Introduction to Economic Reasoning, 8e (Rohlf)
Chapter 1: The Study of Economics
Multiple Choice Questions
1) Economics is the study of how to use
A) limited resources to fully satisfy unlimited wants.
B) unlimited resources to satisfy unlimited wants as fully as possible.
C) limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants as completely as possible.
D) unlimited resources to partially satisfy limited wants.
E) limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants as fairly as possible.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
2) Economics is the study of
A) how to distribute goods and services in as fair or just a manner as possible.
B) how to become a successful businessperson.
C) how to use limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants as fully as possible.
D) how to create wants or "needs."
E) happiness and how to achieve it.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
3) The four categories of economic resources are
A) raw materials, land, equipment, and management.
B) labor, capital, entrepreneurship, and land.
C) raw materials, land, labor, and management.
D) equipment, raw materials, capital, and labor.
E) money, land, labor, and equipment.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
4) In economics, the term "capital" means
A) stocks and bonds.
B) raw materials, such as timber and mineral resources.
C) money.
D) machinery and other human-made aids to production.
E) managerial talent.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
5) Which of the following is an example of "capital" as the term is used by economists?
A) the stoves and other food preparation equipment in a restaurant
B) minerals and other resources in their natural state
C) money
D) stocks and bonds owned by businesses and individuals
E) the managers who run the company
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
6) The opportunity cost of the U.S. space exploration program is
A) negative, because it is generally agreed that the benefits derived from space exploration far exceed the costs.
B) whatever other goods and services could have been produced with the resources devoted to the space program.
C) nonexistent, because the space program was paid for by the government rather than by private consumers.
D) equal to the sum of all the salaries paid to the government personnel involved in the space program.
E) equal to the sum of the salaries of the astronauts.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
7) The opportunity cost of a college education is
A) the income you must forgo to attend college.
B) the cost of tuition, books, and fees.
C) the recreational activities you must sacrifice.
D) the other goods you must sacrifice plus any foregone income and activities.
E) the income you could have earned and the work experience you could have obtained if you had not attended college.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
8) If you were given a free ticket to a rock concert, then
A) there would be no opportunity cost associated with attending the concert.
B) the opportunity cost of attending the concert would be equal to the cost of transportation to the concert.
C) the opportunity cost of attending the concert would be equal to the monetary value of the ticket.
D) there would be no opportunity cost associated with attending the concert unless you could sell the ticket.
E) there would still be an opportunity cost associated with attending the concert.
Answer: E
Question Status: Previous Edition
9) A production possibilities curve shows
A) the combinations of two products that an economy is actually producing with its stock of economic resources.
B) the combinations of two products that an economy is capable of producing with its finite resource stock.
C) the combinations of two products that society desires the most.
D) all the combinations of two economic resources that will maximize the economy's output.
E) all the combinations of two economic resources that are permitted by the existing technology.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
10) A nation's production possibilities curve is constructed under the assumption that
A) the combinations of products produced by the economy will remain unchanged.
B) the economy's resource stock is fixed or unchanged.
C) there is no inflation in the economy.
D) consumer preferences do not change.
E) there is continuous economic growth.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
11) Suppose an economy is operating at a point on its production possibilities curve showing clothing and food. If the economy desires to produce additional clothing
A) it must reduce its output of food.
B) it cannot do so, since the economy is fully utilizing its resources.
C) it must also increase its output of food.
D) it cannot do so, since clothing production has already been maximized.
E) it cannot do so until there is an outward shift in the production possibilities curve.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
12) If an economy is operating on its production possibilities curve for consumer goods and capital goods
A) some of the nation's resources are unemployed.
B) it cannot expand its output of capital goods.
C) it can only produce more consumer goods if it produces fewer capital goods.
D) it is not fully utilizing its production capabilities.
E) it cannot expand its output of consumer goods.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
13) If a nation could produce 300 units of civilian goods and 300 units of military goods or 350 units of civilian goods and 200 units of military goods
A) the opportunity cost of 50 units of civilian goods is 300 units of military goods.
B) the opportunity cost of 100 units of military goods is 50 units of civilian goods.
C) the opportunity cost of 50 units of civilian goods is 50 units of military goods.
D) the opportunity cost of 200 units of military goods is 150 units of civilian goods.
