BTCINSEARCHOFA BOTTOM

MARKETSIGNALS

BitcoinRecordstheThirdLargest
PullbackoftheCycle
MACROUPDATE


USGovernmentShutdownEnds
LeavingEconomicScars





BitcoinRecordstheThirdLargest
PullbackoftheCycle
MACROUPDATE


USGovernmentShutdownEnds
LeavingEconomicScars


Bitcoinhasnowloggeditsthird-largestdrawdownofthecurrentcycle,falling25 percent from it's all-time high to trade below $94,000 and momentum remains towardsthedownsideonlowertimeframes.However,thecurrentpaceofselling and the size of realised losses being experienced by investors has begun to stabilise, hinting that the market may be entering a consolidation phase rather thananextendedcapitulation.
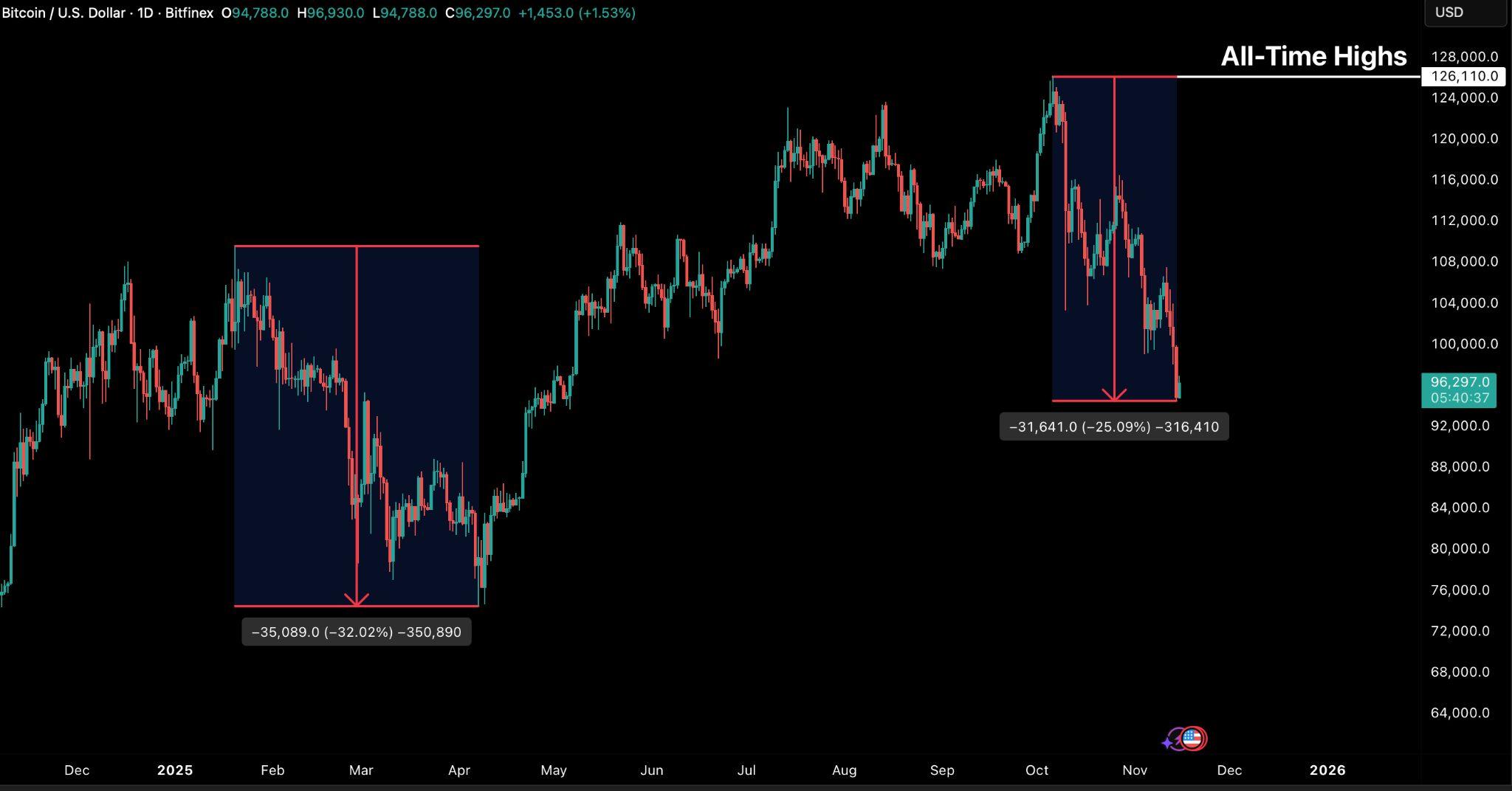
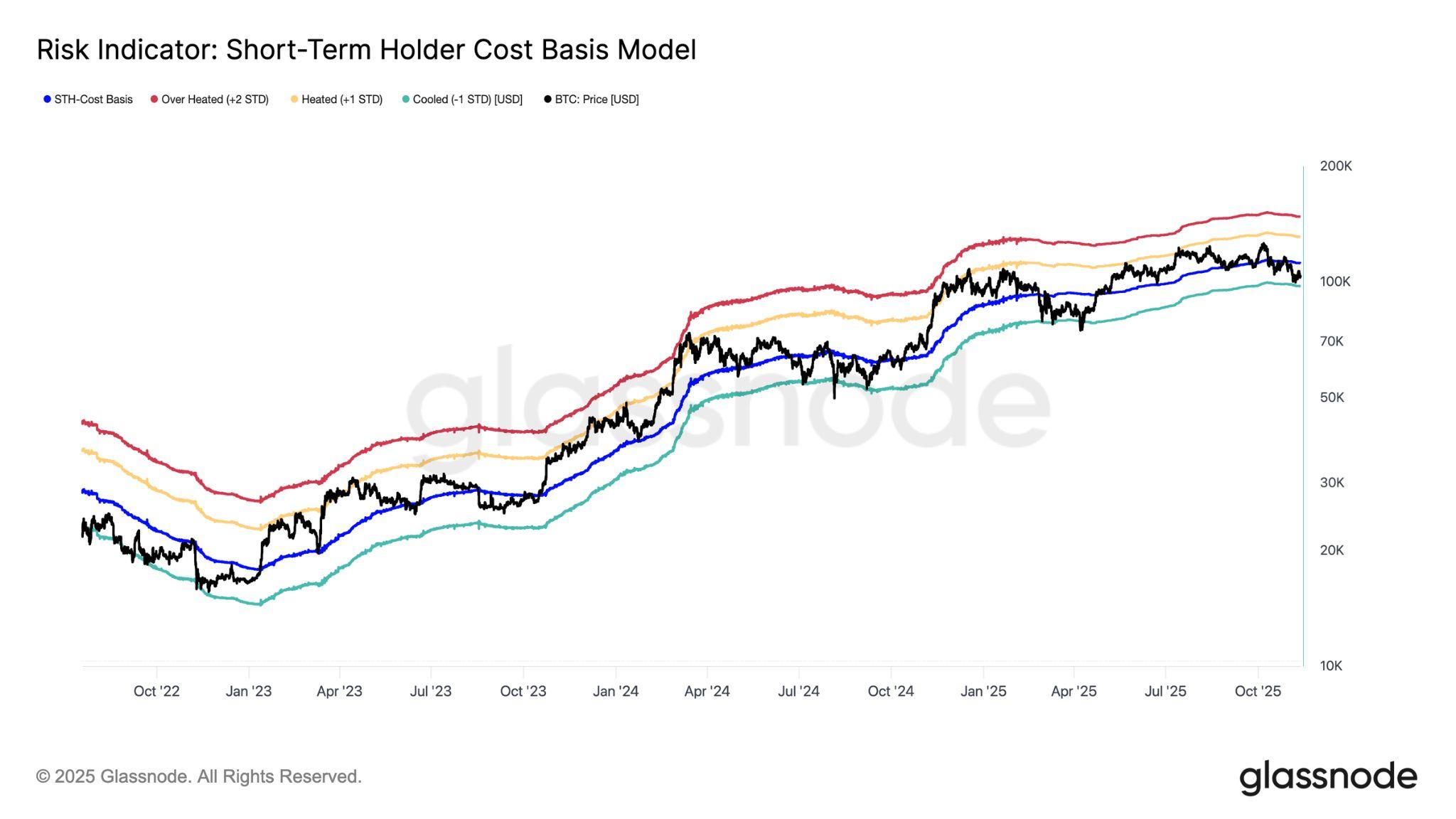
BTC is now trading firmly below the short-term holdersʼ STH) cost basis of $111,900 and the 1 standard-deviation band near $97,500, keeping downside risks alive until this level is reclaimed. Still, on-chain exhaustion signals are emerging.TheSTHRealisedProfit-LossRatiohasdroppedbelow0.20,meaning that over 80 percent of coins moved on-chain are being sold at a loss, a zone historically consistent with local bottoms. Likewise, STH supply in profit has collapsed to 7.6 percent, levels last seen near prior cycle troughs. While further confirmation is needed via renewed demand inflows, this confluence of metrics impliesthatweareduetoformadurablebasesoon,moreintermsof timethan inprice,settingthestageforpotentialstabilisationintolateQ4.
TheUSenterslate2025withanoticeablysoftermacroeconomicbackdrop.The 43-day government shutdown has ended but left clear economic scars, with approximately $7$14 billion in permanent GDP losses, widespread liquidity stress among furloughed workers, and renewed concerns over fiscal brinkmanship ahead of another funding deadline in January. Markets initially shrugged off the disruption, but sentiment deteriorated quickly afterward, with theS&P500pullingbackasinvestorsreassessedfiscalrisksandtheprospectof aFedpause.
