






































































































































































































































































Dear Colleagues,







In 2024, the RBA celebrated its 20th anniversary, marking two decades of industry action, global collaboration, and a steadfast commitment to advancing responsible business conduct. What began as a shared vision among a handful of forward-thinking companies in 2004 has grown into a global alliance of more than 600 members across several initiatives spanning many industries, geographies, and supply chains.
The milestone year was a time for reflection but, more importantly, it was an opportunity to consider what the future might hold and how the RBA can best meet the challenges ahead. It was also a year of transformation and significant progress.



This annual report captures much of our work across critical areas in 2024: advancing due diligence; supporting members with practical tools, programs and training; fostering industry collaboration; increasing awareness on key issues; and driving measurable impact.
We expanded our public policy and environmental expertise, made substantial improvements to our programs, initiatives, tools and operations, and enhanced our data analytics capabilities to better serve our members and provide them with the resources they need to address current and emerging issues.
The RBA facilitated the return of $47 million in recruitment fees to workers in 2024 by engaging members, their suppliers and stakeholders. We met with numerous government officials around the world, including many in producing countries, and the RBA was selected to join the U.S. State Department’s Advisory Committee on Responsible Business Conduct. We added data analytics to key tools and programs to support due diligence and adopted the United Nations Transparency Protocol to govern the exchange of supply chain data in RBA-Online. Meanwhile, the annual number of VAP assessments completed in 2024 exceeded 2,000 for the first time and the VAP expanded to 52 countries. These are just a few examples of our efforts highlighted in this report.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve—ushering in new mandates on human rights, environmental due diligence, minerals sourcing, and corporate accountability—and geopolitical issues add uncertainty to international supply chains, the RBA and its initiatives have responded with agility, ambition and purpose.
Looking ahead, we are energized by the opportunities to lead, innovate and partner for lasting change. Our “One RBA” approach to further unify strategies and resources across our initiatives will help enable even greater impact and alignment with global frameworks and expectations in the years to come.
Thank you, members, partners and stakeholders, for your continued collaboration and support as we take this journey together.
Sincerely,
Rob Lederer CEO, Responsible Business Alliance













In light of continued global regulatory change and expanding definitions of responsible sourcing and due diligence, in 2024 the RBA’s Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) put significant focus on evolving its structure, standards, systems, and industry engagement. These investments strengthened and grew the RMI program scope, opportunities for systems interoperability along the supply chain, from mine to product, and practical tools and data for responsible minerals sourcing. This deepened and improved the RMI’s core and long-term work while supporting efforts to evolve the program and prepare for the next five years.




















In 2024, the RMI restructured and expanded investments in smelter and refiner support and retention, driven by objectives of strong Responsible Minerals Assurance Process (RMAP) conformance and retention rates, improved program experience for facilities engaged in RMAP, and overall greater understanding and implementation of OECD-aligned due diligence among RMAP participants.
In support of these program objectives, the RMI expanded the technical assistance team from 1.5 to three full-time staff, including a new, director-





Forty-six new members joined the RMI in 2024, bringing the year-end RMI membership total to 511 organizations. There continues to be representation across a wide range of sectors among new RMI member companies, demonstrating the value of the RMI across diverse supply chains. In particular, sectors that saw strong increases in new membership included automotive, building controls, electrical manufacturing, and electronics. New sectors represented in RMI membership in 2024 included airport services, video games, and water infrastructure.















level position (Director of Facility Engagement). This expansion allowed the RMI to bring technical assistance in-house, with more expertise and support for smelters and refiners, addressing critical conformance gaps and providing tailored solutions for sourcing challenges. The RMI Facility Engagement Team further developed existing systems to track and manage technical assistance and established new systems to identify and support at-risk facilities to positively impact the RMAP facility retention rate.
With the Facility Engagement Team in place, the RMI identified and addressed recurring conformance challenges through structured technical assistance and risk-based interventions, and responded to urgent needs like one-on-one technical support and guidance on responsible sourcing from the African Great Lakes Region (GLR). The RMI’s actions included the creation of an enhanced due diligence guidance document to clarify actions and documentation needed for high-risk sourcing, combined with trainings for facilities and assessors, engagement with industry associations, and outreach to individual smelters to explain and support utilization of this tool.
The RMI also launched the Facility Advisory Working Group in 2024. The RMI initiated this group to foster dialogue between facilities and the RMI to improve RMAP and practices, especially to help determine key factors and challenges for facilities related to RMAP assessment participation, identify opportunities to
enhance the value proposition of RMAP assessments, and support success of smelters and refiners in the program. The group’s initial focus has been on tin, tantalum, and tungsten (3T), including responsible sourcing from the GLR.
In 2024, the RMI continued building educational offerings, introducing training programs aimed at enhancing the capabilities of a wide audience including members, facilities and assessors in the RMAP program, other suppliers and interested stakeholders. The RMI trained 481 facilities in 2024.
The RMI’s training program aims to deepen stakeholders’ understanding and application of risk management in mineral sourcing via our standards and tools available to members and RMAP facilities. The year kicked off with the global virtual training sessions for the RMI Downstream Assessment Program (DAP), tailored for both assessors and RMAP facilities.
Additionally, the RMI successfully deployed trainings on utilizing upstream due diligence mechanisms and establishing effective grievance mechanisms. To further support the industry, the RMI rolled out virtual training sessions on the updated RMI Global Risk Map and its new features. These sessions also included guidance for downstream companies on leveraging RMI tools for effective due diligence.
The RMI also trained facilities participating in the RMAP program and RMAP assessors on how to design and implement a grievance mechanism in line with the UNGP, and how to use the RBA Voices application as one of their own tools for due diligence.
The RMI’s commitment to education extended to its online learning platform, the RBA Learning Academy, which was updated with an enriched curriculum and personalized learning paths for members, suppliers, assessors, and others involved in the assessment programs.
Facility standard update / supplementary supply chain due diligence module
In 2024, the RMI undertook significant efforts to enhance its standard suite with the aim of ensuring stronger regulatory alignment in preparation for future recognition processes and expanding the scope of its standards to better address emerging environmental, human rights, occupational health and safety, and governance risks. Central to these
efforts is a comprehensive revision of the RMI’s Facility Standard for Social, Environmental, OHS and Governance Risks (RMI Facility Standard) and the development of the RMI Supply Chain Due Diligence Module Plus (RMAP+) to be used in combination with the RMI’s standard suite. These updates incorporate robust criteria reflecting the evolving regulatory landscape and expanding stakeholder expectations, while underscoring the importance of impact through continuous improvement.
The revision process involved a comprehensive benchmarking exercise, comparing the existing standard with key regulations, such as the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), and the EU Battery Regulation (EUBR). Throughout the process the RMI engaged its Multi-stakeholder Standards Advisory Committee, presented the revision process at the OECD Forum, and conducted both member and public consultations to gather diverse input. Feedback from these consultations was carefully reviewed and dispositioned by the end of 2024, with key insights incorporated into a third and final iteration of the revised standard. The revised standard and updated module will be piloted in early 2025.

As part of the broader enhancement of the RMI’s standards suite, significant improvements were made to the assessment tools for the RMAP and DAP. These updates aimed to reorganize and streamline assessment workbooks for improved alignment with the OECD 5-Step framework, while also enhancing their auditability and functionality. Beyond technical improvements, the RMI also developed guidance for third-party auditors to further support accurate interpretation of the RMI’s existing standards. In 2024, work on Auditor Guidance documents covered Step 5 Reporting, Enhanced Due Diligence Guidance, updates to the CAHRA Procedure Guidance, guidance for assessments of transportation routes, warehouses, and co-located mines and processors, among other topics.
The RMI’s Assessment Fund is dedicated to supporting companies’ participation in responsible minerals due diligence by covering the full cost for initial assessments* and up to 75 percent of costs for re-assessments of facilities with demonstrated financial need. In 2024, more than $422,000 was disbursed from the fund, funding 38 initial assessments, one reassessment, and 34 corrective action closures. The top recipients of funding were 10 multi-metal facilities, followed by 7 gold facilities, and 5 tin facilities. The top recipient countries in 2024 included China (10), Indonesia (6), and Peru (3).
In 2024, in response to member requests for a dedicated mechanism to support facility-level and supplementary supply chain due diligence assessments, the RMI established an additional Assessment Fund. This new fund complements the existing Assessment Fund, which continues
to focus exclusively on traditional RMAP OECD Annex II risk assessments. The new Assessment Fund is specifically designed to facilitate RMI member contributions to cover the full cost of initial assessments under the updated standards suite, offering essential support to facilities as they work to comply with evolving regulatory expectations in relation to environmental, human rights, occupational health & safety, and governance performance.
The RMI’s Upstream Due Diligence Fund is designed to provide financial support to entities seeking assistance with on-the-ground due diligence activities in their upstream supply chains. The fund is available to RMAP participants conducting upstream due diligence, local suppliers, and communities involved in assessments or mine-site monitoring. The fund also supports Upstream Mechanisms recognized by the RMI that require reassessment or funding for specific activities.
The RMI’s Recognition Process evaluates and recognizes external standards and activities that support companies in meeting the requirements of the RMAP. The process includes both Upstream Mechanism Recognition and Cross Recognition of standards and assurance programs. Upstream Mechanism Recognition occurs at two levels: Level 1, which provides full recognition for both the standard and its implementation and Level 2, which offers partial recognition for the standard alone.
In 2024, the RMI’s Cross Recognition process continued to recognize existing schemes that align with RMI standards, including the LBMA Responsible Gold Guidance and specific provisions of the Responsible Jewellery Council’s Chain-of-Custody (provision 1) and Code of Practices (provision 7)
The RMI facilitates financial support for responsible minerals due diligence through contributions from its membership.
*The RMI’s Assessment Fund is reserved for tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold assessments when the fund’s balance is below $150,000.
Standards. As part of its ongoing efforts to refine the process, the RMI conducted a survey to gather member feedback on cross recognition, which will inform the evolution of the process under the RMI 2.0 strategy. The RMI also took proactive steps to engage recognized schemes, working to update agreements and enhance mutual recognition for more effective collaboration. In 2024, the RMI cross-recognized 61 facilities, including 48 facilities assessed by the LBMA and 12 facilities assessed by the RJC.
In 2024, the RMI continued to work on preparedness for forthcoming regulations such as the EU Battery Regulation and the EU Corporate Responsibility Due Diligence Directive, including elements requiring supply chain due diligence on a broad range of risks including human rights, community rights, worker rights, and environment protections.
To support members with new requirements, the RMI expanded the Material Insights platform, which analyzes and presents information on 48 minerals and 3 components focusing on risk data. In 2024, the RMI updated data for 38 materials and profiles and ESG risk data for 10 priority materials. The RMI also built an automated data report in RBA-Online, which allows RMI members to visualize aggregated data generated via the Risk Readiness Assessment (RRA) self-assessments undertaken by their trading relationships.
In view of the entry into force of the EU Battery Regulation, the RMI commissioned research on the supply chain of battery materials, including the production of cobalt, nickel, graphite and lithium, pCAM, CAM, battery manufacturing and assembly. The results of the research were shared with RMI members that take part in the Emerging Minerals Working Group via presentations and discussions with experts. This allowed the group to learn about the structure and geographical scope of the supply chain, level of vertical integration, main economic operators producing and trading battery materials as well as blind spots where production processes or operators are unknown or unclear.
The RMI also continued to facilitate the work of
RMI members on battery materials. Peer-to-peer learning sessions were organized for new member representatives acting as Single Points of Contact (SPOC) for facility Engagement. The RMI also coordinated the rollout of the Pilot Reporting Template (PRT) through the Emerging Minerals working group. Activity level increased significantly in those supply chains, with steadily growing numbers of dispositions and an expanding pipeline of assessments.
As a significant share of battery materials are produced or processed in Asia, the RMI encouraged the engagement of RMI member representatives taking part in China Smelter Engagement Team on facility engagement in those supply chains. The RMI organized a learning session with the Policy Team on the EUBR and encouraged the assignment of SPOCs.
Engagement of industry associations and experts has been a cornerstone of RMI work in critical minerals supply chains, and this was expanded in 2024 based on areas of interest and risks identified by member companies. The RMI’s engagement continued with the Nickel Institute, Cobalt Institute, International Lithium Association, Rare Earth Industry Association, The Responsible Mica Initiative, and Drive Sustainability. In addition, the RMI built relationships with the International Wrought Copper Council, and the European Carbon and Graphite Association. The objectives of those engagements were to establish a dialogue with the industry on regulatory due diligence requirements, to build understanding of RMI member needs for responsible sourcing along the value chain and foster collaboration around their implementation, and to introduce RMI tools and support available to midstream facilities. At a company level, the RMI established contact with headquarter offices of major battery actors to build awareness on responsible sourcing practices required under the EUBR and how they can collaboratively support compliance.
Also in 2024, the RMI encouraged its members to identify areas of actions in each of the critical mineral supply chains, which include crude cobalt, lithium, nickel, natural graphite, rare earth elements, mica and copper. Those resulted in dedicated workstreams where the RMI and its members jointly pursued actions for risk identification and mitigation. Such
actions reflected the specificities of the minerals at stake. A few examples are presented below:
l Mica: the RMI member focus in 2024 was on artisanal mica production and processing in Madagascar. Since a significant number of on-theground initiatives are already ongoing in the country, the focus of RMI members was on engaging each of those initiatives to understand their focus and objectives and on advocating for coordination and collaboration. The RMI brokered relationships with the ILO Child Labour Platform, the U.S. Department of Labor Shine project, and with PACT. As a result, all agencies operating in Madagascar and The Responsible Mica Initiative established a quarterly coordination hub meeting.
l Crude cobalt: the RMI member focus in 2024 was on increasing outreach and facility engagement in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The RMI supported these efforts by hiring a local consultant who met with various crude cobalt refiners. As a result, RMI members could hold virtual meetings with the management of a few refiners to explain the need to obtain or maintain conformance with the RMI RMAP and to operate according to responsible mineral sourcing standard requirements. To enable RMI members to engage in on-theground child labor prevention and remedy, the RMI connected its members with the ILO Child Labour Platform, which is a project supporting the DRC government to establish an institutional mechanism to identify victims of child labor and to articulate remediation measures.
l Nickel: The focus of RMI members in 2024 continued to be on nickel and cobalt production in Indonesia, with the objective to prevent and mitigate social, environmental, and governance risks in smelting operations. To support those efforts, the RMI facilitated connections between its members and Indonesian stakeholders, including government institutions, to share recommendations aligned with global regulatory drivers on sustainable mineral sourcing. The RMI held meetings with the Coordinating Ministry for Maritime Affairs and Investments, The Indonesian Nickel Producers Association APNI, representatives from local academia, experts, and researchers. The RMI also collaborated with the Nickel Institute and the Cobalt Institute, hosting a webinar on ESG requirements for nickel and cobalt producers in April 2024. We also partnered with the Indonesian Nickel Miners Association (APNI), participating in various events