E) the opportunity cost of 50 units of military goods is 100 units of civilian goods.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
3
14) If a nation could produce 400 units of civilian goods and 200 units of military goods or 300 units of civilian goods and 240 units of military goods
A) the opportunity cost of 40 units of military goods is 60 units of civilian goods.
B) the opportunity cost of 100 units of civilian goods is 60 units of military goods.
C) the opportunity cost of 40 units of military goods is 100 units of civilian goods.
D) the opportunity cost of 100 units of civilian goods is 200 units of military goods.
E) the opportunity cost of 200 units of military goods is 100 units of civilian goods.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
15) If a society is operating inside its production possibilities curve for guns and butter, then
A) to produce more guns it must sacrifice some butter.
B) to produce more butter it must sacrifice some guns.
C) some economic resources are unemployed.
D) economic growth must occur in order to move the economy to a point on the curve.
E) consumer preferences must have changed.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
16) An economy's production possibilities curve would shift outward as a result of
A) an increase in consumer wants.
B) a decrease in consumer wants.
C) a reduction in the unemployment rate.
D) a resource-saving advance in production technology.
E) a change in consumer preferences.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
17) Economic growth would be depicted by
A) an outward shift of the production possibilities curve.
B) an inward shift of the production possibilities curve.
C) movement from a point inside the production possibilities curve to a point on the curve.
D) movement from a point on the production possibilities curve to a point outside the curve.
E) movement along the production possibilities curve.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
18) Given its present resource stock and existing techniques of production, an economy is capable of producing any combination of products
A) on its production possibilities curve, but no combination inside or outside the curve.
B) inside or outside its production possibilities curve, but no combination on the curve.
C) inside its production possibilities curve, but no combination on or outside the curve.
D) on or inside its production possibilities curve, but no combination outside the curve.
E) on its production possibilities curve, but no combination outside the curve.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
19) According to the law of increasing costs
A) if a society desires more of some particular product, it must sacrifice larger and larger amounts of other products.
B) society can obtain additional units of a given product by sacrificing smaller and smaller amounts of other products.
C) whenever output increases by a given percentage, production costs will increase at twice that rate.
D) whenever input prices increase by a given percentage, production costs will increase at twice that rate.
E) inflation accelerates as economies mature.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
Answer the following question(s) on the basis of the following graph.
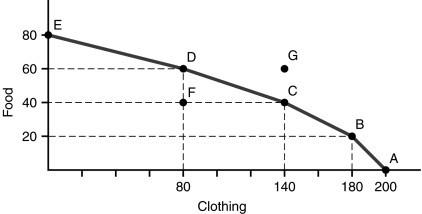
20) Based on the figure above, if the economy is operating at point C, the opportunity cost of producing 20 additional units of food would be
A) 40 units of clothing.
B) 60 units of clothing.
C) 80 units of clothing.
D) 140 units of clothing.
E) 20 units of clothing.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
21) Based on the figure above, which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) If the economy is operating at point A, it is producing only clothing.
B) If the economy is operating at point B, the opportunity cost of producing 20 additional units of food would be 40 units of clothing.
C) If the economy is operating at point D, the opportunity cost of acquiring 100 additional units of clothing would be 40 units of food.
D) If the economy is operating at point E, the opportunity cost of producing 80 additional units of clothing would be 30 units of food.
E) If the economy is operating at point D, the opportunity cost of acquiring 20 additional units of food would be 80 units of clothing.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
22) Based on the figure above, if the economy were operating at point F
A) the opportunity cost of producing 20 additional units of food would be 30 units of clothing.
B) the opportunity cost of acquiring 30 additional units of clothing would be 20 units of food.
C) additional food could be produced at no opportunity cost in terms of sacrificed clothing.
D) the opportunity cost of acquiring 20 additional units of food would be 40 units of clothing.
E) additional clothing cannot be produced unless there is a technological advance or new resources are discovered.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
23) Based on the figure above, point G on the graph represents
A) the same combination of products that is available at point C.
B) a combination of products that reflects the existence of unemployed resources.
C) a combination of products that is beyond the economy's current production capability.
D) the combination of products that the economy is currently producing.
E) a combination of products that is forever beyond the economy's production capability.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
24) Based on the figure above, as we move along the production possibilities curve from point A to point B to point C, the opportunity cost of an additional 20-unit increment of food
A) rises, because resources are not equally well suited to producing food and clothing.
B) falls, because resources are not equally well suited to producing food and clothing.
C) rises, because the economy is moving closer to its maximum production potential.
