PERIOD. COMMUNITY UNITY NETWORK 4 TRANSFORMATION & SOLIDARITY
You would think that at 25 years old I would be making a period guide for young people who are just starting their menstruation journey...but no. (However, this guide would be great for them too.)
Unfortunately, reproductive health education is subpar in the Southeastern United States (and The United States in general). The female reproductive system is getting the least attention. Most of us went through school with only a couple of days learning about our bodies, learning surface-level information about the ovaries, egg, fallopian tube, learning about how our period means we can get pregnant, learning that we must stay abstinent to protect ourselves from pregnancy and STDs (birth control education is either glossed over or left out completely), learn that skirts 4" above the knee is too short and spaghetti straps make boys act up. If we were lucky, we could get more information at home. & if we were reaLLY REALLY lucky our moms dropped this book on our lap.

Although that book was a little traumatizing and may not be the best source of information, it taught me more than school ever did. What none of these things ever taught me was the 4 phases of the menstrual cycle, the exact hormones at play, etc. There is so much to the menstrual cycle I didn’t learn until I downloaded TikTok, as ridiculous as that sounds... it’s true.
That’s why I created this zine, so we can know exactly what's up with our bodies.

COMMUNITY UNITY NETWORK 4 TRANSFORMATION & SOLIDARITY
5 6 7 9 11 19 The Process Hormonal Changes Symptoms & Side Effects Menstrual Blood Color Exploring Period Products Managing the Menstrual Phase THE MENSTRUAL PHASE THE BASICS 3 24 25 26 27 28 The Process Hormonal Changes Follicular & Proliferative Phase: What is the difference? Symptoms & Side Effects Managing the Follicular Phase THE FOLLICULAR PHASE 29 31 32 33 35 The Process Hormonal Changes Symptoms & Side Effects Conditions affecting Ovulation Managing Ovulation OVULATION 37 38 39 40 41 44 The Process Hormonal Changes Luteal Phase or Secratory Phase? Symptoms & Side Effects Discharge Color Managing Ovulation THE LUTEAL PHASE RESOURCES 48 GLOSSARY 49 STAGES OF LIFE 46
B A S I C S
H E

TThemenstrualcycleisa beautifullyorchestratedprocess whereanetworkofhormonesand physiologicalchangeswork togethertopreparethebodywith auterusforapotentialpregnancy. Eachmonth,thisharmoniouscycle repeats.
WHENITUSUALLYSTARTS:
Mostindividualsexperiencetheirfirstmenstrual cycle,knownasmenarche,betweentheagesof 9and16.Theaverageageisaround12.
WHENITUSUALLYENDS:
Menstruationcontinuesuntilmenopause,Itis diagnosedafter12consecutivemonthswithouta menstrualperiod& typicallyoccursbetweenthe agesof45and55,markingtheendofthe reproductiveyears.
CYCLELENGTH
Atypicalmenstrualcyclelastsabout28days, butitcanrangefrom21to35daysinadultsand from21to45daysinteens.
FunFact:
Didyouknow?Theword"menstruation" comesfromtheLatinword"menses,"which means "month."Thishighlightsthecyclical natureoftheprocess!
3

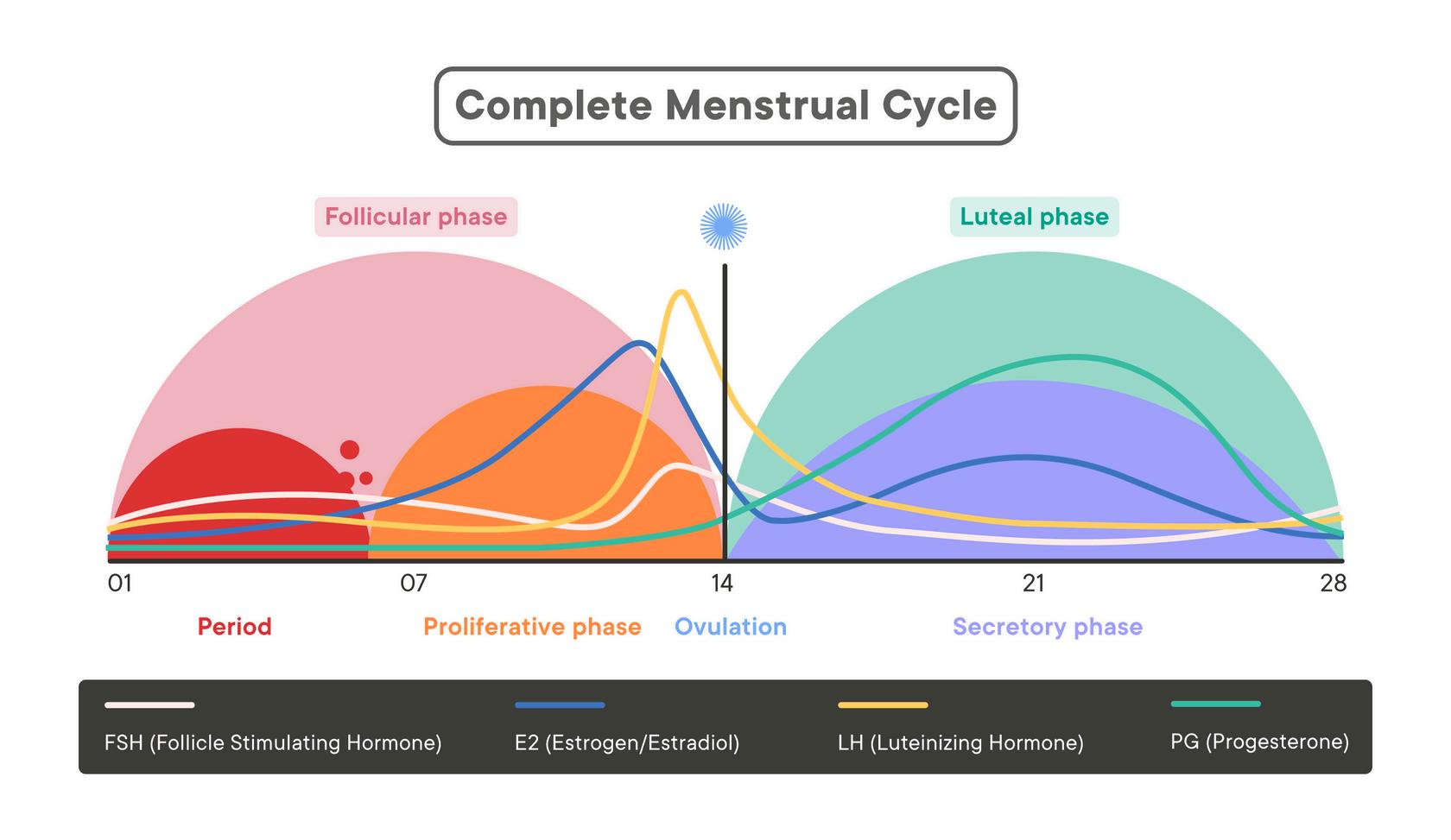
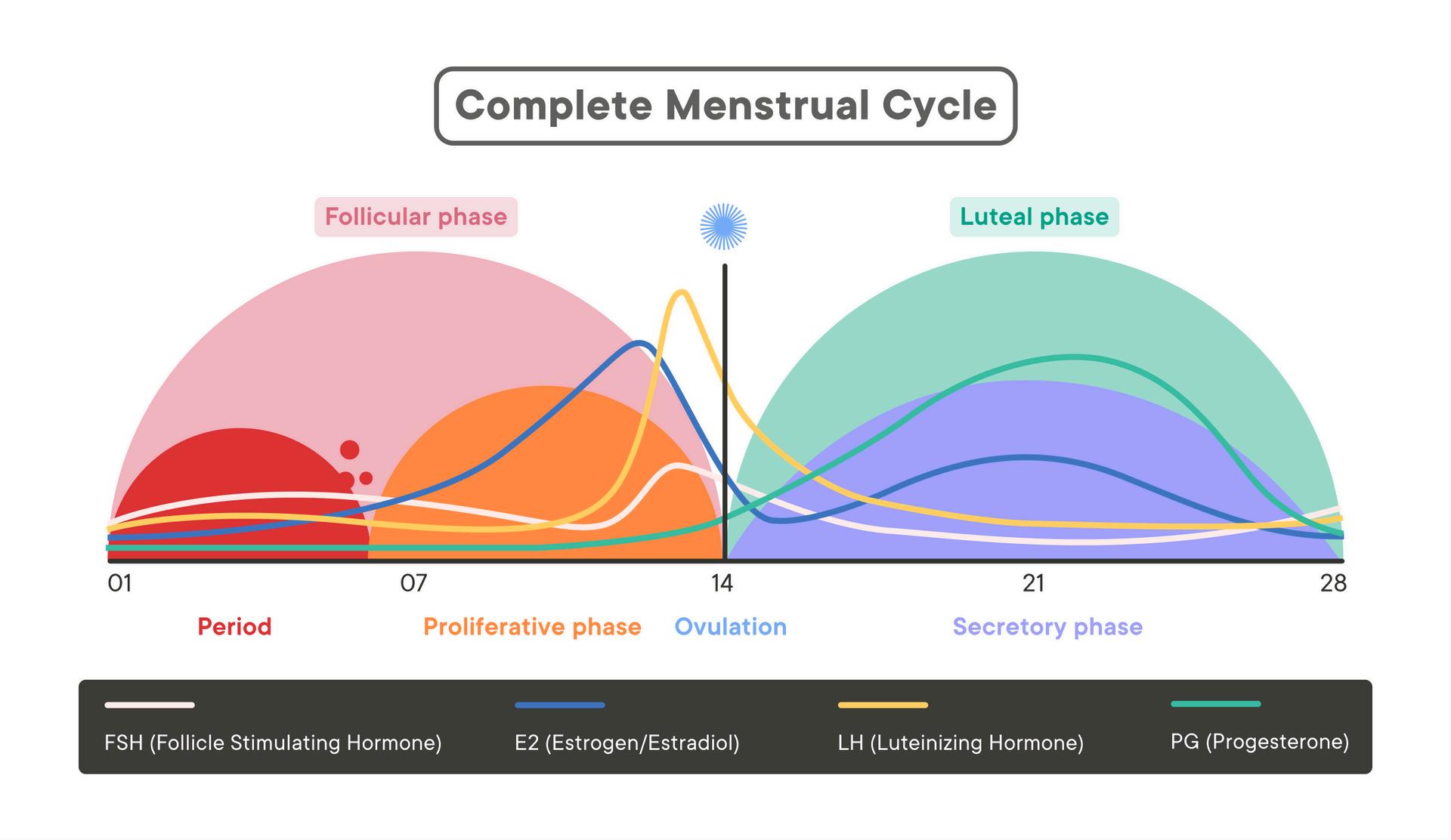
PHASESOFTHECYCLE:
MenstrualPhase:Thesheddingoftheuterine lining,lasting3-7days
FollicularPhase:Thetimebetweenthefirstday oftheperiodandovulation,wherefolliclesinthe ovariesmature.
Ovulation:Thereleaseofamatureeggfromthe ovary,occurringaroundthemidpointofthe cycle.
LutealPhase:Theperiodbetweenovulationand thestartofmenstruation,wheretheuterine liningthickensinpreparationforapotential pregnancy.
Themenstrualcyclecanbecomparedtothechanging seasons,eachphaserepresentingadistincttimewith uniquecharacteristicsandpurposes.Thisanalogyhelpsto understandthecyclicalnatureoftheprocessanditsimpact onthebody.
MenstrualPhase Winter Rest,renewal, shedding.
LutealPhase Fall Preparation, introspection, mixedenergy
Ovulation Phase Summer Peakfertility, vitality,confidence
FollicularPhase Spring Growth,new beginnings, increasedenergy
T H E B A S I C S
4