such as the APNI annual training of trainers with a virtual presentation on ESG assessments and supply chain sustainability in May 2024, an inperson workshop on ESG assessments and GHG emissions calculation in Jakarta in June 2024, and a panel discussion on ESG co-construction at the ASEAN Critical Mineral Conference.
Together with its member companies, the RMI identified industrial parks as key players in nickel extraction areas, with significant roles in the introduction and upholding of responsible nickel sourcing and production practices. By July 2024, the RMI coordinated efforts among 13 member companies, culminating in a joint communication to the industrial parks. Over several months, the RMI provided training for management and staff on due diligence and provided technical assistance to various smelters to prepare for an RMI assessment. Through these concerted efforts, RMI has not only supported responsible mineral sourcing but also fostered a collaborative environment for sustainable practices in Indonesia’s nickel and cobalt industries.
To support member companies’ due diligence in a more systemic way, the RMI launched the ESG Collective Action Task Force, for RMI members that aspire to work collaboratively on the deployment of the RMI standard and tools, as well as on risk mitigation and prevention.
The RMI also focused efforts on the artisanal sector in 2024. The RMI is a partner in the European Partnership for Responsible Minerals-funded Scalable Trade in Artisanal Gold (STAG) project, led by the Artisanal Gold
Council (AGC) in partnership with RESOLVE. The STAG project aims to create a replicable, regional sourcing system to scale up trade in responsible artisanal gold in Burkina Faso. In 2024, the RMI reviewed and advised on the revision and third-party alignment assessment of the CRAFT Code 2.1, and advised on the application of the code in the Burkina Faso and upstream mechanism context. The RMI also participated in an ASM Audit Workshop hosted by RESOLVE and the Alliance for Responsible Mining in December 2024. The workshop provided an overview of the CRAFT Code and its applicability in minerals due diligence as an upstream assurance scheme. The RMI highlighted its upstream recognition of the CRAFT Code and methods for companies and auditors to utilize CRAFT.
With the changing regulatory landscape, the RMI identified the need to update its theory of change to take stock of increased due diligence requirements and complexity of stakeholders affected by and involved in their implementation. The RMI identified a set of baseline indicators that are readily available to describe the RMI’s contributions toward responsible mineral supply chains. In 2024, the RMI published its first Impact Report, which collects those indicators. This is a first step in the direction of the establishment of a more complex monitoring, evaluation and learning system, on which the organization will work in the coming years.
In 2024 the RMI elicited feedback from members on the theory of change and Impact Report and also ran two consultations with external stakeholders. One key learning from this process was the need to organize
stronger outreach to civil society to have even greater representation during the consultation process. This is a principle the RMI plans to implement in 2025.
The RMI assessment program continued its strong growth trajectory in 2024, marked by significant achievements and an ongoing commitment to operational excellence.
Program Growth and Assessment Activity
The RMI assessment program (RMAP and DAP) has grown by 55 percent since 2022. In 2024, the RMI operations facilitated 180 RMAP assessments and 14 DAP assessments. Notably, 23 percent of these assessments were initial assessments, and an additional 7 ESG assessments were conducted.
In 2024 the RMI RMAP’s global reach was evident in the diverse geographic distribution of assessment participants. China accounted for 35 percent of all
participants, followed by other regions in Asia and the Americas. The participation of China-based facilities in the RMI assessment program has increased by 72 percent since 2022. The operations team also observed a steady increase in participants from Indonesia, attributed to new nickel facilities joining the program in the latter half of 2024.
In total, 142 RMAP participants achieved conformance in 2024 (24 newly conformant and 118 reassessments). Among these participants:
l 61 percent were 3TG facilities.
l The remaining participants included those involved in cobalt, mica, critical minerals, and precious metals.
Forty percent of assessed facilities became conformant without entering the Corrective Action Plan (CAP) process. This significant outcome reflects the proactive efforts made by the Operations and Facility Engagement Teams, which provided support to facilities throughout the assessment process.
Throughout the year, RMI Operations dispositioned 130 facilities. Of these, 75 facilities became newly eligible, with 87 percent of these classified as pinchpoint facilities (Smelters and Refiners). The disposition process also accounted for existing facilities ceasing operations, facilities returning to operations, and cross-recognized facilities.
In 2023, the RMI Operations team implemented new KPIs and integrated data analytics to measure progress across the assessment program. The focus on data analysis continued into 2024, as the Operations team remained committed to delivering improved data accuracy and faster results for RMI members.
Data analytics played a pivotal role in identifying target areas for further development. As a result, the team identified key opportunities for improving the overall assessment program, focusing particularly on streamlining processes and enhancing efficiency.
Some key initiatives were launched to ensure continued operational success in 2024:
1. Process Analysis: A comprehensive analysis of the end-to-end assessment process was conducted to pinpoint delays and implement corrective actions, resulting in improved efficiency.
2. Data Analysis: The RMI Operations team implemented data analytics to monitor performance across set KPIs. This close monitoring ensured that all actors progressed through the assessment process smoothly, with a particular focus on pre-assessment activities and CAP evidence submission.
3. Timely Reassessments: Implemented 4-month reassessment initiation, ensuring a timely conformance determination.
The RMI program made significant strides in 2024, both in terms of the number of participants and the overall effectiveness of its operational processes. The ongoing focus on data analytics, and facility engagement will continue to drive improvements in the program and ensure its growth in the years ahead.
In 2024, the RMI convened members to discuss a confluence of significant events and drivers for change. Members and stakeholders observed the pivot from due diligence as good practice to mandatory requirements, as codified in crosssectoral, regional and global regulations, paired with a significant expansion of corporate accountability for environmental, social, and governance risks across raw and secondary materials supply chains. While scrutiny and involvement of regulators, investors, civil society, and impacted communities in due diligence has been a long-term trend, new requirements on remedy and stakeholder engagement came into focus. The RMI followed expanded guidance and expectations for industry programs to demonstrate quality and credibility. Among the extensive discussions on regulations and requirements, we noted the importance of keeping a spotlight not just on compliance but on positive impact and just transition.
With these drivers and the RMI’s mission in mind, we created a roadmap for “RMI 2.0,” with a vision that includes:
l Standards and reporting aligned to new regulatory requirements;
l Improved systems interoperability for broader supply chain coverage;
l Deployment of standards and tools at scale across new minerals supply chains (batteries, critical minerals); and
l Systems and program updates to maintain credibility and meet expectations of regulators, industry, and stakeholders.
The RMI 2.0 vision and strategy also requires greater-than-ever coordination between the RMI and the broader RBA team, to best leverage policy, environmental, data, technology and other expertise for RMI members and meaningful due diligence. This organizational commitment to a “One RBA” approach will further underpin the RMI’s support for responsible minerals sourcing while enabling a new, unified approach to due diligence across supply chains.






















In February 2024, the RBA and the RLI brought together 110 high-level representatives from the private sector, governments, civil society, and other stakeholders for the Global Summit on Collaborative Approaches to Combatting Forced Labor in Washington, D.C. to strengthen collaboration in addressing forced labor in global supply chains.
The Summit featured high-level remarks from senior policymakers emphasizing the importance of partnerships with the private sector and workers, the need for transparency and harmonization of laws, and addressing forced labor through international cooperation. Panel discussions took stock of the prevalence of forced labor in global supply chains, and provided updates on regulatory efforts, policy approaches, and interconnections between jurisdictions, with a focus on creating comprehensive and effective enforcement mechanisms.
The Summit convened four in-depth interactive workshops on root causes of forced labor, policy











In 2024, the RBA’s Responsible Labor Initiative (RLI) scaled its ongoing efforts to identify and remediate forced labor across global supply chains, particularly anticipating emerging global regulatory developments.

coherence, supply chain due diligence, and data interoperability. Key outputs of the Summit included detailed action plans and visions of success over one-, five-, and ten-year timeframes, emphasizing multistakeholder collaboration. The Summit highlighted the need for cohesive policies, multi-stakeholder engagement, and robust data systems to tackle forced labor.
Developed with input from the RLI Steering Committee, RLI and RBA members, the RLI Strategic Priorities 2024-2027 (“Priorities”) outlines key focus areas over the next three years that will guide the RLI’s mission to become a leading cross-industry platform for practical implementation of forced labor due diligence in global supply chains throughout the recruitment and employment experiences. The Priorities help structure and connect RLI activities to the RLI vision and mission. They provide current and prospective members with a clear sense of the RLI’s value proposition while helping companies address existing and emerging legislative efforts related to forced labor due diligence, market access and legal liability.



















