

PREFACE
We have a great pleasure to present the first edition of building estimation notes by Civil Engineering. This book acts as a quick guide for all the civil engineers and quantity surveyors who keep an interest in building estimation.
Quantity Surveying is the branch of civil engineering in which the quantity surveyor makes the BOQ (Bill of Quantities) and analyses the rate, budget, schedule and net profit for an individual or company for a particular project. Main functions of quantity surveyors:
1. Before tendering: Making BOQ (Bill of Quantities) with the help of drawing provided by government/client and schedule rate provided by government/client.
2. During tendering : During tendering the quantity surveyor of any private company analyses the net profit by solving the estimation sheet with the help of BOQ provided by government/client.
3. After tendering: After tendering the quantity surveyor prepares the bill for the work which has been already executed according to order.
We are greatful to our esteemed students and clients, whose suggestions have been incorporated in this book. Any suggestions for further improvement of this book are always welcome.
1. FOOTINGS OF A BUILDING
2. COLUMNS OF A BUILDING
3. BEAMS OF A BUILDING
4. SLABS OF A BUILDING
5. UNIT CONVERSION
(5.1) STANDARD UNITS
(5.2) LAND MEASUREMENT
6. DETAILED BUILDING ESTIMATIONS
(6.1) EXCAVATION QUANTITY OF FOOTING
(6.2) PCC QUANTITY OF FOOTING
(6.3) CONCRETE QUANTITY OF ISOLATED FOOTING
(6.4) SHUTTERING AREA OF ISOLATED FOOTING
(6.5) CONCRETE QTY. OF COLUMN UPTO PLINTH BEAM
(6.6) SHUTTERING OF COLUMN BELOW PLINTH BEAM
(6.7) CONCRETE QUANTITY OF PLINTH BEAM
(6.8) SHUTTERING AREA OF PLINTH BEAM
(6.9) CONCRETE QTY. OF COLUMN ABOVE PLINTH BEAM
(6.10) SHUTTERING AREA OF COLUMN ABOVE PLINTH BEAM
(6.11) CONCRETE QUANTITY OF ROOF BEAM
(6.12) SHUTTERING AREA OF ROOF BEAM
(6.13) CONCRETE QUANTITY OF SLAB
(6.14) SHUTTERING AREA OF SLAB
7. BRICKWORK ESTIMATION
(7.1) INTRODUCTION TO BRICKWORK CALCULATION
(7.2) BRICKWORK OF BUILDING FOUNDATION
(7.3) BRICKWORK ABOVE PLINTH LEVEL
T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S
8. PLASTERWORK
9. STAIRCASE
10. CEMENT, SAND AND AGGREGATE
11. BAR BENDING SCHEDULE
(11.1) PROCEDURE OF BAR BENDING SCHEDULE
(11.2) RINGS
(11.3) CUTTING LENGTH OF RINGS
(11.4) BBS OF FOOTING
(11.5) BBS OF FOOTINGS OF A PLAN WITH EXCEL SHEET
(11.6) BBS OF COLUMN
(11.7) CUTTING LENGTH OF RINGS OF COLUMN
(11.8) BBS OF COLUMNS OF A PLAN WITH EXCEL SHEET
(11.9) BBS OF PLINTH BEAM
(11.10) CUTTING LENGTH OF RINGS OF PLINTH BEAM
(11.11) BBS OF PLINTH BEAMS OF A PLAN WITH EXCEL SHEET
(11.12) BBS OF ROOF BEAM
(11.13) CUTTING LENGTH OF RINGS OF ROOF BEAM
(11.14) BBS OF CONTINOUS ROOF BEAM
(11.15) CUTTING LENGTH OF RINGS OF ROOF BEAM
(11.16) BBS OF ROOF BEAMS OF A PLAN WITH EXCEL SHEET
(11.17) BBS OF ROOF SLAB
(11.18) BBS OF ROOF SLABS OF A PLAN WITH EXCEL SHEET
(11.19) BBS OF RAFT FOUNDATION
(11.20) BBS OF STAIRCASE
FOOTINGSOFABUILDING
Footingsarethepartofthefoundationofastructure.Theyarethe firstRCC(ReinforcedCementConcrete)membersofastructure. Theyareconstructedtoprovidesupportbaseforthecolumns.

