OPTIMISM CREEPINGBACK

MARKETSIGNALS

DowntrendSlowingWhileMarket Compresses
MACROUPDATE


AFragileBalance:Cooling In ation,RisingDebt,andthe UnevenUSRecovery




DowntrendSlowingWhileMarket Compresses


AFragileBalance:Cooling In ation,RisingDebt,andthe UnevenUSRecovery


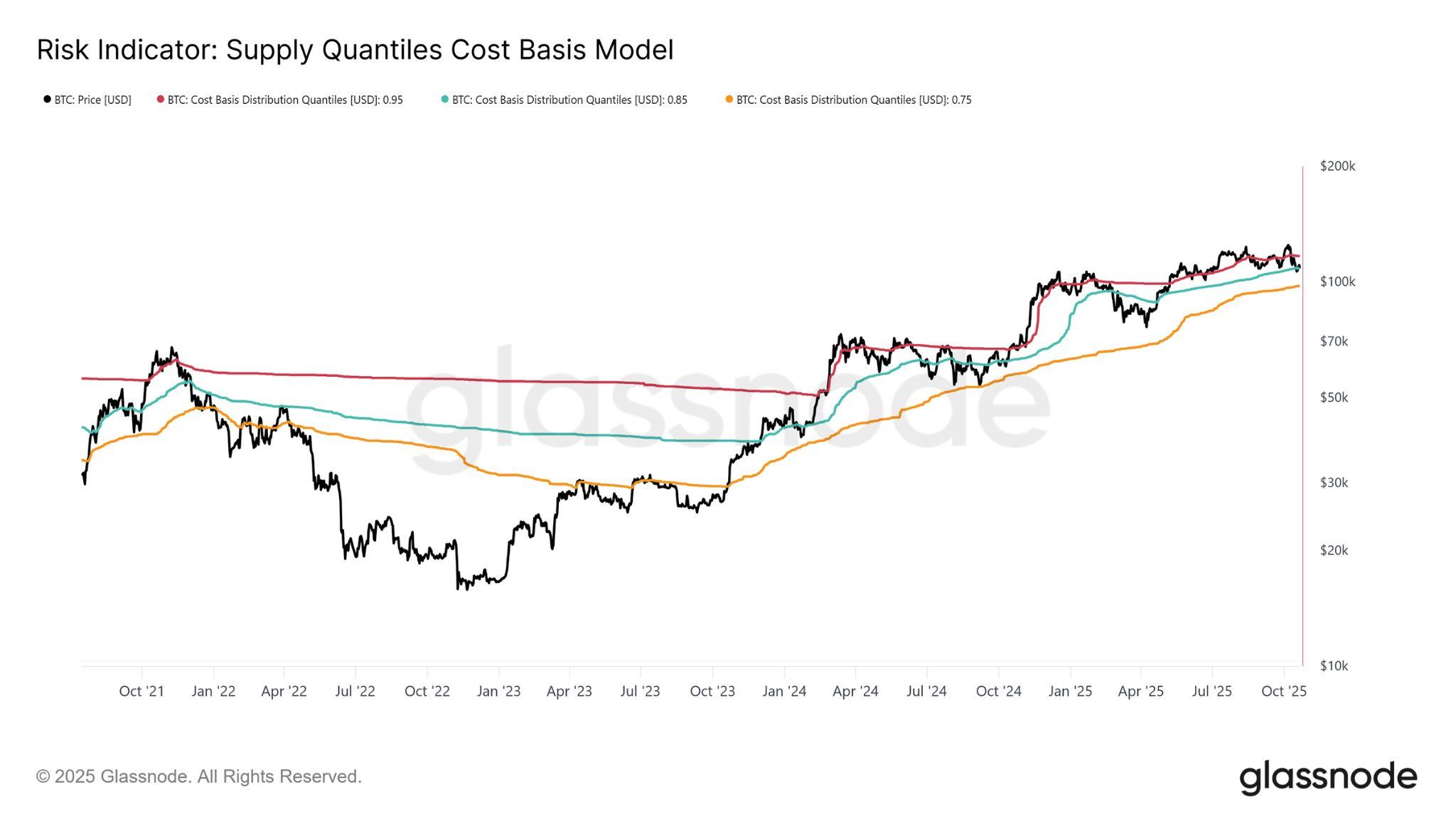
Bitcoin spent much of the week trading below both the short-term holdersʼ STH) cost basis and the 0.85 quantile level discussed in last weekʼs Bitfinex Alpha, reflecting fading momentum and market fatigue. However, a softer CPI print and signs of easing USChina tariff tensions helped BTC rebound above these resistance thresholds, improving near-term structure. Holding above the STH cost basis at $113,600 is now pivotal for confirming a constructive shift. Tradingabovethislevelhashistoricallymarkedthetransitionfromcorrectiveto accumulation phases, while failure to sustain it would risk deeper retracement toward the 0.75 quantile near $97,500, the likely lower bound of the current consolidationrangeifwearetopullbackfurther.
Since the record $19 billion liquidation on 10 October, market volatility has cooledconsiderably,withtotalBTCoptionsopeninterestcontractingbyroughly $7billionto$31billion,thesharpestweeklydropsinceJune.Theunwindingof short-dated upside exposure between $115,000$120,000 strikes has neutralised dealer gamma, and reset speculative positioning. Implied volatility hascompressedintothelow-40s,andrealisedvolatilitycontinuestodriftlower, 30-dayat44.1percentand10-dayat27.9percentsuggestingthattradersnow expect consolidation rather than breakout. The data points to a maturing post-liquidationreset:elevatedbutstabilisingvolatility.
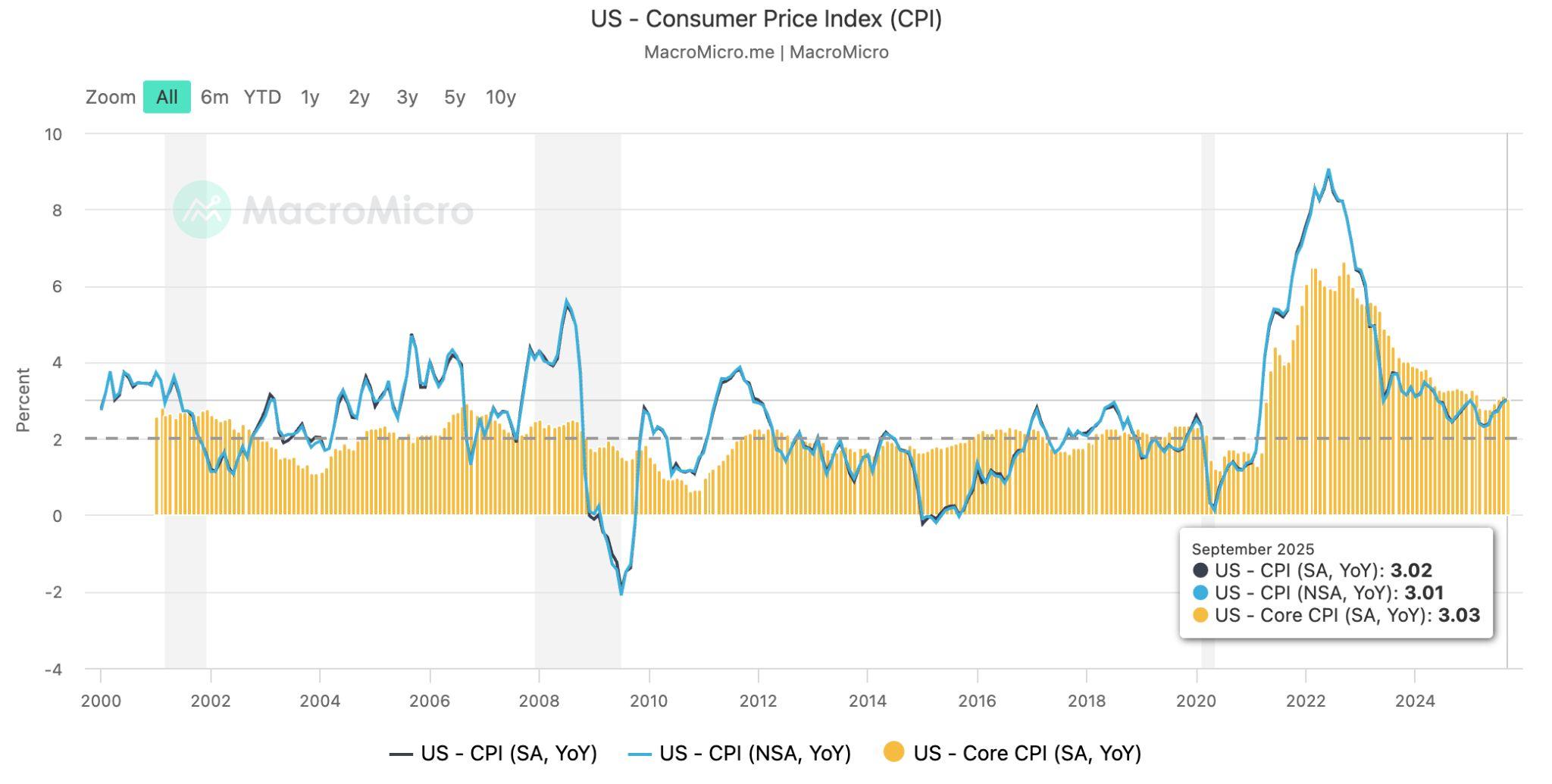
US inflation eased in September, rising just 0.3 percent for the month and 3 percent year-over-year, signalling progress toward the Federal Reserveʼs target andsettingthestageforanexpectedratecutattheendofOctober.