Leadership: Maintain a leadership role in the global effort to combat forced labor in supply chains
Multi-Industry: Promote multi-industry adoption of responsible recruitment practices
Practical Tools: Support practical implementation of forced labor due diligence
Go Deeper: Facilitate engagement deeper into the supply chain
Prevent Forced Labor: Move from remediation to prevention
In 2024 the RLI launched its Implementation Roadmap and outline of specific projects linked to the Priorities. The Roadmap, organized by the Priorities focus areas, informs ongoing resourcing, prioritization, budgeting and progress tracking for the RLI.
Responsible recruitment has been a pillar of the RLI’s work for many years. An important driver of forced labor is the payment of recruitment fees and other related costs incurred by workers to obtain work. In many instances, workers may have to borrow money to pay these fees, taking on debts that leave them vulnerable to exploitation and unable to leave their jobs until the debt is repaid. From 2018-2023 the Responsible Recruitment Program (RRP) provided a maturity pathway for private recruitment agencies
(PRAs), helping to lift them toward ethical recruiter recognition. The RRP was designed to increase the number of recruitment agencies on the pathway toward certification by programs, such as IOM IRIS and On the Level, and help create a market for ethical recruitment.
In 2024 the RLI took stock of the accomplishments of the RRP program while informing the development of the next steps for the program. The RLI hosted consultations with recruitment and labor agencies focused on the future of the recruitment industry progress toward zero-fees recruitment, including the role of the RLI and efforts to drive transformation at scale while reducing the risk of forced labor in global supply chains. The RRP’s first two phases provided significant learnings that we can apply toward future models and partnerships.

Broadly there appears to be a misalignment between increased private and public (regulatory) expectations for responsible recruitment (e.g., zero fees/employer pays) with actions on the ground. Government policies in some sourcing countries (sending and receiving) allow for recruitment fee charging to workers, thus creating a gap with importing country regulations. This creates a negative incentive whereby private recruitment agencies that seek to implement a zerofees recruitment policy are placed at a competitive disadvantage. There is also a lack of understanding on how to implement zero-fees recruitment, particularly considering numerous emerging forced labor regulations that are not necessarily uniform, along with a proliferation of overlapping and confusing requirements, programs and certifications. Finally, there is a need for greater awareness raising for foreign migrant workers to better understand their rights and have access to trusted and reliable grievance mechanisms.
To address these issues, the RLI has ambitious plans to scale its efforts in partnership with others. The RLI is looking to build RRP 2.0, which will focus on the demand side of ethical recruitment while fostering greater collaboration with partner organizations to help increase capacity building, assessment and certification (aligned with RBA standards) of PRAs at scale across
key recruitment corridors. A focus on the demand side of ethical recruitment will involve taking a more holistic approach that focuses on work with RBA members and their suppliers to ensure there is a clear demand signal for ethical recruitment, a viable marketplace and incentives for PRAs to adopt this model.
Beyond the Global Summit, in 2024 the RLI team supported the RBA Public Policy team’s engagement with governments, inter-governmental organizations, and civil society to help drive forced labor due diligence and responsible recruitment. The RLI participated as an expert resource and stressed the importance of forced labor and human rights due diligence that needs to be factored in when forming policies impacting businesses from an environmental, social and governance (ESG) perspective.
Throughout the year the RLI, in partnership with the RBA Public Policy Team, maintained regular dialogues with the U.S. government agencies including the State Department’s Trafficking in Persons (TIP) office, the Department of Labor and its International Labor Affairs Bureau (ILAB), and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS)’s Customs and Border Protection (CBP) agency. The RLI also engaged critical European
institutions, including the European Commission (DG Trade, DG Grow) and member states in the finalization of the European Union Forced Labour Regulation (EU FLR) and implementation of the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD).
Other 2024 highlights including participation in the Human Rights Commission of Malaysia (SUHAKAM) Consultation on Forced Labor Issues in Penang, the signing of an MOU with JP Mirai (Japan Platform for Migrant Workers) in Tokyo, an RLI Recruitment and Labor Agency Consultation in Penang, meeting with the Malaysian Ministry of Human Resources’ Department of Labour in Kuala Lumpur, speaking at the Tech Against Trafficking Summit in London, and participating in the United Nations Business and Human Rights Forum IOM-RBA/RLI Workshop “Making Mandatory Human Rights Due Diligence Work for Migrant Workers” in Geneva.
The RLI will continue to lead industry efforts related to the practical operationalization and implementation of forced labor due diligence, aligned with international standards, including the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, and the OECD Guidelines for Responsible Business Conduct, to include identification, prevention, mitigation, communication, and appropriate remedy. For example, in 2024 RLI staff developed several regulatory readiness assessments related to the EU CSDDD and the EU FLR, helping identify any potential compliance gaps between RLI tools and programs and emerging regulations for members.
Looking ahead, the RLI has outlined a set of practical tools to continue to help operationalize forced labor due diligence for members and their suppliers. These will include:
l Journey Map: Simplified Forced Labor Due Diligence and Remediation Toolkit
l Access to Remedy Standard Operating Procedures (SOP)
l Forced Labor Stakeholder Mapping
l Translation of Responsible Recruitment Due Diligence Toolkit
l Tools to Operationalize RRP 2.0
l Specialty Validated Assessment Program (SVAP) on Forced Labor modification for greater uptake















The RBA’s Responsible Factory Initiative (RFI) was established in 2018 to support suppliers that are not RBA members in their implementation of the RBA Code of Conduct through three core program elements: the Factory Engagement Program (FEP), Factory Lead Certification (FLC), and Consulting Support. These elements enable participating suppliers to assess their performance against the RBA Code and receive guidance and coaching from dedicated RFI staff on areas for improvement.





















In 2024, the RFI refined its tools, services and trainings. As the majority of RFI members are suppliers to RBA members, it was important to align the RFI self-assessment questionnaire (SAQ) with the RBA’s SAQ by replacing the former with the RBA Risk-Based SAQ. In addition, more flexibility was given to suppliers that completed an RBA SAQ, Validated Assessment Program (VAP), or CustomerManaged Assessment (CMA) to become an RFI member without having to also complete the RFI SAQ. This flexibility allows RFI members to jump straight to the on-site assessment, where more focus is on addressing identified gaps with the help of RFI consulting support. The RFI also expanded its offerings in 2024 with FEP closure assessments, customizedin-house trainings, and other specialized services to tackle challenging issues identified during on-site assessments.



















In 2024, the RFI had 62 members enrolled in its program, a 121 percent increase from 28 in 2023. Its geographical coverage also expanded beyond China as RFI members are currently located in Chinese Taipei, Germany, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Vietnam.
While RFI members have different maturity levels, we continue to see encouraging results where RFI members typically improve their RBA assessment scores by an average of 18-20 percent since participating in the initiative.

The RFI aims to provide more customized webinars and trainings to address its members’ needs, especially in light of emerging global regulations on mandatory human rights and environmental due diligence in supply chains. The RFI will also increase its efforts to promote the initiative further beyond RBA members’ suppliers as well as into additional countries such as Australia, Brazil, Canada, Hungary, Mexico, the Netherlands and United Kingdom.






















In May, the RBA Board of Directors approved the REI Roadmap. Central to the Roadmap is the REI Mission with its focus on the development of tools and services to improve environmental performance through value chain alignment and collaboration. The REI Team will leverage core RBA tools, such as the Code of Conduct, the Risk Assessment Platform, the Self-Assessment Questionnaire, and the Validated Assessment Program, to develop, integrate, and promote REI solutions that align to the RBA’s riskbased due diligence model. The REI Roadmap also envisions collaborating with external partners to expand REI’s reach and transform the environmental performance landscape of the entire industry. The REI Team will also partner with the RBA Policy Team to promote recognition of REI tools and services as credible industry solutions for compliance and environmental due diligence conformance.
The REI’s primary goal is to provide resources that support RBA member baseline conformance to the RBA Code of Conduct across four member-chosen environmental priority areas. The REI also develops











The RBA’s Responsible Environment Initiative (REI) marked its one-year anniversary in the spring of 2024 and ended the year with an RBA Board-approved, formal roadmap that will guide REI work going forward. Throughout the year, new REI products and services were developed and released in support of the REI’s mission.
and deploys capacity-building resources to pave the way for companies to improve their environmental performance beyond baseline criteria. Additionally, the REI establishes leadership programs for companies, in their unilateral discretion, to adopt and implement solutions to achieve superior environmental performance with other frontrunner companies.




