T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
Themenstrualphase,often referredtoas"yourperiod,"marks thebeginningofanewmenstrual cycle.Thisphaseinvolvesthe sheddingoftheuterinelining,a crucialpartofthebody's reproductiveprocess.Let’sdive deeperintowhathappensduring thisphase.
SHEDDINGOFUTERINELINING
Process:
Theuterinelining,orendometrium,buildsup eachcycleinpreparationforapotential pregnancy.Iffertilizationdoesnotoccur, hormonalchangessignalthebodytoshedthis lining.
WhatHappens:
Theendometriumbreaksdownandexitsthe bodythroughthecervixandvaginaas menstrualblood.
ComponentsofPeriodBlood:
Menstrualbloodisnotjustblood.Itincludes blood,cervicalmucus,vaginalsecretions,and endometrialtissue.
AmountofBloodLoss:
Onaverage,apersonlosesabout30-40 milliliters(2-3tablespoons)ofbloodduringtheir period.Thiscanrangefrom10to80milliliters, dependingontheindividual.
5

Estrogen:
HORMONALCHANGES
Estrogenlevelsarelowatthestartofthe menstrualphasebutbegintorisetowardsthe end.Thelowlevelscontributetothesheddingof theuterinelining,whilethegradualincrease helpsintheregenerationoftheendometrial liningandthematurationofovarianfollicles
Follicle-StimulatingHormone(FSH):
Secretedbythepituitarygland,FSHispivotalat thestartofthefollicularphase.Itsprimaryroleis tostimulatethegrowthandmaturationof ovarianfollicles.
LuteinizingHormone(LH):
LHremainsrelativelylowbutstartstoincrease graduallyasthemenstrualphaseprogresses, settingthestageforthemid-cycleLHsurgethat triggersovulation.
Progesterone
Thedropinprogesteronelevelsfromthe previouslutealphasetriggersthesheddingof theuterinelining.Lowprogesteronelevels indicatethebodyisnotmaintaininga pregnancy,allowingthecycletorestart.
Testosterone:
Testosteronelevelsarerelativelylowbutpresent duringthemenstrualphase.
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
6
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
SYMPTOMS&SIDEEFFECTS
Cramps(Dysmenorrhea):

Highlevelsofprostaglandins,hormone-likesubstances,cause theuterustocontract,leadingtopain.
Mildtomoderatecrampsarenormal,butseverecrampsmay suggestelevatedprostaglandinlevelsorunderlyingconditions likeendometriosis.
Irritability &ChangesinMood:
Fluctuationsinestrogenandprogesteroneaffect neurotransmitterlevels(e.g.,serotonin),influencingmood.
Severechangesinmood,feelingsofdepression,and/orsuicidal thoughtsmightindicatepremenstrualdysphoricdisorder (PMDD)orsignificanthormonalimbalances.
Fatigue:
HormonalInsight:Lowerlevelsofestrogenandprogesterone duringmenstruationcancontributetotirednessandlowenergy.
CheckforAnemia:Heavybleedingcanleadtoirondeficiency, whichalsocausesfatigue
Headaches:
Adropinestrogenlevelsjustbeforeandduringmenstruation cantriggerheadachesormigraines. Ifheadachesaresevereorfrequent,itmayindicateaneedfor hormonalevaluation.
Bloating:
Fluctuationsinestrogenlevelscancausewaterretention Drinkingwaterandreducingsaltintakecanhelpmanagethis symptom
BreastTenderness:
Fluctuatingestrogenlevelsbeforeandduringthemenstrual phasecanleadtobreasttissueswellingandtenderness. Iftendernessisoverlypersistentandsevere,itmightindicatea hormonalimbalanceorotherconditions.
Acne:
Increasedandrogens(malehormonesliketestosterone)can leadtohighersebumproduction,causingacne.
Persistentacnemightsuggestpolycysticovarysyndrome (PCOS)orotherandrogen-relatedconditions.
Nausea:
Fluctuationsinhormonelevels,particularlyprostaglandins,can affectthedigestivesystem,leadingtonausea.
Occasionalmildnauseaiscommon,butpersistentorsevere nauseamightindicatehormonalimbalancesorunderlying conditions.
7

LessCommonSymptomsandWhatTheyMightIndicate:
1.SevereCramps:
Apossibleindicationof:
Endometriosis,whereuterine-liketissuegrowsoutsidethe uterus,isoftenlinkedtohormonalimbalances.
PolycysticOvarySyndrome(PCOS),isahormonaldisorder thatdisruptsthehormonalbalanceswithexcessivelevels ofandrogens(malehormones),andtheformationof smallfluid-filledsacs(cysts)ontheovaries.
2.ShortMenstrualCycles(Lessthan21Days):
Thiscouldindicatealutealphasedefect,whereprogesterone levelsareinsufficienttomaintainalongercycle.
3.VeryLightPeriodsorMissedPeriods:
PossibleCause:Lowestrogenlevels,highstress,significant weightloss,orthyroiddysfunction.
4.UnusualVaginalDischarge:
Asourorfishysmell,unusualcolor,orconsistency PossibleCondition:Infectionsorhormonalimbalances affectingthevaginalflora.
5.HotFlashesorNightSweats:
PossibleConditions:
Perimenopause,thetransitionphasebeforemenopause, markedbyfluctuatingestrogenlevels.
Endometriosis,whereuterine-liketissuegrowsoutsidethe uterus,isoftenlinkedtohormonalimbalances.
PolycysticOvarySyndrome(PCOS),ahormonaldisorder thatdisruptsthehormonalbalanceswithexcessivelevels ofandrogens(malehormones),andtheformationof smallfluid-filledsacs(cysts)ontheovaries.
6.HeavyBleeding(Menorrhagia):
Needingtochangemenstrualproductseveryhourorpassing largeclotscouldbeasignofmenorrhagia. Canbeasignofhormonalimbalances,suchaslow progesteroneorhighestrogenlevels,leadingtoathicker uterinelining.
HealthCheck:Persistentheavybleedingshouldbeevaluated forconditionslikefibroids,polyps,orthyroidissues.
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
SEVERESIDEEFFECTSARENOTNORMAL
8
BrightRed:
WhatitIndicates:
Freshblood,typicallyseenatthebeginningorduringthepeakofyourperiod.
HormonalSignificance:
Highestrogenlevelsstimulatethesheddingoftheuterinelining,resultingina vibrantredcolor.
HealthyFlow:
Brightred,bloodsuggestsanormalandhealthymenstrualflow,withtheuterus effectivelysheddingitslining.
DarkRed/Brown:
WhatitIndicates:
Olderblood,oftenobservedatthestartorendofyourperiod.Darkredorbrown menstrualbloodtowardstheendoftheperiodisconsiderednormalasit representsolderbloodthathastakenlongertoexittheuterus
HormonalSignificance:
Asyourperiodprogresses,thebloodmaytakeonadarkerhueasitspendsmore timeintheuterusbeforebeingexpelled.Mayindicatelowprogesteronelevelsif sideeffectsindicatinglowerprogesteroneoccur.
NormalVariation:
Darkredorbrownbloodisacommonoccurrenceandisnotusuallycausefor concern.Itsimplymeansthatthebloodhashadmoretimetooxidize.
HormonalImbalances:
Consistentdarkorbrownmenstrualbloodthroughoutthecyclecouldindicate hormonalimbalances,suchasprogesteronedeficiencyorthyroiddisorders
DeepPurple:
WhatitIndicates:
Adeeppurplecoloraccompaniedbyclotsandclumpsinmenstrualblood
HormonalSignificance:
IfDeepPurplewithClots,Hormonalimbalances,suchashighestrogenlevelsora thickeneduterinelining,cancontributetoheavierperiodswithclotsandclumps.
BloodpHorAging:
Whilelesscommon,purplish-coloredmenstrualbloodmayresultfromchangesin bloodpHlevelsorthemixingofolderbloodwithfresherblood.It'sgenerallynot consideredacauseforconcernunlessaccompaniedbyothersymptoms.
UnderlyingConditions:
Insomecases,thismaybeanormalvariation,butthepresenceofthiscolor associatedwithlargeorfrequentclotscanalsobeassociatedwithconditionslike fibroids,adenomyosis,orendometriosis.
ContactHealthcareProvider:
Persistentorsevereclotsaccompaniedbyintensepainshouldprompta discussionwithahealthcareprovidertoruleoutanyunderlyingconditionsand exploreappropriatemanagementoptions.

WHATTHECOLOROFYOURMENSTRUALBLOODCOULD INDICATE T
H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
9
Pinkish
WhatitIndicates:
Pinkish-coloredmenstrualbloodoftenoccursduringlightfloworspottingand mayindicateaverylightmenstrualperiod.Itcouldalsobeduetothemixingof menstrualbloodwithcervicalmucus,whichisusuallynormal
HormonalSignificance:
Reducedestrogenlevelscanleadtoathinneruterinelining,whichmayresultin lighterbleedingduringmenstruation.
PossibleHormonalImbalance:
Aconsistentlypinkishcolorthroughoutyourperiodmightindicatelower estrogenlevels,whichcouldbeasignofhormonalimbalance.It'sessentialto monitoranypersistentchangesincolorandconsultwithahealthcareprovider ifneeded
Orange:
WhatitIndicates:
Orange-coloredmenstrualbloodmayindicatethemixingofmenstrualblood withcervicalmucusorvaginaldischarge Itcouldbeanormalvariationand notnecessarilyindicativeofaspecifichealthissue.
PossibleHormonalImbalance:
Colorsoutsideofthetypicalrange,especiallyaccompaniedbyafoulodoror unusualdischarge,shouldbepromptlyevaluatedbyahealthcareproviderto ruleoutinfectionslikebacterialvaginosisorsexuallytransmittedinfections (STIs).
Gray:
WhatitIndicates:
Graymenstrualbloodisnotatypicalorcommoncolor,anditspresencemay indicateapotentialhealthissuethatrequiresmedicalattention.
HormonalSignificance:
Whilenotdirectlyrelatedtohormonallevels,infectionscandisruptthenormal balanceofvaginalflora,leadingtochangesinthecolorandodorofmenstrual blood.
PossibleInfection:
Colorsoutsideofthetypicalrange,especiallyaccompaniedbyafoulodoror unusualdischarge,shouldbepromptlyevaluatedbyahealthcareproviderto ruleoutinfectionslikebacterialvaginosis,PelvicInflammatoryDisease(PID), cervicalabnormalities,orsexuallytransmittedinfections(STIs)
RetainedMenstrualProducts:
Inrarecases,ifmenstrualproducts(suchastampons)areleftinthevaginafor anextendedperiod,theycanleadtobacterialovergrowthandinfection,which mayresultinchangesinmenstrualbloodcolor,includinggrayishorfoulsmellingdischarge.
Ifyounoticeanyunusualchangesinyourmenstrualblood,it'simportanttoconsultwith ahealthcareproviderforevaluationandappropriatemanagement.Theycanhelp determinetheunderlyingcauseandprovidenecessarytreatmenttoaddressany potentialhealthissues

T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
10

Choosingtherightperiodproductisessentialforcomfort, hygiene,andconvenience.Withavarietyofoptions available,youcanfindproductsthatsuityourlifestyleand menstrualflow.Here'sanoverviewofthemostcommon periodproducts,theirbenefits,andhowtheycanfitinto yourmenstrualcareroutine.
H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
DISPOSABLE PADS (GENERAL)
Padsareabsorbentmaterialsthatadheretoyourunderwear tocollectmenstrualblood.
Top Layer:
Fragrance: Added to some pads for odor control
Backing: Plastic (polyethylene or polypropylene) to prevent leaks
PantyLiners:
Verythinandsmall, minimalcoverageand absorbency.Usefor Lightspotting,daily discharge,orasbackup fortamponsand menstrualcups.

