If you want to buy this or Any Other Test Bank or Solution Manual contact us
At. Premiumbiz379@gmail.com
Introduction to Geography, 5e (Dahlman/Renwick/Bergman) Chapter 1 Introduction to Geography
1) Geography is
A) place names.
B) the study of places, and how places interact spatially to form patterns.
C) rivers and mountains.
D) none of the above
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 2
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
2) The first book titled "Geography" was
A) Greek.
B) Roman.
C) Chinese.
D) Mayan.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 2
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
3) The Greek word for "earth description" is geography. This word was coined by ________, who at the time was the director of the library at Alexandria.
A) Erastosthenes
B) Hipparchus
C) Polymethus
D) Camdus
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 2
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 2, The World in Spatial Terms
4) In 1402, a world map was produced which was by far the most accurate representation for the times. This map was produced in which country?
A) England
B) Spain
C) Korea
D) China
E) the United States
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 3
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 2, The World in Spatial Terms
5) In The Tribute of Yu, the outermost geographical zone was inhabited by A) peasants.
B) the royal family.
C) the army.
D) barbarians.
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 3
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Analysis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 2, The World in Spatial Terms
6) Which of the following may bring about changes in relative location?
A) the discovery of new trade routes
B) the opening of a new highway
C) a new tariff agreement between two countries
D) all of the above
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 5
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
7) Regions
A) are delineated by groups that insist on total agreement.
B) are never political.
C) are recognized by scholars only.
D) are defined by one or more distinctive characteristics or features.
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 8
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
8) Which of the following statements about regions is true?
A) All regions have precise boundaries.
B) Everyone agrees on the extent of all regions.
C) Geographers decide what phenomena to use to define a region.
D) Features used to define regions must be clear and distinct on the landscape.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
9) Which is NOT an example of a formal region?
A) the area where a particular language is spoken
B) the area where most people belong to a particular religion
C) the area of dominance of a particular crop
D) the market area of a supermarket
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
10) A city and its metropolitan area form an example of a
A) climatic region.
B) functional region.
C) nodal region.
D) uniform region.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
11) The study of the distribution of objects across Earth's surface and the processes by which human and environmental phenomena move from one place to another is
A) area analysis.
B) spatial analysis.
C) community succession.
D) biodiversity.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
12) The position, placement, or arrangement of something throughout space is its A) concentration.
B) distribution.
C) density.
D) pattern.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
13) The geometrical arrangement of objects within an area is its A) pattern.
B) density.
C) distribution.
D) concentration.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
14) A culture hearth is
A) a region from which innovative ideas originate.
B) the material traits of a particular culture.
C) a region in which people of different origins live.
D) the evolution of a landscape.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
15) Diffusion
A) is the result of relocation only.
B) sometimes encounters barriers.
C) terminates at a hearth.
D) has decreased greatly in recent years due to advances in technology.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
16) Which is an example of expansion diffusion?
A) English colonists bringing their language to America.
B) The introduction of tulip farms in Michigan by Dutch immigrants.
C) The nearly instant popularity of iPods.
D) The construction of Buddhist temples in Los Angeles.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 15
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
17) Scientists found that the main cause of the diffusion of AIDS in sub-Saharan Africa was
A) people traveling to visit relatives.
B) rhesus monkeys.
C) migrant workers.
D) long-distance truck drivers.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
18) An interdependent group of items interacting in a regular way to form a unified whole is a A) system.
B) network.
C) toponym.
D) hearth.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
19) Which of the following is NOT an abiotic system?
A) land
B) air
C) human
D) oceans
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
20) Earth's crust and a portion of upper mantle directly below the crust is the A) atmosphere.
B) hydrosphere.
C) lithosphere.
D) biosphere.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 17
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
21) A group of organisms and the nonliving physical and chemical environment in which they interact is
A) a biosphere.
B) an ecosystem.
C) a closed system.
D) a vernacular region.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 17
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 8, Physical Systems
22) An ecosystem is a(n) ________ that functions as a community.
A) plant group
B) association of plants and animals
C) oceanic biota
D) animal group
E) rock type
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 17
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 8, Physical Systems
23) The Earth rotates about its
A) great circle.
B) revolution.
C) inclination.
D) axis.
E) equator.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 17
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
24) Longitude and latitude are measured using the unit terms of A) degrees, minutes.
B) degrees, minutes, seconds.
C) degrees, hours, minutes, seconds.
D) miles, feet, inches.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
25) The highest numerical measurement when calculating latitude is ________°.
A) 90
B) 100
C) 180
D) 360
E) 450
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
26) The meridian of 0 degrees longitude is also called the A) equator.
B) prime meridian.
C) 90 degree meridian.
D) International Date Line.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 19
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
27) Most of the International Date Line follows
A) 0 degrees latitude.
B) 0 degrees longitude.