The REI is guided by a Senior Environmental Advisory Team (SEAT), consisting of environmental leaders from a cross-section of RBA member companies. The SEAT provides guidance to the REI team to help ensure it fulfills the greatest needs of RBA members and their industries consistent with the REI mission.
There are three working groups that facilitate RBA member engagement in the REI: the Environmental Sustainability Working Group, the Chemical Management Working Group, and the Circular Materials and Waste Minimization Working Group (newly formed in 2024). An Environmental Due Diligence Task Force was also formed to help develop RBA tools to meet new environmental due diligence requirements, including the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (EU CSDDD). During 2024, the REI remained focused on four member-identified priority issues: decarbonization, water stewardship, circular materials and chemical management.
Key REI resources and services that were further developed or deployed in 2024 included the Emissions Management Tool; the Chemical Management SVAP, Leadership Program and Due Diligence Guide; Water Stewardship Tools; and the RBA Circular Materials Landscape Report and Waste Minimization Toolkit.
The RBA’s Emission Management Tool (EMT), launched in 2023, is a standardized greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions tool for calculating and reporting industry emissions in RBA member supply chains. The EMT leverages the RBA’s unique capability to map industry supply chains, creating efficient and accurate methods for sharing emissions data at both corporate and facility levels. The EMT enables respondents to report on critical emissions data, including energy and fuel consumption, renewable energy use, and emissions reduction efforts. Data from the EMT is intended to inform RBA members’ Scope 3 calculations, increasing visibility into their supply chain emissions and making it faster and easier to report GHG emissions data to customers and external entities like the CDP and regulatory agencies.
The EMT has demonstrated significant growth, with the number of participating companies increasing from 949 in 2023 to 1,610 in 2024, maintaining a 33 percent response rate and resulting in 527 submissions. Additionally, a report analyzing the aggregated data from the 2024 survey was published, providing RBA members with actionable insights and reinforcing the EMT’s role as a critical resource for emissions management.
Looking ahead to 2025, the RBA plans to build on the momentum of 2024 by further expanding the EMT’s
reach and impact. Efforts will focus on increasing supplier participation, refining the tool’s capabilities to address industry-specific needs, and enhancing data analytics to support more strategic decision-making.
The RBA also aims to foster greater collaboration among members by using aggregated EMT data to identify and act on shared carbon “hot spots” within supply chains. The RBA will also explore opportunities to integrate the EMT with other sustainability initiatives, providing members with a more holistic approach to GHG management and reporting.
The RBA’s Specialty Validated Assessment Program on Chemical Management (SVAP-CM) is a focused, rigorous assessment program designed to identify, evaluate, and address chemical management risks at supply chain facilities. In 2024, the RBA onboarded a second SVAP-CM audit firm, refined the SVAPCM protocol for greater efficiency, and conducted a SVAP-CM pilot phase. The RBA initiated the SVAP-CM pilot phase to enable members to experience the new specialty assessment program at no cost, during which the RBA offered 100 percent sponsorship of SVAP-CM pilots. The SVAP-CM pilot phase concluded in October 2024 and resulted in 10 SVAP-CM pilots in Mexico, China, Chinese Taipei, Thailand, and the Philippines within the supply chains of eight RBA members. Based on analysis of aggregated data from SVAP-CM pilots, SVAP-CMs are more effective than VAPs at identifying non-conformances across 16 common criteria shared by the two assessment protocols. The SVAP-CM pilot data analysis also identified several improvement opportunities that RBA is acting upon to enhance the SVAP-CM.
In June 2024, the RBA announced the formation of the RBA’s Chemical Management Leadership Program (CMLP) as a risk-based, voluntary commitment program to advance responsible chemical management in global electronics supply chains. In collaboration with its member companies, the RBA developed the CMLP to harmonize chemical management due diligence efforts and support industry leaders in demonstrating continuous improvement through increased transparency and
action. Participation in the CMLP is designed to align with the due diligence process articulated in the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Business Conduct, and the program seeks to advance progress on the sound management of chemicals toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In consultation with RBA members and external stakeholders, the RBA is seeking international recognition of the CMLP as a sector-specific implementation program of the new Global Framework on Chemicals for the electronics production industry.
In August 2024, the RBA published its Practical Guide to Chemical Management Due Diligence in Supply Chains Leveraging the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Business Conduct sixstep due diligence process, the Practical Guide seeks to promote a collective understanding among businesses, governments, NGOs, worker and employer organizations, and other stakeholders on responsible chemical management conduct. The Practical Guide promotes awareness on chemical management as a global sustainability issue and communicates how members may navigate and use RBA resources to support chemical management due diligence practices within their supply chains.
In 2024, the RBA reinforced its commitment to water stewardship through the continued implementation of its facility water survey, designed to track water utilization and efficiency among RBA members and their suppliers. The survey aligns with leading industry frameworks such as the Alliance for Water Stewardship (AWS) Standard and WWF Water Risk Filter, ensuring the data collected supports internal decision-making and broader use in risk and maturity assessment tools. By focusing on both facility operations and localized water contexts, the survey empowers RBA members and their suppliers to adopt improved water stewardship practices. The RBA’s partnership with the AWS further underscores this commitment, with RBA actively participating in the AWS Forum to collaborate on advancing global water management initiatives.

In 2024 the REI strengthened its circular materials and waste minimization efforts with a new Circular Materials Program Director and updates to the RBA Circular Materials Landscape Assessment Report, last issued in 2021 but revised with the latest e-waste generation statistics. The Report contains three primary recommendations for enabling more circular material flows and will set the stage for the REI’s circular material workstreams in 2025.
The REI also developed a Waste Minimization Toolkit that includes a Waste Tracking Record Tool and a video learning module that aims to promote and enable responsible waste minimization practices across electronics industry supply chains. The Waste Minimization Toolkit is now available in the RBA’s e-Learning Academy, where it is accessible to all RBA members and their suppliers.
The Waste Minimization Toolkit was developed by the RBA in collaboration with numerous members primarily to support compliance with RBA Code of Conduct Solid Waste provisions. The Toolkit will help RBA members and their suppliers to systematically identify, manage, reduce, and responsibly dispose of or recycle solid waste to mitigate environmental impacts and contribute toward a circular economy.
Data Standardization: Identify opportunities for data standardization and material measurement, including frequently used/requested data, metrics, and reports.
RBA Goal: Harmonize data metrics, methodologies, and inquiries to drive greater transparency and measurement into reverse supply chains’ performance and material movement, so that gaps and opportunities for safe expansion of circular material use can be identified.
Supply Chain Design: Identify material traceability tools needed to drive the integration of reclaimed materials into procurement supply chains.
RBA Goal: Convene actors across forward and reverse supply chains to evolve practices that lower barriers and optimize processes to achieve more efficient circular material use.
Greater Assurance: Identify and address environmental and labor challenges in e-waste processing and assurance, primarily within the formal sector.
RBA Goal: Provide greater assurance regarding protection of human rights and the environment, allowing actors to make more informed decisions and create more globally inclusive circular supply chains. 1 2 3
The European Union Battery Regulation and the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive will require many RBA members to conduct environmental due diligence on their suppliers and certain value chain partners. A new Environmental Due Diligence Task Force has been formed to discuss potential RBA solutions and the development of an industry approach to value chain environmental risk assessment and mitigation. Any REI approach that emerges will leverage existing and developing RBA, RMI, and REI work to facilitate risk mitigation, compliance, and reporting.
The REI team will follow the REI Roadmap while conducting its work in 2025 and plans to revise and replace existing REI tools and resources based on member feedback. It will add new tools and resources to fill any identified gaps, following a due diligence approach, and will also collaborate and partner across the RBA to establish value chain alignment and promote policy recognition and leverage RBA tools for maximum impact.
















l The finalization of the RGA ESG Audit Criteria and Minimum Standard, providing a roadmap for the acceptance of various audit schemes for RGA member compliance
l Reinforced membership compliance process and tools to help members gauge progress on their journeys toward responsible sourcing
l Continued training and capacity building, including on the RBA’s Risk Assessment Platform and SAQs, Validated Assessment Program (VAP), SVAP on Forced Labor, and RBA Voices grievance mechanism
l Revised the RGA Vision and Mission to include the broader glove industry
l Launch of an RGA Working Group to engage all RGA members
l Integration of RGA into thematic Responsible Labor Initiative (RLI) working groups













The RBA’s Responsible Glove Alliance (RGA) was established in 2022 to prevent, identify and remediate conditions that contribute to forced labor in the rubber glove industry. In 2024, the RGA consolidated its efforts to engage members and their supply chains more deeply. RGA members looked to build on RGA efforts to address forced labor and create comprehensive due diligence programs to meet emerging regulatory requirements. As part of the RBA ecosystem, the RGA continued to support members in their supply chain due diligence journeys through standardized tools, processes, and learning opportunities.




l The Responsible Glove 2024 annual conference was held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia with more than 160 attendees. Key speakers included the United Kingdom Modern Slavery Envoy, U.S Customs and Border Protection, U.S. Department of Labor, and the EU Delegation to Malaysia.
l RGA presented at the 11th International Rubber Glove Conference and Exhibition (IRGCE) and sponsored a booth educating potential members on the benefits of responsible sourcing.
l Discussed collaboration with the Malaysian Rubber Glove Manufacturers Association (MARGMA) and the Malaysian Rubber Council (MRC) to engage the rubber glove industry more broadly, including smaller suppliers.
l RGA members participated in the RBA Annual Conference, including on a panel about forced labor due diligence.
l The RGA and its members met with representatives of the U.S. State Department’s Trafficking in Persons (TIP) office to understand progress in the rubber glove industry to combat forced labor.



















l The RBA extended its portfolio of policy engagement in Asia to eight producing countries. With the objective of raising governments’ understanding of market and legal requirements around responsible business conduct and supply chain sustainability due diligence, the RBA had a number of bilateral meetings and policy dialogues with more than 150 government officials including ministers, vice ministers and director generals.
l The RBA was acknowledged as a trusted expert organization in responsible business conduct for governments in Asia:
RBA staff was invited to keynote the Indian Inter-ministerial Taskforce on Responsible Business Conduct, which included 17 ministries, to speak to mandatory human rights due diligence regulations and how they are impacting international businesses.
The RBA provided technical inputs to the Ethical Recruitment Guidelines in Japan
RBA staff conducted a training on mandatory human rights due diligence for 22 government officials from five ministries of Malaysia.
The RBA provided technical inputs to the National Dialogue on Responsible Business Conduct in Indonesia and Vietnam.
l To inform and support the alignment of national policies with international standards, the RBA organized two research projects in Indonesia and India. The research was implemented by prestigious local stakeholders and focused on the gaps between the local laws and practices and international standards. The results will serve as the foundation for public-private dialogues and partnerships to address the root causes of nonconformances.
l Senior government officials from Malaysia, India and Japan, and the Executive President of the Indonesian National Economic Council, spoke at the RBA annual conference about using policy initiatives to drive responsible business conduct and held multiple dialogues with RBA membership.

In 2024, critical policy and legislative developments significantly reshaped the global regulatory landscape and the RBA continued its ongoing efforts to help its members prepare for and meet the evolving requirements.












l Nearly 2,000 people from RBA member companies and their suppliers in producing countries benefited from in-person and virtual trainings on key mandatory human rights due diligence regulations and practical measures to prepare for implementation.
l RBA held webinars for members on critical topics such as child labor and forced labor reporting, trafficking and persons reports, U.S. domestic legislation on climate change disclosures, and various other impactful regulations from federal U.S. departments and agencies, as well as from non-U.S. geographies, including hosting representatives from Public Safety Canada to present on the ongoing compliance with the Supply Chains Act.
l Engaged policymakers and coordinated member input with Public Safety Canada, U.S. Customs and Border Protection, the U.S. State Department, and the Senate Finance Committee, which informed procedural changes on regulations and enforcement as well as provided guidance to counterparts on traceability efforts and future research around forced labor.
l Brought policymakers from the U.S. Department of Labor and U.S. Customs and Border Protection and RBA members together to create a community of learning at events such as the RBA Outreach Meeting in Guadalajara, Mexico and the Responsible Glove Alliance Annual Conference in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Discussions included Mexican laws and regulations impacting members operating in Mexico and collaborative efforts to reduce incidences of forced labor in the rubber gloves industry.
l The RBA was selected to join the U.S. State Department’s Advisory Committee on Responsible Business Conduct and took part in the committee’s inaugural meeting. The committee is a direct outcome and one of the four priority areas of focus of the U.S. National Action Plan on Responsible Business Conduct.












































RBA members and their suppliers continue to navigate an increasingly complex responsible sourcing landscape, shaped by geopolitical tensions and a growing number of evolving regulations. The RBA’s Advisory Services consulting team is uniquely positioned to help members and their suppliers effectively manage supply chain risks by providing targeted programs, services, tools, and expert guidance.








l Developed and delivered a Malaysia based training with the RBA’s Responsible Labor Initiative (RLI)
l Facilitated a Specialty Validated Assessment Program (SVAP) on Forced Labor for members and suppliers of Responsible Glove Alliance (RGA)
l Trained hundreds of suppliers to conduct robust forced labor due diligence on their own operations and upstream supply chains




l Ran tailored workshops for suppliers and recruitment agencies, emphasizing the zero-fees principle.


l Helped member companies align with emerging forced labor legislation in both sending and receiving countries
l Delivered executive-level and general services providers awareness sessions
l Facilitated root causes investigations and Corrective Action Plans (CAP) management




l Conducted close to 50 fees investigations based on the RBA Fees Investigation Standard. More than 20,000 workers benefited from the fees investigations where employers reimbursed millions of dollars to eligible workers.

l Assisted suppliers in institutionalizing RBA selfassessment tools to ensure greater compliance.
l Guided suppliers through self-assessments and gap closure plans












The RBA will expand its Advisory Services capacity in 2025, adding new resources to support more member companies with enhanced training offerings by creating new courses tailored to the needs of specific industries, scalable consulting support, and strategic collaboration with other industries.




