D) falls, because the economy is using its resources more and more efficiently.
E) remains constant.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
25) Foreign trade can enable a nation to
A) acquire products at a lower opportunity cost than they can be produced domestically.
B) acquire products at zero opportunity cost.
C) acquire products at a higher opportunity cost than they can be produced domestically.
D) operate inside its production possibilities curve.
E) fully satisfy the wants of its population.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
26) Trade with other nations can make it possible for a country to
A) acquire products at zero opportunity cost.
B) eliminate the problem of scarcity.
C) operate outside its production possibilities curve.
D) operate inside its production possibilities curve.
E) have unlimited production possibilities.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
27) Which of the following is not an economic resource?
A) capital
B) land
C) money
D) entrepreneurship
E) labor
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
28) Economic efficiency requires that
A) the economy's output be distributed in a fair or just manner.
B) each product be produced using the maximum amount of scarce resources.
C) the economy produce the goods and services most desired by consumers.
D) each product be produced without using scarce resources.
E) the economy's output of goods and services expand over time.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
29) Which of the following is an example of a normative statement?
A) College enrollment is expected to decline by 5 percent next year.
B) The price of gasoline increased by 10 percent in the last 2 years.
C) College students ought to spend more time studying and less time partying.
D) Season tickets for the Podunk Hasbeens are selling for $75 each.
E) The weather forecaster says it will be a sunny day, with temperatures in the high 80s.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
30) "The federal government ought to spend more money on medical treatment for the poor and less on the military." This sentence is an example of
A) a statement of fact.
B) an economic theory.
C) a descriptive statement.
D) a normative judgment.
E) a positive statement.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
31) Economic theories
A) are more complex than economic models.
B) leave out some of the complexities of the real world.
C) are also called facts.
D) are tested in laboratories, much as chemists test their theories.
E) are generalizations about the relationship between economic principles and economic models.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
32) The term ceteris paribus means
A) after this, therefore because of this.
B) other things being equal.
C) according to the model.
D) what will be, will be.
E) what "should" be.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
33) When the outcome predicted by a theory is inconsistent with the outcome observed in the real world
A) the theory should always be discarded and replaced with a new theory.
B) we should continue to use the theory and ignore our real-world observations.
C) we should consider discarding the theory if the assumption of ceteris paribus has been violated.
D) we should consider discarding the theory unless the assumption of ceteris paribus has been violated.
E) we should change the real world.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
34) Microeconomics differs from macroeconomics in that
A) microeconomics deals with issues such as unemployment and inflation, while macroeconomics examines topics such as how the prices of particular products are determined.
B) microeconomics deals with value judgments while macroeconomics deals with facts.
C) microeconomics looks at the individual units in the economy, while macroeconomics studies the economy's overall performance.
D) microeconomics uses theory, while macroeconomics relies only on facts.
E) macroeconomics uses theory, while microeconomics relies only on facts.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
35) Which of the following is an example of macroeconomic analysis?
A) a study to determine why corn prices increased in 2007
B) a survey to determine how clothing manufacturers arrive at their selling prices
C) a study of the factors that influence the overall unemployment rate
D) a study of the personal values of business executives
E) a survey to determine the average amount of time required to eat a Big Mac
Answer: C
Question Status: Revised
36) An inverse relationship exists between two variables if
A) the value of one variable increases as the value of the other decreases.
B) the value of one variable increases as the value of the other increases.
C) the value of one variable remains constant as the value of the other increases or decreases.
D) the value of one variable decreases as the value of the other decreases.
E) the value of one variable is independent of the value of the other variable.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
37) If two variables are directly or positively related, then
A) as one variable increases, the other decreases.
B) as one variable decreases, the other increases.
C) as one variable increases, the other does also.
D) the value of one variable remains unchanged as the value of the other increases or decreases.
E) they should never marry.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
Multiple Choice Questions
Reproduced from the Study Questions
1) Economics is the study of how to
A) distribute output fairly.
B) do the best we can with what we have.
C) reduce our unlimited wants.
D) expand our stock of economic resources.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
2) The opportunity cost of attending summer school is
A) whatever you could have purchased with the money spent for tuition and books.
B) negative, because you will finish college more rapidly by attending summer school.
C) the income you could have earned over the summer.
D) the products, income, and recreational opportunities that must be forgone.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
3) The four categories of economic resources are
A) labor, management, machinery, and money.