C) 90 degrees latitude.
D) 180 degrees longitude.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 19
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
28) The 0° meridian is the same thing as the ________ Meridian.
A) International Date Line
B) equator
C) perihelion
D) Prime
E) geographic grid
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 19
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
29) The Greenwich Meridian is also known as the
A) perihelion.
B) aphelion.
C) Prime Meridian.
D) equator.
E) small circle.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 19
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
30) What meridian is opposite the Prime Meridian?
A) Tropic of Cancer
B) 90° meridian
C) 180° meridian
D) 320° meridian
E) Tropic of Capricorn
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 19
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
31) How many time zones are shared by the 48 conterminous U.S. states and the Canadian provinces?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
32) San Diego, California, is in the Pacific Standard Time Zone, while Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, is in the Eastern Standard Time Zone. If it is 1 A.M., Monday, in Philadelphia, what time is it in San Diego?
A) 4 A.M. Sunday
B) 10 P.M. Sunday
C) 4 A.M. Monday
D) 11 P.M. Monday
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
33) Which is true?
A) Every meridian is actually a circle rather than an arc.
B) Parallels are different in length.
C) Meridians are different in length.
D) Every parallel is the same length.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 19-20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
34) Cartography is
A) another name for geography.
B) the science of making maps.
C) the art of making signs.
D) the medical field that specializes in heart disease.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
35) The radius of the earth is about
A) 8000 mi.
B) 30,000 mi.
C) 230,000 mi.
D) 4000 mi.
E) 93,000,000 mi.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Analysis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
36) The relationship between the size of an object on a map and its size on Earth's surface is
A) geography.
B) spatial analysis.
C) relief.
D) scale.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
37) The statement "1:24,000" is an example of
A) a bar scale.
B) a fractional scale.
C) a graphic scale.
D) a map.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
38) Which map would have the largest scale?
A) city
B) continent
C) state
D) world
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Analysis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
39) A large-scale map represents a small portion of surface area at a high level of detail. Which fractional unit is not considered to be large-scale?
A) 1/10
B) 1/1,000
C) 1/10,000
D) 1/10,000,000
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
40) If the scale of a map is 1:36,000, then 1 inch on the map equals how many FEET on Earth's surface?
A) 1
B) 3,000
C) 3,600
D) 36,000
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Analysis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
41) Distortion is least severe on
A) small-scale maps.
B) globes.
C) large-scale-maps.
D) all maps.
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 21
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
42) A map that accurately portrays land shape is called a(n)
A) conformal projection.
B) equidistant projection.
C) equal area projection.
D) azimuthal projection.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 21
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
43) In the Mercator projection, which piece of Earth is portrayed extremely large in comparison to its actual size?
A) low-latitude locations
B) Greenland
C) Brazil
D) the continental U.S.
E) none of the above
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 21
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Analysis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
44) The original purpose of the Mercator projection was A) to produce an accurate equal area map.
B) for the guidance of intercontinental missiles.
C) for ocean navigation.
D) to make the first map of the world.
E) to befuddle introductory physical geography students.
Answer: C
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 22
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
45) An orbiting satellite provides data for analysis by A) GIS.
B) cartography.
C) projection.
D) remote sensing.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
46) GIS refers to A) Landsat.
B) surveying.
C) a computer system that stores and organizes geographic data.
D) an agency of the United Nations.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
47) GIS would not be practically possible without A) computers.
B) satellites.
C) cell phones.
D) government agencies.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
48) Which method of data acquisition is not considered to be in the class of remote sensing?
A) aerial photography
B) weather satellite data
C) landsat satellite data
D) rain gauge data
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
49) The Internet
A) has been in existence since the end of World War II.
B) routes all information through one central server.
C) began as a project of the U.S. Department of Defense.
