Cambridge International AS and A level Physics
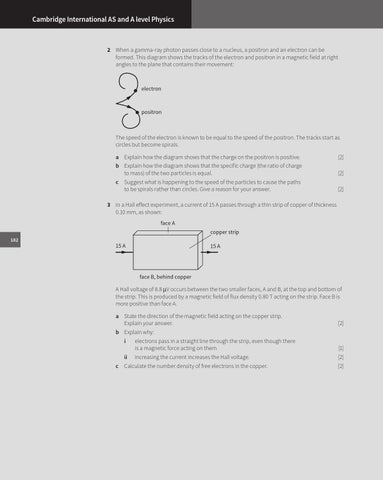
2 When a gamma-ray photon passes close to a nucleus, a positron and an electron can be formed. This diagram shows the tracks of the electron and positron in a magnetic field at right angles to the plane that contains their movement:
electron
positron
The speed of the electron is known to be equal to the speed of the positron. The tracks start as circles but become spirals. a Explain how the diagram shows that the charge on the positron is positive.
[2]
b Explain how the diagram shows that the specific charge (the ratio of charge to mass) of the two particles is equal.
[2]
c Suggest what is happening to the speed of the particles to cause the paths to be spirals rather than circles. Give a reason for your answer.
[2]
3 In a Hall effect experiment, a current of 15 A passes through a thin strip of copper of thickness 0.10 mm, as shown: face A copper strip 182
15 A
15 A
face B, behind copper
A Hall voltage of 8.8 ÎźV occurs between the two smaller faces, A and B, at the top and bottom of the strip. This is produced by a magnetic field of flux density 0.80 T acting on the strip. Face B is more positive than face A. a State the direction of the magnetic field acting on the copper strip. Explain your answer.
[2]
b Explain why: i
electrons pass in a straight line through the strip, even though there is a magnetic force acting on them
[1]
increasing the current increases the Hall voltage.
[2]
c Calculate the number density of free electrons in the copper.
[2]
ii