B) land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
C) money, land, capital, and labor.
D) air, soil, water, and money.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
4) Producing the most-wanted products in the least costly way is A) full employment.
B) economic growth.
C) a fair income distribution.
D) economic efficiency.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
5) Economists have trouble testing their theories because A) people are unpredictable.
B) the real world is too complicated to be explained.
C) they can't hold constant the "other factors" that might influence the outcome of the experiment.
D) the necessary economic data are almost never available.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
6) Economists should not be permitted to
A) devise policies to achieve economic goals.
B) determine society's economic goals.
C) explain how the economy works.
D) explain how particular economic goals conflict.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
7) Which of the following statements reflects a normative judgment?
A) A newspaper headline that reads, "Gas prices headed up after supply disruptions."
B) A doctor who tells you, "If you consume more calories than you burn, you will gain weight."
C) An editorial that argues, "We are spending too many of our tax dollars on the military and too few on preventative health care."
D) A scientist who predicts that "San Francisco will suffer a major earthquake sometime in the next 100 years."
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
8) Was Ted Williams the greatest hitter ever to grace a baseball diamond? An economist would say it's hard to know because there is a ceteris paribus problem. In this context what does that mean?
A) Officials didn't keep the careful records needed to make a valid comparison.
B) Ted faced different pitchers and conditions than those confronting modern batters.
C) Some comparisons are normative judgments and can't be made objective..
D) All of the above..
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
9) Of the three fundamental questions, the "distribution" question has to do with
A) who will receive the output.
B) how the output will be shipped from the place of production to the consumer.
C) how economic resources are distributed to producers.
D) what products will be produced.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
10) Suppose that you have just found $10 on the street and are thinking of using it to buy a ticket to the movies. The opportunity cost of going to the show would be
A) nothingsince you found the money, you are sacrificing nothing to spend it.
B) whatever you would have bought with the money if you hadn't used it to go to the show.
C) the other activities you would have to sacrifice to attend the show.
D) B and C
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
11) The production possibilities curve slopes downward because
A) some resources are better suited to the production of one product than another.
B) economic resources are limited.
C) economic wants are unlimited.
D) All of the above
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
Use the production possibilities curve represented below in answering the following question(s).
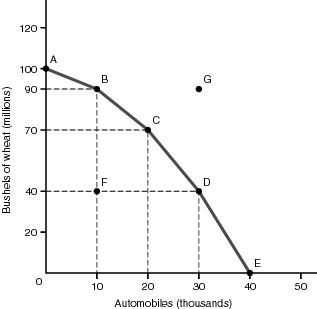
12) Based on the figure above, if the economy is operating at point C, the opportunity cost of producing an additional 10,000 automobiles will be
A) 10 million bushels of wheat.
B) 20 million bushels of wheat.
C) 30 million bushels of wheat.
D) 40 million bushels of wheat.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
13) Based on the figure above, point G on the diagram represents
A) an optimal use of the society's resources.
B) a combination of outputs beyond the economy's productive capacity.
C) a situation in which some of the economy's resources are unemployed.
D) the same output combination as point B.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
14) Based on the figure above, the production possibilities curve might shift outward to include G if
A) the economy put all unemployed resources to work.
B) the economy experienced more rapid price inflation.
C) improved training increased the productivity of workers.
D) the nation's population declined.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
15) Foreign trade permits an economy to
A) eliminate the problem of scarcity.
B) operate inside its production possibilities curve.
C) shift its production possibilities curve outward.
D) consume a combination of products beyond its own production possibilities.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
Multiple Choice Reproduced from the Companion Web Site
1) Economics is the study of how to
A) discover more economic resources.
B) satisfy all of society's wants.
C) divide-up the economy's output fairly.
D) satisfy our society's wants as fully as possible.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
2) Which of the following is not an economic resource?
A) money
B) labor
C) land
D) entrepreneurship
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
3) When economists say that "there is no free lunch," they mean that A) poor decisions always have costs.
B) everything we buy costs us money.
C) the costs of a decision sometimes outweigh the benefits.
D) all of our choices entail sacrifices.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
4) If something has an opportunity cost, we should
A) avoid that action.
B) take that action
C) be sure that the benefit of the action exceeds the cost.
D) be sure that the cost of the action exceeds the benefit
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
5) An economy's production possibilities curve is downward sloping because A) a society's wants are unlimited.
B) an economy's resources are limited.
