Financial Basics
Content prepared by Francesca Gnesutta, Zerrin Cengiz and Leida Rijnhout for World Fair Trade Organization

Content prepared by Francesco Rocca, for Impact Hub Lisbon



Content prepared by Francesca Gnesutta, Zerrin Cengiz and Leida Rijnhout for World Fair Trade Organization

Content prepared by Francesco Rocca, for Impact Hub Lisbon


Every successful business starts with defining the purpose of the organization: asking yourself WHY you do what you do is fundamental to understanding the reason for your business to exist. You should be clear about the need you are solving and what makes your solution different from existing alternatives.
Secondly, for you to be in business, it is key to have a clear financial plan and understand if the project is economically viable.
This toolkit is made for you to understand the basic financial rules that determine if your business can be profitable and to have an overview of different instruments you can use to fund your business idea.
We assume you already defined your PURPOSE, and decided you want to start a BUSINESS. What we will cover are concepts like costs, prices, sales volumes and funding, for you to gain stronger financial control of your venture.
20% of businesses fail in their first year, according to experts, and 3 of the top 5 reasons are linked to financial issues (source, link):
1. Lack of research
2. Not having a business plan
3. Not having the business funding they need
4. Financial mismanagement
5. Poor marketing
20% of businesses fail in their first year, according to experts, and 3 of the top 5 reasons are linked to financial issues.*
1. Lack of research
According to Kirsty Fitzgerald, the most important practices to master if you wish to give your business more chances to succeed are:
• Improve your cash flow management
According to Kirsty Fitzgerald, the most important practices to master if you wish to give your business more chances to succeed are:
2. Not having a business plan
3. Not having the business funding they need
• Improve your cash flow management
4. Financial mismanagement
• Gain control of your finances
• Gain control of your finances
• Plan and strategize well
5. Poor marketing
• Plan and strategize well
Now, let’s improve our financial mindset and take the opportunity to rethink your costs & pricing strategy, and how to access funding!
Now, let’s improve our financial mindset and take the opportunity to rethink your costs & pricing strategy, and how to access funding!
• Does the world need my solution?
• Am I solving a real need?
• Make your idea a sustainable business
• Business or hobby?
• Make sure you can live from it
• How to reach your sales goals
• Financial control of the project
The first exercise you should do when you decide to start a business is to understand your costs, set the right price for your product/service and calculate your break-even point.
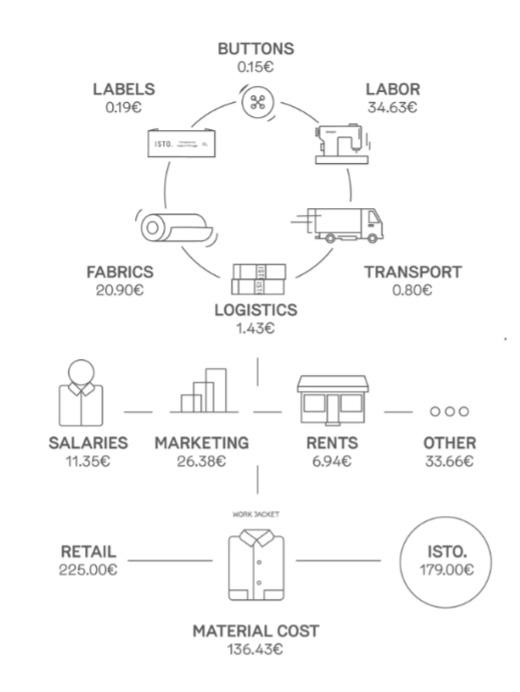
A great example of a fashion brand that transparently shows its cost structure is ISTO. On their website, they share all the costs associated with every product they sell.
Here you can see an example of how they differentiate between Variable and Fixed costs.