In 2024, the RBA added the following courses for members and their suppliers:




















l RBA Code of Conduct v8.0 - Implementation Training v8.0.1 (English)
l RMI Tools: Supporting Due Diligence for Downstream Companies (English)


l Corrective Action Plans (German, Portuguese)
l First Aid (English, Chinese)


l Assessing Chemical Risks (English, Chinese)
l Forced Labor Due Diligence (Italian)
l Forced Labor Prevention for Farms (English, Chinese)

l Hazardous Chemical Inventories (English, Chinese)
l Preventing Forced Labor During Recruitment (English, Chinese)
l Supply Chain Monitoring (English, Portuguese, Chinese, Spanish)
l Transparency Verification (English, Chinese)
l Recognizing Child Labor (English, Chinese)
l Recognizing Forced Labor (German, Italian)
l Handling Chemicals (German)







More than 11,000 new accounts were created in the Learning Academy in 2024 and there were approximately 37,000 course completions. Visit the Learning Academy website
l Controlling Chemical Risks (English, Chinese)






l Electrical Safety Inspections (English, Chinese)
l Migrant Worker Orientations (English, Chinese)
l Waste Management (German)
l Managing Worker Feedback (Bengali)
l Introduction to Human Rights Due Diligence (German, Spanish)












Within the Learning Academy in 2024, there were more than 155 completions of the Factory Lead Certification Program, a training and certification program for factory staff. Factories with a Certified Factory Lead typically have 26 percent to 34 percent higher audit scores (varies by industry), fewer priority findings, and fewer overall findings.













In 2024 the RBA held 24 virtual Code of Conduct and VAP preparation workshop trainings for 905 participants, three Responsible Supply Chain Initiative (RSCI) trainings for 54 participants, and an RBA Specialty VAP on Forced Labor (SVAP) training for seven participants. In addition, we held several in-person trainings, including:
RBA members and their suppliers participated in a three-day, inperson training held in Guadalajara, Mexico. This immersive training provided attendees with insights into the Validated Assessment Program (VAP) and the RBA Code of Conduct. Participants left with actionable strategies to enhance implementation across their organizations, reinforcing their commitment to responsible business practices.


The RBA held a training in Taipei City on June 20 to help prepare members and their suppliers to respond to Mandatory Human Rights Due Diligence (MHRDD) regulations. The training included a detailed analysis of the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (EUCSDDD) and updates on the RBA’s work on emerging issues.

The RBA’s Responsible Environment Initiative (REI) held its first in-person training on greenhouse gas emissions management in Taipei City on June 20. This half-day series focused on target setting, emissions reduction and reporting, and Scope 3 management.

On March 7, following the RBA Outreach Meeting in Tokyo, the RBA held a training for members and suppliers with a focus on mandatory human rights due diligence regulations highlighting case studies and action scenarios as well as RBA tools and standards that relate to new and emerging regulatory requirements.








The RBA Outreach Meeting in New Delhi, India on October 3 featured insightful discussions on the evolving landscape of responsible business practices, with a focus on India’s role in global supply chain transformation.
RBA CEO Rob Lederer opened with an update on the RBA’s key initiatives, followed by a keynote from BJP leader Professor Gourav Vallabh. Dr. Garima Dadhich, Dean of SBE at the Institute of Corporate Affairs, Ministry of Corporate Affairs, also addressed the meeting. Key sessions included an engaging discussion on sustainable energy solutions in India.
























In 2024 RBA held eight in-person Outreach Meetings in cities around the world, including Berlin, Guadalajara, Kuala Lumpur, New Delhi, Penang, Taipei City, and Tokyo, for 1,438 participants.






The RBA held an Outreach Meeting in Guadalajara on September 11 featuring Mauricio Cortes, Labor Attaché, U.S. Department of Labor, U.S. Embassy in Mexico City; and Ricardo Barbosa, Senior Partner at Barbosa Huerga Abogados, Presidente Nacional de Asuntos Laborales de Coparmex; who spoke about USMCA labor provisions as well as ongoing legal developments in Mexico related to the environment and labor; and industry expert panelists from RBA members HP, HPE and Samsung, who spoke about best business practices related to social and environmental issues in international supply chains.
The RBA held an Outreach Meeting in Taipei City on June 19. Minister Peng Chi-Ming, Ministry of the Environment, delivered the keynote address, "Towards a Sustainable and Low-Carbon Supply Chain." Session discussion topics included the global regulatory landscape, mandatory due diligence and reporting legislation, audit findings in the region, best business practices, RBA Code of Conduct 8.0, and updates on the RBA and its Initiatives.
The RBA’s Outreach Meeting in Penang on April 25 featured discussions on the global regulatory landscape, mandatory due diligence and reporting legislation, human rights due diligence best practices, environmental sustainability, advancing responsible chemical management in supply chains, RBA Code of Conduct 8.0, updates on the RBA and its Initiatives, and more. After the general sessions, the RBA held a workshop that provided an overview of RBA resources for exercising chemical management due diligence.




On April 10, the RBA hosted an outreach meeting in Berlin. Discussions focused on the global regulatory landscape, mandatory due diligence and reporting legislation, emerging issues, forced labor, raw materials and critical minerals, greenhouse gas emissions management, supply chain mapping, RBA Code of Conduct 8.0, updates on the RBA and its Initiatives, and more.

On March 6, the RBA held an Outreach Meeting in Tokyo with speakers and panelists including Orii Sunao, Director of the Business and Human Rights Policy Office, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry; Shishido Kenichi, Director of JP-Mirai; and representatives from RBA member companies including Canon Inc.; Fujitsu; Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd; Sony Group Corporation; and Tokyo Electron Limited.
Responsible Business 2024 Conference Highlights
Our annual conference, Responsible Business 2024, in San Jose, California, celebrated two decades of collaboration and progress while taking stock of current and emerging challenges in global supply chains. Under the theme "Impact. Together.," members, non-member companies, stakeholders, and representatives from government and civil society came together to explore solutions to today’s most pressing issues—from human rights and sustainability to geopolitics and supply chain resilience. Thank you to our speakers, panelists, and the nearly 800 attendees who participated in these important discussions.

Before the conference, we held a Members Day on November 18. The first general session looked back on 20 years of industry action, with current and former board members.



After more general sessions and breakout panel discussions, members of the RBA and RMI participated in roundtable discussions on various initiatives, tools, and emerging priorities.

The first day of the conference portion of Responsible Business 2024, November 19, began with reflections on the RBA's history and impact from our CEO Rob Lederer, current and previous board members, and early players in the development of the organization.

Later, U.S. Secretary of Homeland Security Alejandro Mayorkas, Septian Hario Seto, President of Indonesia's National Economic Council, and Fayrouz Saad, Assistant Secretary for Partnership and Engagement at DHS, spoke on the importance of collaboration between government and industry for responsible business conduct in global supply chains.

Afterward, Professor Chris Miller, an expert on international politics, economics, and technology, and author of the New York Times best-selling book, Chip War: The Fight for the World’s Most Critical Technology, delivered the keynote address and participated in an engaging fireside chat.

The second day of the conference, November 20, began with Alison Taylor, Clinical Associate Professor at NYU Stern School of Business, Executive Director of Ethical Systems, and author of Higher Ground: How Business Can Do the Right Thing in a Turbulent World


insights
the Climate Corporate Data Accountability Act, which he authored, as well as on current sustainability challenges and opportunities.
EU Battery Regulation session provided a summary of the regulation’s requirements and key takeaways for the August 2025 deadline. From supplier reports to tools for progress, the audience learned about the challenges and necessary steps for regulatory preparedness.
There were many other great speakers, sessions and panels not highlighted here. View our conference posts on LinkedIn and photos on Flickr
View the Annual Conference photo album
View the Members Day photo album
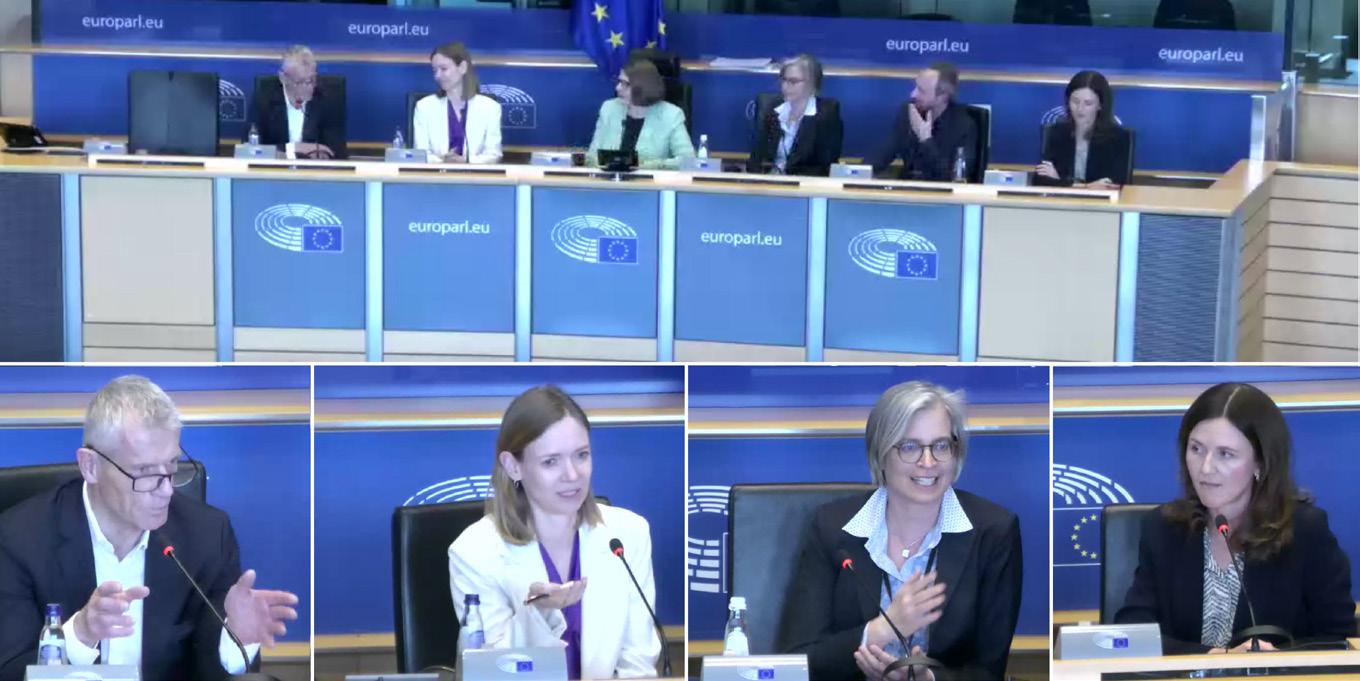
On September 4, the RBA and MEP Axel Voss of the EPP Group in the European Parliament co-hosted an event in Brussels, Belgium: “Over to Implementation: Decoding Due Diligence & Equipping Industry for CSDDD Success.“ Key speakers included Allan Jorgensen, Head of Centre for Responsible Business Conduct, OECD; and Nils Behrndt, Deputy DirectorGeneral, European Commission DG Justice; and panelists from industry, government, intergovernmental and nongovernmental organizations.