C) resources are generally better-suited to the production of one product than another.
D) B and C
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
6) An economy's production possibilities curve is curved (concave to the origin) because A) a society's wants are unlimited.
B) an economy's resources are limited.
C) resources are generally better-suited to the production of one product than another.
D) B and C
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
Use the production possibilities curve found below in answering the following question(s).
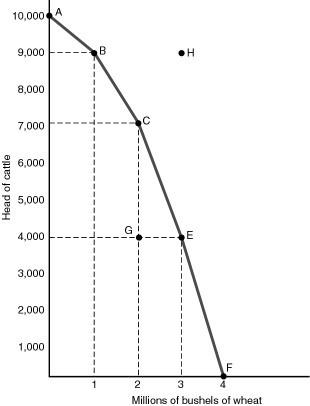
7) Based on the figure above, if the economy is operating at point B, the opportunity cost of producing another one million bushels of wheat is
A) 1,000 head of cattle.
B) 2,000 head of cattle.
C) 3,000 head of cattle.
D) 4,000 head of cattle.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
8) Based on the figure above, if the economy is operating at point C, the opportunity cost of producing another million bushels of wheat is
A) 1,000 head of cattle.
B) 2,000 head of cattle.
C) 3,000 head of cattle.
D) 4,000 head of cattle.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
9) Based on the figure above, which of the following is not a true statement about the production possibilities diagram found above?
A) If the economy is operating at point G, it is not fully utilizing its resources.
B) The economy's production possibilities curve is downward sloping because its resources are limited.
C) This curve illustrates the law of increasing costs.
D) Society would prefer point C to point H.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
10) If an economy's production possibilities curve were a downward-sloping straight line, this would indicate that
A) the economy had unlimited economic resources.
B) the society had limited wants.
C) resources were equally well suited to producing both products.
D) production was subject to the law of increasing costs.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
11) Economic growth is represented by
A) moving from a point inside an economy's production possibilities curve to a point on the curve.
B) shifting an economy's production possibilities curve outward.
C) moving from a point on an economy's production possibilities curve to a point outside the curve.
D) shifting an economy's production possibilities curve inward.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
12) We generally expect students who spend more time studying economics to earn higher grades, ceteris paribus. In this context, ceteris paribus means
A) assuming they have equal abilities.
B) assuming they have equally demanding professors.
C) assuming they all have access to the same study materials.
D) All of the above.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
13) The decision to use scarce resources to combat aids rather than to improve the quality of elementary education is an example of
A) an economic theory.
B) a normative judgment.
C) the law of increasing costs.
D) the concept of ceteris paribus.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
14) Which of the following represent the "three fundamental questions" of economics?
A) What to produce, where to produce it, and how to distribute it.
B) What to produce, where to produce it, and who will receive it.
C) What to produce, how to produce it, and how to distribute it.
D) What to produce, how to market it, and how to distribute it.
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
15) Economic efficiency has two separate elements. Those elements are
A) producing the products that consumers desire the most and producing each of those products with as few scarce resources as possible.
B) fully employing all economic resources and using those resources to produce the goods and services that consumers desire the most.
C) producing as much output as possible and ensuring that the resulting output is distributed fairly.
D) producing as much output as possible while maintaining a stable price level.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
16) Which of the following involves a macroeconomic event?
A) The price of wheat increases dramatically.
B) The unemployment rate rises.
C) Higher gas prices cause Joan to sell her SUV.
D) Improved technology lowers the price of personal computers.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
17) Which of the following is an example of "capital" as economists use the term?
A) money
B) stocks and bonds
C) natural resources such as coal deposits
D) tools and machinery
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
18) "Producing more of one thing means producing less of something else." This statement illustrates
A) the law of increasing costs.
B) the concept of ceteris paribus.
C) a normative statement.
D) opportunity cost.
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
19) Imagine a production possibilities curve with agricultural products measured on one axis and manufactured products measured on the other. A massive earthquake, that destroyed farms and factories alike, would
A) shift the production possibilities curve inward.
B) shift the production possibilities curve outward.
C) force the economy to operate at a point inside its production possibilities curve.
D) make the production possibilities curve steeper.
Answer: A
Question Status: Previous Edition
20) You're a high-school graduate who is contemplating attending college next year. Which of the following should not be considered a cost of attending college?
A) the cost of meals
B) the income forgone to attend school full time
C) the cost of books
D) tuition and fees
Answer: A
Question Status: Revised
21) Which of the following is least consistent with the cost-benefit model?
