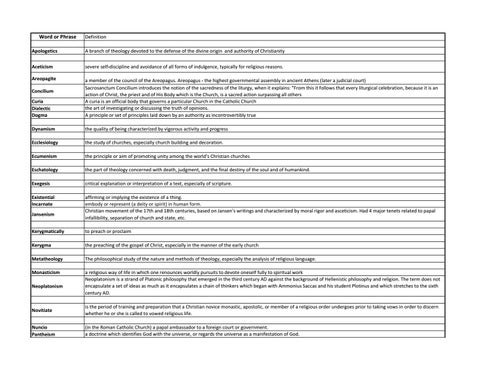
Word or Phrase
Definition
Apologetics
A branch of theology devoted to the defense of the divine origin and authority of Christianity
Aceticism
severe self-discipline and avoidance of all forms of indulgence, typically for religious reasons.
Areopagite
Curia Dialectic Dogma
a member of the council of the Areopagus. Areopagus - the highest governmental assembly in ancient Athens (later a judicial court) Sacrosanctum Concilium introduces the notion of the sacredness of the liturgy, when it explains: "From this it follows that every liturgical celebration, because it is an action of Christ, the priest and of His Body which is the Church, is a sacred action surpassing all others A curia is an official body that governs a particular Church in the Catholic Church the art of investigating or discussing the truth of opinions. A principle or set of principles laid down by an authority as incontrovertibly true
Dynamism
the quality of being characterized by vigorous activity and progress
Ecclesiology
the study of churches, especially church building and decoration.
Ecumenism
the principle or aim of promoting unity among the world's Christian churches
Eschatology
the part of theology concerned with death, judgment, and the final destiny of the soul and of humankind.
Exegesis
critical explanation or interpretation of a text, especially of scripture.
Existential Incarnate
affirming or implying the existence of a thing. embody or represent (a deity or spirit) in human form. Christian movement of the 17th and 18th centuries, based on Jansen's writings and characterized by moral rigor and asceticism. Had 4 major tenets related to papal infallibility, separation of church and state, etc.
Concilium
Jansenism Kerygmatically
to preach or proclaim
Kerygma
the preaching of the gospel of Christ, especially in the manner of the early church
Metatheology
The philosophical study of the nature and methods of theology, especially the analysis of religious language.
Monasticism
a religious way of life in which one renounces worldly pursuits to devote oneself fully to spiritual work Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the third century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as it encapsulates a chain of thinkers which began with Ammonius Saccas and his student Plotinus and which stretches to the sixth century AD.
Neoplatonism
Novitiate
is the period of training and preparation that a Christian novice monastic, apostolic, or member of a religious order undergoes prior to taking vows in order to discern whether he or she is called to vowed religious life.
Nuncio Pantheism
(in the Roman Catholic Church) a papal ambassador to a foreign court or government. a doctrine which identifies God with the universe, or regards the universe as a manifestation of God.
Word or Phrase
Definition
Patristic Patrology
Relating to early Christian theologians The study of the lives, doctrines, and writings of the Fathers of the Church
Pluralism
condition or system in which two or more states, groups, principles, sources of authority, etc., coexist.
Presbyterium
is a modern term used in the Catholic Church and Eastern Catholic Churches after the Second Vatican Council in reference to a college of priests, in active ministry, of an individual particular church such as a diocese or eparchy.
Sacralization
the act or process of acquiring sanctity in a religious context.
Schism
a split or division between strongly opposed sections or parties, caused by differences in opinion or belief. also called East-West Schism, event that precipitated the final separation between the Eastern Christian churches (led by the patriarch of Constantinople, Michael Cerularius) and the Western church (led by Pope Leo IX).
Schism of 1054
Scholasticism
the system of theology and philosophy taught in medieval European universities, based on Aristotelian logic and the writings of the early Church Fathers and having a strong emphasis on tradition and dogma.
Soteriology
the doctrine of salvation.
Syllogism
an instance of a form of reasoning in which a conclusion is drawn (whether validly or not) from two given or assumed propositions (premises), each of which shares a term with the conclusion, and shares a common or middle term not present in the conclusion. Deductive reasoning as distinct from induction.
Tridentine
relating to the Council of Trent, especially as the basis of Roman Catholic doctrine.
Ultramontane
advocating supreme papal authority in matters of faith and discipline.
Vitiate
spoil or impair the quality or efficiency of.