6 minute read
Rohit Voleti (International Management Institute, New Delhi
ROHIT VOLETI
International Management Institute, New Delhi
Advertisement
Technology Potential
Banking in the age of FinTech:
Partner or Perish Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
“A crisis is a terrible thing to waste.” - Paul Romer Every crisis brings to us an opportunity to reimagine the way we operate in this dynamic world. The banking industry over the past few years has witnessed changing customer expectations and growing competition from fintech companies and technology leaders who have forayed into the banking space, leaving banks with no choice but to embrace digital technology. The COVID-19 pandemic has not only catalysed this change but has also depicted that inculcating technological practices is critical to continuity, consistency and resilience. For a world that is recovering from the adverse effects of the pandemic, banks which are at the nerve center of global economies must collaborate with technology providers such as fintechs in shaping the future of economic growth.
Unveiling the potential of technology
Blockchain
5G
Internet of things (IoT) • Leverage data to derive customer insights • Customer centricity through hyper personalisation • Smart pricing, product bundling
• Data privacy and security • Fraud detection • Risk management
• Cross-industry collaborations
• Cutting-edge analytics • Seamless connectivity and services
• Customer care automation
• Voice support, language processing • Enhanced experience
Banks have sustained desirable levels of stability and continue to command a high level of trust and confidence among customers. This advantage must be leveraged so that banks remain relevant to customers as financial intermediaries in a digital future that will be driven by personalisation, enhanced experience and transparency. It is under this context that technology plays a pivotal role in building upon the inherent strengths of banks in delivering value. The technology giants of today have forayed into most if not all sectors of the economy and their entry
into the banking space has been a question of “when” rather than “if”. These companies have reset the standards of customer experience and offer lessons to traditional banks - to either adopt or collaborate. • Tech giants command a high level of customer loyalty largely due to the frictionless ecosystems that they have created in effectively mapping sellers with customers and offering one-stop-
shop solutions. Banks must rethink their offerings in such that they are tailor-made to the needs of their customers.
• A survey by Bain & Company reports that several people tend to trust tech companies more than banks, which correlates to their increasing preference in seeking banking and financial services offered by fintechs. Traditional banks must prioritise customer experience and service quality by making simple digital interventions in their business models, which will go a long way in not only winning over new customers but also resisting customer churn.
Source: Bain & Company
• Data harnessing capabilities of the tech companies is what differentiates their competitive edge in understanding consumer needs and behaviour. Banks that preside over an ocean of customer data must leverage it in offering better products and services.
Win-Win
With the ever-increasing digital presence and usage across all major economies in the world, banks can no longer remain aloof to the new realities of the world. Given that the banking and financial services industry is highly regulated, it limits the potential and scope of fintech companies in making significant inroads into the banking space. These factors indicate a “partner or perish” scenario for traditional banks and fintech companies.

Source: PwC
• Fintech companies bring innovative offerings to the table but lack the expertise and competence in managing the entire financial life cycle. This is where traditional banks could offer their valuable experience in managing customer relationships across diverse segments and channels. Together, such collaborations can capture a wider market across geographies. For example, Commerzbank of Germany had collaborated with IDnow for a mobile-app offering banking services, which had resulted in a 50% increase in customer conversion for the bank.
• Strategic synergies between fintechs and traditional banks provide mutual benefits to both as it facilitates the creation of omnichannel customer offerings that would increase overall profitability. A case in point would be the example of CurrencyCloud providing a payment engine to Fidor Bank, which was incorporated into their service model with no requirement for any extra infrastructure, which resulted in significant forex cost reduction for their customers.
• Fintechs have the first mover advantage over
traditional banks in prioritising user experience and the overall customer journey, which has led to rapid growth in their customer base and has enabled them capture market share. For example, major global traditional banks such as ANZ and Westpac have made investments in a fintech startup - ‘Data Republic’, which provided a data hub for them through which their enterprise customers could save, share and analyse data under a safe and secure environment.
• Physical branches could continue to remain critical for the legacy services of the banks but it is important to take note of the declining traffic in these branches, which poses a question on cost-effectiveness for traditional banks. By partnering with fintech companies, banks can create models that deliver both physical as well as digital banking to its customers, which would elevate the customer experience to a whole new level.
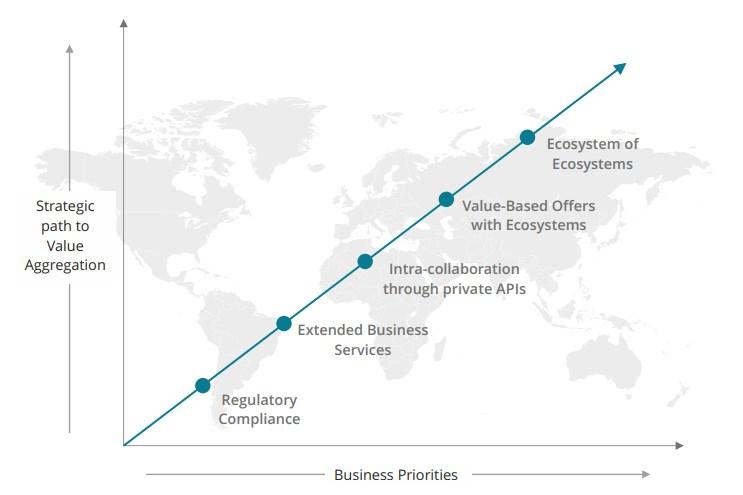
New-age banking ecosystem Source: Deloitte
• The emergence of open banking and application programme interface (API) based ecosystems provides immense opportunities for collaborations between banks and fintechs in such that they are a step forward in the journey of Banking as a Service (BaaS) - ecosystem of third -party service providers access to data to generate insights and deliver unique products/ services. For example, HSBC’s partnership with Tradeshift enables the bank use the Tradeshift platform in automatically generating invoices, thereby reducing the payment cycle.
Challenges
Despite the fact that traditional banks and fintech companies are approaching a natural convergence in catering to the needs of the new digital world, there are certain factors that impose a challenge to the success of these collaborations.
• Legacy issues faced by traditional banks are difficult to overcome as there are deep rooted systems and processes that hamper the flexibility of these banks.
• Regulatory and compliance norms for the banking industry imposed by governments across different nations poses a challenge on the extent and speed at which new collaborations can be made and brought into action. • Security and privacy management becomes critical to win over the confidence of customers who are otherwise wary of digital transactions. Any threat of data theft or security breaches could impose a significant damage to the reputation of these banks.
On the whole, it can be understood that collaborations between traditional banks and fintech companies would result in enhanced profitability, reduction in costs and offers greater value to users. The coming decade would witness path breaking transformations in the financial industry and the success of banks would depend on their ability to collaborate with strategic partners to adopt emerging technologies. The way ahead for banks to thrive in a digital market context would be to drive innovation through technology, for which they must build a comprehensive ecosystem that benefits all stakeholders.
References
1. https://www.pwc.in/ 2. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en.html 3. https://www.imf.org/en/Home 4. https://www.fintechweekly.com/ 5. https://www.bain.com/insights/