[18]S.MukherjeeandS.Acton,“Regionbasedsegmentationinpresence ofintensityinhomogeneityusinglegendrepolynomials,”IEEESignal Process.Lett.,vol.22,no.3,pp.298–302,Mar.2015.
[19]V.Caselles,R.Kimmel,andG.Sapiro,“Geodesicactivecontours,” Int.J.Comput.Vis.,vol.22,no.1,pp.61–79,1997.
[20]D.MumfordandJ.Shah,“Optimalapproximationsbypiecewise smoothfunctionsandassociatedvariationalproblems,”Commun.Pure Appl.Math.,vol.42,no.5,pp.577–685,1989.
[21]T.F.ChanandL.Vese,“Activecontourswithoutedges,”IEEETrans. ImageProcess.,vol.10,no.2,pp.266–277,2001.
[22]A.Pratondo,B.P.Nguyen,C.-K.Chui,andS.-H.Ong,“Vocalcord segmentationfromCTimagesusingmachinelearning,”inProc.10thAsian Conf.ComputerAidedSurgery(ACCAS2014),2014,pp.40–41,TheJapan SocietyofComputerAidedSurgery.
[23]J.Wu,Z.Yin,andY.Xiong,“Thefastmultilevelfuzzyedgedetection ofblurryimages,”IEEESignalProcess.Lett.,vol.14,no.5,pp.344–347, 2007.
Refereance
[1]FooJL.Asurveyofuserinteractionandautomationinmedicalimage segmentationmethods.TechrepISUHCI20062,HumanComputer InteractionDepartment,IowaStateUniv;2006.
[2]OlabarriagaS,SmeuldersA.Interactioninthesegmentationofmedical images:asurvey.MedImageAnal2001;5:127–42.
[3]YaoJ.Imageprocessingintumorimaging.Newtechniquesinoncologic imaging;2006.p.79–102.
[24]D.Smeets,D.Loeckx,B.Stijnen,B.DeDobbelaer,D.Vandermeulen, andP.Suetens,“Semi-automaticlevelsetsegmentationoflivertumors combiningaspiral-scanningtechniquewithsupervisedfuzzypixel classification,”Med.ImageAnal.,vol.14,no.1,pp.13–20,2010., [25]S.KrinidisandV.Chatzis,“Fuzzyenergy-basedactivecontours,” IEEETrans.ImageProcess.,vol.18,no.12,pp.2747–2755,2009., [26]S.OsherandR.Fedkiw,LevelSetmethodsandDynamicImplicit Surfaces,S.S.Antman,J.E.Marsden,andL.Sirovich,Eds.NewYork,NY,USA: Springer-Verlag,2003.
[27]J.A.Sethian,LevelSetMethodsandFastMarchingMethods: EvolvingInterfacesinComputationalGeometry, Science,P.G.Ciarlet,A.Iserles,R.V.Kohn,andM.H.Wricht,Eds.NewYork,, NY,USA:CambridgeUniv.Press,1999,vol.3.
Volume5Issue2,February2016 www.ijsr.net
LicensedUnderCreativeCommonsAttributionCCBY
InternationalJournalofScienceandResearch(IJSR)
ISSN(Online):2319-7064
IndexCopernicusValue(2013):6.14|ImpactFactor(2014):5.611
[28]C.Li,C.Xu,C.Gui,andM.D.Fox,“Distanceregularizedlevelsetevolution anditsapplicationtoimagesegmentation,”IEEETrans.ImageProcess., vol.19,no.12,pp.3243–3254,Dec.2010.
[29]KohKH,ShenWA,ShuterB,KassimAA(2009)Segmentationof kidneycortexinMRIstudies:aconstrainedmorphological3Dh-maxima transformapproach.InternJMedEngInf1:330–341
[30]K.O.Babalola,B.Patenaude,P.Aljabar,J.Schnabel,D.Kennedy,W. Crum,S.Smith,T.Cootes,M.Jenkinson,andD.Rueckert.Anevaluation offourautomaticmethodsofsegmentingthesubcorticalstructuresinthe brain.Neuroimage,47(4):1435–1447,2009.
Volume5Issue2,February2016 www.ijsr.net
LicensedUnderCreativeCommonsAttributionCCBY