LongPads
Idealformoderateto heavyfloworforextra protectionduringthe day,usuallyaround910inches.
Synthetic Fibers like polupropylene or polyethylene
Adhesives: Used to Secure the pad to underwear
Chemicals:
May contain chlorine, dioxins (from bleaching), and other synthetic substance
Ultra-Thin:
Forthosewhoprefera lessbulkyfeelwhile stillmaintaininggood absorbency.Available inregularorlong length.

MaxiPads
Designedforheavy flow.Thickerandmore absorbent,often availableinboth regularandlong.
RegularPads:
Standardsizewith moderatethickness, typicallyaround7-8 incheslong.Suitable forlighttomoderate flow.
Overnight:
Forovernightuse.Longer andwiderattheback, typicallyaround10-12 inchesormore,toprevent leakswhilelyingdown.
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS
T
11

AverageCost:
Pricesofnon-organicdisposablepadscanvaryby stateandcountry.TheaveragecostintheUnited Statesis $5-$10perpack(typicallycontains20-40pads). Thecostperpadrangesfrom$0.25to$0.50.
PossibleEffectsontheBody:
Syntheticmaterialsandfragrancescancauseskin irritationandallergicreactions. Chemicalresiduesandmoistureretentioncanincrease theriskofinfections.SomeChemicals,likedioxins,have beenlinkedtohormonaldisruptions.
EnvironmentalImpact: Disposablepadscontributetolandfill wasteandcantake500-800yearsto decomposeduetotheirplasticcontent.
ORGANIC DISPOSABLE PADS
Organicmenstrualpadsofferanaturalandenvironmentally friendlyalternativetoconventionalpads.
Absorbent Core:
100% Organic Cotton or a blend of Organic Cotton and other natural absorbent materials (e.g., bamboo fibers)
Backing:
Biodegradable plantbased materials (e.g., cornstarch-derived bioplastics)
Top Layer: 100% Organic Cotton
Optional Components: Wings can be made of 100% Organic Cotton or plantbased materials
Adhesives: Non-toxic, plant-based adhesive
AverageCost:
Pricesoforganicdisposablepadscanvarybystate andcountry.TheaveragecostintheUnitedStatesis $6-$12perpack(typicallycontains10-20pads).The costperpadrangesfrom$0.60to$1.20.Making themalmostdoublenon-organic.
PossibleEffectsontheBody: ReducedIrritation,Lowerriskofinfections,andno hormonaldisruption

EnvironmentalImpact: Biodegradable,compostable,andfreefromharmful chemicals,makingthembetterfortheenvironment
Everyonedeservesaccesstohealthieralternativesregardlessof cost,learnhowtogetfreeorganicmenstrualsuppliesinyourschool orworkplaceathttps://goauntflow.com/
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS 12
A L P H A S E
H E M E N S T R

REUSABLE PADS
Reusableclothpadsarewashablepadsmadefromfabric, oftenwithanabsorbentcoreandwaterproofbacking.
Absorbent Core:
Layers of organic cotton, bamboo, microfiber, or thicker fabric material
Backing:
PUL, Fleece, Wool, Nylon or recycled Materials
Top Layer: Organic Cotton, Bamboo, Microfiber, or thin fabric material.
Buttons or snaps: Used to Secure the pad to underwear
(Synthetic, reusable)
(Depends on type)
AverageCost:
Pricesofreusablepadscanvarybystateandcountry.The averagecostintheUnitedStatesis $5-$20perpad;cost-effectiveovermultipleuses(average lifespan:2-5years).
T
Material Water proof Breathable Comfort Enviroment Impact PUL Yes Yes High Moderate
Fleece Med Yes High Variable
Wool Med Yes High Low (Biodegradable) Nylon Yes Limited Med Moderate (Synthetic, reusable) Organic Cotton No Yes High Low (Organic) Regular Cotton No Yes High Moderate (Conventional Farming) Bamboo No Yes High Low (Organic) Microfiber Varies Yes Med Moderate
reusable)
U
(Synthetic,
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS
LearnHowtoMakeYourownresusablepad inour “PeriodsDon’tStopforWar”Zine 13

Periodunderwearisarevolutionaryproductthatofferscomfort,convenience, andsustainabilityinmanagingmenstrualflow.Designedwithbuilt-in absorbentlayers,periodunderwearprovidesleakprotectionwithouttheneed foradditionalpadsortampons.
Breathable Fabric:
Allows air circulation to keep you feeling fresh and comfortable.
Available in different styles (briefs, boyshorts, thongs) and absorbency levels to suit varying flow intensities.
Absorbent Layers:
Multiple layers of fabric designed to absorb and lock away moisture
Waterproof or water-resistant layers prevent leaks and stains.
ChoosingtheRightPeriodUnderwear:
Absorbency: Selectthe absorbencylevel basedonyour flowintensity. Style: Chooseastyle thatfitsyour preferenceand comfort.

Material: Considerthe material's absorbency, breathability, and environmental impact.
AverageCost:
Theaveragecostofperiodunderweartypicallyfallsbetween $20and$40perpair,withvariationsbasedonbrandand material. Typicallylastingforapproximatelytwotothree yearswithpropercareandmaintenance.
PossibleEffectsontheBody:
Size: Ensureproper fitfor maximum comfortand effectiveness. brand Brand: Research reputable brandsknown forqualityand reliability. T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
Periodunderwearisgenerallysafeandcomfortable,but individualsshouldbemindfulofpotentialdiscomfortrelated tofactorssuchasbreathabilityandskinsensitivity.,and effectsfromimpropercareandmaintenance
Material Absorbency Breathable Enviroment Impact Cost Cotton High Yes Moderate $$ Bamboo No Yes Low (Organic) $$$ Synthetic Varies Varies High (Nonbiodegradable) $-$$
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS PERIOD PANTIES
14
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS
TAMPONS (GENERAL)
Tamponsareapopularmenstrualproductchoiceformany individualsduetotheirconvenienceandeaseofuse.
Applicator:
Applicators for regular tampons are commonly made from cardboard or plastic, specifically polyethylene or polypropylene. Plastic applicators provide smooth insertion and ease of use but contribute to plastic waste.
String:
The string attached to regular tampons is usually made from cotton or a blend of cotton and polyester. While cotton is a natural fiber, polyester is a synthetic material that may be included for added strength.
Light:
Lighttamponsare suitableforlight flowdays.These tamponshavelower absorbencylevels andaredesignedto handlelighterflow withoutfeeling uncomfortableor overlybulky.
Regular:
Regulartampons aredesignedfor moderateflowdays. Theytypicallyhave asmallerdiameter andshorterlength comparedtolarger sizes.Regular tamponstypically absorbbetween6 to9gramsof menstrualfluid.
SuperPlus:
Super-plustamponsare designedforveryheavy flowdays.Theyare largerindiameterand lengthcomparedto supertampons.Superplustamponsabsorb between12to15grams ofmenstrualfluid.

Absorbent Core
Regular tampons typically feature an absorbent core made from a blend of rayon and conventionally grown cotton. Rayon is a synthetic fiber derived from wood pulp, known for its high absorbency. Conventionally grown cotton may be treated with pesticides and herbicides during cultivation.
Super:
Supertamponsare intendedfor moderatetoheavy flowdays.They havealarger diameterandlonger lengthcomparedto regulartampons& absorbbetween9 to12gramsof menstrualfluid.
Ultra:
Ultratamponsarethe largestsizeavailableand areintendedforextremely heavyflowdays.Theyare thelongestandwidest tamponsintherange. Ultratamponsabsorb between15to18gramsof menstrualfluid.
Choosethelowestabsorbencyneededforyourflowtoreducetheriskof infection.Considerusingregularorlighttamponsonlighterflowdays. Adjustabsorbencylevelsbasedonyourflowthroughoutyourperiod. Avoidusingahigherabsorbencytamponthannecessary.
15

Tamponsareaconvenientandpopularmenstrual product,butit'sessentialtousethemsafelytoavoid potentialhealthrisks.
WashYourHands
Alwayswashyourhandsbeforeandafter insertingorremovingatamponto preventintroducingbacteriaintothe vaginalarea.