Yet beneath the headlines, the data revealed a tale of two economies: one buoyed by market gains and another strained by everyday costs. While investorscelebratedfreshrecordhighsintheS&P500andDowJonesindices, many households continue to struggle with higher gas, food, and service prices.
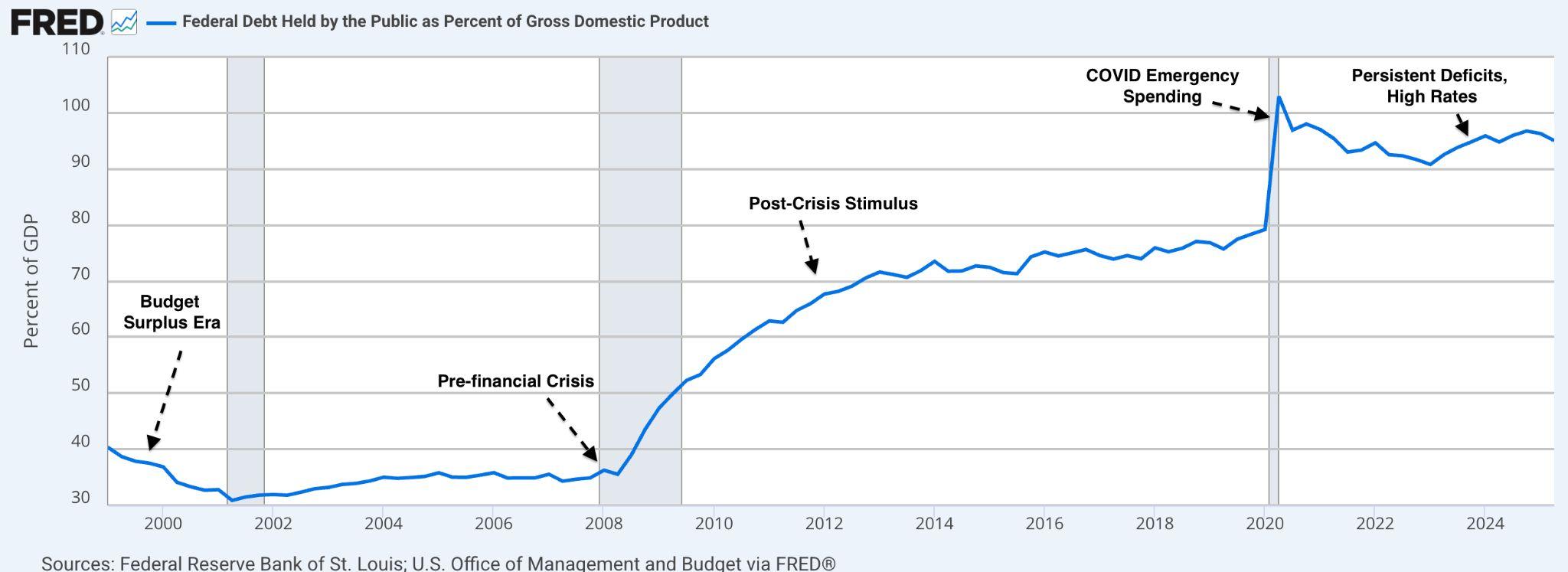
Atthesametime,surgingdebtintheUS,nowat$38trillion,or124percentof GDP is testing global confidence. With rising interest costs, political gridlock, and waning demand for Treasuries, the US risks borrowing more just to pay interestonwhatitalreadyowes.JapanandChinahavereducedholdings,while domestic institutions increasingly shoulder the burden. Though US bonds still offer attractive yields, cracks are forming in the “safe havenˮ narrative that underpins global finance. Together, easing inflation and a swelling debt load paint a complex picture: an economy stabilising at the surface but carrying deepstructuralimbalancesbeneath.
Japanʼs Financial Services Agency is set to relax its strict stance on digital assets by allowing domestic banks and their subsidiaries to trade, hold, and potentially offer crypto exchange services. This marks a significant shift from Japanʼspreviouspolicy,whichprohibitedbanksfromowningcryptocurrencies due to volatility and financial stability concerns. Meanwhile, US President DonaldTrumpgrantedafullpardontoBinancefounderChangpeng“CZˮZhao, who was convicted of anti-money-laundering violations and served four months in prison. The administration framed it as ending the “war on crypto,ˮ though critics raised concerns about potential political motives and Binanceʼs tiestoTrump-linkedventures.ThepardonremovesakeyobstacletoBinanceʼs USre-entryfollowingits$4.3billionsettlementwithregulators.
At the same time, gold advocate and Bitcoin critic Peter Schiff announced a blockchain-basedgoldplatformviahiscompanySchiffGold.Theprojectallows userstobuyandtokenisevaultedgold,spendfractionsthroughadebitcard,or redeemitphysically.
● DowntrendSlowingWhileMarket Compresses
● OilandForexVolatilityMayDriveLiquidity TowardCrypto

● InflationModeratesbutInequalityDeepens asFedPreparesforOctoberRateCut
● AmericaʼsGrowingDebtBurdenFacesa ConfidenceTest
● JapanʼsFinancialServicesAgencyPoised toOpenBankingSectortoCryptoAssets
● TrumpPardonsBinanceFounder ChangpengZhao
● PeterSchiff,LongtimeBitcoinCritic, LaunchesBlockchain-BasedGold
Bitcoinspentmuchofthepastweektradingbelowboththeshort-termholdersʼ STH) cost basis and the 0.85 quantile level discussed in last weekʼs Bitfinex Alpha, signalling fading momentum and increasing signs of market fatigue. However,asofter-than-expectedCPIprint,coupledwithencouragingsignalsof progressintheUSChinatariffdiscussionsonSunday,hastriggeredarebound thatpushedBTCbackabovetheseresistancethresholds.
Whilerepeatedfailurestoreclaimandsustaintheselevelsinrecentweekshad pointed toward an extended consolidation phase, with weakening confidence amongrecentbuyersandinsufficientdemandtoabsorblingeringsellpressure, the latest move up improves near-term prospects. It is now critical that BTC holds above the STH cost basis near $113,600 to establish a sustainable short-term uptrend and confirm a shift in market structure from defensive to constructive.

To place the current market structure in proper context, it is essential to understandwhyreclaimingtheshort-termholdersʼSTH)costbasisremainsa pivotal factor in sustaining a bullish phase. The Supply Quantile Cost Basis model (see Figure 1 above) provides a valuable lense as it divides supply into loss-holding segments: the 0.95, 0.85, and 0.75 quantiles represent the price levels at which 5, 15, and 25 percent of circulating supply are held at a loss, respectively.
At present, BTC has just reclaimed the STH cost basis of $113,600 and continues to trade above the 0.85 quantile level, currently near $108,600 implyingthereisapossibilitythatthelowofourconsolidationperiodisalready in. Historically, persistent weakness beneath this threshold has indicated structural fatigue and often preceded deeper retracements toward the 0.75 quantile,nowlocatedaround$97,500.
This $97,500 region likely defines the lower boundary of the ongoing consolidation phase. A move toward this level would be consistent with prior cyclepatterns,whereafinalcapitulationnearthe0.75quantiletypicallymarked the exhaustion of selling pressure and provided the foundation for the next phaseofthebroaderuptrend.
Trading around the STH cost basis often represents a decisive point in each marketcycle,whereconvictionamonginvestorswhoenterednearrecenthighs is put to the test. Historically, when BTC breaks below this level following the formationofanewall-timehigh(wheretheoretically100percentofthesupply isinprofit),thepercentageofsupplyheldinprofittypicallydeclinestoward85 percent,meaningmorethan15percentofcoinsareheldataloss.