At the same time, domestic business sentiment is cooling. The NFIB Small Business Optimism Index slipped in October, reflecting weaker sales, tighter profits, and persistent labour shortages. This fall aligns with weakening global demand:the GlobalPMINewExportOrdersIndex fellto48.5,markingitsfastest contraction in nearly two years, with both manufacturing and services showing broad-baseddeclines.
Inflation adds another layer of pressure. With official CPI data unavailable during theshutdown,alternativeindicatorspointtopersistentpricestickiness,NewYork Fedexpectationssitat3.2percent,andmarket-basedbreakevenshovernear2.2 percent. Elevated inflation expectations and heavy fiscal spending suggest the Fed may keep rates higher for longer, keeping mortgage rates above 6 percent andleavinghouseholdswithlittlerelief.
US crypto regulation took a major step forward this week as a bipartisan Senate draftbillproposedshiftingprimaryoversightofdigitalassetsfromtheSECtothe CFTC. The legislation would classify most tokens as “digital commoditiesˮ and require exchanges and custodians to register under a commodities-style framework, though key questions around DeFi, AML rules, and agency coordinationremainunresolved.
CryptoalsoexpandedfurtherintoentertainmentasTKOGroupHoldings,parentof the UFC, signed a multiyear deal with Polymarket to integrate real-time prediction-market data into live events starting in 2026. The partnership marks a deeperconvergenceofsportsengagementandWeb3tools.
MeanwhileinEurope,theCzechNationalBanklauncheda$1millionpilotportfolio containing Bitcoin, a stablecoin, and a tokenised deposit, its first direct exposure to digital assets. Framed as a technical experiment, the initiative reflects growing central-bank interest in understanding how blockchain-based instruments may shapefuturefinancialinfrastructure.
1.MarketSignals
● BitcoinRecordsThirdLargestPullback offtheCycle
2.GeneralMacroUpdate
● USGovernmentShutdownEnds,Leaving EconomicScarsandHeightenedFiscal Risks
● USSmallBusinessesTurnCautiousas GlobalTradeWeakens
● InflationExpectedtoStayElevatedInto NextYear,

3.NewsFromTheCryptosphere
● SenateDraftLegislationCouldShiftCrypto OversightFromSECtoCFTC
● TKOGroupHoldingsandPolymarketInk MultiyearDeal
● CzechNationalBankLaunches$1MDigital AssetTestPortfolio,IncludingBitcoin
Bitcoinfellbelow$100,000againlastweek,thistimedroppingtoaslowas $93,673.Therecentdeclinehasnowextendedtoalmost26percentfromthe current BTC all time high of $126,110, and marks the third-largest pullback sincethecurrentbullcyclebeganinearly2023.

Risk sentiment on BTC remains subdued amid ongoing macro uncertainty, andtheassethasunderperformedagainsttraditionalfinancialmarkets.While itremainsprematuretoidentifyadefinitivelocalbottombeforeanybroader uptrendresumes,bothon-chainandorderflowindicatorssuggestthatselling pressurefromShort-TermHoldersisbeginningtoease.Thismarksthefirst meaningfulmoderationinsell-sidemomentumsinceearlyOctober,hintingat early signs of stabilisation following one of the sharpest corrections of the cycle.
Glassnode)
SinceearlyOctober,whenBTCfirstbrokebelowtheshort-termholdersʼSTH cost basis (see Figure 2 above), the market has confirmed a range defined by weakeningconvictionanddiminishedliquidity.BTChascontinuedtogrindlower throughoutthemonth,eventuallyfallingbeneaththe1standarddeviationband near$97,500toregisteranewlowof$93,673.Theinabilitytoreclaimeventhe lower statistical band signals vulnerability on the higher timeframes - despite early signs that pressure from short-term holders is beginning to moderateand opens the price to further downside risk. Long-term holders and large holders — the two cohorts responsible for much of the October–November distribution - continue to distribute holdings at a decent pace (see Figure 3 below).

This drawdown mirrors the contraction phases observed during June–October 2024 and February–April 2025, both periods in which BTC stabilised only after anextendedintervaloftradingwithinacompressedlowerrange.Untiltheprice can reclaim the STH cost basis near $111,900 as a sustained support, the probability of revisiting the lower boundary of the current $94,000$106,000 consolidation range remains elevated. Such a recovery would require renewed demand inflows and a shift in market structure; absent that, the market is likely tocontinueoscillatingnearthebottomofthisrange.
Building on this structural backdrop, the sub-$98,000 area has now become a criticalbattlegroundwhereclearsignsofsellerfatiguearebeginningtoemerge.
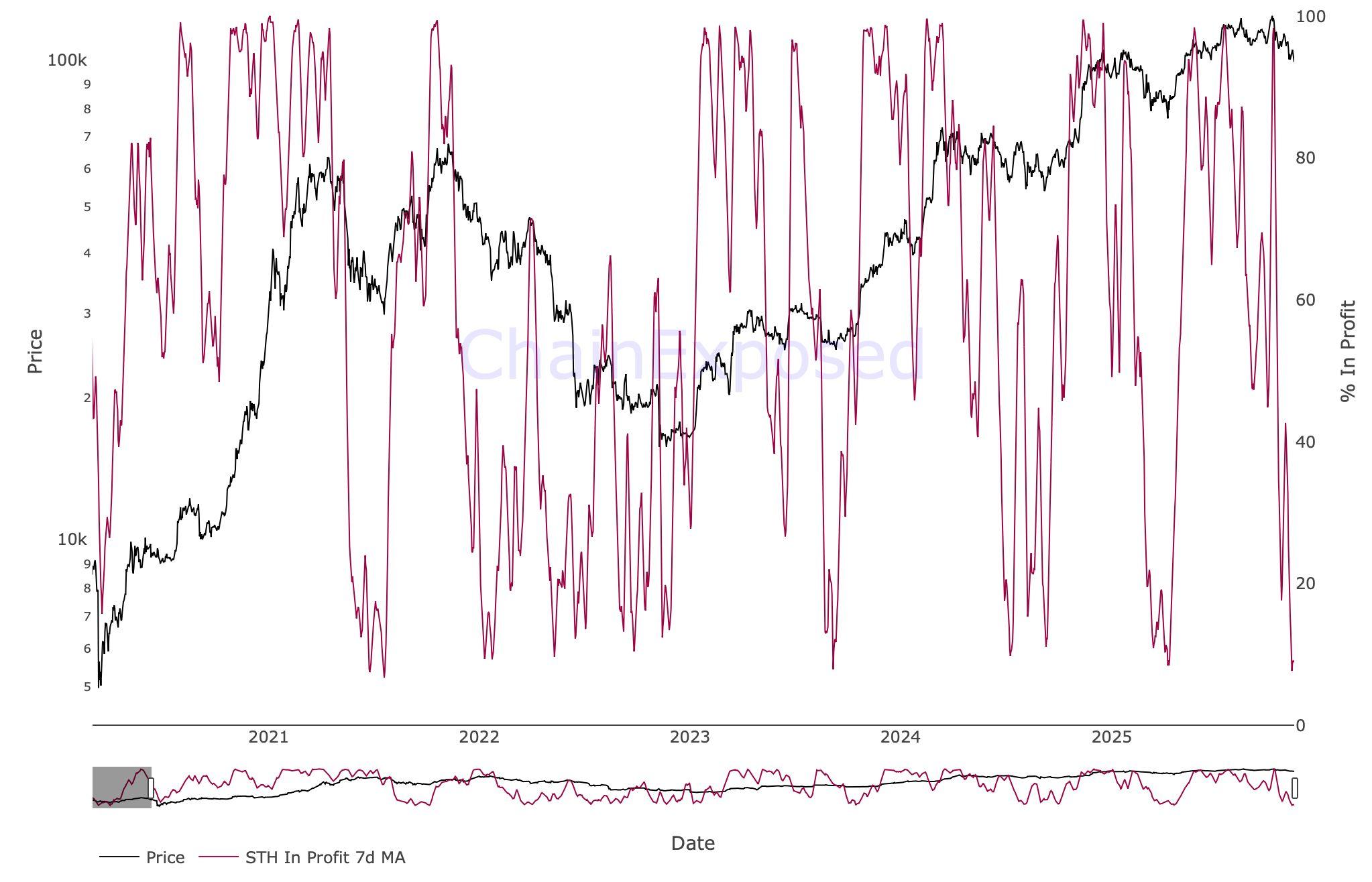
Figure4Short-TermHoldersinProfitSmoothenedCurveforBitcoin. Source:ChainExposed)
Much of the recent downward pressure has come from top buyers within the short-termholdercohort,whohavebeenrealisingsubstantiallossesthroughout thedecline.
As BTC went below the $98,000 level, the STH Realised Profit–Loss Ratio dropped below 0.20, indicating that more than 80 percent of the value being spent on-chain came from coins sold at a loss. Historically, this 80 percent thresholdhasoftenmarkedlocalexhaustionpoints,typicallyleadingtoatleasta moderatereliefbounceevenwithinbroadermacrodowntrends.

STHsupplyinprofithasnowfallento7.6percent.AsillustratedinFigure4 above, such deeply depressed readings frequently accompany local bottom‐formation zones, reflecting the cyclical nature of STH capitulation. Notably, the severity of this capitulation briefly exceeded the prior two major drawdowns of the current cycle, underscoring how top-heavy the market had become and highlighting the importanceofthe$98,000$100,000regionforshort-termstabilisation.
Across multiple historical cycles, sustainable bottoms have only formed after short-term holders have capitulated into losses and not before. The market appears to be approaching that threshold once again, with near-term resilience contingent on whether this capitulation phase can exhaust remaining sell-side pressure. Statistically, given that this is the third largest pullback since 2023 and thesecondlargestsinceBitcoinETFslaunchedacrossmajorUSproviders,itfeels likeitistimeforalocalbottomtobeestablishedrelativelysoon.
This is because we are reaching points where metrics such as Realised Profit-Loss ratio and STH supply in profit indicate that the time seems ripe for a bottom to be found soon. But this is distinct from whether the price is at a level whichconstitutesabottom.
Allthatsaid,orderflowandpriceneedmoreconstructivedevelopmentsbeforewe canassumealocalbottomtobein.

The longest US government shutdown on record ended late on November 12, 2025, after President Trump signed a continuing resolution that funds federal agencies through January 30th, 2026. The 43-day standoff, which began on October 1, inflicted an estimated $7$14 billion in permanent GDP losses, accordingtoCongressionalBudgetOfficeCBOprojections.Whilemuchofthe delayed output will be recovered as agencies work through their backlogs, the CBO notes that a significant portion of economic activity is likely to be lost permanently.
The toll on the middle class was even more visible. Roughly 670,000 federal workers were furloughed, while another 730,000 “essentialˮ employees were required to work without pay, together missing nearly $16 billion in wages. The financial strain pushed thousands toward food banks, forced delayed mortgage payments, and widened household liquidity stress. Although federal employees will receive back pay, contractors, who make up a major portion of the federal workforce, typically receive none, deepening long-term income losses. Meanwhile, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits for 42 million low-income households faced partial or delayed disbursements, intensifyingpressureonsome working-classfamilies.
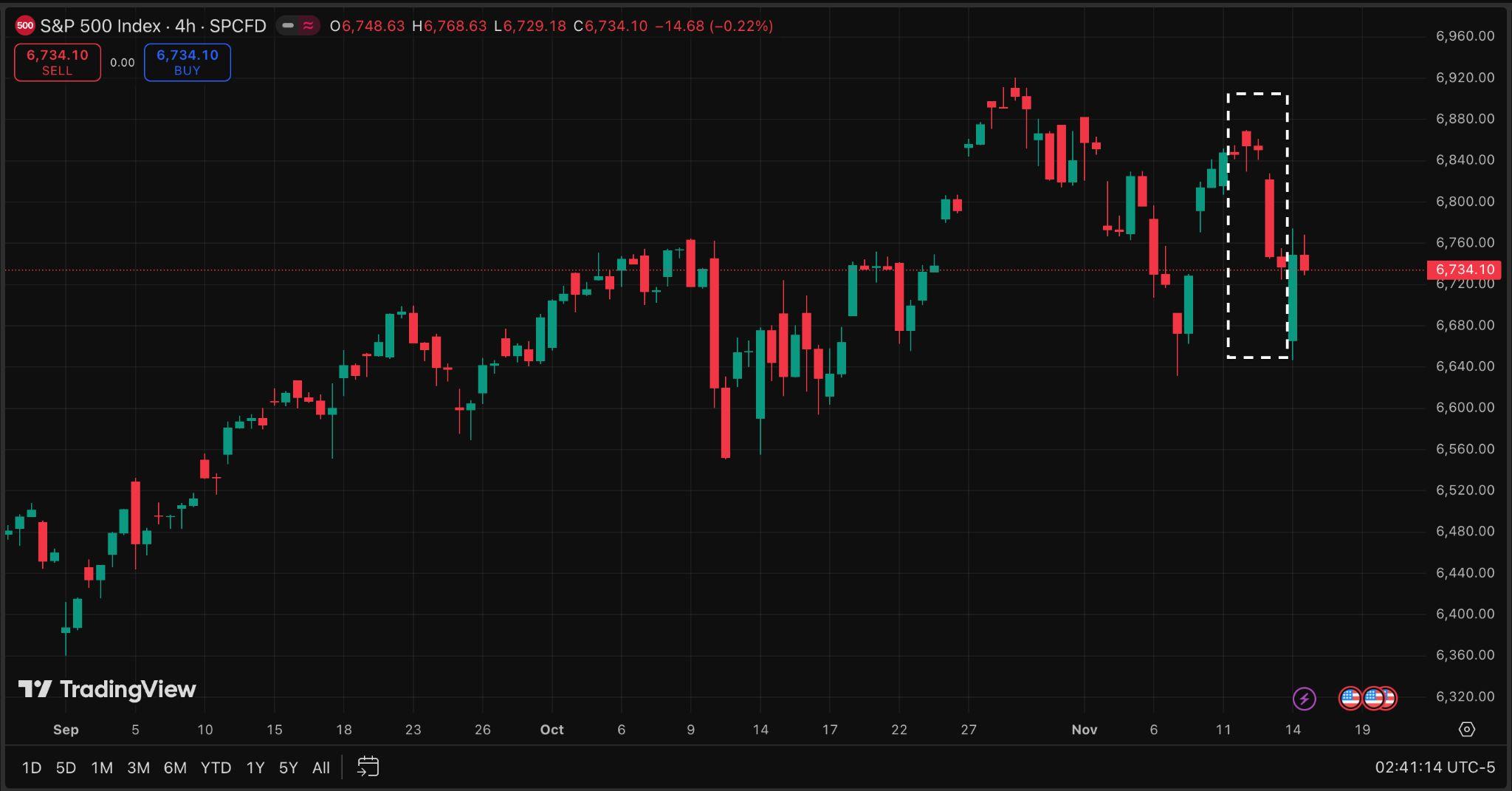
5.S&P500Source:Tradingview)

Financialmarketsinitiallyappearedinsulatedfromthepoliticalgridlock.TheS&P 500 rose 2.4 percent during the closure amid a broader risk-on environment. However,marketoptimismfadedfollowingtheendoftheshutdown,asinvestors reassessed unresolved fiscal cliffs and interpreted incoming data as potential signalsofafutureFederalReservepause,sendingmajorindexessharplylower.
With federal funding now extended for only seven weeks, another episode of brinkmanship looms in January, reviving fears of renewed disruption at a time when economic momentum is already uneven. Economists warn that repeated shutdown cycles undermine confidence, dampen consumer spending, and heighten volatility across risk assets. For now, cautious optimism persists, but the US working and middle class population continues to absorb the clearest andmostimmediatecostsofpoliticaldysfunction.

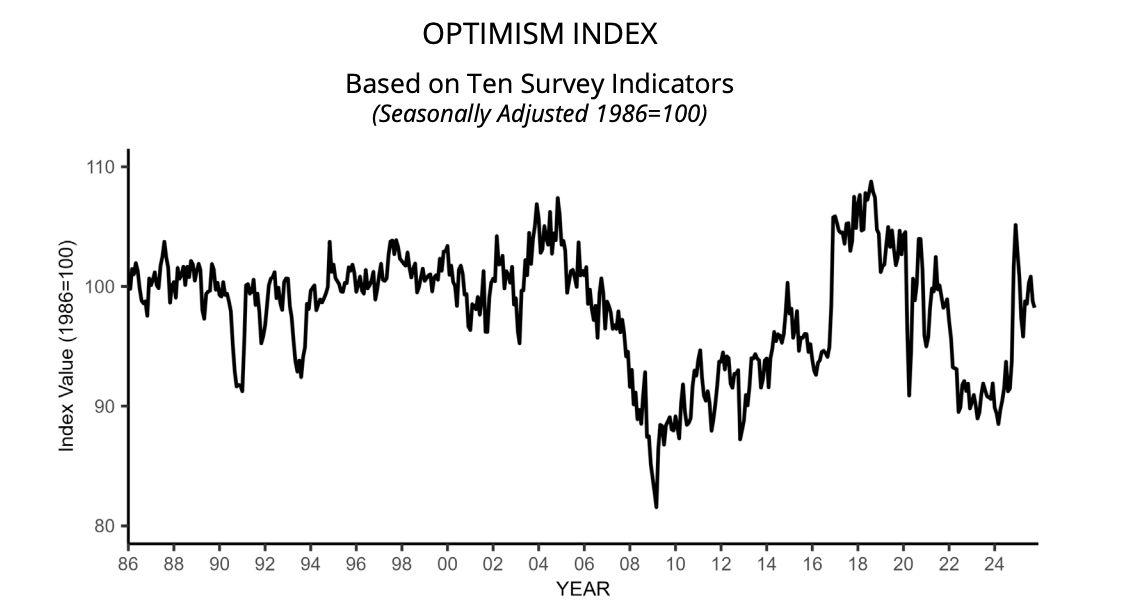
ThelatestdataonAmericaʼssmallbusinesssectorshowsgrowingcautionon Main Street, the part of the economy made up of everyday businesses, workers, and consumers. At the same time, global trade is recording its sharpestdeclineinnearlytwoyears.Together,thesedevelopmentspointtoa potentiallysoftereconomiclandscapeheadinginto2026.

Figure6.SmallBusinessOptimismIndexSource:NFIBResearchCenter)
AccordingtotheNFIBSmallBusinessOptimismIndex,releasedbytheNational Federation of Independent Business last Tuesday, November 11th, sentiment among US small firms slipped by 0.6 points in October to 98.2, though it remainedslightlyabovetheindexʼs52-yearaverageof98.Theaccompanying UncertaintyIndexdroppedsharplyby12pointsto88,itslowestlevelthisyear, signalling that while business owners are uneasy, they are not yet in crisis mode.Smallbusinessownersreportlowersalesandreducedprofits.Thereport showsclearsignsofstrainbeneaththesurface:
● A net negative 13 percent of owners reported higher nominal sales over thepastthreemonths.
● Profittrendsdeterioratedtoanetnegative25percent,thelargestdragon overallsentiment.
● Labour quality remained the top challenge, cited by 27 percent of respondents,thehighestratesincelate2021.

● Thirty-two percent of owners reported job openings they could not fill, consistentwithelevatedlabourtightness.
● Price pressures are easing but still elevated, with 21 percent of owners raisingpricesinOctober.
This cautious domestic backdrop mirrors an even more troubling trend abroad. TheGlobalNewExportOrdersIndex,publishedbyS&PGlobalandJ.P.Morgan last week for October, fell to 48.5, its lowest level since December 2023. A reading below 50 indicates contraction, marking the fastest decline in global exportdemandinalmosttwoyears.Thedownturnwaswidespreadacrossboth manufacturingandservices,especiallyinEuropeandAsia,wherefirmsreported weakeningoverseasdemandamidpolicyuncertainty,geopoliticaltensions,and still-high borrowing costs. The manufacturing sector recorded a faster rate of deteriorationcomparedtoservices.

While the US economy continues to show comparatively resilient domestic activity, history shows that prolonged weakness in global export orders eventually flows into production cuts, slower hiring, and reduced consumer spending. As companies scale back inventory building and delay investment plans,supplychainstendtoexperiencesofteningvolumesthatultimatelyreach retailers. When households sense rising economic uncertainty, discretionary purchasesaretypicallythefirsttoslow.

ForUSsmallbusinesses,alreadyreportingweakersales,hiringdifficulties,and declining profit margins, the global backdrop amplifies existing pressures. A cooling world economy, paired with high interest rates at home, creates an environment in which both demand and risk appetite are likely to weaken further.
Central banks worldwide are monitoring these developments closely. Many policymakers remain focused on services inflation and wage dynamics, meaning restrictive policy may persist longer than businesses anticipate. The NFIBreportandthelatestglobaltradedatarevealaneconomyenteringamore delicate phase, where small business caution at home intersects with weakening demand abroad. As sales soften, profits tighten, and export momentum wanes, both Main Street and global markets may face a more challengingpathahead.

Inflation in the US looks set to remain above the Federal Reserveʼs target for longerthanpolicymakershadhoped,raisingthelikelihoodthatborrowingcosts, especially mortgage rates, will stay elevated well into next year. Due to the government shutdown, there will be no October Consumer Price Index CPI report,thesecondconsecutivemonththatthepublicandfinancialmarketshave hadnoofficialreadonpricingpressures.Thelastavailabledatafor September showed inflation rising 3 percent over the past year and 3.6 percent on a three-monthannualisedbasis.
With official data unavailable, the clearest view comes from alternative indicators. The New York Federal Reserveʼs year-ahead inflation expectations, released last month, point to 3.2 percent inflation over the coming year, far abovetheFedʼs2percenttarget.Market-basedgaugesaremoremoderate,with the five-year, five-year forward breakeven implying a 2.18 percent long-term rate(seeFigure8below),butthesestillsuggestinflationwillrunhotterthanthe Fedprefers.
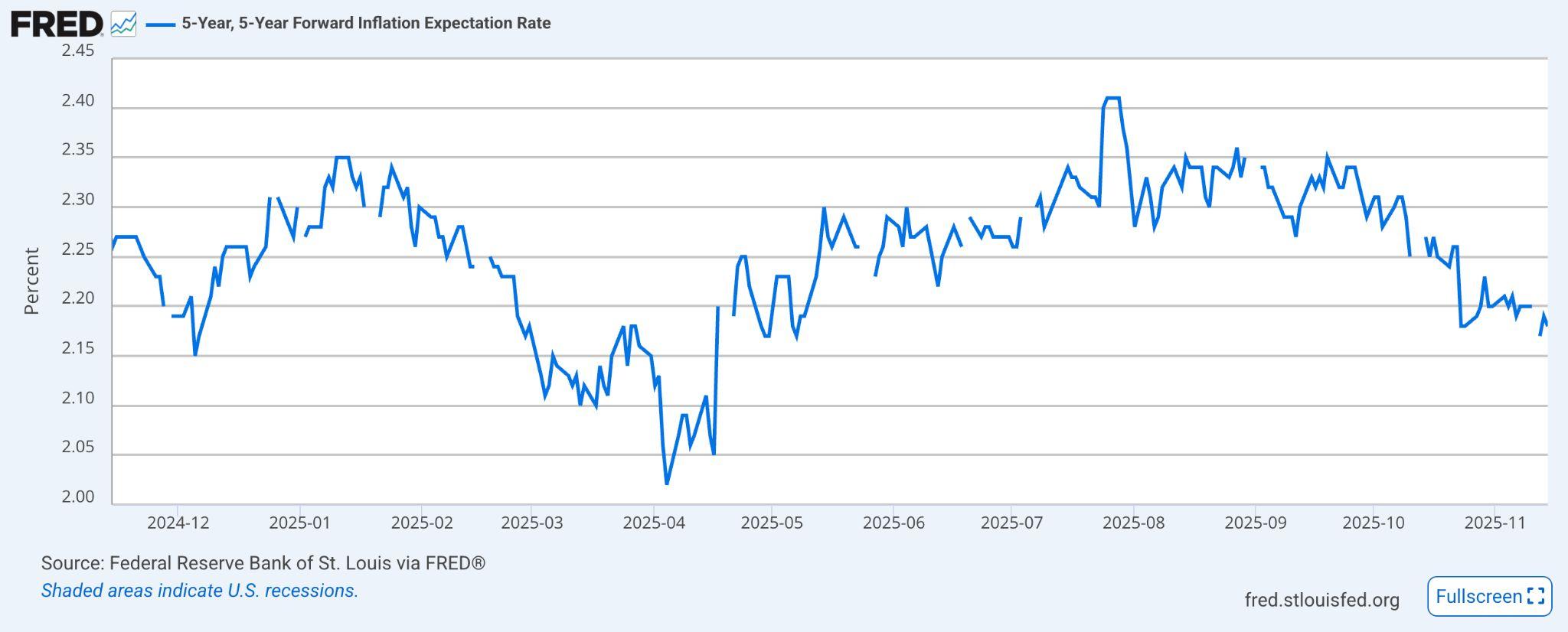
Inflation risks may rise further as expansionary fiscal policies take effect next year,boostingeconomicactivityandfuelingpricepressures.Giventhiscontext,it isprudentandlikelythattheFederalReservewillwaittoobservethefullimpact of these policies before making any major shifts to interest rates. However, the consequence is clear: the groups most vulnerable in todayʼs economy will continuetofeelthestrainthroughareducedstandardofliving,limitedeconomic opportunities,andwagesthatfailtokeeppacewithrisingcosts.

These inflation dynamics feed directly into the housing market, where there is littlechanceofmeaningfulreliefforUSmortgageborrowers.Expansionaryfiscal spending, increased government borrowing, and a surge in private-sector demandforcapitalareallintensifyingcompetitionforfunding.Theentryofmajor technologycompanies,or“hyperscalersˮ,intocapitalmarketstofinancemassive data-centerconstructionisfurthertighteningconditions.
Inthisenvironment,long-terminterestratesremainunderupwardpressure,and 30-yearmortgageratesareexpectedtostayabove6percentfortheforeseeable future. The only two events that could materially lower mortgage rates: a near-term recession or a renewed effort by the Federal Reserve to purchase mortgage-backedsecurities.Asofnow,neitherappearslikely.
For US households already struggling with high living costs, the combination of persistentinflationandstubbornlyhighmortgageratesmeansaffordabilityissues will remain front and center. With both price pressures and borrowing costs proving sticky, consumers may face another challenging year as the economy adjuststoanewnormal.



A bipartisan draft bill introduced by John Boozman RArk. and Cory Booker DN.J.wouldfundamentallyrealigntheregulatoryarchitecturegoverningdigital assets by assigning primary authority to the Commodity Futures Trading Commission CFTC) instead of the Securities and Exchange Commission SEC. Under the proposal, most cryptocurrencies would be defined as “digital commoditiesˮ, for example, as any fungible digital asset that can be exclusively possessed and transferred on a cryptographically secured distributed ledger withoutrelianceonanintermediary.
The draft grants the CFTC several expanded powers: it would oversee registration of spot-market trading platforms (exchanges), brokers, and custodiansinthedigital-assetspace;imposenewdisclosureandrecord-keeping obligations; enforce anti-fraud and fund-segregation rules; and collect transaction fees for its regulatory operations. Importantly, the bill outlines a transition period, roughly 270 days after enactment, for existing operators to complywhilethenewregimebecomeseffective.Despiteitsbroadambition,the draft leaves several key issues unresolved. Many sections remain in bracketed form, indicating further negotiation is required, including how to regulate decentralised finance DeFi protocols, how AML (anti-money-laundering) rules apply,andhowtheCFTCandSECwillcoordinatetheirsharedjurisdictions.Also under scrutiny is whether the CFTC is adequately resourced: with roughly 543 full-timestaffcomparedtotheSECʼs4,200,questionsremainaboutwhetherthe agencycanmanagethenewworkload.
From a market perspective, supporters argue this legislation provides long-sought clarity by replacing the SECʼs enforcement-first framework with a regulatory model more familiar to commodities and futures markets. However, critics warn that shifting so much authority to the CFTC without concurrent safeguardscouldweakeninvestorprotectionsandcreatearegulatoryvacuumin parts of the ecosystem. For instance, some argue the SECʼs securities-law tools arevitalforprotectingretailinvestorsintokenisedassets.
The path ahead remains challenging: the draft must still be voted out of the Senate Agriculture Committee (which oversees the CFTC) and the Senate Banking Committee (which oversees the SEC, then reconciled with the House versionofthelegislation.AfullSenatefloorvotemaynotoccuruntilearly2026, dependingontheprogressofnegotiationsandtheamendmentsmadetothebill.



Inasignificantcrossoverbetweencombatsportsandcrypto‑finance,TKOGroup Holdings, the parent company of the UFC and Zuffa Boxing, has entered a multiyear partnership with Polymarket, a blockchain‑based prediction‑market platform, to integrate real‑time prediction‑market functionality into live event broadcasts and in‑arena experiences. The deal positions UFC and Zuffa as the firstmajorsportsorganisationstoembedprediction‑markettechnologyalongside traditionalsports‑bettingandfan‑engagementtools.
Under the agreement, Polymarket will supply live visualisations of fan‑sentiment data and momentum indicators during fights, enabling viewers and arena audiences to track how expectations evolve in real time with every round. This additional layer of interactivity is meant to shift passive spectatorship toward more engaged participation. As Polymarket CEO Shayne Coplan noted, the initiative gives fans “a new way to be part of the action, not just watching outcomesbutwatchingtheworldʼsexpectationsevolvewitheveryround.ˮ
ForTKO,executivechairman&CEO Ariel Emanueldescribedthecollaborationas unlocking “a new dimension of fan engagement,ˮ and said that integrating Polymarket into the UFC/Zuffa live experience will meaningfully enhance how fans interact with events. The move reflects a broader trend of sports‑entertainmentcompaniesexploringweb3andblockchain‑enabledtoolsto boostviewership,retentionandmonetisation.
The deal comes as Polymarket expands beyond its earlier focus on politics and globaleventsintoliveentertainmentandsport.
Overall, the announcement signals a meaningful step toward merging prediction‑market mechanics with mainstream sport‑entertainment: a shift that could open new revenue streams (via sponsorship, data licensing, fan‑data monetisation) and raise novel questions around regulation, data privacy and the overlapwithsports‑bettingframeworks.


The Czech National Bank CNB) has initiated its first direct experiment with blockchain-based assets, establishing a $1 million pilot portfolio containing Bitcoin, a USD-denominated stablecoin, and a tokenised deposit. The Central Bankclarifiedthatthispurchasesitsoutsideitstraditionalinternationalreserves and will not be expanded, framing the move strictly as a controlled trial rather thanastrategicrepositioning.
The project aims to provide the CNB with practical experience in holding and managing digital assets while evaluating the technical, legal, and operational requirementsinvolved.
"TheaimwastotestdecentralisedBitcoinfromthecentralbank'sperspective and to evaluate its potential role in diversifying our reserves," Governor Aleš Michl said. He added that internal discussions later widened the initiative to include research on future payment systems and asset tokenisation. A full assessmentisexpectedwithintwotothreeyears.
The central bank noted that the pilot will help it compare different blockchain instruments while examining secure storage, settlement procedures, accounting treatment, auditing requirements, key-management systems, multi-layerapprovals,crisisprotocols,andAMLsafeguards.
Although much of this is theoretically understood, the CNB emphasised that real-worldoperationsprovidetheonlymeaningfulinsights.
Michl also underscored that the test has no link to monetary policy or foreign exchangemanagement."Thekorunaisourlegaltender,"hesaid."TheCNBwill continue to strive to keep inflation low and the koruna strong. However, new ways of paying and investing will emerge rapidly in the years ahead... As a centralbank,wewanttotestthispath."

The small size of the portfolio means market swings will not materially affect the bank. Michl cautioned that the project should not be interpreted as a recommendation to retail investors, adding: "It is important to emphasise that thevalueofBitcoinmayfluctuatesubstantially.NoinvestorshouldbuyBitcoin withoutbeingawareofthesignificantrisksinvolved."
The CNBʼs move comes after a year of gradual exploration into digital assets, includingpublicdiscussionsaboutpotentialbitcoinexposureandasmallequity investmentinCoinbaseaspartofbroaderdiversificationefforts.Whilethenew test portfolio does not signal a shift toward Bitcoin-backed reserves, it represents a meaningful milestone: the first time the Czech central bank has directly acquired Bitcoin. This step underscores the CNBʼs growing interest in understanding how emerging technologies, from blockchain to tokenised assets,couldshapethefutureofpayments,reservemanagement,andfinancial marketinfrastructure.