ProperInsertion&Removal:
Followtheinstructionsprovidedwiththe tamponorscantheQRcodehere.Insert itgentlyandremoveitcarefullytoavoid discomfortorinjury.
FrequentChanges:
Changetamponsevery4to6hoursto reducetheriskofbacterialgrowth, infection,andToxicShockSyndrome (TSS).
Discomfortandpain:
Ifinsertionispainfulorthetamponfeels uncomfortable,itmightnotbepositioned correctly.Removeitandtryagainwithanewone oradifferentproduct.
ToxicShockSyndrome(TSS):
TSSisararebutseriousconditioncausedby toxin-producingbacteria.Symptomsinclude suddenhighfever,rash,vomiting,anddizziness.
UnusualSymptoms:
Ifyouexperienceunusualsymptomslikeafoul odor,itching,orirritation,discontinueuseand consultahealthcareprovider.
TakeBreaks:
Considerusingpads,menstrualcups,orperiod underwearoccasionallytogiveyourbodya breakfromtampons.Someindividualsmay benefitfromalternatingbetweentamponsand othermenstrualproductstoreducetheriskof irritationandmaintainvaginalhealth.
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS
16
H E M E N S T R
TAMPONS (GENERAL)
AverageCost:

Thecostoftamponsvariesbasedonsize, absorbency,brand,andlocationsold,Theaverage costoftamponsintheUnitedStatesis$5-$15per box(typicallycontains20-40tampons) Thecost pertamponrangesfrom$0.15to$0.75pertampon
PossibleEffectsontheBody:
Syntheticmaterialslikerayonandpolyesterintampons,aswellas plasticcomponentsinapplicators,maycauseirritationorallergic reactionsinsomeindividuals.Sensitivitytothesematerialscanlead todiscomfortorskinirritationduringuse.Additionally
Tampons,especiallythosewithahighabsorbencylevel,may increasetheriskof(ToxicShockSyndrome)TSSwhenleftinthebody forextendedperiods TSSisararebutseriousconditioncausedby toxinsproducedbycertainstrainsofbacteria.
EnvironmentalImpact:
Conventionalcottonfarmingofteninvolves pesticideandinsecticideuse,contributing toenvironmentalpollution Additionally, plasticapplicatorscontributetoplastic wasteinlandfills.
TAMPONS (ORGANIC)
Absorbent Core:
Applicator:
Some brands offer biodegradable cardboard applicators or noapplicator options for minimal environmental impact.
Certified organic cotton, grown without the use of synthetic pesticides or fertilizers.
String: Organic cotton or biodegradable materials.
AverageCost:
Thecostoftamponsvariesbasedonsize,absorbency,brand,andlocation sold,TheaveragecostoforganictamponsintheUnitedStatesis$7-$18per box(typicallycontains20-30tampons) Thecostpertamponrangesfrom $0.30to$0.90pertampon
PossibleEffectsontheBody:
Organiccottonreducesexposuretopesticidesandsyntheticadditives, potentiallyloweringtheriskofallergicreactionsorirritation.
, EnvironmentalImpact: Organiccottonfarmingpromotessoilhealthandbiodiversitywhile reducingchemicalrunoffandpollution.Biodegradableapplicators furtherminimizeenvironmentalimpact.
Everyonedeservesaccesstohealthieralternativesregardlessof cost,learnhowtogetfreeorganicmenstrualsuppliesinyourschool orworkplaceathttps://goauntflow.com/
T
U
H A
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS
A L P
S E
17

MENSTRUAL CUPS AND MENSTRUAL DISCS
Menstrualcupsanddiscsofferversatileandsustainableoptionsfor menstrualcare.Byunderstandinghowtouseandmaintaintheseproducts, youcanenjoythebenefitsofreducedwaste,costsavings,andextended weartime,makingyourperiodmoremanageableandeco-friendly.
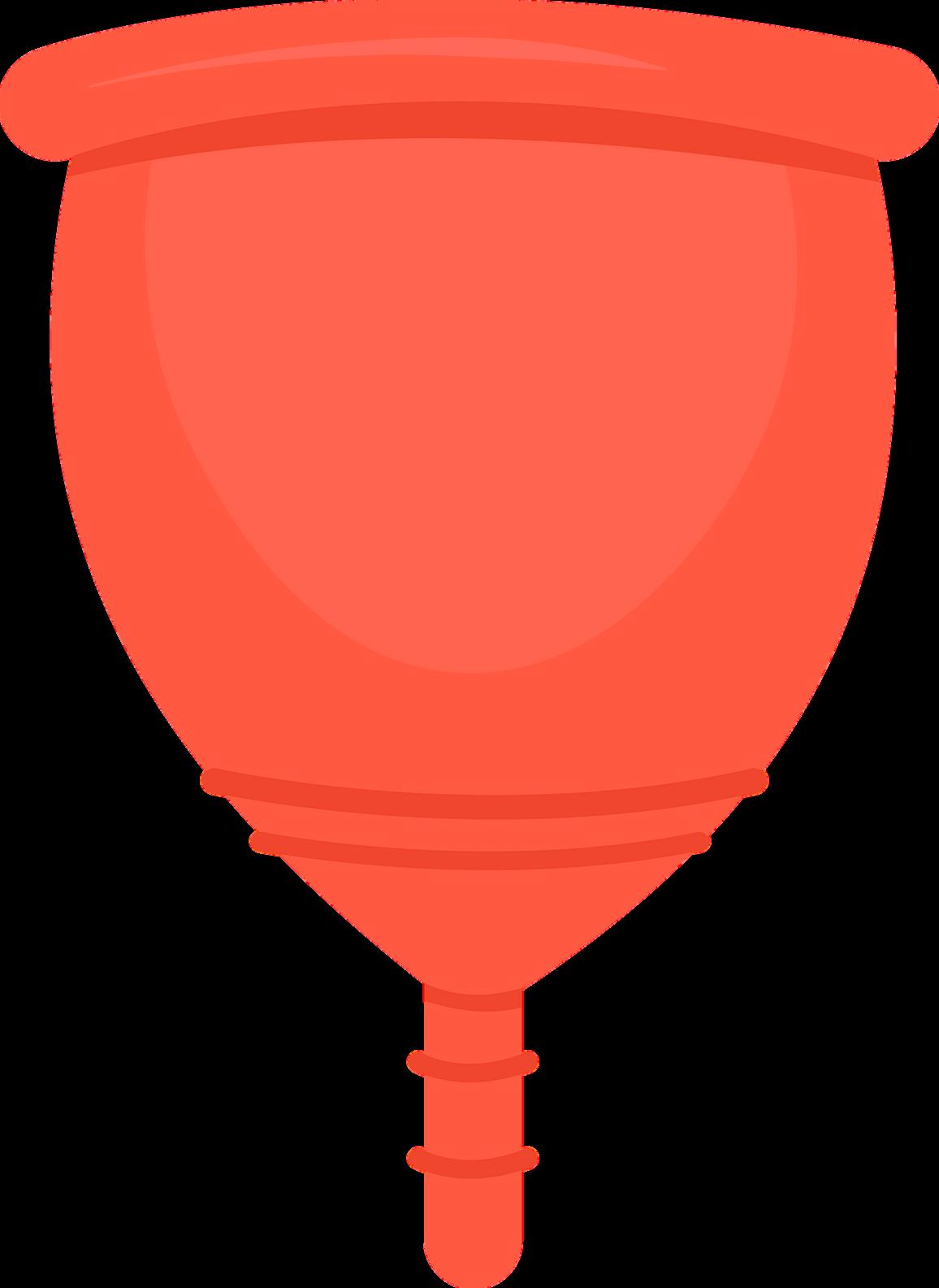
Menstrual cups are flexible, bell-shaped devices made from medical-grade silicone, rubber, or TPE (thermoplastic elastomer). They are inserted into the vagina to collect menstrual blood.

Menstrual discs are flexible, disc-shaped devices made from medical-grade silicone or polymer. They are inserted at the base of the cervix to collect menstrual blood. Menstrual discs can be worn during sex without discomfort.
Disposable Disc $10 - 20 / pack
High (Significant waste from disposal) Single Use
Wearingtime:
CupsandDiscscanbewornupto12hoursdependingon flow
Insertion&Removal:
Cups:Foldthecup(severalfoldingtechniquescanbeused,liketheC-foldor punch-downfold),insertitintothevagina,andallowittoopenandcreatea sealagainstthevaginalwalls.Toremove:Pinchthebasetoreleasethesealand gentlypullitout.Emptythecontents,rinse,andreinsert.
Disc:Pinchthedisc,insertitintothevagina,andpushitbacksoitsitsatthe baseofthecervix.Toremove, Hookafingerundertherimtopullitout.Empty thecontents,rinse,andreinsert
WashingInstructions: Washwithmildsoapandwaterbetweenuses Sterilizebyboiling inwaterforafewminutesbetweenmenstrualcycles.
H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
T
EXPLORINGPERIODPRODUCTS
Product Initial Cost Enviromental Impact Lifespan Cup $20-$40 Low (Sustainable, minimal waste) Up to 10 Years Disc $30-$50 Low (Sustainable, minimal waste) Up to 10 Years
18

Managingthisphaseeffectivelyinvolvesacombinationof propernutrition,appropriateexercises,calmingactivities, andself-carepracticestoalleviatediscomfortandpromote well-being.
TRACK YOUR CYCLE
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
Useamenstrualcalendarorapptotracksymptomsand flow.Thiscanhelppredictpatternsandprepareforyour period.WerecommendEuki,itsthemenstrualappthat doesn’ttrackyourdata.Bewearyofappsthattrackyour data.
GET REST!!
Duringthemenstrualphase,estrogenandprogesterone levelsareattheirlowest,whichcanleadtofatigue. Ensureadequaterestandaimfor8-10hoursofsleep eachnighttosupportyourbody'srecoveryandreduce fatigue.
PAIN MANAGEMENT
Itisnormaltohavelighttomildheadaches,discomfort, andcramping.Herearesomewaystomanagethat pain.
over-the-counter painrelieverslike ibuprofenor acetaminophen Thesemedications reduceinflammation andpain.
EssentialOilssuchas Lavender,ClarySage,and Marjoramoilcanreduce muscletension&provide relief.Diluteoilsand massageintoabdoment orusediffuser
HerbalTeassuchas Chamomile,ginger,and peppermintteaantiinflammatoryand antispasmodicproperties thatcanhelpreduce discomfortandpromote relaxation.
Remember:severepainorprolongedpainisNOT normal. Exerciseincreasesblood flowandreleases endorphins,whichare naturalpainrelievers. Yogaandstretchinghelp torelievetensioninthe musclesandpromote relaxation.
Heathelpstorelax theuterinemuscles andimproveblood flow,reducing cramps.Usea heatingpad,hot waterbottle,orbath.
Hormonal contraceptivescan reducetheseverity ofcrampsby regulatingor stopping menstruation.
MANAGINGTHEMENSTRUALPHASE
19

HOW TO GET BLOOD OUT OF SHEETS
Grabalargebowl andputstained sheetinit
pourhydrogen peroxideoverthe stain,about1/2cup.
Dabinthe peroxide,donot rub

Addcoldwater Letsoakinwaterfor24 hours Machinewash& airdry
HOW TO GET BLOOD OUT OF MATTRESS
Removebedding& Blotstainwithacloth dippedincoldwater, usecoldwateronly
Createabakingsodaand ahydrogenperoxide pasteusing1/2cup bakingsodaand1/4cup hydrogenperoxide
Workinthepaste withamicrofiber cloth
Letthepaste restforawhile andthenclean withwetcloth anddetergent.
Ifstainstillpersistscreate apasteofoxygenbleach andwaterusing1/2cup powderoxygenbleachand 1/2cupwater
Repeatprocess withoxygen bleachpaste untilstainis gone
T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E
MANAGINGTHEMENSTRUALPHASE
20
H E M E N S T R U A L P

IRON RICH FOODS
Toreplenishironlostduringmenstruationandcombatfatigue.
OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
Toreduceinflammationandhelpwithcramps.

MAGNESIUM - RICH FOODS
Consumingmagnesium-richfoodscanhelpalleviatesomesymptomslike cramps,fatigue,andmoodswings.


