S CARBON DIOXIDE IN THE ATMOSPHERE
respiration, burning and decay
dissolves
burning fossil fuels
heating in industry
CHALK and LIMESTONE
oil and natural gas
GREEN PLANTS photosynthesis
concentration in shells
COAL
sedimentation
decay and pressure
decay and pressure
respiration and decay
feeding ANIMALS
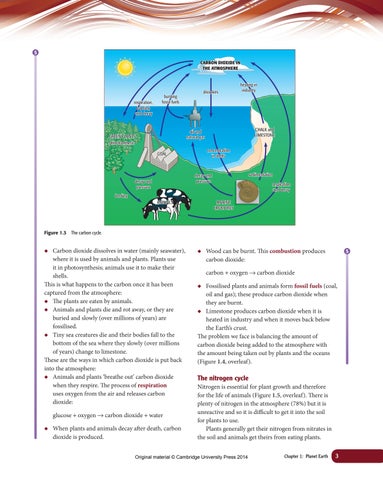
Figure 1.3
The carbon cycle.
◆
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water (mainly seawater), where it is used by animals and plants. Plants use it in photosynthesis; animals use it to make their shells. This is what happens to the carbon once it has been captured from the atmosphere: ◆ The plants are eaten by animals. ◆ Animals and plants die and rot away, or they are buried and slowly (over millions of years) are fossilised. ◆ Tiny sea creatures die and their bodies fall to the bottom of the sea where they slowly (over millions of years) change to limestone. These are the ways in which carbon dioxide is put back into the atmosphere: ◆ Animals and plants ‘breathe out’ carbon dioxide when they respire. The process of respiration uses oxygen from the air and releases carbon dioxide: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water ◆
MARINE CREATURES
When plants and animals decay after death, carbon dioxide is produced.
◆
Wood can be burnt. This combustion produces carbon dioxide:
S
carbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide ◆
Fossilised plants and animals form fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas); these produce carbon dioxide when they are burnt. ◆ Limestone produces carbon dioxide when it is heated in industry and when it moves back below the Earth’s crust. The problem we face is balancing the amount of carbon dioxide being added to the atmosphere with the amount being taken out by plants and the oceans (Figure 1.4, overleaf).
The nitrogen cycle Nitrogen is essential for plant growth and therefore for the life of animals (Figure 1.5, overleaf). There is plenty of nitrogen in the atmosphere (78%) but it is unreactive and so it is difficult to get it into the soil for plants to use. Plants generally get their nitrogen from nitrates in the soil and animals get theirs from eating plants.
Original material © Cambridge University Press 2014
Chapter 1: Planet Earth
3