Variable cost
This cost is a direct cost for producing your product (cost of materials, labour, packaging, etc.). This will increase or decrease as sales increase or decrease. (top of the picture)
Fixed cost
This cost is fixed and will not change as sales increase or decrease. This cost will include items like rent/ utilities, payroll expenses, monthly website hosting, etc. These are expenses that your business will have regardless of the sales volume. (bottom of the picture)
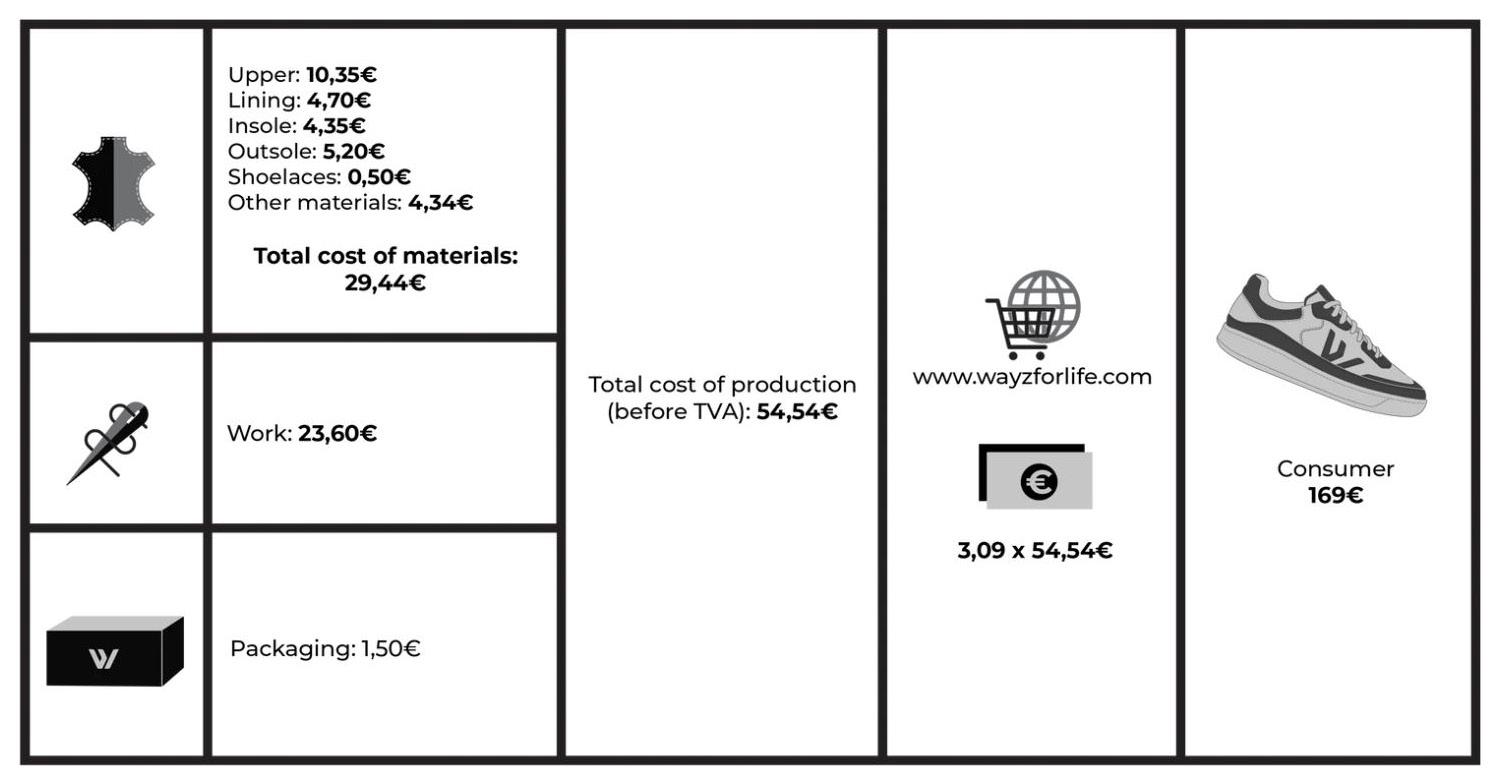
Setting a price for your product/service is a hard task. There is never a one-fits-all answer since different factors come together. However, there are a couple of strategies you can use. Let’s see together two that might help you:
The price of a product is determined by adding a profit element (percentage) in addition to the cost of making the product. It uses the manufacturing costs of the product as its basis for coming to the final selling price of the product.