WARMING FOODS
Warmingfoodscanhelpwithbloodflowandcramps.
GUT FRIENDLY FOODS
Maintainingguthealthduringyourperiodcanhelpalleviatesymptomslike bloating,constipation,ordiarrhea

T
H A S E
EAT MANAGINGTHEMENSTRUALPHASE
Spinach WHAT TO
Lentils Red Meat Pumpkin Seeds
Salmon Walnuts
Chia Seeds Flaxseeds
DarkChocolate Bananas Edamame Avacado
Soups
Herbal Teas Curries Oatmeal
WholeGrains BoneBroth Leafy Greans Ginger 21

TECHNIQUES
Breathing Exercises T H E M E N S T R U A L P H A S E

GENTLE HOBBIES
GENTLE EXERCISE
ACTIVITIES TO TRY MANAGINGTHEMENSTRUALPHASE
Therapy AWarm Bath
RELAXATION
Meditation Sound
Reading Journaling WatchTV YOGA Child’s pose cat-cow Legup thewall Forward SeatPose
Makea playlist
Walking Stretching Foam Rolling TaiChi REST 22
U L A R P H A S E
T H E F O L L I
Thefollicular&proliferativephase isthesecondphaseofthe menstrualcycle,beginningright aftermenstruationandlasting untilovulation.Thesecocurrent phasestypicallyspansfromDay1 toDay14ofthecyclebutcanvary amongindividuals.

RECRUITMENTANDACTIVATION
Atbirth,theovariescontainafinitenumberofprimordial follicles.Thesearethemostimmaturefollicles,consistingof aprimaryoocytesurroundedbyasinglelayerofflattened granulosacellsAcohortofprimordialfolliclesisrecruitedto beginmaturation.Thisprocessiscontinuous,buteach menstrualcycletypicallyinvolvestherecruitmentofseveral follicles.
PRIMARYFOLLICLEDEVELOPMENT
Theselectedprimordialfolliclesdevelopintoprimary follicles.Thisinvolvesthegrowthoftheoocyteandthe proliferationofgranulosacells,whichbecomecuboidal.A glycoproteinlayercalledthezonapellucidaformsaround theoocyte,providingprotectionandplayingarolein fertilization
ANTRALFOLLICLEFORMATION& SELECTION
Fluid-filledspacesmergetocreateacentralcavityknown astheantrum,transformingthesecondaryfollicleintoan antral(tertiary)follicle.Amongthedevelopingantral follicles,onebecomesdominant.Thisdominantfolliclehas moreFSHreceptorsandgrowslarger,whiletheothers undergoatresia(degeneration).
C
23

FINALMATURATION
Thedominantfollicleundergoesfinalmaturationdueto thesurgeinluteinizinghormone(LH),whichistriggered byrisingestrogenlevels.
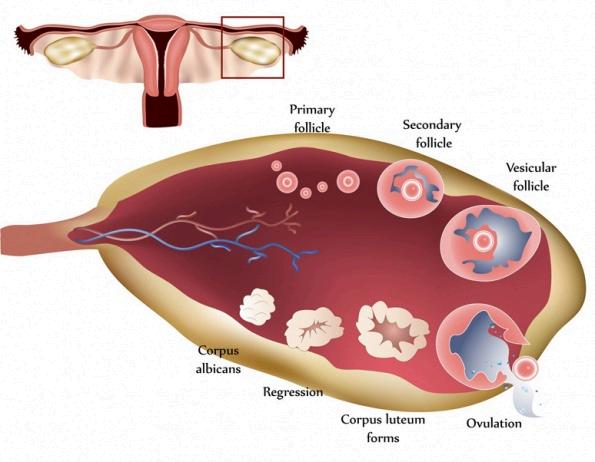
HORMONALCHANGES
Estrogen:
Asthefolliclesdevelop,theyproduceincreasing amountsofestrogen.Estrogensendsfeedback tothebraintomodulateFSHproductionand promotethedominanceofonefollicle.
Follicle-StimulatingHormone(FSH):
Secretedbythepituitarygland,FSHispivotalat thestartofthefollicularphase.Itsprimaryroleis tostimulatethegrowthandmaturationof ovarianfollicles.
LuteinizingHormone(LH):
LHlevelsrisetowardstheendofthefollicular phaseinresponsetohighestrogenlevels.This surgeinLHwilleventuallytriggerovulation.
Progesterone
Progesteronelevelsareminimalduringthe follicularphase.
Testosterone:
Testosteronelevelsaregenerallyhigherinthe mid-follicularphase.Testosteronesupportsthe developmentofovarianfolliclesandservesasa precursorforestrogensynthesis.
T H E F O L L I C U L A R P H A S E
24
T H E F O L L I C U L A R P H A S E
C U L A R P H A S E
T H E F O L L I

Whilebothphasesoccursimultaneouslyandestrogen playsacrucialroleinboth,thefollicularphaseis centeredontheovarianchangespreparingfor ovulation,andtheproliferativephaseiscenteredon theuterinechangespreparingtheendometriumfor potentialpregnancy.
FollicularPhase.
Characterizedbythegrowthandmaturationof ovarianfolliclesstimulatedbyfolliclestimulatinghormone(FSH)releasedbythe anteriorpituitarygland.Estrogenlevelsstartto riseasthefolliclesmature.
Concernstheovariesandthematurationof follicles.
PrimarilyinfluencedbyFSHandestrogen.
ProliferativePhase:
Estrogencausestheliningoftheuterus (endometrium)togrowandthickenafter menstruation.Theendometrialglandsandblood vesselsproliferatetoprepareforthepossible implantationofafertilizedegg. Concernstheuterusandthethickeningofthe endometriallining.
Primarilyinfluencedbyestrogen.
FOLLICULAR&PROLIFERATIVEPHASE WHAT’STHEDIFFERENCE?
25
Duringthisphase,thelevelsofestrogenand testosteronegraduallyincrease.These hormonesplaycrucialrolesinregulating mood,energylevels,andemotions.
INCREASEDENERGY&IMPROVEDMOOD
Youmayexperienceasurgeinenergyduringthefollicular phase.Thisincreaseinvitalitycanleadtoamorepositive moodandoutlookonlife.
ENHANCEDCREATIVITY
Youmayexperienceheightenedcreativityduringthe follicularphase.Thismaybeattributedtoincreasedenergy andagreatersenseofmentalclarity.
HEIGHTENEDLIBIDO
Asestrogenlevelspeak,youmayexperienceanincreasein libido,orsexualdesire.Thiscancontributetofeelingsof excitementandanticipation.
CHANGESINCERVICALMUCUS
Theconsistencyofcervicalmucuschanges,becoming clearerandmoreslipperyasovulationapproaches.Thisisa naturaladaptationtofacilitatespermmovementfor potentialfertilization.
MILDCRAMPING
Asthefolliclesintheovariespreparetoreleaseanegg,you mightfeelmildtwingesorcramps,knownasmittelschmerz, ononesideofthelowerabdomen.
WEIGHTFLUCTUATIONS
Duetochangesinwaterretentionandpossiblyincreased physicalactivity,youmaymightnoticeslightfluctuationsin weight
BLOATING
Duetochangesinwaterretentionandpossiblyincreased physicalactivity,youmightnoticeslightfluctuationsin weight
It'simportanttonotethateveryone’sexperienceofthe follicularphasecanvarywidely.Somemayexperienceall esesideeffects,whileothersmaynoticeonlyafewor noneatall.

T H E F O L L I C U L A R P H A S E
26
WHAT TO EAT
LEAN PROTIEN FOODS

Proteinsupportsmusclerepairandgrowth,andprovidesthebodywith essentialaminoacids.

OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
Omega-3splayaroleintheproductionofhormonesthatregulatethe menstrualcycle.

HYDRATING FOODS
Topreventbloatingandkeepthebodyhydrated.

FIBER RICH FOODS
Fiberaidsindigestionandhelpsinmaintainingstablebloodsugarlevels.

PROBIOTIC FOODS

Probioticssupportguthealth,whichislinkedtooverallhormoneregulation.


T
I C U L A
P H A S E
H E F O L L
R
Chicken
Salmon
Cucumbers
Whole Grain
Yogurt
Legumes
Walnuts
Watermelon
Apples
Kefir
Tofu
Chia Seeds
Oranges
Quinoa
Sauerkraut
Fish
Flaxseeds
Celery
Berries
Kimchi
MANAGINGTHEFOLLICULARPHASE 27

ACTIVITIES TO TRY
MINDFULNESS PRACTICES
Breathing Exercises
FiberArts
Meditation Gratitude
CREATIVE ACTIVITIES

Writing
CARDIO
EXERCISES

Walking
Push-Ups

Weightlifting

H E F O L L I C U L A R P H A S E
Resistance
Lunges
Bands
Pose TreePose Triangle pose BridgePose
Journaling Mindful Listening WarriorI
T
MANAGINGTHEFOLLICULARPHASE
Painting Coloring
Swimming Dancing
TRAINING YOGA
Cycling
STRENGTH
28
U L A T I
Theovulationphaseisthethird phaseofthemenstrualcycle, occurringmidwaythroughthe cycleandmarkingthereleaseofa matureeggfromtheovary.This phaseistypicallyaroundDay14in a28-daycyclebutcanvary dependingonindividualcycle length.
LHSURGE

TheLHsurgeiscausedbyhighlevelsofestrogen fromthedominantfollicle.ThissurgeinLHcauses thematureGraafianfollicletoruptureandrelease theegg.
EGGRELEASE
Thematureegg(oocyte)isreleasedfromtheovary intotheadjacentfallopiantube.Ovulationusually occurs24to36hoursaftertheLHsurge.
FALLOPIANTUBETRAVEL
Thereleasedeggiscapturedbythefimbriae (finger-likeprojections)ofthefallopiantubeand beginsitsjourneytowardtheuterus.Theegg remainsviableforabout12to24hoursafterrelease, andthisisthewindowforpotentialfertilizationby sperm.
FERTILIZATIONWINDOW
Themostfertileperiodisconsideredtobethefive daysleadinguptoovulationandthedayof ovulationitself.Thisisbecausethepresenceof sperminthereproductivetractduringthistime increasesthechancesoffertilization.
O V
O N
29

SPERMVIABILITY
Whiletheeggisviablefor12to24hours,spermcan surviveforupto5days.Ifintercourseoccursinthe daysleadinguptoovulation,spermcanremainalive andviableinthefallopiantubes,waitingfortheeggto bereleased.Ovulationcansometimesoccurearlieror laterthanexpected.Ifovulationhappenslaterthan anticipated,spermfromearlierintercoursecanstill fertilizetheegg.

V U L A T I O N
O
30
C U L A R P H A S E O V U L A T I O N
T H E F O L L I
Estrogen:
HORMONALCHANGES

Estrogenlevels,whichhavebeenrisingduring thefollicularphase,reachtheirpeakjustbefore ovulation.Thishighlevelofestrogenstimulates theLHsurge.
Follicle-StimulatingHormone(FSH):
FSHlevelsalsoincreaseduringthisphase, stimulatingthegrowthandmaturationof ovarianfollicles.
LuteinizingHormone(LH):
ThesurgeinLHisthedefiningeventofthe ovulatoryphase,triggeringthereleaseofthe eggfromthefollicle.Thishormoneisalso associatedwithchangesinmoodandemotional sensitivity.
Progesterone
Duringovulation,progesteroneproduction beginstoincrease,thoughitsmostsignificant effectsareobservedinthelutealphase
Testosterone:
Thereisaslightincreaseintestosteronelevels aroundovulation,whichcanenhancelibidoand assertiveness.