This same structure is now unfolding for the third time in the current cycle whereBitcoinsupplyheldinprofithasgonetoalowof78.3percentfollowing the October 10th pullback, and is currently at 89.1 percent (refer Figure 2 above).ShouldBTCfailtosustainabovethereclaimoftheSTHcostbasisnear $113,600, the resulting contraction could push a larger portion of supply into loss,heighteningpressureonrecententrants.Suchashiftinprofitabilityoften precedes broader capitulation events, as weaker hands exit the market and volatilityspikesbeforestabilityreturns.
Since the historic $19 billion liquidation was recorded on 10 October, the volatility landscape has shifted materially. This weekʼs option expiry appears significantly smaller in scope following the washout, which erased roughly $7 billioninBTCoptionsopeninterestOI.TotalOIfellfromaround$38billionto approximately $31 billion, the sharpest weekly contraction since June. The forced unwinding of short-dated upside exposure, concentrated between the $115,000 and $120,000 strikes, effectively neutralised dealer gamma positioninganddampenedspeculativemomentum.
Impliedvolatilityacrossallexpirieshassincecompressed,backtothelow40s, suggesting that traders now anticipate consolidation rather than a directional breakout. Despite several upcoming catalysts, including last weekʼs CPI release, this weekʼs FOMC meeting, and the anticipated Trump–Xi summit, optionstradersappearreluctanttotakelargeshort-dateddirectionalpositions.
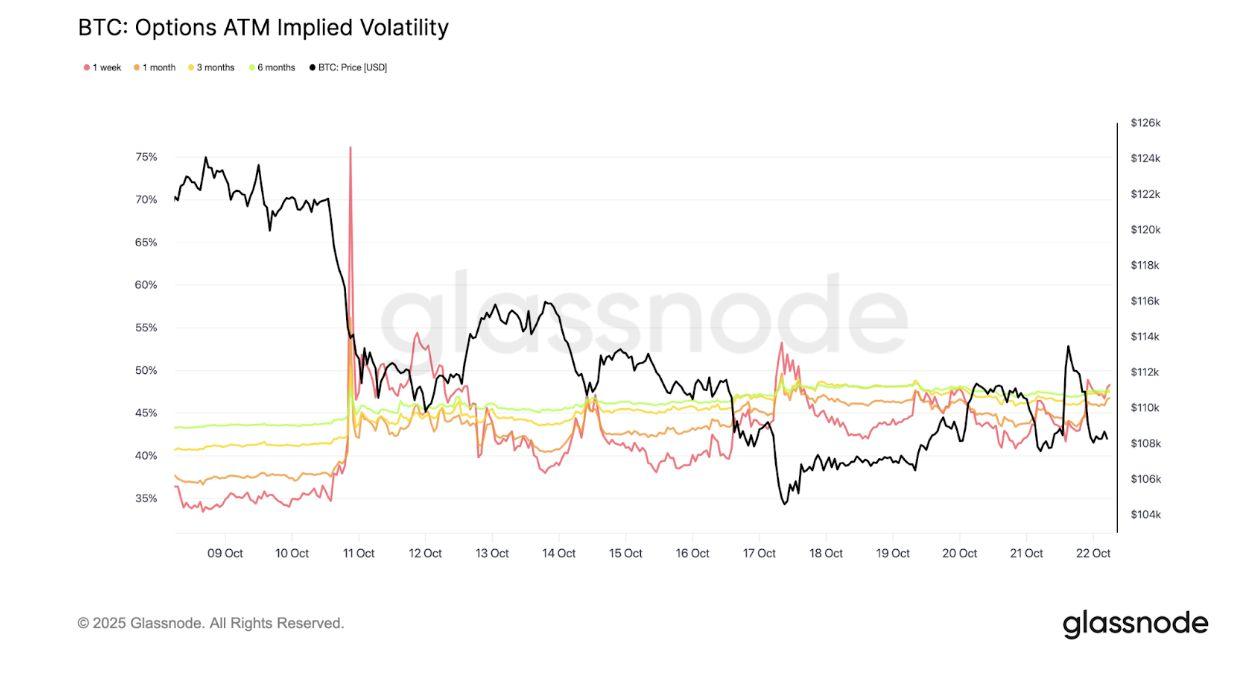

Across near-term maturities, implied volatility (for expiries within the next 34 weeks) currently averages around 48 percent, compared with 3643 percent just two weeks ago. The market has yet to fully absorb the shock from the October 10th deleveraging, and dealers remain cautious, unwilling to sell volatilityatlowerpremiums.Meanwhile,30-dayrealisedvolatilitystandsat44.1 percent,withthe10-dayrealisedmeasureat27.9percent.Asrealisedvolatility continuestocool,impliedlevelsarelikelytofollow,normalisingoverthecoming weeks.
For now, volatility remains relatively elevated, though the data suggests this is moreacaseofshort-termrepricingafterastructuralresetratherthantheonset ofaprolongedhigh-volatilityregime.

Crypto markets are showing signs of stabilisation even as traditional asset classesexperienceheightenedvolatility.Shocksinenergypricesandforeign exchangemarketsarereshapinggloballiquidityflows,andcryptoappearsto beabsorbingsomeoftherotation.


Brent crude has surged to around $65 per barrel, propelled by Red Sea shipping disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and ongoing OPEC+ supply constraints. Meanwhile, the Japanese yen has weakened to nearly ¥152 per dollar, a level that has sparked growing speculation that the central Bank of Japanmaystepintosupportthecurrency.Whilenointerventionhasoccurred yet, markets are on edge, traders recall past episodes when Japan suddenly enteredthemarkettopropuptheyen,andmanynowviewthispricezoneasa potential trigger point. These cross-asset dislocations have prompted institutional investors to reassess their exposures across bonds, equities, and alternativeassets,includingdigitaltokenssuchasBitcoinandEther.