The RBA and the European Parliament Responsible Business Conduct Working Group conference, “A New Era for Responsible Business Conduct: Towards the Implementation of the CSDDD,” began on April 18 with remarks from Heidi Hautala, MEP and Chair of the RBC working group; Lara Wolters, MEP and Rapporteur on the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive; and a representative of Minister PierreYves Dermagne, Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Economy and Employment.
The first panel featured a multistakeholder discussion on the outcome of the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (EUCSDDD), with MEP Anna Cavazzini; MEP Helmut Scholz; Rachel Davis, VP and CoFounder, Shift; Nele Meyer, Director, European Coalition for Corporate Justice; and Francesco Tramontin, Vice President, Ferrero.
RBA CEO Rob Lederer provided keynote remarks prior to the second panel on aligning due diligence practices with the new standard. The panel included Escipion Joaquin Oliveira Gomez, Director, International Trade Centre; Lucrezia Busa, Commissioner Didier Reynders cabinet; Isabelle Schömann, Deputy General Secretary, CES – ETUC; Linda Kromjong, CEO, amfori - Trade with Purpose; and Maria GorsuchKennedy, Global Sustainability Director, Cisco.


We greatly appreciated the insights of our keynote speakers, Minister Svenja Schulze, Germany's Federal Minister for Economic Cooperation and Development, and Minister Hubertus Heil, Germany's Federal Minister of Labor and Social Affairs, during our conference, From Policy To Action: Collaborative Approaches to Raw Materials Due Diligence, in Berlin, Germany on April 11.
A series of expert panels followed, covering important topics such as lessons learned from the implementation of Germany’s Supply Chain Due Diligence Act and implications for emerging mandatory human rights due diligence (MHRDD) legislation; building a common roadmap for delivering EU due diligence; implementing MHRDD in critical raw material supply chains; the role of multi-stakeholder collaboration; and responsible supplier engagement.


The conference was organized by the RBA in cooperation with the Initiative for Global Solidarity (IGS), which is implemented by Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH on behalf of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ).

The RBA's Responsible Glove Alliance (RGA) held its second annual conference in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on Sept 6. The conference brought together stakeholders from government, industry and civil society to discuss current and emerging trends, challenges and best practices in global supply chains. Key speakers included Justin Bedford, Modern Slavery Envoy, Government of the United Kingdom; Denis Baresch, Minister Counsellor, Head of Section, Delegation of the European Union to Malaysia; Chad Salitan, U.S. Department of Labor Attaché for Southeast Asia; Auco N. Ho, Branch Chief, Communications & Outreach, Forced Labor Division, Trade Remedy Law Enforcement Directorate, Office of Trade, U.S. CBP; and industry leaders.















The RBA's Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) chaired a panel at the Resourcing Tomorrow forum in December that brought together energy providers, OEMs, industry associations and mining companies to discuss ESG expectations and challenges. The RMI also held a workshop with speakers from OECD, Cisco and Stewart Investors, on the role of industry associations in promoting responsible sourcing and mining as well as greater trust in the green transition.









The RBA spoke at a conference organized by Ho Chi Minh Law School and chaired by the Chief Judge of Labour of Ho Chi Minh City on November 30. The conference examined the transition from corporate social responsibility to responsible business conduct in Vietnam and policy options to promote responsible business conduct in export-oriented industries.








































On November 26, the RBA and the International Organization for Migration (IOM) hosted a discussion on "Making Mandatory Human Rights Due Diligence Work for Migrant Workers" during the UN Forum on Business and Human Rights in Geneva. It brought together stakeholders from governments, civil society, businesses, and international organizations to explore MHRDD regulations and their impact on migrant workers.
The RBA participated in the National Industry Dialogue for a Responsible and Sustainable Electronics Supply Chain, hosted by the ILO in Jakarta, November 28-29. Participants included Indonesia’s Ministries of Investment, Economic Affairs, Human Rights, Industry, and Manpower, alongside the Indonesian Employers Association and the National Federation of Trade Unions.

The RBA participated in the opening panel of the Tech Against Trafficking Summit that took place from November 13-14 in London. The RBA highlighted work related to supply chain mapping and its Responsible Labor Initiative's emerging forced labor data strategy. A critical point was the need for greater data interoperability to drive forced labor prevention alongside a need for increased worker engagement.
On November 14, the RBA participated in a panel on the application of human rights due diligence at the Promise of Integrity’s Annual Conference in Penang. Promise of Integrity is an alliance of companies focused on ethics and integrity within the business community in Malaysia. Several RBA members are founding members of the organization.

At the Electronics Sustainability Summit, hosted by SERI from October 22-24 in Austin, the RBA’s Responsible Environment Initiative (REI) spoke on a panel titled “A Roadmap to Recycling in the Battery Age.” The REI and the Recycled Materials Association presented their respective roadmaps to achieve more circular material flows and discussed how the organizations could work together.


On October 4, the RBA addressed the Inter-Ministerial Roundtable on Responsible Business Conduct in New Delhi, hosted by India’s Ministry of Corporate Affairs. Senior officials from 17 ministries and agencies, including the Ministries of Finance, External Affairs, Social Justice and Empowerment, Mines, and Labour and Employment, and organizations including the ILO, UNDP, UNICEF and others, discussed human rights due diligence.

Members of the RBA’s Responsible Labor Initiative (RLI) and Responsible Glove Alliance (RGA) met with the U.S. State Department’s Office to Monitor and Combat Trafficking in Persons and the U.S. Embassy in Malaysia. The group shared insights into efforts to promote ethical recruitment and employment within global supply chains through various RBA initiatives and programs.

The RBA Public Policy team held a workshop in early October for government officials on "Mandatory Due Diligence Legislation: Impacts and Implications for Malaysia." Participants included representatives from the Ministries of Human Resources; Investment, Trade and Industry (MITI); and Plantation and Commodities; and the Human Rights Commission of Malaysia (SUHAKAM).
The RBA’s REI attended several Climate Week NYC events in September, including an Axios News event with former Secretary of State John Kerry and former Vice President Al Gore, a Wilson Center Dialogue on Circularity and Sustainability, and an American Council on Germany panel on “Meeting Common Challenges in a Complex Environment: Sustainability, Supply Chains, and Semiconductors.”




The RBA, members, and stakeholder partners participated in the UN Responsible Business and Human Rights Forum, Asia Pacific in Bangkok in September. The theme, "The Remedy Blueprint: Bridging Gaps and Accelerating Access," focused on access to remedy for victims of forced labor and trafficking, environmental degradation, and other important issues.
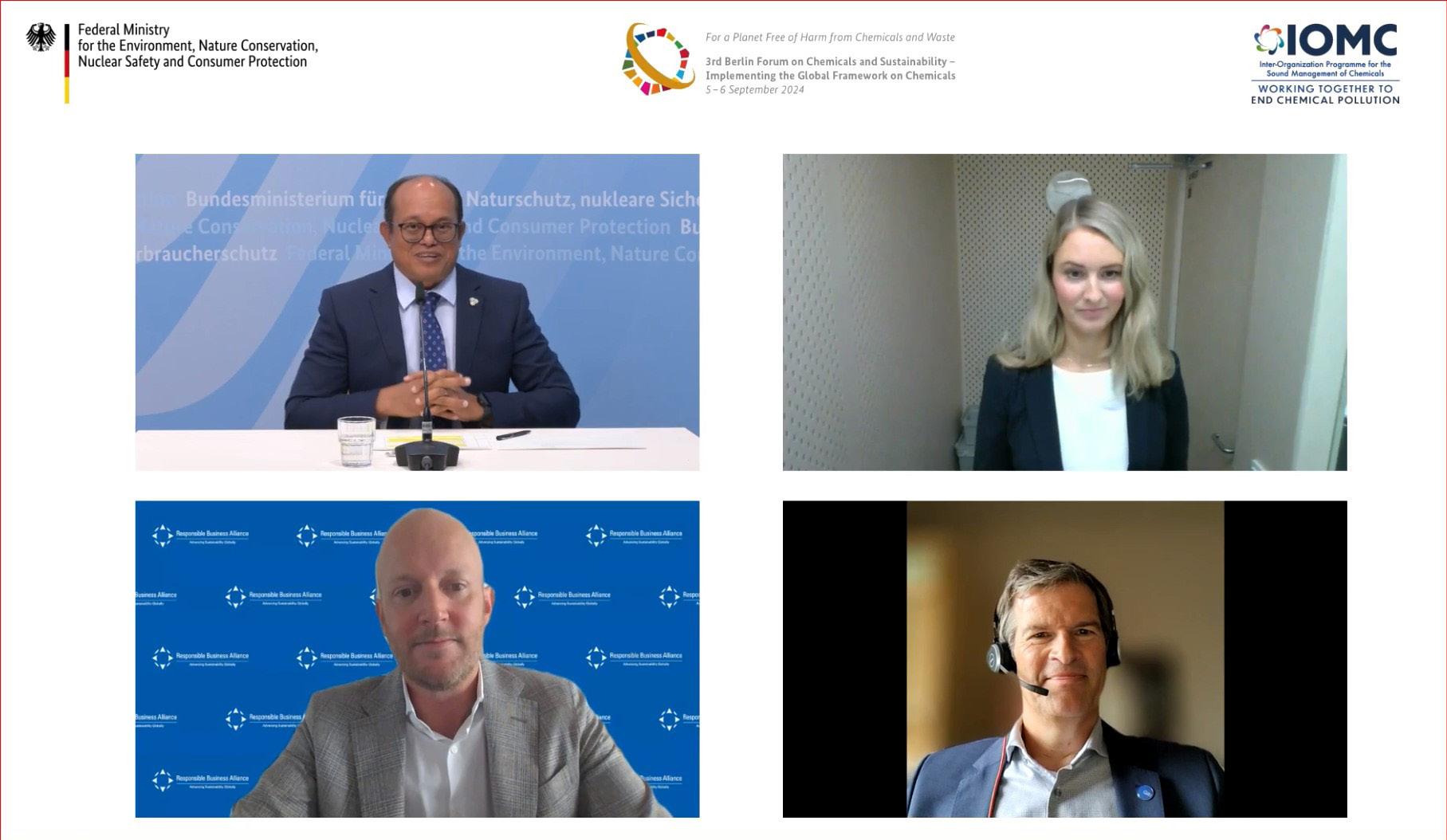
On September 6, the RBA participated in the Berlin Forum on Chemicals and Sustainability, co-hosted by the German government and the InterOrganization Programme for the Sound Management of Chemicals (IOMC). The Forum themes focused on fostering commitment in key sectors; engaging other sustainable development fora; strengthening frameworks, mechanisms, and capacities; transforming supply chains; and scaling innovative financing.

The RBA met with Mr. Kamal bin Pardi, Director-General of Labour, Ministry of Human Resources, and his team in Malaysia on September 4 to discuss opportunities for increased labor due diligence in supply chains and provide updates on RBA tools and programs.

The RBA participated in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce’s event, Bolstering Efforts to Address Human Trafficking on July 29. The RBA provided remarks alongside representatives from U.S. Customs and Border Protection and the U.S. Department of Labor’s Bureau of International Labor Affairs.
The RBA was selected to join the U.S. State Department's Advisory Committee on Responsible Business Conduct and took part in the committee's inaugural meeting in late July. The committee is a direct outcome and one of the four priority areas of focus of the U.S. National Action Plan on Responsible Business Conduct.