31
Thesehormonalshiftscanhavevariouseffectson moodandemotionalwell-being.Herearesome commonsideeffectsduringovulation.
CONFIDENCEANDSOCIABILITY:
Duringovulation,youmayfeelmoreconfidentandsociable. Thiscanbepartlyduetothehormonalboostbutalsodue toanaturalinclinationtoseeksocialinteractionsand connectionsduringthefertilewindow.
ENHANCEDSENSITIVITY
Hormonalchangesduringovulationcanheightenemotional sensitivity.Womenmayfindthemselvesmoreresponsiveto emotionalstimuli,experiencingbothpositiveandnegative emotionsmoreintensely
INCREASEDANXIETYORANTICIPATION
Forsomewomen,thehormonalsurgecancausefeelingsof anxiety,nervousness,oranticipation.
HEIGHTENEDLIBIDO
Asestrogenlevelspeak,youmayexperienceanincreasein libido,orsexualdesire.
INCREASEDCERVICALMUCUS/DISCHARGE
Aroundthetimeofovulation,somewomenmaynoticean increaseinvaginaldischargethatisclearandstretchy, resemblingraweggwhites.Thiscervicalmucushelps facilitatethemovementofspermthroughthereproductive tracttoreachtheegg.
MILDCRAMPING
Youmayexperienceabrief,sharppainorcrampingonone sideofthelowerabdomenorpelvisduringovulation.This pain,knownasmittelschmerz,occursduetothestretching orirritationoftheovarianwallasthefolliclerupturesand releasestheegg.
SPOTTING
Somewomenmaynoticelightvaginalbleedingorspotting aroundthetimeofovulation.Thisspottingistypicallylight andshort-livedandmaybeduetothereleaseofasmall amountofbloodfromtheovaryduringovulation.

mayexperienceallthesesideeffects,whileothersmaynotice onlyafewornoneatall.
V U L A T I O N
O
32
U L A T I
CertainConditionscansignificantlyimpactovulation throughvariousmechanisms,oftenleadingtoirregular orabsentmenstrualcyclesandfertilityissues.Here’san in-depthlookathoweachoftheseconditionsaffects ovulation
POLYCYSTICOVARYSYNDROME(PCOS)
PCOSisacommonhormonaldisorderamongwomenof reproductiveage,characterizedby:
IrregularMenstrualPeriods.
Elevatedlevelsofmalehormones(androgens)such astestosteronecancausephysicalsignslikeexcess facialorbodyhair(hirsutism)andacne.
Enlargedovaries.
InsulinResistance.
HormonalImbalance
SevereCramping
Diagnosis: Diagnosedbasedonclinicalcriteria(Rotterdamcriteria) whichincludeirregularovulation,hyperandrogenism, andpolycysticovariesonultrasound.
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Thischronicdisorderoccurswhentissuesimilartothe lininginsidetheuterus,knownastheendometrium, growsoutsidetheuterus,causinginflammation,pain, andsometimesadhesions.Itcancause:
ChronicorSeverePelvicPain
PainduringIntercourse
IrregularMenstrualPeriods
PelvicInflammation
OvarianCysts
FormationofScarTissueonreproductiveorgans.
HormonalImbalance
Diagnosis: Diagnosedbasedonsymptomsandmedicalhistory. PhysicianwillperformanUltrasoundorMRItoidentify endometriomasandotherabnormalities.Additionallya minimallyinvasivesurgicalprocedure.Laprascopy,that allowsdirectvisualizationandbiopsyofendometrial lesions,whichisconsideredthegoldstandardfor diagnosis.

O V
O
N
33

THYROIDDISORDERS
Hypothyroidism
Thisoccurswhenthethyroidglanddoesnotproduce enoughthyroidhormone.Itcancause: Fatigue
WeightGain
Constipation
DrySkin
ImpairedFollicularDevelopment
Hyperthyroidism
Thisconditioninvolvesanoveractivethyroidglandthat producestoomuchthyroidhormone.Itcancause:
WeightLoss
RapidHeartRate
Sweating
IrregularMenstrualCycle
IrregularorAbsentOvulation
Diagnosis:
DiagnosedthroughbloodtestsmeasuringTSH,T3,and T4levels
HYPERPROLACTINEMIA
Hyperprolactinemiaisaconditioncharacterizedby elevatedlevelsofprolactin,ahormoneproducedbythe pituitarygland.Prolactinisprimarilyknownforitsrolein stimulatingmilkproductionafterchildbirth,butitalso haseffectsonthereproductivesystem.Itcancause:
BreastMilkProductionOutsideofPregnancy& Breastfeeding(Galactorrhea)
DecreasedLibido.
IrregularorAbsentMenstrualCycle.
ProlongedBleedingduringMenstrualPeriod. Headaches
VaginalDryness
Infertility
Diagnosis: Diagnosedthroughbloodtestsmeasuringprolactin levels.
O V U L A T I O N
34
WHAT TO EAT
LEAN PROTIEN FOODS

Proteinsupportsmusclerepairandgrowth,andprovidesthebodywith essentialaminoacids.


OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
Omega-3splayaroleintheproductionofhormonesthatregulatethe menstrualcycleandimprovefertility.

VITAMIN-E RICH FOODS
vitaminEactsasanantioxidant,protectingcellsfromdamage,supporting hormonalbalance,andpromotingoverallreproductivehealth

PHYTOESTROGEN-RICH FOODS
beneficialforovulationbyhelpingregulatehormonelevels,balance estrogen,promotemenstrualregularity,alleviatemenopausalsymptoms, andprovideantioxidantandanti-inflammatorysupport.

ZINC-RICH FOODS
zincsupportshormoneregulation,promoteshealthyeggdevelopment, enhancesimmunefunction,andcontributestooverallreproductivehealth andfertility.





































































O V U L A T I O N
Chicken Legumes Tofu
Fish
Salmon
Walnuts
Chia Seeds Flaxseeds
Grain
Nuts&Seeds
Whole
Yogurt
Eggs
Oysters
Soybeans
Mangoes Carrots Cooked
Shrimp
Berries Chickpeas
MANAGINGTHEOVULATIONPHASE
35
Spinach

ACTIVITIES TO TRY
OUTSIDE ACTIVITIES
SOCIAL ACTIVITIES

GameNight
HIGHER-INTENSITY EXERCISES

CIRCUIT TRAINING


Resistance Bands Lunges
Pose BridgePose
Garland Pose Crunches Boxing
WarriorII
Cycling
BookClub Concerts FarmersMarkets
Climbing
Surfing Hiking Paddle Sports O V U L A T I O N MANAGINGTHEOVULATIONPHASE
Rock
Running
HIIT
YOGA
Push-Ups
Legup thewall 36
L U T E A L P H A S E
T H E

Thelutealphaseisthefinalstageof themenstrualcycle,following ovulationandpreceding menstruation.Spanning approximatelyfromDay15toDay28 ofa28-daycycle,thisphaseis characterizedbysignificanthormonal changesandphysiological preparationsforpotentialpregnancy.
EARLYLUTEALPHASE
Thisphaseimmediatelyfollowsovulationandis characterizedbytheformationofthecorpus luteum.Thecorpusluteum,formedfromthe collapsedfollicleafterovulation,becomesthe primaryproducerofprogesterone.Theuterinelining thickensinpreparationforpotentialimplantation, andcervicalmucusbecomesthickerandless conducivetospermpenetration.
MIDLUTEALPHASE
Peakprogesteronelevelssustainthethickened endometrialliningandcreateanoptimal environmentforembryoimplantation.Estrogen levelsmayfluctuateslightlybutgenerallyremain elevated.Basalbodytemperature(BBT)typically risesduringthisphaseduetotheincreasein progesterone.
LATELUTEALPHASE
Iffertilizationandimplantationdonotoccur,the corpusluteumbeginstodegenerate,leadingtoa decreaseinprogesteroneproduction.Thedeclinein hormonalsupporttriggersthesheddingofthe uterinelining,resultinginmenstruation.
37


HORMONALCHANGES
Estrogen:
Estrogenlevelsdecreaseslightlyafterovulation,but remainrelativelyhighasthecorpusluteumforms, Estrogenlevelsdropagainasthecorpusluteum beginstodegenerateifthereisnopregnancy, leadingtoadecreaseinbothestrogenand progesteronelevels.
Follicle-StimulatingHormone(FSH):
Onceovulationhasoccurred,FSHlevelsdecrease asthefocusshiftstomaintainingthecorpusluteum andsupportingprogesteroneproduction.
LuteinizingHormone(LH):
Onceovulationhasoccurred,LHlevelsdeclineas thecorpusluteumformsandbeginstoproduce progesterone.
Progesterone:
Progesteronelevelsrisesignificantlyduringthe lutealphase,producedprimarilybythecorpus luteum.Ifpregnancydoesnotoccur,progesterone levelsdeclinetowardstheendofthelutealphase asthecorpusluteumdegenerates.
Testosterone:
Remainsstable,supportingenergyandmood.It alsoservesasaprecursorforestrogensynthesis, althoughitsdirectroleislessprominentduringthe lutealphasecomparedtothefollicularphase.
T H E L U T E A L P H A S E
38
C U L A R P H A S E T H E L U T E A L P H A S E
T H E F O L L I
LUTEALPHASEORSECRATORYPHASE?
Thelutealphaseandsecretoryphasereferto differentaspectsofthemenstrualcycleandareoften usedinterchangeably,buttheyhaveslightlydifferent meanings.
LutealPhase:
Thelutealphaseisthesecondhalfofthemenstrual cycle,beginningafterovulationandendingwiththe startofmenstruation.Itischaracterizedbythe formationandactivityofthecorpusluteum,which producesprogesteronetopreparetheuterinelining forpotentialimplantationofafertilizedegg.The lutealphasetypicallylastsaround10-16days,with aconsistentriseandfallinprogesteronelevels.
SecretoryPhase
Thesecretoryphasespecificallyreferstotheperiod ofthemenstrualcyclewhentheendometrium(the liningoftheuterus)becomesmoreglandularand vascularinpreparationforpossibleembryo implantation.Thisphasecoincideswiththelatter partofthelutealphaseandisdrivenbythe secretionofprogesteronefromthecorpusluteum. Thesecretoryphaseisessentialforcreatinga receptiveenvironmentintheuterusforembryo implantation.