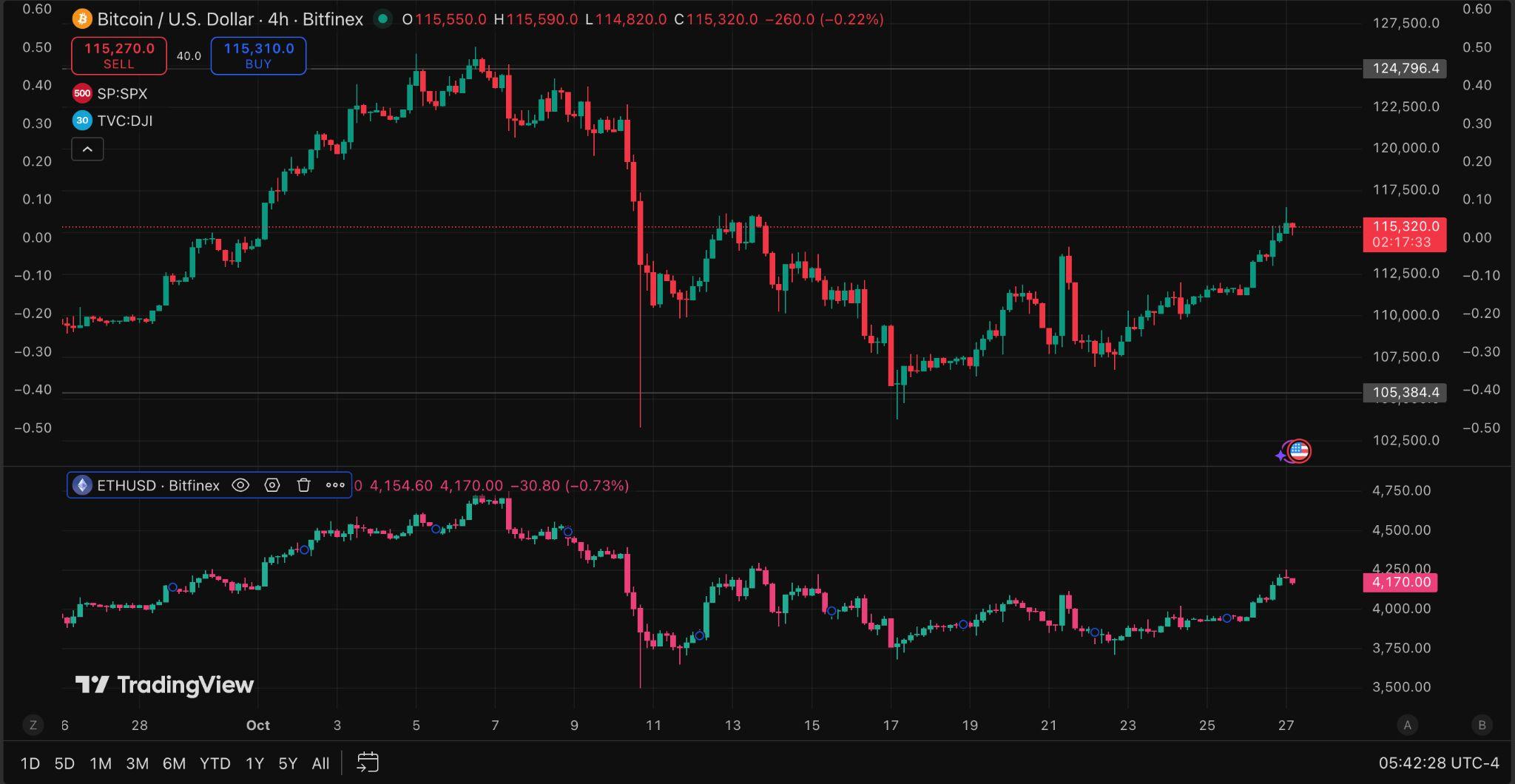
This macro backdrop coincides with a modest rebound in crypto. Bitcoin is tradingabove$115,000,whileEtherhoversaround$4100,bothrecoveringfrom theOctober10thmarketliquidations.
EnergyMarketShocksReigniteInflationConcerns
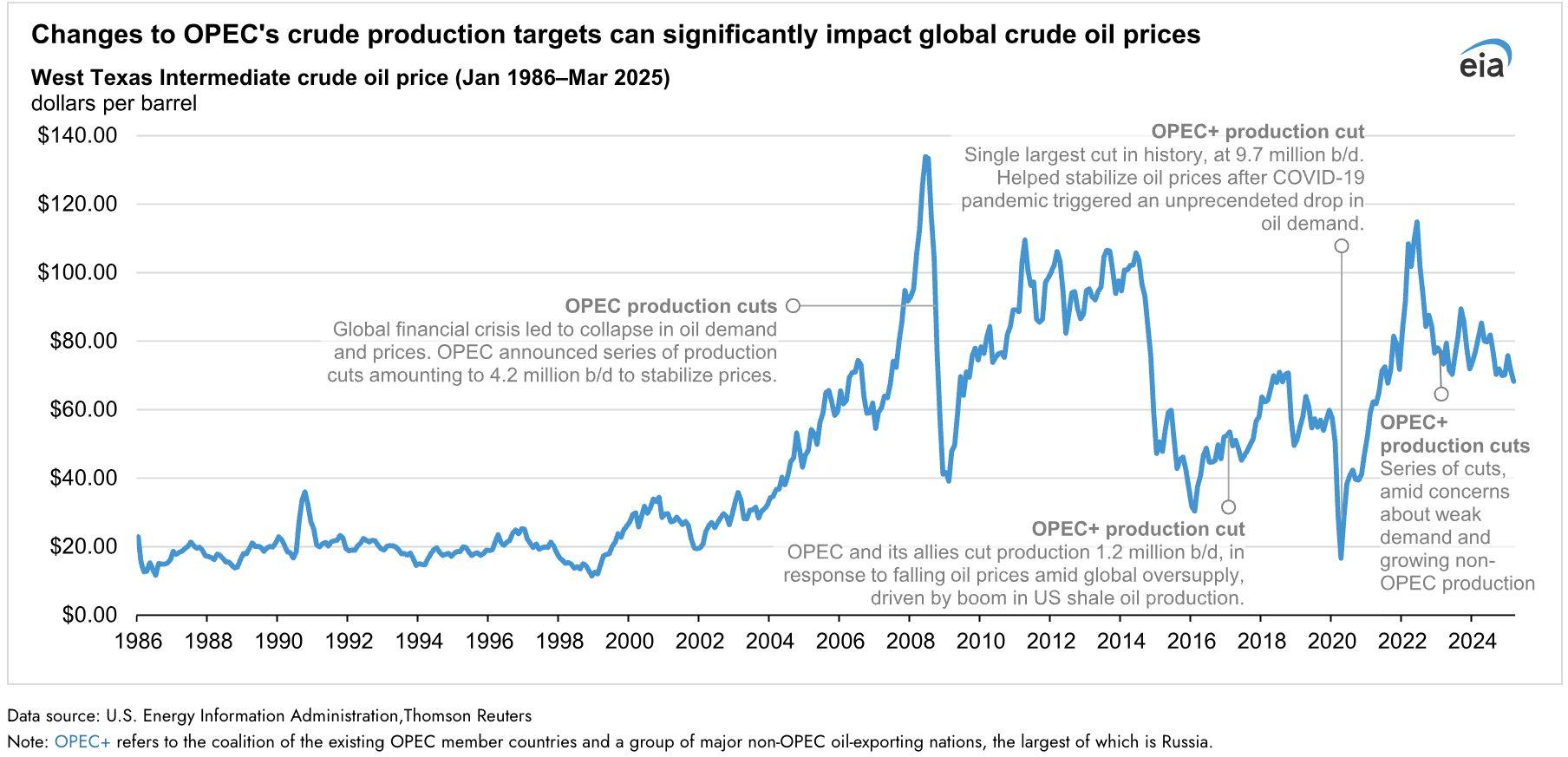
6.ChangestoOPECʼsProductionTargetsFrom1986to2025
The oil price surge is reflective of current macro tensions. Geopolitical flashpoints have tightened freight capacity, raising global transport and insurance costs. OPECʼs coordinated supply caps and a broader Middle East risk premium have added a new inflationary layer just as central banks try to winddownpolicytightening.
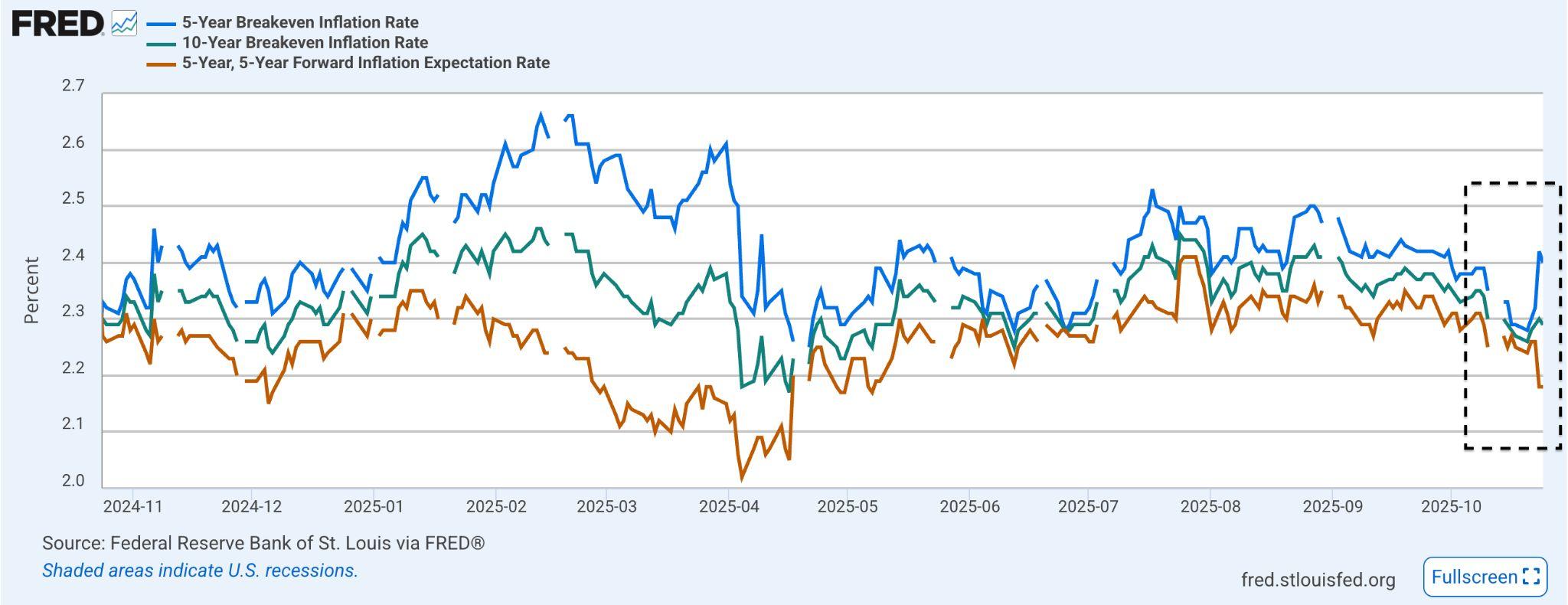

