BIOREACTOR & FERMENTER








A bioreactor is a device or system used to support and control the growth and activity of living cells or organisms in a controlled environment. It is commonly used in industrial biotechnology and pharmaceuticals to produce various products, such as enzymes, vaccines, and biofuels. Bioreactors come in different sizes and designs and can be operated in batch, fed- batch, and continuous modes. They have various components such as a vessel, impeller, sensors, probes, and controllers that enable control of different parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and nutrients. The primary aim of bioreactors is to optimize the biological system's growth and activity to maximize productivity, minimize costs, and ensure product quality and safety.
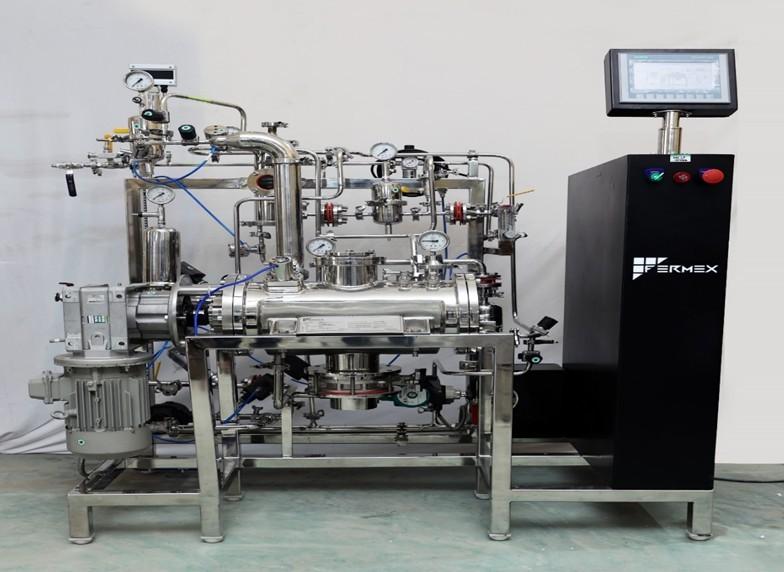
A bioreactor is a complex system that consists of several key components. The main component is the vessel, which is where the biological system is grown and maintained. Other essential components include the agitator or impeller, sensors and probes, controllers, inlet and outlet ports, and a sterilization system. The agitator or impeller facilitates mixing and aeration, while sensors and probes measure various physical and chemical parameters, such as temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen. Controllers adjust the bioreactor's parameters based on the data from the sensors and probes. Inlet and outlet ports allow for the addition of nutrients and removal of waste, while the sterilization system ensures a contamination-free environment. These components work together to optimize the growth and activity of living cells or organisms, making bioreactors an important tool in biotechnology and industrial production.

Bioreactors have numerous applications in biotechnology and industrial production. Some of the key applications include:
1.Production of biofuels and other bioproducts
2.Production of therapeutic proteins and other biopharmaceuticals
3.Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
4.Environmental remediation and waste treatment

5.Agricultural biotechnology, such as production of plant-based vaccines
6.Food and beverage production, such as fermentation of beer and wine
7.Microbial ecology and research

A fermenter is a type of bioreactor that is specifically designed for microbial fermentation. It provides a controlled environment where microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, or fungi, can grow and metabolize nutrients, producing desired products such as ethanol, organic acids, or enzymes. Fermenters are equipped with agitators or impellers, sensors, controllers, and ports for nutrient addition and waste removal.

Fermenters are used in various industries, such as biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage production, to produce a wide range of products. They offer several advantages over traditional batch processes, including increased productivity, reproducibility, and scalability.
Fermenters are an essential tool in the development of sustainable and innovative solutions to various global challenges.
A fermenter typically consists of several key components, including a vessel, agitator or impeller, sensors and probes, controllers, inlet and outlet ports, and a sterilization system. The vessel is the main component of the fermenter, where microbial fermentation takes place. The agitator or impeller facilitates mixing and aeration, while sensors and probes measure various physical and chemical parameters, such as temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen. Controllers adjust the fermenter's parameters based on the data from the sensors and probes.
Inlet and outlet ports allow for the addition of nutrients and removal of waste, while the sterilization system ensures a contamination-free environment. These components work together to optimize the growth and activity of microorganisms, making fermenters an essential tool in biotechnology and industrial production.

Fermenters have a wide range of applications in biotechnology and industrial production. Some of the key applications include:
1.Production of biofuels, such as ethanol, and other bioproducts
2.Production of pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics, enzymes, and therapeutic proteins
3.Food and beverage production, such as fermentation of beer, wine, and yogurt
4.Agricultural biotechnology, such as production of biopesticides and plantbased vaccines
5.Environmental remediation and waste treatment


Bioreactors and fermenters are vessels used for the cultivation of microorganisms or cells in a controlled environment. While they share many similarities, such as agitators or impellers, sensors, controllers, and inlet and outlet ports, there are also several key differences between them. Bioreactors are designed for a wider range of applications, including cell culture and tissue engineering, and often have more advanced control systems to optimize cell growth and metabolism.
Fermenters, on the other hand, are specifically designed for microbial fermentation and typically have simpler systems that are more suitable for microbial growth and metabolism. Both bioreactors and fermenters play crucial roles in biotechnology and industrial production, offering efficient and cost- effective solutions for a wide range of applications.