39
Duringthelutealphase,someindividualsmay experiencesymptomscommonlyreferredtoas premenstrualsyndrome(PMS)Thesesymptoms occurduetohormonalfluctuationsasthebody preparesformenstruationifpregnancydoesnot occur.
CHANGESINMOOD
Hormonalchanges,includingfluctuationsinestrogenand progesteronelevels,canimpactneurotransmitteractivityin thebrain,leadingtomoodchangessuchasirritabilityand anxiety.
DIFFICULTYCONCENTRATING
Thehormonalfluctuationscanimpactneurotransmitter activityinthebrain,affectingcognitivefunctionand concentrationlevels
DECREASEDSTAMINA
Changesinhormonelevels,alongwithotherfactorssuchas fluidretentionandmoodfluctuations,canaffectphysical performanceandenduranceduringthisphaseofthe menstrualcycle.
CRAMPS
Progesteronelevelsriseduringthelutealphasetoprepare theuterusforpotentialpregnancy,whichcancauseuterine contractionsandmildcramping.
BLOATING
Theriseinprogesteronecancausefluidretentionleadingto bloatinganddiscomfort.
BREASTTENDERNESS
Estrogenandprogesteronestimulatebreasttissuegrowth andmayincreasesensitivitytohormonalchanges,resulting inbreasttenderness.
FATIGUE
Theincreaseinprogesteronecancontributetofeelingsof fatigue.Progesteronehassedativeeffectswhichmayresult indecreasedenergylevels

memayexperienceallthesesideeffects,whileothers maynoticeonlyafewornoneatall.
T H E L U T E A L P H A S E
40
T H E L U T E A L P H A S E

Thecolorandconsistencyofcervical mucusordischargeduringtheluteal phasecanprovideinsightsinto hormonalchangesandreproductive health.Here'swhatdifferent characteristicsmightindicate:
CLEARORWHITE
Duringthelutealphase,dischargeisoftencleartowhite andhasalotion-likeorcreamyconsistency. Progesterone,whichrisesafterovulation,influencesthis typeofdischarge.Highlevelsofprogesteronecause cervicalmucustobecomethicker,lessstretchy,and moreopaquecomparedtotheclear,mucusduring ovulation.Thistypeofdischargeisanormalresponseto thehormonalenvironmentofthelutealphaseand indicatesahealthybalanceofhormones.
BROWNORBLOODY
Brownorbloodydischargeduringthelutealphasecan resultfromspottingorthepresenceofoldblood.Light spottingcanbenormalforsomeindividualsandmay happenduetoslighthormonalfluctuationsorthe beginningofthebreakdownoftheuterinelining. However,consistentspottingorbleedingoutsideof menstruationshouldbeevaluatedbyahealthcare provider.
WHATYOURDISCHARGECOULDINDICATE
41

YELLOWORGREEN
Yelloworgreendischargemaybeasignofabacterial infectionorsexuallytransmittedinfection(STI),suchas bacterialvaginosisortrichomoniasis.Accompanying symptomsmayincludeitching,burning,irritation,ora foulodor.Infectionsneedtobediagnosedbya healthcareproviderandappropriatelytreatedwith antibioticsorothermedications.




THICKORCLUMPY
Thick,clumpydischargeresemblingcottagecheeseis typicallyasignofayeastinfection(Candidiasis).This dischargeisusuallyaccompaniedbyitching,redness, swelling,andirritation.Yeastinfectionsrequiretreatment withantifungalmedications,eitherover-the-counteror prescribedbyahealthcareprovider.
GRAYISH&WATERY
Wateryorgrayishdischarge,particularlyifithasafishy odor,isoftenassociatedwithbacterialvaginosis. Alongsidethedischarge,theremaybediscomfort, itching,orirritation.Thisconditionneedstobediagnosed andtreatedwithappropriateantibioticsbyahealthcare provider.
T H E L U T E A L P H A S E
WHATYOURDISCHARGECOULDINDICATE 42
WHAT TO EAT
LEAN PROTIEN FOODS

Proteinsupportsmusclerepairandgrowth,andprovidesthebodywith essentialaminoacids.


Toreplenishironlostduringmenstruationandcombatfatigue.
OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
Omega-3splayaroleintheproductionofhormonesthatregulatethe menstrualcycle.

FIBER RICH FOODS
Fiberaidsindigestionandhelpsinmaintainingstablebloodsugarlevels.

RICH FOODS

VitaminB6isimportantforhormoneregulationandmoodstabilization.




































































MANAGINGTHELUTEALPHASE
T
E A L P H A
H E L U T
S E
Whole Grain
Chicken Salmon
Legumes
Apples
Seeds
Walnuts
Tofu Chia
Quinoa Fish
Flaxseeds Berries
43
VITAMIN-B6
Spinach
IRON RICH FOODS Lentils
Cheese Fish Eggs Cooked Oysters
Red Meat Pumpkin Seeds

ACTIVITIES TO TRY
MINDFULNESS PRACTICES
Breathing Exercises
FiberArts

OUTSIDE ACTIVITIES
CREATIVE ACTIVITIES CARDIO EXERCISES


Walking Meditation Gratitude
Seated Forward Bend BridgePose MANAGINGTHELUTEALPHASE Writing Painting Coloring Cycling Swimming
Journaling
Supine Spinal Twist
T H
P H A S E
Mindful Listening
E L U T E A L
Dancing YOGA 44 Rock Climbing Surfing Hiking Paddle Sports
Legup thewall
S T A G E S
STAGESOFLIFE
Understandingmenstrualhealthiscrucialat everystageoflife.Fromtheonsetof menstruationinadolescencetothechanges experiencedduringthereproductiveyears,and finallytothetransitionintomenopause,each phasepresentsuniquechallengesand considerations.
ADOLESCENCE (ONSET TO LATE TEENS)

Onset
Theonsetofmenstruationistypicallybetweenages9and16.
CycleCharacteristics:
Irregularcyclesarecommonasthebodyadjuststonew hormonalchanges.
Fertility:
Irregularcyclesarecommonasthebodyadjuststonew hormonalchanges.
Commonissues:
Periodsmaybeheavyorlight,andsomeadolescents experienceseverecramps(dysmenorrhea)orpremenstrual syndrome(PMS).
Tips:
Ensureadietrichinironandcalciumtosupportoverall health.
Learnaboutmenstrualhygieneandthevariousproducts available(pads,tampons,menstrualcups).
Seekadviceifperiodsareexcessivelypainful,irregular,or heavy.
20S TO EARLY 30S
CycleRegularity:
Menstrualcyclestendtobecomemoreregularduringthis stage.
Fertility:
Irregularcyclesarecommonasthebodyadjuststonew hormonalchanges.
CommonIssues:
Conditionslikepolycysticovarysyndrome(PCOS)or endometriosismaybecomeapparent.
Tips:
Routinegynecologicalexamstomonitorreproductivehealth. Maintainahealthylifestylewithregularexerciseandstress management.
Considercontraceptiveoptionsifpregnancyisnotdesired.
L
F
O F
I
E
45

CycleRegularity:
MID 30S TO EARLY 40S
Cyclesmaybecomeshorterorlesspredictableashormone levelsbegintofluctuate.
Fertility:
Fertilitygraduallydeclines,andtheriskofconditionslikefibroids increases.
CommonHealthConcerns:
Increasedawarenessofreproductivehealthissuesand screenings(e.g.,forcervicalcancer).
Tips:
Getregularscreeningsforreproductivehealthissues.
Maintainahealthylifestylewithregularexerciseandstress management.
Managestressthroughmindfulness,yoga,orotherrelaxation techniques.
Considercontraceptiveoptionsifpregnancyisnotdesired.
MID 40S TO EARLY 50S
CycleRegularity:
Menstrualcyclesbecomemoreirregular,withvaryingflow intensity.
Fertility:
Fertilitydeclinessignificantly,butpregnancyisstillpossibledueto occasionalovulation.
CommonIssues:
Hotflashes,nightsweats,andmoodswingsarecommondueto fluctuatinghormonelevels.
Tips:
IncreaseintakeofcalciumandvitaminDtosupportbonehealth. Payattentiontomentalhealthandseeksupportifexperiencing moodswingsordepression.
Considercontraceptiveoptionsifpregnancyisnotdesired.
CycleRegularity:
MID 50S+
Menstrualcyclesendwithmenopause.MenopauseisDefinedas 12consecutivemonthswithoutamenstrualperiod.
Fertility:
Menopausemarkstheendofnaturalfertility
CommonIssues:
Symptomsofmenopausemaycontinue,includinghotflashes, vaginaldryness,andsleepdisturbances.Increasedriskof osteoporosisandcardiovasculardisease.
Tips:
Monitorhearthealth&getregularbonedensityscans. Maintainregularvisitstothehealthcareproviderforongoing healthmanagement.
S T A G E S O F L I F E
46
E S O U R C E S
Gynecologists
HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
Specialistsinreproductivehealthwhocanprovide personalizedadvice,screenings,andtreatmentoptions.
PrimaryCarePhysicians:

Generalhealthsupportandreferralstospecialistsasneeded.
Endocrinologists: Expertsinhormonalissuesandmanagement.
EDUCATIONAL WEBSITES
PLANNEDPARENTHOOD.ORG
Resourcesonreproductivehealth,contraception,menstrual education,andaccesstohealthcareservices.
PERIOD-ACTION.ORG/EDUCATION
Offerseducationandresourcestopromotemenstrualhealth advocacyandawareness.
DIVINEDROPS.ORG
Providesholisticapproachestomenstrualhealth,including herbalremedies,yoga,andself-carepractices.
FINANCIAL
Foodbanks,diaperbanks,andshelterstypicallyofferfree menstrualproducts.
AllianceforPeriodSuppliesisanorganizationsponsoredbyU byKotex.Ifyouorsomeoneyouknowneedsperiodsupplies,text 211orvisit211.orgtofindalocationnearyouthatoffersfree tamponsandpads.
AuntFlow(goauntflow.org)Provideshigh-qualityand sustainableperiodproductsforyourschoolorbusiness. AtlantaGLOW(atlantaglow.org/help)submitarequestfor assistancethroughAtlantaGLOW’sneed-basedFHSA&period+ assistance
HelpingMamas(helpingmamas.org)HelpingMamasworkswith schooldistricts,shelters,healthdepartmentsandother organizationstomakesurethatnooneisleftbehindbecauseof periodpoverty.
APPS
EUKI
Developedbyleadingreproductivehealthresearchers, privacyexperts,andusers,Eukiisdesignedtoempower individualstolearnabouttheirbodiesandtakecontroloftheir health.Theycallthemselves:"Aperiodtrackerthatdoesn’t trackyou."
REDDIT
Subredditssuchasr/Periods&r/PCOSofferpeersupport, sharedexperiences,anddiscussionsonmenstrualhealth topics.
R
47