In the US, the 5-year breakeven inflation rate recently climbed to 2.4 percent (seeFigure7above),reflectingrenewedpricingpressure.Despitethis,theCME FedwatchTool(seeFigure8below)stillimpliesanother91percentchanceofa Federal Reserve rate cut in December as weaker growth and softening consumerdemandtugintheoppositedirection.
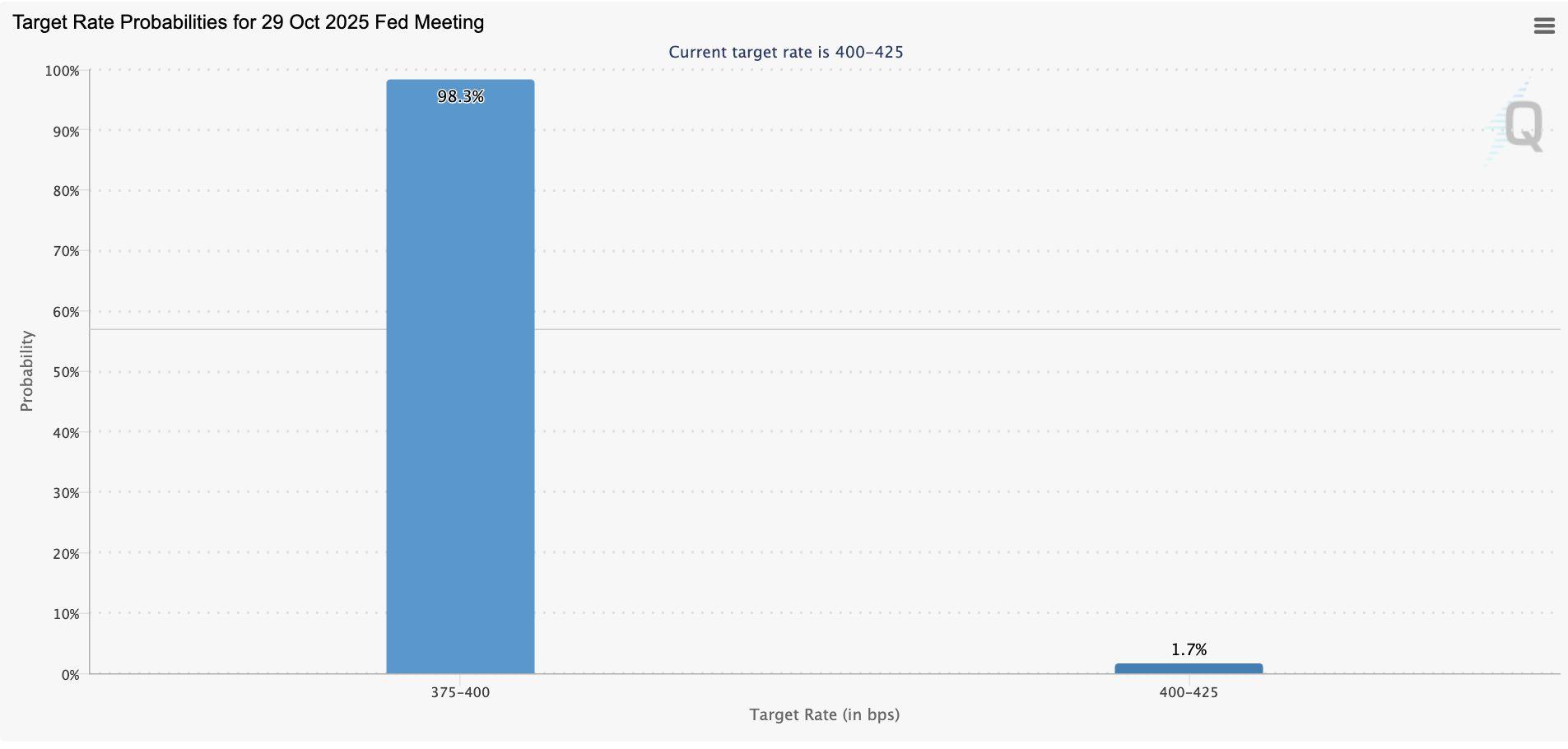
CMEFedwatchTool)
For crypto, this creates a mixed macro setup: higher energy prices lift mining costsandcompressmargins,butpersistentinflationcouldforcecentralbanks torepricefiatliquidity,indirectlyfavouringdecentralisedalternatives.
VolatilityinFXmarketshasaddedanotherlayerofcomplexity.Theyenʼsslide toward ¥152 has reignited speculation of BOJ action, which, if realised, could absorb dollar liquidity and ripple into leveraged funding markets that intersect withcrypto.
Amid these macro moves, stablecoins are expanding. Tether USDt issuance hasgrownbyseveralbilliondollarsoverrecentweeks,signallingfreshcapital rotation. This expansion often mirrors dollar demand offshore and can be an earlysignalofriskdeploymentintodigitalassets.
InstitutionalPositioningandCorrelationBreakdown


Institutional flows into crypto remain sensitive to volatility and interest rate expectations.Impliedvolatilityon1-monthBitcoinoptionshaseasedtoaround 45 percent, suggesting a more balanced risk appetite. Open interest in CME Bitcoin futures is up moderately on the week, an indicator of renewed institutionalengagement.


Notably,correlationsareshifting.The30-dayrollingcorrelationbetweenBitcoin andtheS&P500hasdroppedtoapproximately0.32,whilecorrelationwiththe Dollarindexremainsnegative.Thisreinforcesthethesisthatcryptoisevolving intoaliquidityproxyratherthanapurelyhigh-betaasset.
Looking ahead, policy divergence will shape near-term sentiment. The Federal Reserve is juggling oil-driven inflation with softening manufacturing and services data. Meanwhile, the ECB and Bank of England lean dovish, and the BOJfacesincreasingscrutinyoveritsyieldcurveandcurrencydefencestance.
In this environment, cryptoʼs relative calm may reflect maturation in structure, liquidity depth, and institutional alignment. Recent volatility across oil and currencymarketsunderscoresacriticalmacroevolution:cryptoisnowtrading as a liquidity-sensitive asset class, not merely a risk-on vehicle. Despite yen pressureandenergyinflation,stablecoingrowthanddecliningvolatilitysuggest capitalisredeploying,notretreating.
This cycle of rotation, not rejection, reveals structural integration. If it holds, crypto could become a barometer for global capital adjustment, signalling how marketsadaptinrealtimetomacroshocks.


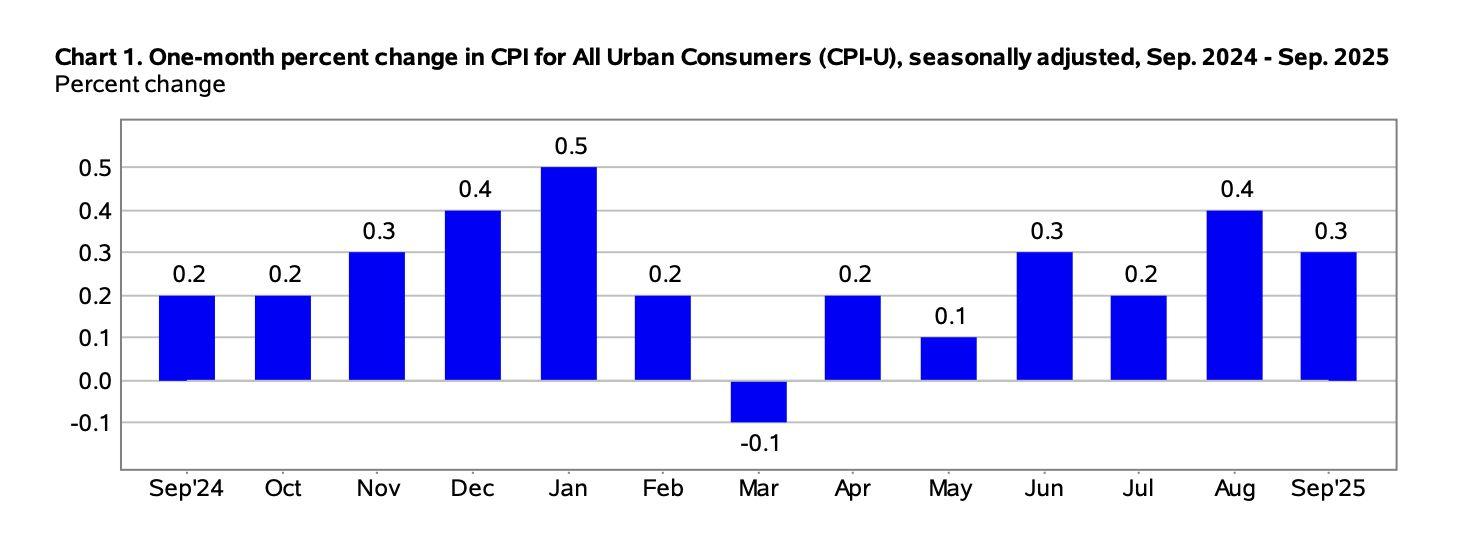
Figure11. One-MonthPercentChangeinConsumerPriceIndex Source:BureauofLaborStatistics)
The delayed US Consumer Price Index CPI) report for September showed both progress and pain across the economy. Inflation cooled modestly, giving the FederalReserveroomtocutinterestrateslaterthismonth,yettheunevenimpact ofpricechangescontinuestorevealdeepdividesamongAmericanhouseholds.
According to data released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics BLS, consumer pricesrose0.3percentinSeptember,followinga0.4percentgaininAugust,and were3percenthigherthanayearearlier.Coreprices,whichexcludevolatilefood and energy categories, increased by 0.2 percent on the month and 3 percent annually,stillwellabovetheFedʼs2percentinflationtarget.
ThelatestfiguresareexpectedtogivetheFedconfidencetomoveaheadwitha 25 basis-point rate cut at its October 29th meeting, followed by another in December, gradually bringing policy rates closer to the central bankʼs long-run neutral estimate of 3 percent. The softer reading in inflation and ongoing labour marketweaknesswilllikelyjustifythismove.
GasolineandFoodCostsStillBite
Whileheadlineinflationeased,underlyingpressuresremain.Energycostssurged 1.5 percent on the month, driven by a 4.1 percent jump in gasoline prices and rising energy commodities amid ongoing geopolitical tensions and sanctions on Russianoilfirms

