If you want to buy this Solution Manual Or Any Other Solution Manual Or Test Bank
Contact us at. Premiumbiz379@gmail.com
Import Settings:
Base Settings: Brownstone Default
Information Field: Difficulty
Information Field: Link to Information Field: Topic Information Field: Type
Highest Answer Letter: D
Multiple Keywords in Same Paragraph: No
Chapter: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Geography
Multiple Choice
1. The South American country with the highest average daily calorie consumption per capita is A) Argentina
B) Peru
C) Brazil
D) Chile
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
2. It is estimated that _____ of the world's population is seriously malnourished.
A) 1/20th
B) 1/10th
C) 1/6th
D)
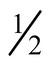
Ans: C
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
3. Most of the one billion malnourished people in the world:
A) have little power
B) have little money
C) are women or children
D) all of the above
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
4. Two countries with very high percentages of arable land are:
A) the United States and South Africa.
B) Colombia and Togo.
C) Rwanda and Poland
D) Russia and India.
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
5. Much of Kenya's income comes from:
A) oil
B) coffee and tea production
C) iron ore
D) tourism
Ans: B
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
6. _____% of Kenya's land is arable.
A) 72
B) 48
C) 23
D) 8
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
7. The set of processes that are increasing interactions, deepening relationships and heightening interdependence regardless of national boundaries are called __________ processes.
A) spatial
B) nationalizing
C) ecological
D) globalization
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
8. Human geographers focus _____________
A) on how people make places.
B) on how we organize space a society.
C) on how we interact with each other in places and across space.
D) all of the above
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.1
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
9. The branch of geography that focuses upon natural landforms, climate, soils and vegetation of the Earth is:
A) cultural geography
B) human geography
C) physical geography
D) biogeography
Ans: C
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.2
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: factual
10. The importance of the spatial approach that geographers use in their studies is that it shows:
A) the arrangement and organization of things on the surface to the Earth
B) the history of an area
C) human activity only
D) the political impact of boundaries
Ans: A
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
11. Cholera is an ancient disease with its source area in:
A) China
B) India
C) Afghanistan
D) Indonesia
Ans: B
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
12. By the time the last great cholera pandemic began in 1865, people knew to take precautions against _____ and ended the great waves of cholera.
A) traveling in groups
B) contaminated water
C) eating canned food
D) improper disposal of garbage
Ans: B
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
13. In 1990, an outbreak of cholera killing over 10,000 people occurred in:
A) the Western Hemisphere
B) Africa
C) West Asia
D) Bangladesh
Ans: A
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
14. Cholera vaccines exist, but the problem is that:
A) they are too expensive
B) they have serious side effects
C) many people refuse to take them
D) they do not remain effective for longer than about 6 months
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
15. Which geographical theme would involve the study of the impact of the drainage of part of the Florida Everglades?
A) human-environment
B) movement
C) place
D) location
Ans: A
Difficulty: Difficult
Link to: 1.2.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
16. _________________ refers to the infusing of a locality with meaning and emotion.
A) Regionalization
B) Human-environment interaction
C) Sense of place
D) Location theory
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
17. The degree of direct linkage between one particular location and other locations in a transport network is referred to as:
A) spatial interaction
B) movement
C) landscape
D) connectivity
Ans: D
Difficulty: Difficult
Link to: 1.2.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
18. Geographer Carl O. Sauer is most closely connected with:
A) natural landscape
B) cultural landscape
C) regional geography
D) location theory
Ans: B
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
19. In their study on students' perceptions of place, Gould and White found that ____________
A) students would prefer to live near the Rocky Mountains.
B) students would prefer to live in Utah over California.
C) students have no place preferences.
D) students have a strong bias for their home region.
