Cambridge International AS Level Chemistry
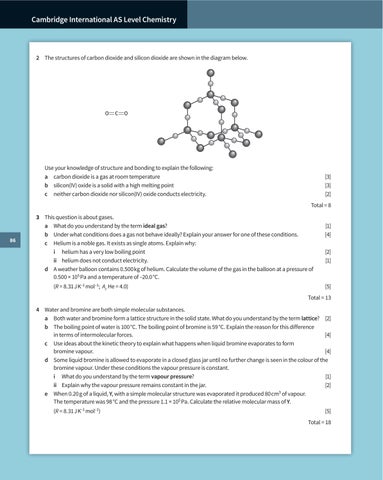
2 The structures of carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are shown in the diagram below.
O
C
O
Use your knowledge of structure and bonding to explain the following: a carbon dioxide is a gas at room temperature b silicon(IV) oxide is a solid with a high melting point c neither carbon dioxide nor silicon(IV) oxide conducts electricity.
[3] [3] [2] Total = 8
86
3 This question is about gases. a What do you understand by the term ideal gas? b Under what conditions does a gas not behave ideally? Explain your answer for one of these conditions. c Helium is a noble gas. It exists as single atoms. Explain why: i helium has a very low boiling point ii helium does not conduct electricity. d A weather balloon contains 0.500 kg of helium. Calculate the volume of the gas in the balloon at a pressure of 0.500 × 105 Pa and a temperature of –20.0 °C. (R = 8.31 J K–1 mol–1; Ar He = 4.0)
[1] [4] [2] [1]
[5] Total = 13
4 Water and bromine are both simple molecular substances. a Both water and bromine form a lattice structure in the solid state. What do you understand by the term lattice? [2] b The boiling point of water is 100 °C. The boiling point of bromine is 59 °C. Explain the reason for this difference in terms of intermolecular forces. [4] c Use ideas about the kinetic theory to explain what happens when liquid bromine evaporates to form bromine vapour. [4] d Some liquid bromine is allowed to evaporate in a closed glass jar until no further change is seen in the colour of the bromine vapour. Under these conditions the vapour pressure is constant. i What do you understand by the term vapour pressure? [1] ii Explain why the vapour pressure remains constant in the jar. [2] e When 0.20 g of a liquid, Y, with a simple molecular structure was evaporated it produced 80 cm3 of vapour. The temperature was 98 °C and the pressure 1.1 × 105 Pa. Calculate the relative molecular mass of Y. (R = 8.31 J K–1 mol–1)
[5] Total = 18