D) has always included the World Wide Web.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 26
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
50) Geography as a discipline began during the Renaissance period in Europe. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 3
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
51) Europeans are the only people to have developed geography. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 2
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
52) Absolute location and relative location are the same thing. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 5
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
53) The bookstore is a ten-minute walk from campus. This is an absolute measure of distance.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 5
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
54) Timbuktoo (Tombouctou) has always been an insignificant place.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 6
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
55) A study of people's commuting habits, focusing on where they live in relation to where they work, would be a study of spatial interaction.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 5
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
56) Russia is the largest country in the world.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 7
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
57) Everything about a formal region is the same throughout the region.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 7
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 5, Places and Regions
58) Vernacular regions normally do not have well-defined boundaries.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 5, Places and Regions
59) In geography, density normally means a measure of the amount of something per unit of area on Earth's surface.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
60) The area in which an idea originates is known as a hearth. Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 13
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
61) The most important barriers to diffusion today are physical features of Earth's surface. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 15
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
62) A system is an interdependent group of items interacting in a regular way to form a unified whole.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
63) Pure dry air in the lower atmosphere is 78 percent oxygen by volume. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
64) Oxygen is the most abundant element in the atmosphere. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
65) Of Earth's water, 97 percent is in lakes and rivers.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
66) Atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere function together to create environments for the biosphere.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 17
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 7, Physical Systems
67) The Earth's circumference is close to 24,900 miles.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
68) Absolute location can be pinpointed on the Earth's surface through use of latitude and longitude.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
69) On the globe, meridians cross all parallels perpendicularly.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
70) Of seconds, degrees, and minutes of latitude, minutes are associated with the shortest distances.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Analysis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
71) Meridians are lines on a map that are drawn east-west and measure latitude.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
72) Lines of latitude are called meridians.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
73) A line of measurement extending from pole to pole which is at a 90-degree angle with the equator is called a meridian.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 18
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
74) The world is divided into twenty different time zones.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 19
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
75) A globe is a better model of the Earth than a flat map.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
76) Maps are inherently inaccurate because they attempt to depict the curved surface of Earth on a flat sheet.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
77) A map is usually much smaller than the part of the Earth's surface it represents.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
78) A map scale 1:5000 would be better for showing city streets than a map of scale 1:500,000. Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Evaluation
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
79) Conformity and equivalence are, in general, mutually exclusive properties.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 22
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
80) An equal-area map projection is one that has no distortion. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 22
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
81) GIS relies on information stored in a computer database. Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
82) Global positioning systems (GPS) were developed originally for commercial applications. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 26
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
83) In GIS use, vector data specify location.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 28
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
84) Currently there is no body responsible for setting Internet standards.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 32
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
85) An approach to geography that focuses on the characteristics of places and regions is called
Answer: area analysis
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 5
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
86) Which two of the following boxes have the lowest density of dots? In which two is the distribution of dots least concentrated?
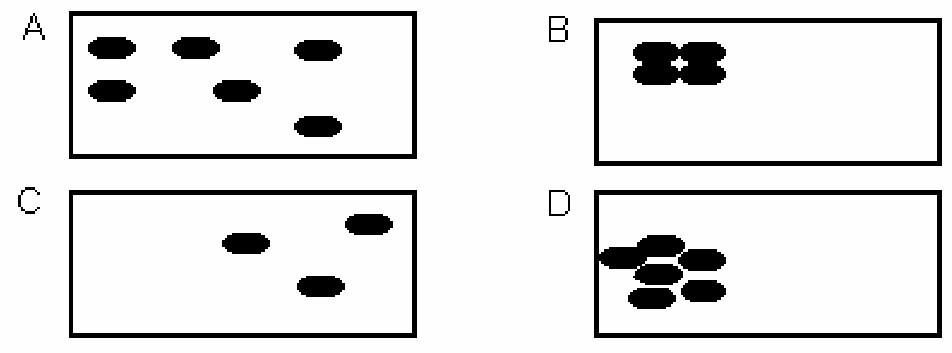
Answer: Boxes B and C have the lowest density. Boxes A and C have the least concentrated distributions.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 11
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
87) What does "distance decay" mean?
Answer: As the distance between two things increases, the degree of interaction between them decreases.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
88) Name Earth's four physical systems.
Answer: Atmosphere; biosphere; hydrosphere; lithosphere.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 16
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
89) The science of making maps is called ________.
Answer: cartography
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
90) A two dimensional representation of the Earth's surface is a ________.
Answer: map
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
91) What does the term "scale" mean, in the context of maps?
Answer: The size of an object on the map in comparison to its size on Earth's surface.
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 20
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
92) Data concerning Earth's surface obtained from satellites or high-flying aircraft are referred to as ________.
Answer: remote sensing
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
93) What is a pixel?
Answer: The smallest feature of Earth's surface that can be detected by a sensor such as on a satellite.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 27
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
94) Discuss the nature of geography.
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 2
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
95) Discuss the change in the discipline of geography over the past 500 years in terms of the kinds of questions geographers ask.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 2-3
Topic: What Is Geography?
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
96) Explain relative location and situation.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 5
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
97) Choose a defining characteristic for the function region in which your home town or the town where you attend college is located. What is the characteristic, and why is your town in that region?
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 7
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 4, Places and Regions
98) Provide an example of one of each of the following: a) formal region; b) functional region; c) vernacular region.
Answer:
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 7
Topic: Contemporary Approaches in Geography
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Application
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 3, The World in Spatial Terms
99) How do maps communicate geographic information?
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 20-25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Comprehension
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
100) Describe how GIS works and discuss some of its applications.
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 27-33
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
101) If there were no maps, could geography exist as a discipline? Why or why not?
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 2, 20-25
Topic: Describing Earth
Skill: Bloom's Taxonomy: Synthesis
Objective: U.S. Geography Standards: 1, The World in Spatial Terms