Food prices rose more moderately, by 0.2 percent in September, but remain a key source of frustration for consumers. Grocery prices increased 0.3 percent, ledbycerealsandbeveragesup0.7percent,whilebeefrose1.2percentaftera sharpincreaseinAugust.
The service sector continues to be a key driver of inflation, with prices up 3.5 percentyear-over-year,ledbyhousing,healthcare,andpersonalservicessuch ashomecaregiving,whichrose7percentinjustonemonth.
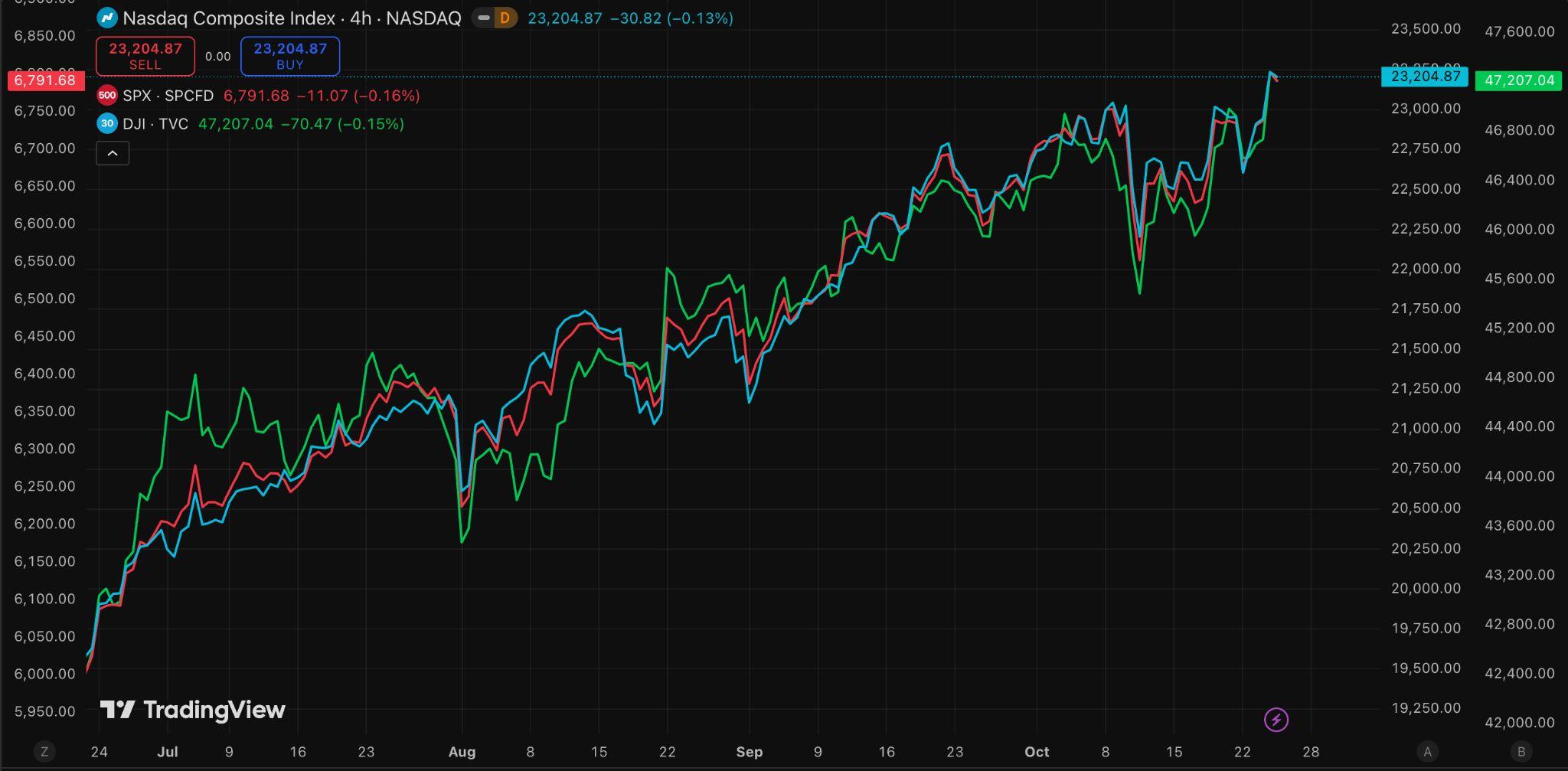
Figure12.S&P500,NasdaqCompositeandDowJonesIndustrialAveragePrice Source:TradingView)
InvestorscheeredthemilderinflationreportonFriday,drivingallthreemajorUS stockbenchmarkstofreshrecordhighs.
However, for most households, the economy is defined not by financial market rallies but by the cumulative pressure of higher utility bills, grocery costs, and service fees. While upper-income households benefit from rising stock portfolios, home prices, and lower borrowing costs as rates fall, middle- and lower-income families remain strained. The latest CPI report highlights how economicgainsaredistributedunevenly;thosewithaccesstofinancialmarkets and assets prosper, while those relying on wages struggle to keep pace with livingcosts.

With inflation hovering around 3 percent and rate cuts approaching, the US economy appears to be stabilising, but not for everyone. Wealthier households continue to gain from buoyant markets while lower-income groups face persistentcost-of-livingstress.
Inshort,theinflationreportrevealsatwo-trackrecovery:onepoweredbyasset growth and financial stability, and another weighed down by rising everyday expenses. As the Fed begins its easing cycle, its challenge will be not only to guideinflationlowerbuttoensurethatthebenefitsofstabilisationreachbeyond thetopoftheeconomicladder.


Figure14.USNationalDebtSource:PetersonFoundation)
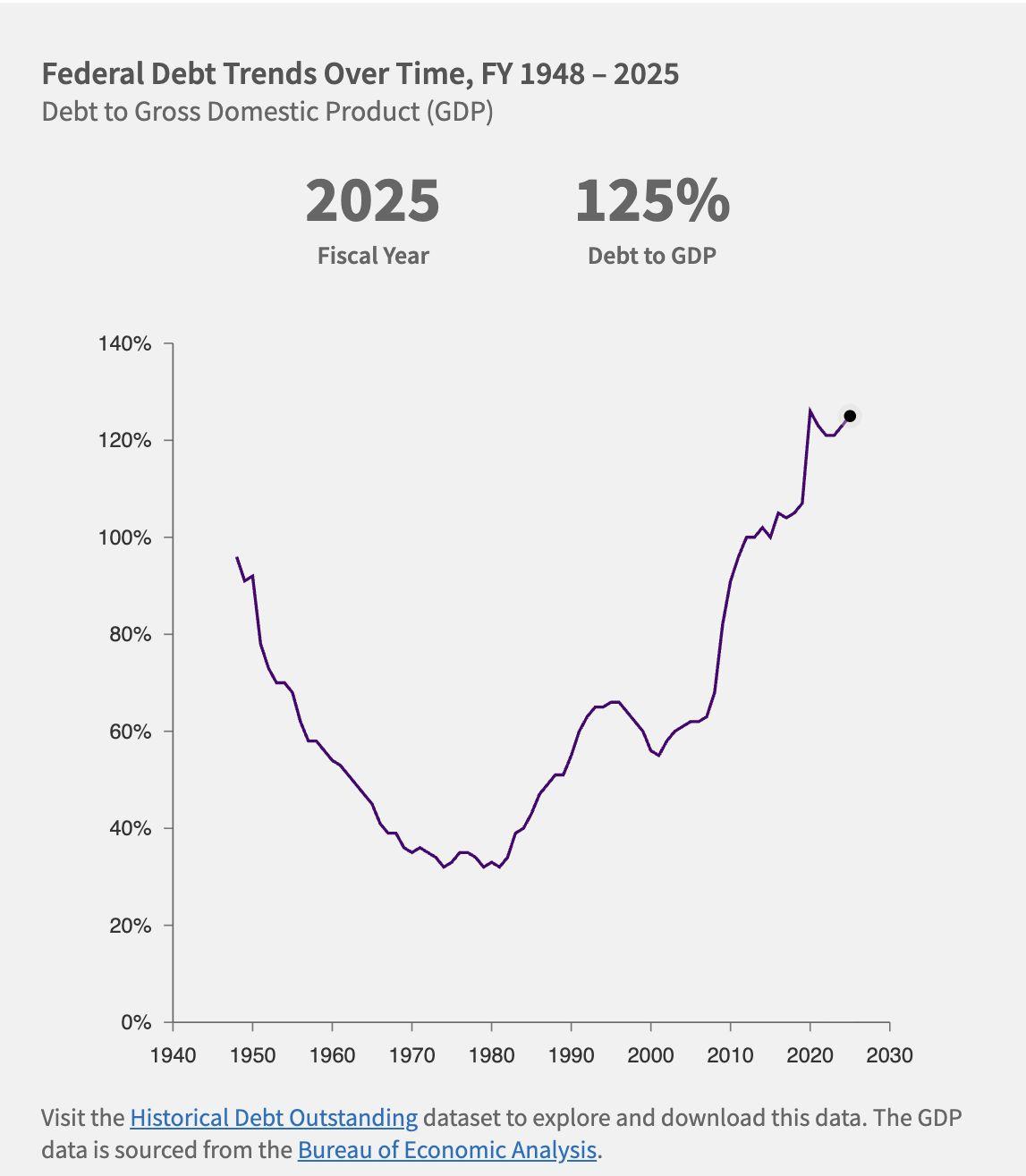
AsofSeptember,theUnitedStates'totalfederaldebtclimbedto$38trillion,with roughly$30trillionheldbythepublic.Thisfigurenowrepresents124percentof the nationʼs annual economic output, a level that has prompted increasing concern among global investors and policymakers alike. Whatʼs different today isnʼtjustthesizeofthedebt;itʼstheconvergenceofrisinginterestcostsdriven bythelegacyofpastratehikes,politicaldysfunction,andfadingforeignappetite forUSTreasurysecuritiesthatmakesthismomentfeelunstable.
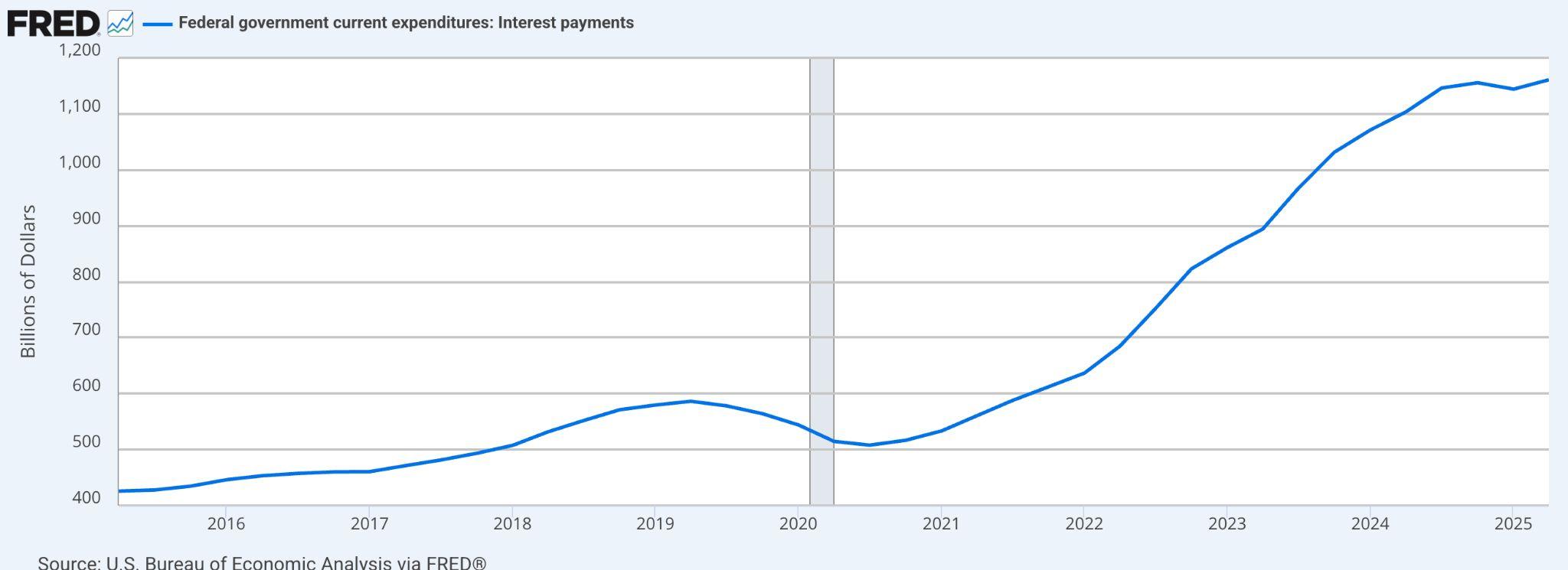
Figure15.FederalGovernmentInterestPayments: GovernmentʼsCumulativeDebtServicingBurden