Have a look at how WAYZ sneakers determine their sales price by using the 3x markup on the cost of production.
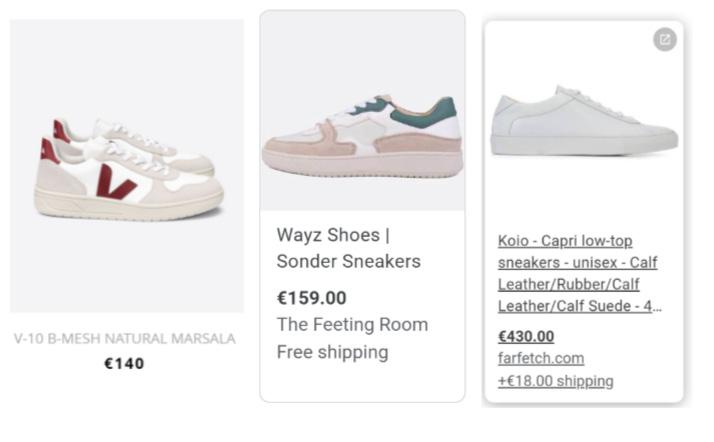
• Competitive pricing: selecting strategic price points to best take advantage of a productbased market relative to the competition. This pricing method is used more often by businesses selling similar products.
• Competitive pricing: selecting strategic price points to best take advantage of a productbased market relative to the competition. This pricing method is used more often by businesses selling similar products.
Competitive pricing
• Competitive pricing: selecting strategic price points to best take advantage of a productbased market relative to the competition. This pricing method is used more often by businesses selling similar products.
Selecting strategic price points to best take advantage of a productbased market relative to the competition. This pricing method is used more often by businesses selling similar products.
• Below you can see how WAYZ sneakers are positioned in comparison to other similar products.
• Below you can see how WAYZ sneakers are positioned in comparison to other similar products.
• Below you can see how WAYZ sneakers are positioned in comparison to other similar products.
Below you can see how WAYZ sneakers are positioned in comparison to other similar products.


To know how many units you will need to sell to start making your business profitable, you should calculate your break-even point.
Break-even is the point at which expenses are covered, and anything that is sold above that point means that your business is making a profit.
The formula to calculate your break-even point is:
• Helps you set sales targets: know exactly how much you need to sell to be profitable
• Gives you a number to critically analyze your cost structure and know where there is space for improvement
Section 4:
After having analyzed the cost and revenue structure of your business, through the break-even analysis you should be able to assess if and when your company can start being profitable. The following diagram shows 4 situations that you might encounter and according to where you are, different financing instruments can be employed.
In case you are positioned in a situation where the business is not working and the whole business model needs to change, you should go back to the previous step and try either to reduce your costs or increase sales targets.
After having analyzed the cost and revenue structure of your business, through the break-even analysis you should be able to assess if and when your company can start being profitable. The following diagram shows 4 situations that you might encounter and according to where you are, different financing instruments can be employed.
If you are in the other 3 situations, start asking yourself the following questions overleaf.
Is the business working?
but I face cash flow issues
but if I scaled it would work I want to scale
the business model needs to change
What is the stage of your business?
(idea stage, startup stage, scaling stage)
How much money do you need?
Which different types of investments could you use?
Do you have all the necessary resources to obtain funding?
What tool to access finance is the most suited for your intention?
We have compiled a simple framework to help you understand the investment landscape for businesses and guide you through some of the possible funding instruments you should know to support you in the financial management of your organisation.
Look at the following tables on pages 14-20 and try to position your organisation according to your business stage, this will allow you to understand:
• Which investments stage you are positioned in
• What investment size you should aim for
• What type of funding you could look for
• Which milestones you should have achieved before applying to a specific funding size
Business stage
Impact Stage
Investment stage
founder/team are driven by purpose and mission
team has defined and KPIs on their making change
Investment size
• Bootstrapping
• Pre-seed
• Pre-seed 0-50K 50—500K
• Seed
Start-up
The impact has been measured, tracked and the model has been proven on bigger scope.
Disrupting the market and streamlining the impact
• Seed
• Series A
• Series A Series B
500K—2m
Financial Basics 15 Image Source: Impact Hub GmbH
partners
• Angel investors
• Strategic partners
• Venture capital
• Banks
• Own revenue
• Crowd equity
• Strategic partners
• Venture capital
• Institutional investors
• Banks
Checklist to successfully fundraise
• Clear story
• Website
• Company name (does not need to be formally registered)
• Positive market/ client feedback
• Market research
• Realistic plan
• Legal structure
• Financial projections
• Validated product market)
• Clear investment needs + Exit strategy
• Pitch & Send
• Core team least one person working
Start-up market/ feedback research growth structure Financial projections Validated Service/ (on the investment Exit Send deck team with at one full-time working
Growth Scaling
500K—2m + 2m
• Data structure and indicators (Customer acquisition cost,...)
• Proven traction with growth potential
• Partner & Vendor network
• Accurate financials (P&L, Cash Flow, Balance Sheets)
• Go-to-market plan
• Core team working full time
• Due diligence ready
• Specialized and professional team for scale
• International network and partners
• Analysis of growth markets (markets of scale)
Financial Basics 19 Image Source: Impact Hub GmbH
Now that you have navigated a wide range of possibilities that can support your organisation in accessing investment, we would like to zoom into 4 key tools that are the most used by small fashion businesses in the idea and startup stages.
Bank Loan
• Historic of your balance
• Business P&L
• Personal liability from
We are summarizing in a diagram the pros and cons of each tool, as well as the necessary documentation you should have in place before trying to access each of them. This framework helps you assess which tool is most suited for your case and that can support you in creating the optimal combination of different financing instruments. Remember that the idea is not to go only for one, but rather to build a good mix of funding streams.
Equity Increase
• Pitch deck
• Historic of your balance
• Growth plan - return & impact model
• Pitch deck
• Historic of your balance
• Growth plan - return & impact model
Public Grants / Sponsorships
• Proven track record
• Clear theory of change organization / project
• Pitch deck + narrative
Sales
• Product portfolio
• Corporate presentation
• Collaboration opportunities
Usually, entrepreneurs follow a similar journey in their investment path over the years.
balance sheet
from partners change of the project narrative application
balance sheet of investment balance sheet of investment presentation opportunities
years
• Pay back the money with interest recurrently
• Keep the ownership and the profit
• Harr to obtain for new businesses
• Fast and low rate (e.g. 2,5% in Portugal)
• Self financing, family & friends, angels, VC, IPO
• Suited for early stage businesses
• Give up shares and control
• Time consuming but good to scale
• No need to give back money
• Time and resource consuming
• Public fund vs corporate mix stabilizes the business
• Reinvest your profit to grow
• Might need some years to generate profit
• Increasing sales is the most sustainable strategy on the long term
Public Grants
Equity Increase - angel investors
3—5 years
5 years
To better understand what is the relation between costs, pricing strategies and breakeven point, we have designed an exercise on excel that you can do using your company numbers.
23
To help you fill in the different fields, we are using as a case study a t-shirt shop.
After going through 4 different scenarios, you will be able to compare the different cases. In the example above, we are modifying some variables of the business for the different scenarios, such as variable cost, fixed costs and price (physical vs online store; number of employees; high vs low price) and we can see how the break-even points change.
After going through 4 different scenarios, you will be able to compare the different cases. In the example above, we are modifying some variables of the business for the different scenarios, such as variable cost, fixed costs and price (physical vs online store; number of employees; high vs low price) and we can see how the break-even points change.
After completing the exercise,


After completing the exercise, we suggest you ask yourself the following provoking questions:
Is it worth increasing the purchasing order and obtaining a discount on the material?
Can you live out of your business?
Is your salary fair?
Do you need to move to a high-end market and increase the selling price?
Is it worth having a shop alone?
Retail vs wholesale?
Details about different financing options View document