The RBA’s REI presented at Chemical Watch’s Product Sustainability USA 2024 conference, which was held in Boston, June 26-27. The RBA focused on the legal and market drivers of sustainability, emerging legal requirements for ESG reporting and environmental due diligence, and RBA tools and services that help supply chains meet these challenges.
The RBA’s REI spoke on emerging due diligence programs on minerals sourcing and recycling at the Electronics Goes Green Conference held in Berlin, June 18-20. The REI highlighted the RBA’s emerging programs to close the loop between downstream recyclers and upstream material suppliers in terms of recycled content and responsible sourcing.



The RBA’s RMI participated in the ASEAN Tin Industry Conference, which was held in Jakarta in June. The RMI presented its work to promote responsible sourcing from tin smelters in Indonesia, its global team and support services, and its assessment process.

The RBA’s RMI participated in the Critical Mineral Conference, organized by the Shanghai Metals Market, in Jakarta, Indonesia in June. The RMI shared insights on its work in Indonesia, focusing on support for nickel and cobalt processors; market and regulatory drivers of ESG performance and verification; supply chain collaboration; and RMI assessment programs and tools.
In May, the RBA’s RMI participated in the OECD Forum on Responsible Mineral Supply Chains in Paris, France. Highlights included a May 21 session on collaboration between upstream and downstream programs in the African Great Lakes Region, co-hosted by the RMI, ICGLR, and CCCMC; May 23 panels and sessions about due diligence in Myanmar, responsible sourcing of sand and silicates, and a consultation on the RMI RMAP/ESG Standard Revision; a May 24 session on the EU Battery Regulation, co-orgainzed by the RMI, Drive Sustainability and RCI, and a session on recycled materials, co-hosted by the RMI, The Copper Mark, and the Roundtable on the Responsible Recycling of Metals.


The RBA participated in a panel during the "Empowering Responsible Businesses in Cambodia: Navigating Global Mandatory Standards on Human Rights and Environmental Due Diligence" conference in Phnom Penh on May 7. The event was organized by EuroCham Cambodia, GIZ and others, and keynoted by the Undersecretary of Labour and Vocational Training of Cambodia, HE. Lim Suyhong.

In Brussels on April 16, the RBA hosted a small-group roundtable between the German State Secretary Dr. Bärbel Kofler, RBA members, and other industry experts to highlight business priorities to EU policymakers toward facilitating supply chain sustainability due diligence and industry readiness for compliance with the EUCSDDD. The RBA also met with the EU Special Representative for Human Rights, Olof Skoog, and discussed collaborative approaches to the Directive.


The RBA’s REI spoke on the “Spotlight on Electronics” panel at the Recycled Materials Association (formerly ISRI) convention in April, highlighting the important role of recyclers in value chains for addressing human rights and environmental issues, and the need for recycling assurance standards to support green claims and trusted trader programs to facilitate used electronics cross-boundary movement and recovery.
The RBA’s REI joined the IPC E-31 Supplier Declaration Subcommittee meeting at IPC APEX EXPO 2024 in Anaheim, California on April 8 to engage technical experts of multiple industries on standardizing the exchange of process chemical data across supply chains. The RBA is participating in a newly formed A-Team of the IPC E-31 Committee to work on a process chemical declaration standard that will promote a unified approach toward enhancing supply chain transparency.

The RBA’s REI spoke at the Intel Sustainability Summit in Santa Clara, California in March, which convened more than 140 organizations, including corporations, academia, government, and NGOs, with the aim of reducing the industry’s environmental footprint. The REI provided an overview of key drivers of sustainability in the electronics industry, such as legal mandates, market requirements, and stakeholder demands.

The RBA’s RMI moderated a panel on the role of social responsibility at the LBMA Sustainability and Responsible Sourcing Summit in London in March. Topics of discussion focused on defining the social aspect of environmental, social and governance, highlighting the direction industry initiatives and companies are moving toward in the ESG space.

On March 18, the RBA’s REI hosted a workshop in Santa Clara, California to highlight the RBA’s existing and emerging supply chain due diligence tools for environmental sustainability. The event included an overview and demonstration of the RBA’s Emissions Management Tool, an update on RBA chemical management initiatives, the REI workplan and future roadmap.

On March 12, the RBA participated in Atea's Sustainability Forum in Stockholm, Sweden, sharing insights on dealing with uncertainty in a fast-changing sustainability landscape, and how the RBA is promoting supply chain transparency and incentives to bring due diligence impact at scale in the IT industry.

In March, the RBA met with the Japanese government, including the DG of Immigration Service Agency, Ministry of Justice; Director of Human Rights, Ministry of Foreign Affairs; DG of Business and Human Rights, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry; SVP of the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), and Chairman of the Platform for Migrant Workers towards Responsible and Inclusive Society (JP-MIRAI).

On March 4, during the Human Rights Commission of Malaysia (SUHAKAM) Consultation on Forced Labor Issues, held in Penang, Malaysia, the RBA's RLI presented its work and provided recommendations on improving the responsible recruitment of migrant workers. The event was part of a series of consultations with different sectors across the country.

The RBA met with Australia Ambassador for Human Rights Bronte Moules in January to discuss joint priorities for advancing business and human rights.
The RBA has a long-standing relationship with the government of Australia on key issues including private sector preparedness for mandatory human rights legislation, and support for producing country governments to uphold rights of workers.

The RBA’s RMI participated in Investing in African Mining Indaba in Cape Town, South Africa in February. In addition to speaking on panels, the RMI hosted a panel on "Bridging Downstream & Upstream,” featuring the RMI’s support for value chain collaboration. Discussions focused on a just energy transition, critical minerals, mining, and ESG requirements.

On January 11, the RBA’s REI spoke at CES 2024 in Las Vegas, Nevada, on the panel “A Circular Economy to Benefit People, the Planet and Business.” REI emphasized existing tools to achieve efficient solutions across value chains, and modifications to standards to allow recyclers to demonstrate the return of recycled materials to manufacturing channels.
















RBA members gained access to new analytics capabilities such as those related to Worker Voice surveys and Workforce Composition data, and practical tools such as a comprehensive workbook to analyze data from the Emissions Management Tool in greater detail than before. The Data Analytics team also fielded questions and requests for custom data sets and analysis from dozens of RBA, RMI, and RLI member companies.










In 2024, RBA’s Data Analytics team continued to enhance the organization’s suite of data tools, further bolstering the power and reach of RBA’s online sustainability data management system, RBA-Online. The tools available to members allow them to monitor, analyze and benchmark their data available in the RBA ecosystem.


The RBA Supply Chain Mapping Task Force began 2024 with a renewed focus on building a mapping and interoperability framework. Through a series of meetings, the construction of white papers, coalition building among external stakeholders and the participation of hundreds of members, the Task Force agreed in November at the RBA Annual Conference to adopt and extend the United Nations Transparency Protocol (UNTP) with the aim of establishing several common data frameworks to govern the exchange of data up and down the electronics, automotive and critical raw minerals supply chains, among others.
UNTP was considered alongside several similar data exchange and interoperability frameworks and was ultimately chosen in part because it represented the best blend of uptake from other organizations and initiatives and the most adaptability for RBA’s members’ unique needs related to supply chain transparency and due diligence.
As part of its efforts to expand the reach and utility of its supply chain database, the RBA also signed an agreement with Open Supply Hub for a private, members-only version of the company’s supply chain database. Integration of this enhanced data into the RBA’s databases will form a crucial link between member supply chain data and data that resides in other systems through the OSID – Open Supply Hub’s own global entity identifier.





















In 2024, demands for assessments increased by 34 percent in Europe, 16 percent in Japan, and 10 percent in Mexico and the United States, contributing to the annual number of VAP assessments completed exceeding 2,000 for the first time. Despite this growth, as part of its ongoing commitment to improving efficiency and coverage, the VAP achieved a 17 percent average reduction in assessment cycle time through the implementation of procedural changes and the introduction of new third-party assessment firms in key regions experiencing increasing demands.












The Validated Assessment Program (VAP) remains a leading standard for onsite compliance verification conducted by independent, third-party assessment firms. In 2024, the RBA made a number of significant improvements to the program.
Operational enhancements included optimizing the pre-audit process to reduce cycle time and improve efficiency in the initial audit preparation phase, refining the scoping for auditees to ensure a more precise and tailored approach, enhancing the auditee experience by simplifying participation in the VAP and improving overall engagement, and improving the final assessment report to eliminate redundancy and provide clearer, more actionable insights.

Starting in 2024 every assessment request submitted to the RBA undergoes an automated due diligence check to assess potential links to entities or activities associated with economic sanctions, trade restrictions, or financial compliance risks. This enhanced verification process leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to efficiently analyze requests against global compliance databases. The additional measure is a critical step in the RBA’s compliance framework, reinforcing our commitment to transparency, risk mitigation, and regulatory alignment.




Since the RBA’s Code of Conduct 8.0 went into effect in January of 2024, the RBA VAP team updated its instructor-led trainings on the Code and VAP preparation workshops and held 24 trainings for more than 900 participants throughout the year. In addition, online training modules in the RBA eLearning academy were updated and additional language versions are continually being added.

The RBA introduced an updated process in 2024 to improve compliance, efficiency, and data security while safeguarding the credibility of its program. Beginning in January of 2025, all third-party CustomerManaged Audits and Auditee-Managed Audits using the RBA name must be initiated through RBA-Online, ensuring standardized processes, ISO27001-certified data protection, and streamlined audit management. Members benefit from bulk audit initiation, updated tools, enhanced analytics, and secure report sharing.
An appeals mechanism is available for all RBA assessment activities, which the reviewees can use to escalate their concerns if a finding was raised on a topic that is not explained clearly in the relevant
Standard documents. Appeals can be submitted up to 90 days following the release of the activity report in RBA-Online, and valid appeals are reviewed by the respective Appeals Board for RBA or RMI.
In 2024, the RBA received a total of 57 appeals cases for VAP, SVAP and RMAP activities. Out of the 57, three were sent beyond the 90-day appeal window and therefore were not accepted into the process. Out of the remaining 54, 49 were for the VAP, two were for the SVAP on Forced Labor, two were for the RMAP, and one was for an Indirect Spend VAP assessment. The plurality of the appeals cases, 24 percent, were related to forced labor; e.g., excessive cooperative loan requirements, recruitment fees and related costs. In 2024, 83 percent of all appeals cases resulted in agreement with the auditors’ conclusions, so the findings remained as is. Visit the VAP webpage





n Closure Assessments
n Initial Assessments



2024 ASSESSMENTS BY LOCATION





n Initial Assessments n Closure Assessments












In 2024, factories in China continued to represent the plurality (45 percent) of all assessments conducted, with the next highest percentages of assessments conducted in Chinese Taipei and Vietnam (8 percent each), Japan (6 percent), and Malaysia, Mexico, Thailand, and the United States (4 percent each).

The total number of VAP and SVAP assessments conducted increased from 1,958 in 2023 to 2,136 in 2024, and average initial assessment scores increased slightly while closure assessment scores decreased slightly year over year.














Other (38 Sections)




















































































In 2024, China had the highest number of average working hours per week (54.0), followed by Cambodia (52.4), Thailand (49.7), Vietnam (49.6), and the Philippines (49.6).
On average, workers in RBA member facilities worked 5 fewer hours per week than their counterparts in nonmember facilities in 2024.


























RBA membership has continuously grown, year over year. The RBA and its initiatives (RMI, RLI, RFI, RGA) ended 2024 with a total of 614 members, up from 587 in 2023. The total number of core RBA members (not counting the initiatives) was 256 at the end of 2024, up from 247 in 2023.