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
20. The cultural landscape of Dar es Salaam is a composite of several different culture groups which have administered the place. British policy stimulated the development of a district of 3 to 4 storey apartments reminiscent of:
A) London
B) Bombay
C) Nairobi
D) Paris
Ans: B
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
21. The coordinates of absolute location are useful mainly in determining exact:
A) distance
B) directions
C) distance and directions
D) elevations
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.3
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
22. The physical location of a place using the Earth latitude-longitude grid is properly called the:
A) relative location
B) absolute location
C) referenced location
D) grid plan
Ans: B
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.3
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
23. The location of a place in relationship to other places or features around it is called:
A) absolute location
B) site
C) relative location
D) index of placeness
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.3
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
24. Chicago's absolute location has not changed but its relative location changed markedly in 1959 because:
A) Lake Michigan shrank
B) O'Hare international airport opened
C) the St. Lawrence Seaway was opened
D) new railroads were completed
Ans: C
Difficulty: Difficult
Link to: 1.3
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
25. The mental map you have of places you routinely visit is a map of your:
A) neighborhood
B) inner world
C) region
D) activity spaces
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.3.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
26. Except for South and Southeast Asia, which ocean influences the moistest areas of the world?
A) Pacific
B) Indian
C) Arctic
D) Atlantic
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.3.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
27. The concern of geography with space puts _________ at the center of its agenda.
A) patterns
B) distance
C) scale
D) places
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
28. A good example of a formal region would be a:
A) region surrounding a manufacturing complex
B) city and its surrounding region
C) region of similar language
D) region showing the migration to a central location
Ans: C
Difficulty: Difficult
Link to: 1.4.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
29. A good example of a functional region would be:
A) a city and its surrounding region
B) region where everyone speaks French
C) region where farming practices are the same
D) region of a similar climate
Ans: A
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
30. The cultural geographer Wilbur Zelinsky approached the task of defining and delimiting the perceptual regions of the United States and southern Canada by analyzing:
A) results from thousands of personal interviews
B) results of census data
C) contents of hundreds of telephone directories of metropolitan areas
D) data of social workers
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
31. Of the 12 major perceptual regions of the United States and southern Canada identified by
Zelinsky, the one that is unlike any of the others is:
A) Southwest
B) New England
C) Middle Atlantic
D) the South
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
32. The concept of culture is closely identified with:
A) archaeology
B) anthropology
C) sociology
D) psychology
Ans: B
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.4.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
33. Cultural geographers identify a single element of normal practice (e.g. cattle herding) as:
A) a culture trait
B) a cultural peculiarity
C) a culture region
D) a cultural heritage
Ans: A
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
34. A cultural complex is defined as:
A) a single trait spread over a geographic region
B) a discrete combination of traits, for example Masaai cattle herding
C) several groups sharing the same trait
D) several groups occupying the same region
Ans: B
Difficulty: Difficult
Link to: 1.4.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
35. The spread of ideas, cultural traits, knowledge and skills from their place of origin to other areas where they are adopted is called:
A) diffusion
B) adjustment
C) spreading
D) cultural invasion
Ans: A
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
36. Hagerstrand emphasized that culture hearths should be viewed in the context of ______ as well as space.
A) time
B) location
C) innovations
D) population
Ans: A
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
37. The greater the distance from the hearth the less likely an innovation will be adopted. This is referred to as:
A) inverse innovation rule
B) adoption avoidance
C) distance decay
D) cultural repulsion
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
38. The lack of penetration of alcoholic beverages in Islamic regions illustrates the effect of ______________________ on cultural diffusion.