The US fiscal trajectory is under sharper scrutiny as both macroeconomic pressures and geopolitical shifts collide. Inflation that surged post-pandemic pushed the Federal Reserve into an aggressive interest-rate-hiking cycle, driving theaveragecostofnewgovernmentborrowingsharplyhigher.Today,theaverage interestrateongovernmentdebtsitsat3.4percent,butlong-termissuanceisnow pricedinarangeof45percent,wellaboverecenthistoricalnormsandoutpacing mostadvancedeconomiesexcepttheUK.
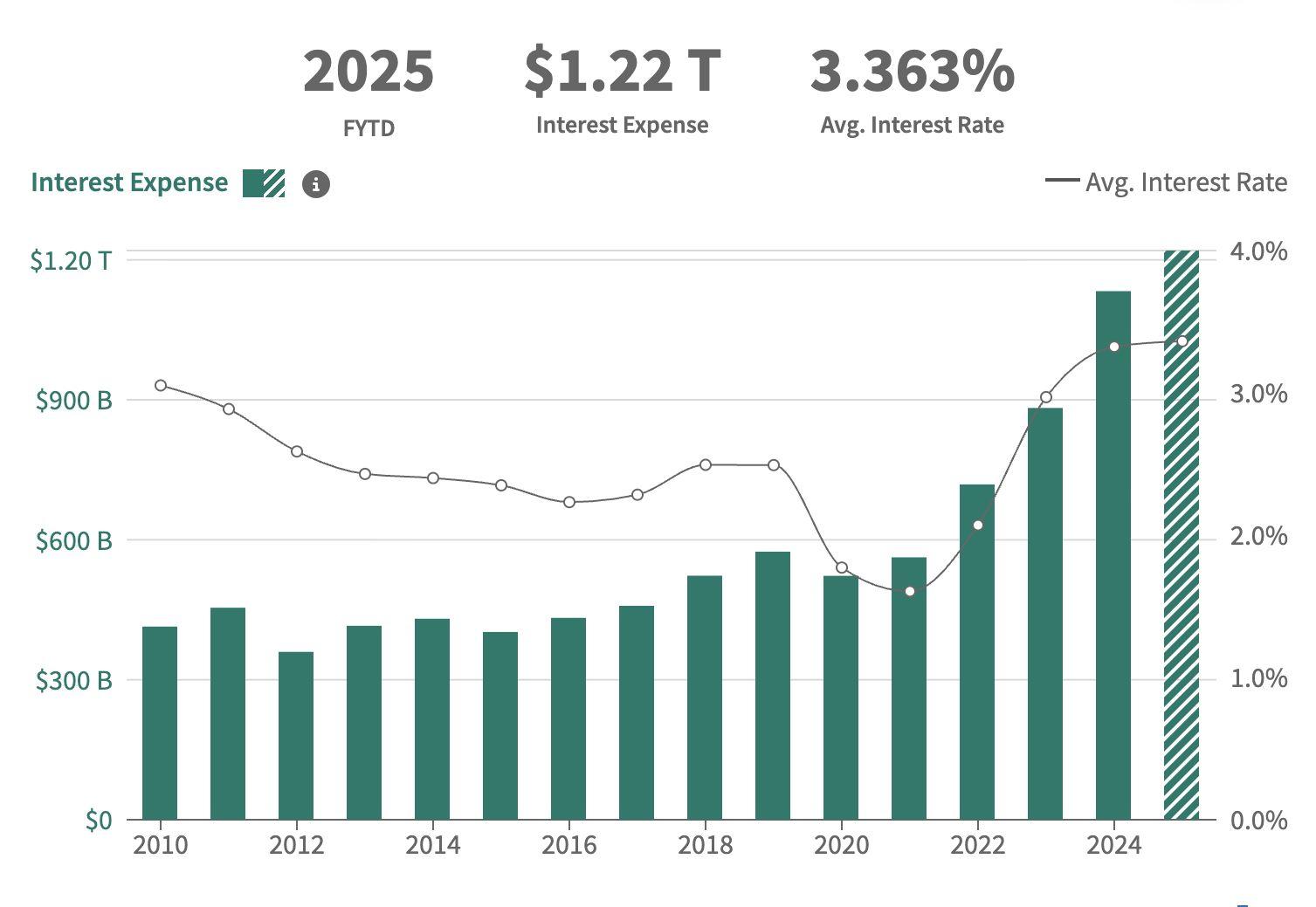
Figure16.InterestExpenseandAverageInterestRatesontheNationalDebt
Thisriseininterestratesdoesnʼtjustimpacthouseholdsandbusinesses;itraises the cost of servicing government debt itself. With the Congressional Budget OfficeCBO)projectingsustainedfederaldeficitsabove5percentofGDPupuntil 2053,theUSiseffectivelyborrowingmorejusttopayinterestonwhatitalready owes.ToputthisintoperspectivetheCBOnotesCBOthattherehaveneverbeen more than five successive years of deficits this high, and that was during World WarII,andtookplacebetween1942and1946.


At the same time, the political landscape in Washington continues to erode investor confidence. The current government shutdown is an unwelcome backdropforthoseholdingtrillionsinUSsovereignbonds.
TheUSdollarandTreasurymarkethavelongbeenconsideredthebackboneof globalfinance,a“safehavenˮthatinvestorsrushtointimesofuncertainty.But cracks are starting to show. While the dollar remains the worldʼs primary reserve currency, emerging debates around “de-dollarisationˮ and a more multipolarfinancialsystemarebeginningtochallengethatdominance.
Still, Treasuries have remained attractive due to the yield differential, which is the gap between US bond yields and those of other major economies. Even amid market volatility, US debt continues to offer higher returns than many peers. A historically strong dollar has amplified that appeal, as it boosts the value of foreign investorsʼ dollar-denominated holdings when converted back intotheirlocalcurrencies.
Thiscombinationdrewsignificantforeigndemandearlierintheyear.However, the momentum has since reversed: last April, foreign holdings declined by $50.6 billion. This decline suggests that some foreign investors are beginning to reduce their exposure to US debt, either locking in gains or reallocating toward assets in their home markets as local yields rise and currency risks grow.