A) A promising college football player who drops out of college to try his luck as a pro.
B) Tiger Woods taking 2 years off from golf to pursue an MBA degree.
C) A harried mother of 12 ordering pizza instead of preparing a home-cooked meal.
D) A low-wage worker arriving before a store opens to have first crack at newly discounted clothing.
Answer: B
Question Status: Previous Edition
22) Economists sometimes reach different conclusions on a given issue because
A) they disagree about goals
B) they disagree about how the economy works
C) a and b
D) neither a nor b
Answer: C
Question Status: Previous Edition
23) Macroeconomics deals with the study of
A) international trade
B) production possibilities
C) individual economic units
D) the economy's overall performance
Answer: D
Question Status: Previous Edition
True/False Questions
1) The fundamental economic problem is the fact that our wants exceed our capacity for satisfying those wants.
Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
2) Economics is the study of how to distribute an economy's output in a fair manner. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
3) Economics is the study of how to completely satisfy our wants. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
4) Economics is the study of how to use our limited resources to satisfy as many of our unlimited wants as possible.
Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
5) The opportunity cost of an action is the most valued alternative you give up to take that action. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
6) The statement that there is no "free lunch" means that every decision has an opportunity cost. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
7) If someone gives you $20, there is no opportunity cost to spending that money. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
8) Economists use the term "land" to refer to all production inputs created by nature. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
9) Economists use the term "capital" to refer to money. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
10) Societies must always operate on their production possibilities curves. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
11) If economic resources were equally well suited to the production of both products, the production possibilities curve would be a downward sloping straight line.
Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
12) The production possibilities curve is downward sloping because resources are limited. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
13) The production possibilities curve is downward sloping because some resources are better suited to the production of one product than another.
Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
14) The discovery of more efficient production methods will shift an economy's production possibilities curve to the right.
Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
15) An economy cannot operate inside its production possibilities curve. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
16) When an economy is operating on its production possibilities curve, additional units of one product can be obtained only by sacrificing units of the other product.
Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
17) Trade with other nations can enable a country to acquire products at a lower opportunity cost than they can be produced domestically.
Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
18) Trade with other nations eliminates the problem of scarce resources. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
19) Trade with other nations allows a country to consume a combination of products beyond its own production capabilities. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
20) In deciding what materials and methods to use in production, a society is answering the "What to produce" question.
Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
21) Only poor economies must decide "For whom to produce."
Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
22) Economic theories simplify the real world in order to make it more easily understood. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition Page 20
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
23) Economic theories are generalizations about causal relationships between variables. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
24) Ceteris paribus literally means "in a controlled experiment." Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
25) When a prediction proves incorrect and the assumption of ceteris paribus has been violated, it is clear that the economist's theory is invalid. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
26) Issues involving what "should be" are described as normative issues. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
27) When economists describe how the economy works, they are engaging in normative analysis.
Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
28) Microeconomics is the study of the overall performance of the economy. Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
29) Microeconomics is the study of the individual units that make up the economy. Answer: TRUE
Question Status: Previous Edition
30) The only reason that economists ever disagree is because they have different opinions about which of the society's economic goals are the most important.
Answer: FALSE
Question Status: Previous Edition
Essay Questions
1) The countries of the former Soviet Union are attempting to convert factories that once produced military goods to the production of civilian products. Why might we expect the output of civilian products to increase much less than the output of military goods declines?
Answer: No Answer Given
Question Status: Previous Edition
2) Economists can disagree either because they have different views about what "is" or because they have different views about what "should be." Explain these two different types of disagreement and provide an example of each.
Answer: No Answer Given
Question Status: Previous Edition
3) Suppose that you are an exceptionally bright student attending your first calculus lecture. The instructor begins the class by noting that "Students who have completed college algebra tend to do better in this class than those who have not, ceteris paribus." If you have not completed college algebra should you expect to finish near the bottom of the class? Why or why not?
Answer: No Answer Given
Question Status: Previous Edition
4) Suppose that your uncle sends you $500 as a graduation gift. Is there any opportunity cost associated with spending this "free" money? Defend your conclusion.
Answer: No Answer Given Question Status: Previous Edition
5) Suppose that human wants were limited instead of unlimited. Would there still be a job for economists? Might some societies need them and not others? Defend your conclusion. Answer: No Answer Given Question Status: Previous Edition