A) cultural taste
B) poor transport systems
C) cultural barriers
D) psychological barriers
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
39. The diffusion of the idea of the hamburger to India but with a vegetable patty instead of the religiously prohibited beef is an example of:
A) cultural mimicry
B) cultural barrier
C) stimulus diffusion
D) independent invention
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
40. Which of the following is not an example of a form of expansion diffusion?
A) hierarchical
B) stimulus
C) contagions
D) independent invention (ancient agricultural hearths)
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
41. The spread of disease where nearly all adjacent individuals are affected is an example of:
A) relocation diffusion
B) independent infection
C) contagious diffusion
D) stimulus diffusion
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
42. The diffusion of Birkenstock shoes or of new styles of music tend to be examples of:
A) independent adoption
B) contagious diffusion
C) hierarchical diffusion
D) stimulus invention
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
43. Which form of diffusion cannot be transmitted by media (television, internet, radio)?
A) relocation diffusion
B) hierarchical diffusion
C) stimulus diffusion
D) expansion diffusion
Ans: A
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
44. Nineteenth Century American English contains words that are Dutch, Native American, Spanish, French and German. Most of this growth of the language was the product of:
A) multi-cultural curriculum in the schools
B) international broadcast media
C) a fashion for including exotic words
D) relocation diffusion of various groups
Ans: D
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
45. The notion that cultural factors are the product of environmental conditions (e.g. the ancient Greek idea that Europeans were fierce and brutish because of the cold climate), is an example of:
A) environmental prejudice
B) modern environmental psychology
C) environmental determinism
D) environmental possibilism
Ans: C
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.5.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
46. The study of human cultures and their ability to adapt and exist within a particular physical environment is called:
A) possibilism
B) cultural ecology
C) culture history
D) cultural determinism
Ans: B
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.5.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
True/False
47. The world's cultures live in spatial isolation and show little change that is the result of interaction and diffusion.
Ans: False
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.0
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
48. Geographers study the spatial aspects of phenomena. This is similar to historians who study the temporal aspects of phenomena.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.1
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
49. The study of landforms, climates, and environmental change is referred to as physical geography.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.1
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
50. The cause of cholera was deduced by mapping the spatial relationship between the use of particular London public wells and the incidence of cholera infection.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.2.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
51. Cholera outbreaks have not occurred in the Twentieth Century and never in the Western Hemisphere.
Ans: False
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.2.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
52. A city's relative location can change over time.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.3
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
53. Activity spaces refer to neighborhood playgrounds in large cities.
Ans: False
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.3.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
54. Details of the distribution of wealth within the United States are a feature typical of maps of Gross National Product at the global scale.
Ans: False
Difficulty: Difficult
Link to: 1.4
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
55. Functional regions are the product of interaction and movement.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Easy
Link to: 1.4.A
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
56. Baseball is a cultural trait adopted by the Japanese.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.B
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
57. Diffusion which proceeds through the levels of an urban hierarchy, from largest to smallest places, is hierarchical diffusion.
Ans: True
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Factual
58. Migration of individuals is not a form of diffusion.
Ans: False
Difficulty: Medium
Link to: 1.4.C
Topic: Intro. to Human Geography
Type: Applied/Critical Thinking
Essay
59. Discuss the problems that “geographic illiteracy” can present to a country such as the United States in the Twenty-First Century. Give examples of the need for geographic knowledge in diverse areas such as international politics, domestic politics, economics, and popular culture.
Ans:
60. Discuss the difference between absolute and relative location. What is the absolute location of your college or university? How would you describe the relative location of the town or city where your college is located?
Ans:
61. Discuss mental geography from two personal perspectives: the mental map of your activity spaces and the map of your preferred place of residence in the United States.
Ans:
62. Describe the use of spatial analysis in the discovery of the cause of cholera. Give one or two examples of the spatial aspects of diseases which are commonly in the news (e.g. AIDS, flu, etc.).
Ans:
63. What is a functional region and how does it differ from a formal region? Discuss the functional region associated with a nearby metropolitan center—describe movement, communication and interaction between the metro area and its surrounding region.
Ans:
64. Briefly describe the difference between expansion and relocation diffusion. Give several example of each.
Ans:
65. The South region of the United States, it is argued, persists as a region which is different from other U.S. regions. Identify some of the material and nonmaterial cultural attribute associated with this region. Discuss possible boundaries of the region and what you would use to establish the boundaries. In your opinion, is the South becoming more or less like the rest of the country? Give evidence for your opinion.
Ans:
