Cambridge International AS Level Physics
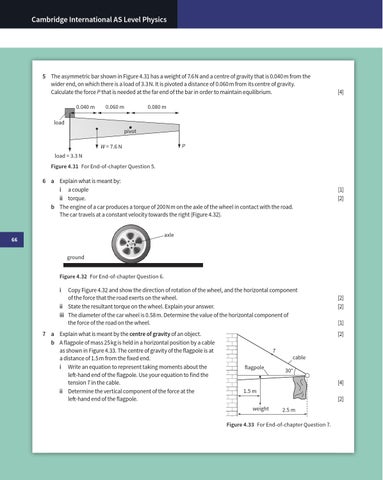
5 The asymmetric bar shown in Figure 4.31 has a weight of 7.6 N and a centre of gravity that is 0.040 m from the wider end, on which there is a load of 3.3 N. It is pivoted a distance of 0.060 m from its centre of gravity. Calculate the force P that is needed at the far end of the bar in order to maintain equilibrium. 0.040 m
0.060 m
[4]
0.080 m
load pivot P
W = 7.6 N load = 3.3 N Figure 4.31 For End-of-chapter Question 5.
6 a Explain what is meant by: i a couple ii torque. b The engine of a car produces a torque of 200 N m on the axle of the wheel in contact with the road. The car travels at a constant velocity towards the right (Figure 4.32).
[1] [2]
axle
66
ground Figure 4.32 For End-of-chapter Question 6.
i
Copy Figure 4.32 and show the direction of rotation of the wheel, and the horizontal component of the force that the road exerts on the wheel. ii State the resultant torque on the wheel. Explain your answer. iii The diameter of the car wheel is 0.58 m. Determine the value of the horizontal component of the force of the road on the wheel.
7 a Explain what is meant by the centre of gravity of an object. b A flagpole of mass 25 kg is held in a horizontal position by a cable as shown in Figure 4.33. The centre of gravity of the flagpole is at a distance of 1.5 m from the fixed end. i Write an equation to represent taking moments about the left-hand end of the flagpole. Use your equation to find the tension T in the cable. ii Determine the vertical component of the force at the left-hand end of the flagpole.
[2] [2] [1] [2]
T flagpole
cable 30째
[4] 1.5 m
[2] weight
2.5 m
Figure 4.33 For End-of-chapter Question 7.