Thepullbackispartlylinkedtoshiftingconditionsabroad.InJapan,longamajor buyerofUSdebt,endeditsultra-lowrateerainMarch2024byraisingitspolicy rate to 00.1 percent, with market expectations of further hikes later in 2025, making yen-based assets more attractive and reducing the incentive to hold dollar-denominated Treasuries. In Europe, renewed political tension in France hasshakeninvestorconfidenceinEuropeanassets,whiletheeurohasrecently rallied(drivenbybothdollarweaknessandimprovingeuro-areafundamentals). As the euro strengthens, hedging costs on dollar exposures rise and the yield advantage of US Treasuries diminishes — signalling growing caution among foreignbuyerstowardUSassets.
To understand how the US arrived at this fiscal juncture, a look back helps. In 2000,federaldebtheldbythepublicwasjust35percentofGDP.Overthenext two decades, it climbed steadily due to military spending, tax cuts, and slow growth. The 2008 financial crisis caused a major spike, and debt reached 69 percentofGDPby2012.
ThencameCOVID19.Emergencyreliefprogramsandeconomicstimulusdrove theratioabove100percentby2021.Whilegrowthhasrecoveredsince,thedebt hasnotfallen,ithasstabilisedaround100120percentofGDPandcontinuesto trendhigher(seeFigure18 below).

Treasury securities continue to find buyers, but the composition of those buyersisshifting:
● Foreign investors: Once the dominant holders, their share has shrunk to about 2530 percent of total US debt. China, forexample,hascutitsholdings below $1 trillion, while Japan remains the largest foreign holder at around $1.1 trillion. These shifts reflect not just economic tensions but the need for some countries to defend theirowncurrencies.
● FederalReserve: The Fed played a key role during the pandemic, buying vast amounts of Treasuries under quantitative easing. But it has now reversed course, shrinking its balance sheet and reducing demand. The FedʼsTreasuryportfoliopeakedataround$5.7trillionin2022buthassince declined to about $4.2 trillion as of October 2025. Its share of total Treasury securities outstanding continues to fall as the balance sheet normalises.
● Domesticinvestors:USpensions,banks,andmutualfundshavepickedup the slack. These institutions now account for over half of all Treasury holdings. With higher yields and low-risk appeal, domestic demand remains strong but it may not be unlimited, especially if inflation expectationsshiftorriskperceptionsrise.
The US faces a structural challenge: it must issue trillions in new debt annually just to meet its obligations, refinance maturing bonds, and fund persistent deficits. With the Fed stepping back and foreign buyers cautious, more of this burden will fall on domestic investors, a group whose appetite may not always alignwithTreasuryissuanceneeds.
Intheshortterm,higherinterestratesareattractingbuyers.Butinthelongterm, confidence in US governance, inflation control, and economic stability will determinewhetherTreasuriesretaintheiruniquestatus.Withoutfiscalreformor renewed growth, even small shifts in investor sentiment could make borrowing moreexpensiveandtesttheresilienceofAmericaʼsfinancialfoundation.



Japanʼs Financial Services Agency FSA) is preparing to revise longstanding supervisory guidelines to permit domestic banking groups to engage in trading, holdingandpossiblyprovidingexchangeservicesforcryptoassets,according a local report. This marks a substantive shift in the countryʼs regulatory posture towarddigitalassets.Underthepresentregime,banksarebarredfromowningor trading crypto assets such as bitcoin and ether, largely due to concerns about extremepricevolatilityandpotentialriskstofinancialstability.Thecontemplated reforms would allow banks, or their securities/unit-subsidiaries, to buy and sell crypto much like they do stocks or bonds, provided robust risk-management frameworks and oversight are put in place. Furthermore, the FSA is also deliberating whether to allow banking units to register as crypto exchange operators,therebyofferingretailaccesstocryptoviatraditionalbankingentities, whichenjoyhighertrustinJapan.
Alongside these proposals, regulatory guardrails are expected to be strengthened: this includes potential amendments to explicitly outlaw trading based on non-public information in the crypto market and to institute capital/risk-management requirements for banks entering the space. Although the move signals a more open stance toward digital assets, the FSA remains cautious:whilebanksmightbeabletoholdcryptoasinvestments,thequestion of allowing them to sell crypto to clients remains under strict scrutiny. If implemented, this strategic pivot could accelerate the integration of crypto assetsintoJapanʼsmainstreamfinancialsystem,aligningwithroughly12million cryptoaccountsalreadyinthecountryandrespondingtoevolvingglobalnorms, yet it also underscores the regulatorʼs balancing act between innovation and safeguardingmarketintegrity.


US President Donald Trump has granted a full pardon to Changpeng Zhao (commonlyknownas“CZˮ),founderofthecryptocurrencyexchangeBinance, whopleadedguiltytoanti-money-launderingviolationsin2023andservedfour months in prison in 2024. The pardon was formally issued on October 22, 2025, and publicly reported via a White House announcement the following day.
TheWhiteHouseframedtheactionaspartofTrumpʼsagendatoreversewhat his administration describes as the previous administrationʼs “war on crypto.ˮ PressSecretaryKarolineLeavittstatedthatZhao“wasprosecutedbytheBiden Administration in their war on cryptocurrency,ˮ declaring that “the war on cryptoisover.ˮ
Zhaoʼs conviction had stemmed from allegations that under his leadership Binance failed to maintain adequate anti-money-laundering AML) controls, facilitated transactions involving US users and jurisdictions under sanctions, and mis-categorised US users to evade regulatory scrutiny. Binance itself agreedtoarecord-breakingsettlementofapproximatelyUS$4.3billionwithUS authoritiesaspartoftheresolution.
Beyondthelegalandregulatoryimpact,thispardonhassignificantimplications forBinanceʼsbusinessprospectsintheUS.Themoveiswidelyinterpretedas clearing a major hurdle for Binanceʼs potential return or expansion into the US market, which had been severely constrained by Zhaoʼs guilty plea and the companyʼsmonitoringobligations.
However, the decision has sparked intense scrutiny and criticism from US lawmakers and watchdogs. Democratic senators have flagged potential conflicts of interest, citing reports that Zhao and Binance engaged in lobbying andhadtiestoacryptoventurelinkedtoTrumpʼsfamily.


PeterSchiff,awell-knownadvocateforgoldandoneofBitcoinʼsmostpersistent sceptics,istakingasurprisingturntowardblockchaintechnology.
In a recent interview with crypto influencer Michael Jerome last Thursday, October23rd,Schiffrevealedthathisfirm,SchiffGold,isbuildinganapplication that will allow users to buy vaulted gold, tokenise its ownership, and transfer it instantly.Theplatformwillalsoenableuserstospendsmallportionsoftheirgold via a debit card or redeem it for physical coins, effectively merging traditional goldinvestingwiththeconvenienceofdigitalpayments.
Schiffframedtheconceptasanaturalevolutionofgoldʼsroleinfinance.“Goldis theoneassetthatactuallymakessensetoputonablockchain,ˮhesaid,arguing thattokenisationprovidesapracticalbridgebetweenphysicalassetsanddigital transfersystems.
However, not everyone is convinced. Binance founder Changpeng “CZˮ Zhao, whowasrecentlygrantedapresidentialpardonbyDonaldTrump,criticisedthe concept on X (formerly Twitter). Zhao argued that tokenised gold doesnʼt truly exist “on-chainˮ but instead relies on the trust that a third party will deliver the physicalmetal.“Itʼsa‘trust-me-broʼtoken,ˮZhaowrote.
Schiffdismissedthecritique,sayingthatintermediarieshavealwaysbeenacore part of capitalism. He pointed to vault operators like Brinks, emphasising that trustedcustodianshiphaslongbeenthefoundationofthegoldmarket.

Bloomberg Intelligence analyst Eric Balchunas commented that the model resembles something that already exists in traditional finance. “Congratulations, you just invented an ETF,ˮ he joked on X, referencing gold-backed exchange-traded funds which also allow investors to redeem their holdings for physicalmetal.Balchunasadded,however,thatmostinvestorsultimatelyprefer tocashoutratherthanredeemgolditself.
Schiffʼs pivot toward blockchain marks a fascinating convergence between traditional and digital finance. While he remains critical of Bitcoin, his move highlightshoweventhestaunchestscepticsrecogniseblockchainʼspotentialfor real-world assets. As tokenisation gains traction, from gold to real estate and beyond,theboundariesbetweenoldandnewmoneyareblurring.Schiffʼsproject could help legitimise blockchainʼs role in bridging tangible value with digital utility, signalling a broader shift in how markets think about trust, custody, and ownershipinthedigitalage.