GLOSSARY
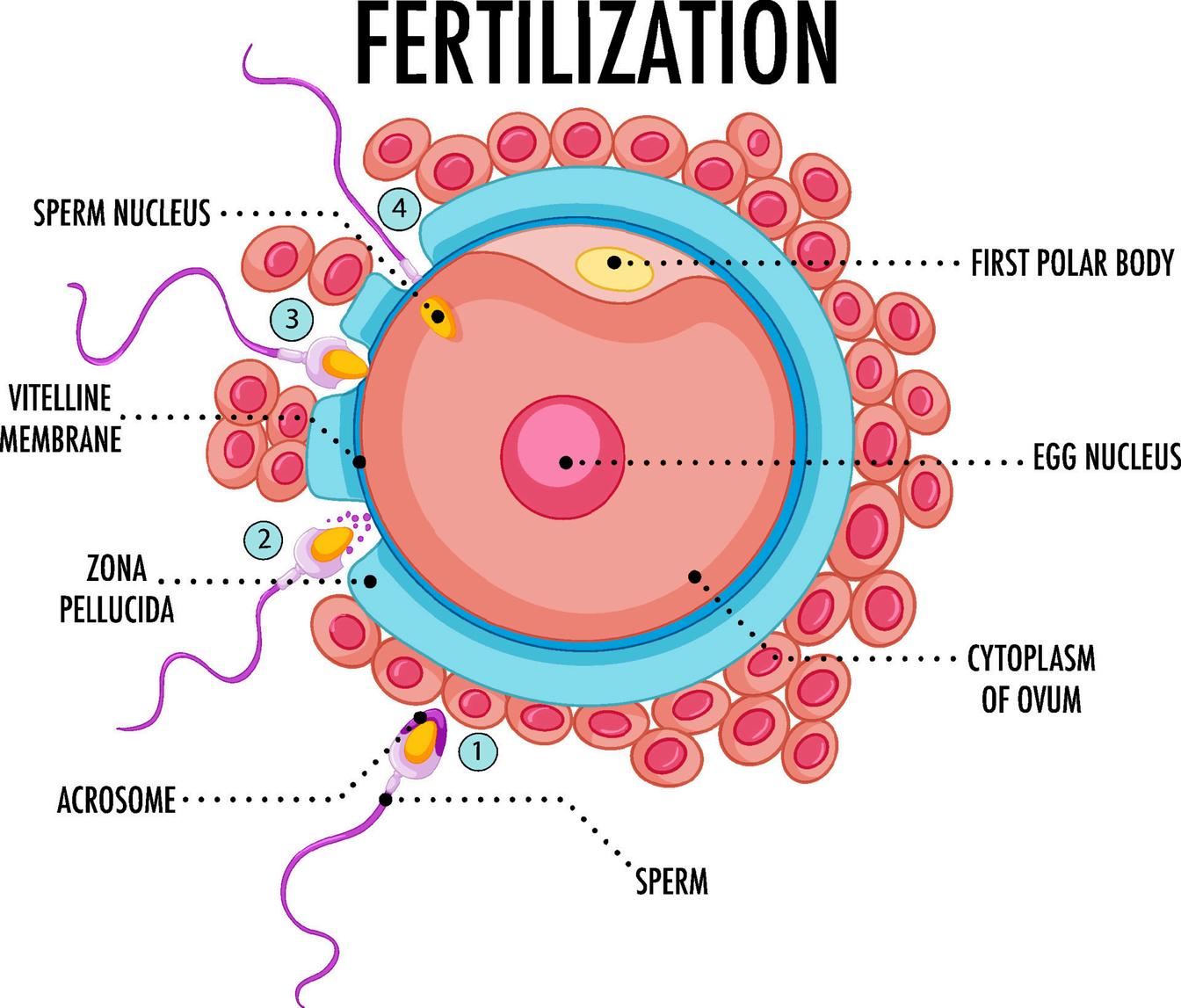
Acrosome:Acap-likestructurecoveringtheheadofaspermcell,containing enzymesnecessaryforfertilization.
Anemia:Aconditioncharacterizedbyadeficiencyofredbloodcellsor hemoglobinintheblood,oftenassociatedwithheavymenstrualbleeding.
AntralFollicle:Asecondaryfolliclewithafluid-filledcavity(antrum) surroundingtheoocyte.
Antrum:Thefluid-filledcavityintheovarianfolliclesurroundingtheoocyte.
Amenorrhea:Theabsenceofmenstruation.
CorpusAlbicans:Theremnantofthecorpusluteumafteritregressesif pregnancydoesnotoccur.
CorpusLuteum:Atemporaryendocrinestructureformedintheovaryafter ovulation,secretingprogesteronetopreparetheuterusforimplantation.
CervicalMucus:Fluidproducedbythecervix,whichchangesinconsistency duringthemenstrualcycleandcanbeusedtotrackfertility.
Cervix:Thelowerpartoftheuterusthatopensintothevagina.
CytoplasmofOvum:Thesubstanceinsidetheeggcell(ovum)containing organellesnecessaryforfertilizationandearlyembryodevelopment.
Dysmenorrhea:Painfulmenstruationthatcaninvolveseveremenstrualcramps.
Endometriosis:Aconditioninwhichtissuesimilartothelininginsidetheuterus (theendometrium)growsoutsidetheuterus,causingpainandpotentially affectingfertility.
Endometrium:Theinnerliningoftheuterus,whichthickensduringthemenstrual cycleandshedsduringmenstruation.
Estrogen:Ahormoneproducedbytheovariesthatregulatesthemenstrual cycleandpreparestheendometriumforpregnancy.
FallopianTubes:Tubesthatconnecttheovariestotheuterusandthroughwhich aneggtravelsduringovulation.
Follicle-stimulatinghormone(FSH):Ahormoneproducedbythepituitarygland thatstimulatesthegrowthofovarianfollicles.
Follicles:Smallsacsintheovariesthatcontainimmatureeggs.
FirstPolarBody:Asmallcellcontaininggeneticmaterialexpelledfromtheegg duringoocytematuration.
Galactorrhea:Thespontaneousflowofmilkfromthebreast,unrelatedto breastfeeding,oftencausedbyhormonalimbalances.
GranulosaCells:Cellssurroundingtheoocytewithintheovarianfollicle,playing aroleinfolliculardevelopmentandhormoneproduction.
Glycoprotein:Atypeofproteinthatcontainsacarbohydratemoiety,playing variousrolesinthebody,includingstructuralandsignalingfunctions.
Hyperthyroidism:Aconditioncharacterizedbyanoveractivethyroidgland, whichcanaffectmenstrualcyclesandreproductivehealth.
48
GLOSSARY
Hypoprolactinemia:Aconditioncharacterizedbyabnormallylowlevelsof prolactinhormone,whichcanaffectmenstrualcyclesandfertility.

Hypothyroidism:Aconditioncharacterizedbyanunderactivethyroidgland, whichcanaffectmenstrualcyclesandreproductivehealth.
Insulin:Ahormoneproducedbythepancreasthatregulatesbloodsugarlevels andcanaffectmenstrualcyclesandfertility.
Libido:Aperson'soverallsexualdriveordesireforsexualactivity.
LuteinizingHormone(LH):Ahormoneproducedbythepituitaryglandthat triggersovulationandthedevelopmentofthecorpusluteum.
Menarche:Thefirstoccurrenceofmenstruation.
Menopause:Thetimethatmarkstheendofmenstrualcycles,diagnosedafter12 monthswithoutamenstrualperiod,typicallyoccurringbetweentheagesof45 and55.
Menorrhagia:Abnormallyheavyorprolongedmenstrualbleeding.
MenstrualCups:Reusable,bell-shapedcupsmadeofsiliconeorrubberinserted intothevaginatocollectmenstrualblood.
MenstrualDiscs:Disposableorreusablediscsthatareinsertedintothevaginal fornixtocollectmenstrualblood.
MenstrualPhase:Thephaseofthemenstrualcycleduringwhichtheliningof theuterusisshed,resultinginmenstrualbleeding.
Oligomenorrhea:Infrequentmenstrualperiods,definedascycleslongerthan35 daysorfewerthansixtoeightperiodsperyear.
Oocyte:Animmatureeggcell.
Ovulation:Thereleaseofamatureeggfromthesurfaceoftheovary,usually aroundthemid-pointofthemenstrualcycle(day14ina28-daycycle).
PMDD(PremenstrualDysphoricDisorder):Asevereformofpremenstrual syndromecharacterizedbydebilitatingemotionalandphysicalsymptoms.
Pantyliners:Thinabsorbentpadsworninsideunderwearforlightmenstrualflow orspotting,oftenusedatthebeginningorendofaperiod.
PeriodPanties:Underweardesignedwithextraabsorbentlayerstoabsorb menstrualflowwithouttheneedforadditionalmenstrualproducts.
PremenstrualSyndrome(PMS):Agroupofsymptomsthatoccurinwomen, typicallybetweenovulationandaperiod,includingmoodswings,tenderbreasts, foodcravings,fatigue,irritability,anddepression.
PrimaryFollicle:Animmatureovarianfolliclecontaininganoocytesurrounded byasinglelayeroffollicularcells.
Progesterone:Ahormoneproducedbytheovariesthatpreparesthe endometriumforthepotentialimplantationofanembryo.
49

GLOSSARY
Prostaglandins:Chemicalsinthebodythatareinvolvedinpainand inflammationandarereleasedduringmenstruation,leadingtomenstrual cramps.
ProliferativePhase:Thephaseofthemenstrualcyclefollowingmenstruation, characterizedbythethickeningoftheendometriuminpreparationforpotential implantationofafertilizedegg.
ReusableClothPads:Washablefabricpadsworninsideunderweartoabsorb menstrualflow.
SanitaryPads(MenstrualPads):Absorbentitemsworninsideunderwearto absorbmenstrualflow.
SecondaryFollicle:Adevelopingovarianfolliclecontaininganoocyte surroundedbymultiplelayersoffollicularcells.
Sperm:Malereproductivecellsproducedinthetestes,necessaryforfertilizing anegg.
SpermNucleus:Thegeneticmaterial-containingpartofthespermcell.
Tampons:Absorbentcylindersinsertedintothevaginatoabsorbmenstrual blood.
Testosterone:Ahormoneprimarilyproducedinthetestesinmalesandin smalleramountsintheovariesinfemales,playingaroleinlibidoand reproductivehealth.
ToxicShockSyndrome(TSS):Ararebutseriousconditioncausedbybacterial infection,oftenassociatedwithtamponuse.
Uterus:Theorganinthefemalereproductivesystemwhereafertilizedegg implantsandgrowsduringpregnancy.
Vagina:Themusculartubeleadingfromtheexternalgenitalstothecervixofthe uterusinwomen.
VesicularFollicle(GraafianFollicle):Amatureovarianfolliclecontainingafully developedoocytereadyforovulation.
VitellineMembrane:Amembranesurroundingtheeggcell(oocyte).
ZonaPellucida:Aglycoproteinlayersurroundingtheplasmamembraneof mammalianoocytes,playingaroleinfertilization.
Menstrualhealthisacrucialaspectofoverallwell-being.Bystaying informedandproactive,youcantakecontrolofyourmenstrualhealth andsupportothersindoingthesame.Thankyoufortakingthetime toreadthisbooklet,andforyourcommitmenttounderstandingand promotingmenstrualhealth.
Ifyouhaveanyfurtherquestionsorneedadditionalsupport,don't hesitatetoreachout.
Emailcommunityunitynetwork4change@gmail.com
50
PERIOD.
Menstruationisanaturalandvitalaspectof reproductivehealth,yetitremainssurroundedby misinformationandculturaltaboos.Bygaininga comprehensiveunderstandingofmenstruation,we canfosteramoreinformedandsupportive environmentforeveryone. Throughoutthiszine,weexploretheintricaciesofthe menstrualcycle,thephysicalandemotional symptomsassociatedwithmenstruation,andthe variouswaystomanageandmaintainmenstrual health.




























































