FY 2024 Operating Revenue
$ 33,863,736


FY 2024 Operating Expenses $ 32,838,489





























Joel Eurich



Mitsu Shippee
Mary Wroten
Kristofer Clark
RBA Board Chair, and Vice President, Global Compliance and EH&S, Molex
Thomas Cetta
Sheila Dannunzio











RBA Board Vice-Chair, and Senior General Manager, Head of Sustainability Dept., Sony Group Corporation


RBA Board Treasurer, and Director, Global Sustainability & ESG, Ford Motor Company

Leigh Anne DeWine

Senior Vice President & Chief Compliance Officer, Jabil
Senior Director, Corporate Social Responsibility, STMicroelectronics
Director of Social Responsibility, Amazon
Justin Murrill
Director, Corporate Responsibility, AMD
Nadine Philipp
Vice President, Sustainability Supply Chain, BMW Group
Brian Rybarik
Senior Director, Supply Chain Integrity, Microsoft
Laurie Webb
Vice President, Legal and Chief Compliance Officer, Seagate Technology

RBA Board At-Large Representative, and Head of Supply Chain Assurance, Dell Technologies














Rob Lederer
Chief Executive Officer
Deborah Albers Chief Operations Officer
Tyler Gillard Chief Strategy Officer
Jennifer Peyser
Senior Vice President, Responsible Sourcing
Holly Evans Senior Vice President, Environmental Policy and Legal Affairs
Jack Cutts Senior Vice President of Technology
Kenneth Anderson Vice President of Member Experience
Bart Devos
Vice President of Public Policy
Carlos Busquets Vice President of Labor Affairs
Jarrett Bens Senior Director of Communications
Fabiana Di Lorenzo, Ph.D. Senior Director, RMI Impact and Innovation
Juan Carlos Martinez Senior Director of Operations
Bobby Terrell Senior Director of IT Operations
Chee Keong Lai Senior Director, Advisory Services
Ka Ea Lim
Senior Director, Compliance
Yakut Oktay Senior Director of Operations
Catherine Soong
Senior Director, RFI/Advisory Services Supply Chain Management
Laura Landrau Senior Director of Events and Internal Operations
Adam Rolfe RMI Senior Director of Standards and Partnerships
Benjamyn Marks Director of Environment, Health & Safety
Chi Q. Do, Ph.D. Director of Asia Public Policy
James Gyenes Director of Americas Public Policy
Andy Chiu Director of OperationsAssurance
Sandra Carvalho Director of OperationsMinerals
Josue Ruiz RMI Director of Facility Engagement
Edith Cecchini Circular Materials Program Director
Catherine Tyson Director of Strategy and Stakeholder Engagement
Anna Stancher Senior Program Manager, RMI
Mann Chyun Sim Senior Account Manager
Ross Landis Database Project Manager
Surya Herny Mahdzir VAP Program Manager
Mariana Osuna VAP Program Manager
Celina de la Torre VAP Program Manager
Gavin Wu Manager of RMI Member Services
Diana Trigo Manager, RMI Training
Dana Battistello Manager, IT Projects
Kyle Rand Systems Administration Manager
Ronnie Tan Asia Compliance Manager
Maggie Gabos RMI Technical Manager
Olena Stanislavchuk Assessment Program Manager
Jordan Davis Program Manager, Environment
Sarah Kildall Membership Manager
Serena Gilbert Content Marketing Manager
Shu-Yuan Chang Program Manager, RLI & RGA
Whitney Chan Quality Assurance Manager
Tauqueer Alam Quality Assurance Manager
Shelita Bradshaw-Cortez Quality Assurance Manager, RMI
Zoul Pio IT Service Manager
Adriana Escobar Events and Membership Manager
Vaishna Santhar
Compliance and Labor Affairs Program Manager
Giorgia Miccoli Public Policy Analyst
Sowmi Chandrakumar Business Process Analyst
Rich Stover Program Data Analyst
Charles Teh VAP Project Coordinator
Montserrat Vega Assessment Program Coordinator
Christina Renzetti Events and Operations Coordinator
Joanie Belo HR Generalist
Charlotte Atkinson Chief Financial Officer
Anastasiia Olvera Controller
Malcolm Boardley Senior Accountant
Mohsen Mousavi Senior Accountant
Tahrima Sultana Staff Accountant



Alexandrea Crawford Membership Coordinator








OF JULY 2025


AcBel Polytech Inc. - R
Acer Inc. - R
Advanced Micro Devices - F
Advanced Micro-Fabrication Equipment Inc. China
Advania AB - R
Allegro MicroSystems
Alphabet Inc. - R
Alphawave Semi, Inc.
Altria Client Services LLC
Amazon.com, Inc. - R
Amkor Technology, Inc. - F
Amphenol Corporation
ams OSRAM
Analog Devices, Inc. - R
Apple Inc. - F
Applied Materials - R
Arista Networks, Inc. - R
Arrow Electronics
ASM International - F
ASML Holding - R
ASUSTeK Computer Inc. - F
Atea ASA - R
Avaya
Belden
Best Buy - F
Beyondsoft International
BMW Group - R
Bosch Sensortec - R
Bose Corporation – R
Bourns, Inc.
Broadcom Inc.
Brooks Automation
Brother Industries Ltd.
BSR Group Holdings Limited
BT plc
Cadence Design Systems
Canon Inc. - R
CECONOMY AG
Celestica - R
Century Bond Bhd
CGI IT UK Ltd. - R
Changhong Meiling Co., Ltd.
ASE Technology Holding Co., Ltd.


ChargePoint, Inc.

Foxconn - R

The RBA has four membership categories for its core members: Full, Regular, Affiliate, and Supporter. View the criteria of each category on our website Full and Regular members as of July 2025 are designated by an “F” or “R” following their company names below. The most current list can be found on our member page
Ciena - R

Fujitsu Limited





Cirrus Logic, Inc.
Cisco - F
Coherent Corp.
Cohesity Inc. - R
Comcast Corporation
Compal Electronics - R
Continental AG
CoreWeave, Inc.
Corning Incorporated - R
Currys PLC
Dell Technologies - F
Dexcom Malaysia – R


Chicony Electronics Co., Ltd. - R

Dustin AB
Dysons Operations
Eaton Corporation
Edwards Ltd - R
EIZO Corporation

Disney Worldwide Services
Dupont Electronics & Industrial
Electric Connector Technology Co., Ltd.
Element Solutions Inc.
Element TV Company, LP
Entegris, Inc.
Ericsson - R
Extreme Networks, Inc.
Fabrinet - R
Fairphone B.V.
F5 Networks
First Solar Inc. - R
Flex - R
FLSmidth A/S
Ford Motor Company - R

FUJIFILM Business Innovation Corp.
Funai Electric Co., Ltd. - R
Generac Power Systems
General Motors Company

GlobalFoundries - R
GN Store Nord A/S
HARMAN International
Hasbro, Inc. - F
Hisense - R
HP Inc. - F







HTC Corporation


Hewlett Packard Enterprise - F
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. - R
Hypertechnology Ciara Inc.
Hyundai Mobis
Hyundai Motor Company
Hyve Solutions - R
IBM Corporation - R
Ichor Systems
Impinj
Infineon Technologies AG - R
Insulet Corporation
Intel Corporation - F
Intuitive Surgical, Inc.
Inventec Corporation - R
iRobot Corporation
ISU Petasys Co., Ltd. - R
Jabil - F
JB HI-FI Limited
JK Imaging Ltd. - R
JT International SA
Juniper Networks - R
Keurig Dr Pepper - F
Keysight Technologies, Inc.
Kimball Electronics, Inc. - R
Kingston Technology
KINPO GROUP - R





Kioxia Holdings Corporation - R
KLA Corporation - R
Konica Minolta, Inc. - R
Kyndryl
KYOCERA AVX Components Corporation
KYOCERA Corporation
KYOCERA Document Solutions Inc. - R
Lam Research Corporation
Landis+Gyr AG
Legrand
Lenovo - R
Lexmark - R
LG Display
LG Electronics - R
LG Energy Solution
Logitech International S.A. - R
Lucid Motors
Lumentum Holdings Inc. - F
Luxshare Precision Industry Co., Ltd.
Marshall Group AB
Marvell - R
Meta
Microchip Technology Incorporated - F
Micron Technology, Inc. - R
Microsoft - R
Micro-Star Int’l Co. Ltd. - R
MiTAC Computing Technology Corporation - R
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation - R
ModusLink
Molex - R
Monolithic Power Systems, Inc.
Motorola Solutions, Inc. - R
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. - R
NationGate Solution (M) Sdn. Bhd. – R
Navico
NetApp - R
NETGEAR - R
New H3C Group
Nexperia
Nicoventures Trading Limited
Nielsen
Nikon Corporation
Nintendo Co., Ltd.
Nokia Solutions and Networks Oy
Nordic Semiconductor ASA
Nvidia Corporation - F
NXP Semiconductors - F
Omron Corporation
onsemi - F
Onto Innovation Inc.
Oracle America, Inc. - F
Palo Alto Networks
Panasonic Holdings Corporation
Penguin Solutions - R
Pegatron - R
Philips - R
Philip Morris International - R
Plexus - R
Polestar Performance AB
Poly
Positivo Tecnologia S.A.
Powertech Technology Inc. - F
Pure Storage, Inc.
Qorvo, Inc. - R
Qualcomm - F
Quanta Computer Inc. - R
Quest Global
Rambus, Inc. - R
Renesas Electronics Corporation - R
Ricoh Company Ltd.
Rivian Automotive, Inc.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Sagemcom - R
Samsung Display
Samsung Electronics - R
Sandisk Technologies, Inc. - R
Sanmina – R
Schaeffler AG
Schneider Electric
Seagate Technology - F
Seiko Epson Corporation - R
Semtech Corporation
Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd. - R
Sercomm Corporation
Sharp Corporation
Signify - R
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
Silicon Motion Technology Corp.
Siltronic AG - R
Simatelex Manufactory Co. Ltd.
Simplo Technology Co., Ltd
SK hynix Inc. - R
SK keyfoundry Inc.
Skyworks Solutions, Inc. - F
SMC Corporation of America - R
Snap, Inc. - R
Solidigm - R
Sonos, Inc. - R
Sony Group Corporation - F
STMicroelectronics - F
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd.
Synopsys, Inc.
Taiwan Chinsan Electronics Industrial Co., Ltd. - R
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. (TSMC) - F
TCL North America - R
TDK Group
Techtronic Industries Company Limited
TE Connectivity
Teradyne, Inc.
Tesla, Inc.
Texas Instruments - R
The LEGO Group
3M Electronics and Energy Business
Group
Toast, Inc.
Tokyo Electron Limited
Toshiba Corp.
Toyota Motor Corporation
TP-Link Systems Inc.
TPV Technology Ltd
Trimble Inc. - R
Unigen Corporation
United Group B.V. - R
Universal Electronics, Inc. - R
Vantiva SA - F
VAT Group AG
Venture Corporation
Versuni
Vertiv Holdings Co.
Vestel Elektronik A.S.
VIAVI Solutions Inc.
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. - R
Volkswagen Group
Volvo Car Group
V.S. Industry Berhad
Walmart
Watson Marlow Fluid Technology
Solutions
Western Digital - R
Wistron Corp. - R
Wistron NeWeb Corporation
Xerox - R
Xiamen Intretech Inc.
Xiaomi Corporation
XP Power - R
Zaptec - R
Zebra Technologies Corporation - R
Zhen Ding Technology Holding Ltd
ZT Systems
































































