If you want to buy this or Any Other Test Bank or Solution Manual contact us At.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1 Microorganisms are involved in each of the following processes EXCEPT 1) _______ A) infection.
B) decomposition of organic material. C) food production. D) smog production. E) O2 production.
Each of the following organisms would be considered a microbe EXCEPT 2) _______
A) bacterium.
B) virus. C) protozoan.
D) mushroom. E) yeast.
The term used to describe a disease-causing microorganism is 3) _______ A) bacterium.
2
3
virus.
pathogen.
infection.
Common commercial benefits of microorganisms include synthesis of 4)
_______
A) aspirin.
B) antibiotics.
C) insulin.
D) antibiotics and aspirin.
E) antibiotics and insulin.
4
5
Commercial utilization of microbial products has become increasingly popular due to their environmentally friendly nature. Removal of these products from the environment typically utilizes 5) _______
A) enzymes.
B) organic solvents.
C) organic acids.
D) alcohol.
E) soap.
The formal system for classifying and naming organisms was developed by 6)
6
_______
A) Robert Koch.
B) Carolus Linnaeus.
C) Ignaz Semmelweis.
D) Louis Pasteur. E) Aristotle.
In the name Staphylococcus aureus, aureus is the 7)
_______
A) specific name. B) kingdom. C) family name.
D) genus. E) domain name.
A prokaryotic cell may possess each of the following cellular components EXCEPT 8)
_______
A) a cell membrane. B) flagella. C) ribosomes.
D) a cell wall.
E) a nucleus.
Which of the following is NOT associated with viruses? 9)
7
8
9
A) nucleic acid
B) organelles
C) envelope
D) spikes
E) capsid
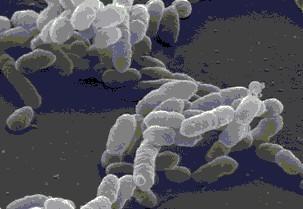
The bacterial shape of the cells in Figure 1.1 would best be described as 10) ______ A) columnar.
spiral.
coccus.
ovoid.
bacillus.
Protozoan motility structures include
______
A) cilia.
B) pseudopods.
C) flagella.
D) cilia and pseudopods only.
E) cilia, flagella, and pseudopods.
Viruses are not considered living organisms because they 12) ______
A) can only be visualized using an electron microscope.
B) are structurally very simple.
C) cannot reproduce by themselves. D) are ubiquitous in nature.
E) typically associated with disease.
The infectious agent that causes AIDS is a 13) ______ A) protozoan. B) virus.
C) bacterium.
D) yeast. E) mold.
Which of the following is NOT a domain in the three-domain system? 14)
1
1
1
1
Classification of organisms into three domains is based on 15) ______ A) the presence of a cell wall.
B) cellular organization.
C) the number of cells in the organism. D) cellular proteins.
E) nutritional requirements.
1 Archaea differ from bacteria in that archaea 16) ______ A) have diverse cell wall compositions. B) lack nuclei.
C) reproduce by binary fission. D) are prokaryotic.
E) use organic compounds for food.
Who is credited with first observing cells?
1
______ A)
Carolus Linnaeus B)
Robert Hooke C)
Robert Koch D)
Anton van Leeuwenhoek E)
Louis Pasteur
Who is credited with first observing microorganisms?
18) ______ A)
Robert Koch B)
Robert Hooke C)
Louis Pasteur D)
Carolus Linnaeus E)
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Biogenesis refers to the 19) ______ A) germ theory of disease. B) development of aseptic technique. C) spontaneous generation of organisms from nonliving matter. D) development of life forms from preexisting life forms.
1
1
2
If you were setting up an experiment to disprove spontaneous generation in a liquid medium, which of the following would be essential to the experiment?
20) ______
A)
supplying the liquid with nutrients
B)
using a sterile liquid and eliminating exposure to microorganisms
C)
starting with a liquid that contains microorganisms
D)
adding antibiotics to the liquid
E)
adding carbon dioxide to the liquid
The arguments supporting spontaneous generation were finally disproved by
21) ______ A)
Lazzaro Spallanzani. B)
Francesco Redi. C)
Louis Pasteur.
D)
John Needham.
E)
Rudolf Virchow.
Regarding Louis Pasteur’s experiments with the S-neck flask, which of the following statements is TRUE?
22) ______ A)
A food source was provided.
B)
The possibility of contamination was removed.
C)
All preexisting microorganisms were killed.
D)
Air exchange was involved.
E)
All of the answers are correct.
The microbial process of converting sugars to alcohol is known as 23) ______ A) fermentation.
2
2
2
B) pasteurization. C) alcoholism.
D) tyndallization. E) lyophilization.
Proof that a microbe could cause disease was provided by 24) ______ A) Koch. B) Pasteur. C) Semmelweis. D) Wasserman. E) Lister.
The use of phenol (carbolic acid) as a wound disinfectant was first practiced by 25) ______ A) Lister. B) Koch. C) Pasteur. D) Holmes. E) Semmelweis.
Mycology is the study of 26) ______ A) protozoa. B) molds.
2
2
2
C) mushrooms. D) mycoplasma.
E)
molds, yeast, and mushrooms.
The first step for directly linking a microbe to a specific disease according to Koch’s postulates is to
27) ______ A)
compare the blood of a sick animal to blood obtained from a healthy animal. B)
inject a sample of blood or other body fluid from a diseased animal into a healthy animal. C)
culture the blood or other body fluid from a diseased animal using nutrient medium.
D)
isolate microbes from the blood of healthy animals.
E)
obtain a sample of blood or other body fluid from a diseased animal.
In which of the following situations would Koch’s postulates be utilized?
28) ______ A)
development of a new antibiotic in a pharmaceutical lab B)
formulation of a vaccine against a new pathogen in a genetic engineering lab C)
determination of the cause of cancer in a patient D)
determination of the cause of a patient’s illness in a hospital microbiology lab E)
whenever the scientific method is used to investigate a microbiological problem
Robert Koch identified the cause of
29) ______ A) diphtheria. B) AIDS. C) anthrax.
2
2
2
________ is the physician first associated with vaccination.
Which of the following findings was essential for Edward Jenner’s vaccination process?
Disease is caused by viruses. B)
Someone who recovers from a disease will not acquire that disease again. C)
A weakened microorganism will not cause disease. D)
Exposure to a milder disease form may produce immunity. E)
Pathogenic microorganisms infect all humans and animals in the same manner.
A) bacteria. B) fungi.
C) viruses. D) protozoa.
E) bacteria and fungi. 3
The first antibiotic to be utilized was
33) ______ A) quinine. B) salvarsan. C) vancomycin. D) sulfonamides. E) penicillin. 3
Who was the first scientist to pursue a “magic bullet” that could be used to treat infectious disease? 34) ______ A) Lister
Fungal infections are studied by 35) ______ A) bacteriologists.
B) herpetologists.
C) parasitologists.
D) mycologists. E) virologists.
Vaccinations are available for all of the following diseases EXCEPT 36) ______ A) rubella. B) mumps. C) measles.
D) hepatitis B. E) strep throat.
Recombinant DNA refers to the 37) ______ A) study of the function of genes. B) DNA resulting when bacterial genes are inserted in an animal genome. C) interaction between human and bacterial cells.
D) study of bacterial ribosomes. E) synthesis of proteins from genes.
Molecular biology is the study of 38) ______ A) DNA synthesis. B) RNA replication.
3
3
3
C) the structure and function of macromolecules essential to life.
D) enzyme function.
E) protein synthesis.
3
Microorganisms are essential to our life. Each of the following is an example of a beneficial function of microorganisms EXCEPT 39) ______
A) gene therapy. B) agriculture. C) bioremediation.
D) increased morbidity. E) alternative fuel production.
The major food producers for other living organisms is/are 40) ______
A) higher plants. B) cyanobacteria. C) algae.
D) higher plants and algae. E) higher plants, cyanobacteria, and algae.
Gene therapy is currently used to treat all of the following diseases EXCEPT 41) ______ A) colon cancer.
B) Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. C)
4
4
severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID).
D) cystic fibrosis.
E)
LDL-receptor deficiency.
4
Recombinant DNA technology has become an increasingly important part of our life. It is used for all of the following EXCEPT
42) ______ A) enhancing food longevity. B) vaccine production. C) synthesis of water.
D) increasing the nutritional value of food.
E) drug production.
Normal microbiota are typically found in and on all the following body locations EXCEPT the
43) ______ A) mouth.
B) skin. C) colon.
D) upper respiratory system.
E) blood.
Which of the following statements about biofilms is FALSE?
44) ______ A)
Biofilms in your body protect mucous membranes from harmful microbes. B)
Compared to free-living bacteria, biofilms are more sensitive to antibiotics. C) Biofilms on rocks provide food for animal life.
4
4
Biofilms in pipes can block the flow of water. E)
Biofilms on medical devices cause infections.
Development of emerging infectious disease can be a result of all of the following EXCEPT 45) ______ A) modern transportation. B) use of genetically modified foods. C) overuse of antibiotics. D) microbial mutation. E) changes in the environment.
Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false.
Infectious disease is almost totally eradicated in our world. 46)
A student has obtained a sample of pond water for study. Using the high-power lens, he observes several cells with nuclei. He can conclude that the cells are NOT bacteria.
The process of pasteurization to reduce food spoilage utilizes high heat to kill all bacteria present.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first microbiologist to use a microscope to examine environmental samples for the presence of microorganisms.
Spontaneous generation refers to living cells arising only from other living cells.
Microbes are associated with life-sustaining benefits as well as life-threatening diseases.
All cells possess a cell wall.
Bovine spongiform encephalitis (BSE, or “mad cow disease”) is caused by a virus. 54)
All pathogens known to infect humans have been identified at this point in time.
55)
ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 56)
What is an emerging disease, and what are some of the sources for these “new” infectious diseases?
57)
Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
58)
What was the function and importance of S-necked flasks in Louis Pasteur’s experiments in disproving spontaneous generation?
the germ theory of disease and discuss why this theory is essential to the treatment of infectious disease.