Steps involved in the execution of foundation of any building
There are about 11 steps involved in the execution of foundation: Fig.(1.1) Side view of a footing
LandSurveyofSitepreparationincludesSoiltesting. Markingandlayout.
Excavationaccordingtodrawing.
Dewateringthroughhydraulicpump.
TermiteControl(antitermitesolutionissprayedbelowthePCC). PolytheneSheet.
P.C.C(PlainCementConcrete)–Ratio(1:4:8),Thickness10-15cm. Footingreinforcement/neckcolumnreinforcement.
Shuttering,Concreting,De-shuttering. Bitumenpainttoallthesurfaceoffootingandneckcolumn. Backfilling.
The PCC work done at the bottom of the footing for providing the base is known as lean concrete.
Anti termite control is done to avoid the presence of termite in building. First we have to secure the PCC of footing and foundation. The treatment is done on plinth level which involves inserting anti termite solution in the soil. After this the soil area is covered with a layer of sand of thickness 75mm. This layer of sand restricts the entry of termites.
RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) members on the basis of bearing Capacity:
TYPES OF FOOTING
Plain footing is the footing with a single neck column. These footings are used in residential buildings. The bearing capacity of soil is usually normal for plain footing.
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering area of Plain footing:

Fig.(1.2) Top view of plain footing
Given:
Footing length (L) = 1.4m
Footing breadth (B) = 1.2m
Footing depth (D) = 0.3m
Column size = (0.3m x 0.3)m
Solution:

Front view of plain footing
Area of Footing = length x breadth = 1.4 x 1.2 = 1.68sq-m
Volume of concrete = area x depth = 1.68 x 0.3 = 0.504cu-m
Shuttering area of footing = 2(length+breadth) x depth
= 2(1.4+1.2) x 0.3 = 1.56sq-m
2. Step Footing
It is the footing with a single neck column and more than two steps of footing. The thickness of all the footings is same in step footing. Step footings are generally used in commercial buildings or high rise buildings where the soil bearing capacity is low. Step footings have more strength than plain and isolated footings. This is why these footings are used in high rise buildings. They can be used for deep to shallow foundations.
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering area of Step footing:

Fig.(1..5) Top view of Step footing
Given:
In step footing all the steps are square shaped, therefore its length and breadth are same.
Length 1st step (L1)= 1.6m
Length 2nd step (L2)= 1.4m
Length 3rd step (L3)= 1.2m
Depth of all steps (D)= 0.15m

Step-1
Fig.(1.4) Side view of Step footing
Area of footing = length (L1) x length (L1) = 1.6 x 1.6 = 2.56sq-m
Volume of concrete = area x depth (D1) = 2.56 x 0.15 = 0.384cu-m
Shuttering area of footing = 4 x (length) x depth
Solution: = 4 x (1.6) x 0.15 = 0.96sq-m
Step-2
Area of footing = length (L2) x length (L2) = 1.4 x 1.4 = 1.96sq-m
Volume of concrete = area X depth (D2) = 1.96 x 0.15 = 0.294cu-m
Shuttering area of footing = 4 x (length) x depth = 4 x (1.4) x 0.15 = 0.84sq-m
Step-3
Area of footing = length (L3) x length (L3) = 1.2 x 1.2 = 1.44sq-m
Volume of concrete = area x depth (D3) = 1.44 x 0.15 = 0.216cu-m
Shuttering area of footing = 4 x (length) x depth = 4 x (1.2) x 0.15 = 0.72sq-m
Total volume of concrete (V) = Vol. step-1+Vol. step-2+Vol. step-3 = 0.384+0.294+0.216 = 0.894cu-m
Total shuttering = shuttering ar.1+shuttering ar.2+shuttering ar.3 = 0.96+0.84+0.72 = 2.52 sq-m
3. Plain Combined Footing
It is a single footing with more than two neck columns. It is generally used in malls, Parking areas, halls etc. Its soil bearing capacity is same as plain footing.
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering of Plain Combined footing:

Fig.(1.6) Top view of Plain Combined footing
Given:
From the top view and side view we can find the given:
Footing length (L) = 2.0m
Footing breadth (B) = 1.8m
Footing depth (D) = 0.4m

Area of Footing = length x breadth = 2.0 x 1.8 = 3.6sq-m
Volume of concrete = area x depth = 3.6 x 0.4 =1.44cu-m
Shuttering area of footing = 2(length+breadth) x depth
Solution: = 2(2.0+1.8) x 0.4 = 3.04sq-m
4. Isolated Tapered Footing
It is the footing with single neck column, tapered from top in a slope form from all sides. Its strength is more than plain footing because of its shape and extra volume. This shape gives it extra strength from all sides. This footing is used in commercial buildings such as school, colleges, malls, etc.
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering area of Isolated Tapered footing:

Given:
Footing Length (L) = 1.6m
Footing Breadth (B) = 1.4m
Footing Top Length (L1) = 0.8m
Footing Top Breadth (B1) = 0.7m
Height (H1) = 0.15m
Height (H2) = 0.35m
H = H2-H1
H = 0.35-0.15 = 0.2m
Solution:

Fig.(1.9) Side view of Isolated Tapered footing
Isolated footing is solved in two parts, first part is the rectangular portion and second part is the tapered portion.
Let us denote:
A1 = Area of Rectangular portion
V1 = Volume of Rectangular portion
A2 = Area of tapered portion
V2 = Volume of tapered portion
Total volume (V) = V1+V2
Now we calculate:
A1 = length (L) x breadth (B) = 1.6 x 1.4 = 2.24sq-m
A2 = length (L1) x breadth (B1) = 0.8 x 0.7 = 0.56sq-m
V1 = area (A1) x height (H1) = 2.24 x 0.15 = 0.336cu-m
V2 = H/3(A1+A2+√(A1 x A2 )) = 0.2/3(2.24+0.56+√(2.24 x 0.56 ) ) = 0.264cu-m
Total volume of isolated footing = V1+V2 = 0.336+0.264 = 0.6cu-m
Shuttering area of isolated footing = 2(L+B) x H1 = 2(1.6+1.4) x 0.15 = 0.9sq-m
5. Isolated Combined Footing
It is the footing having more than two neck columns and a single footing which is tapered. It is generally used in commercial complex or shopping malls.
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering area of Isolated Combined footing:

Fig.(1.10) Top view of Isolated Combined footing

Given:
Fig.(1.11) Side view of Isolated Combined footing
Footing length (L) = 2.0m
Footing breadth (B) = 1.8m
Footing top length (L1) = 1.6m
Footing top breadth (B1) = 1.4m
Height (H1) = 0.15m
Height (H2) = 0.45m
H = H2-H1 = 0.45-0.15 = 0.3m
Let us denote:
A1 = Area of rectangular portion
V1 = Volume of rectangular portion
A2 = Area of tapered portion
V2 = Volume of tapered portion
Total volume (V) = V1+V2
Now we calculate:
A1 = length (L) x breadth (B) = 2.0 x 1.8 = 3.6sq-m
A2 = length (L1) x breadth (B1) = 1.6 x 1.4 = 2.24sq-m
V1 = area (A1) x height (H1) = 3.6 x 0.15 = 0.54cu-m
V2 = H/3(A1+A2+√(A1 x A2)) = 0.3/3(3.6+2.24+√(3.6 x 2.24))
Note: Isolated footing is solved in two parts, first the rectangular portion and second is the tapered portion. = 0.867 cu-m
Total Volume of isolated footing = V1+V2 = 0.54+0.867
Solution: = 1.407cu-m
Shuttering area = 2(L+B) x H1 = 2(2.0 + 1.8) x 0.15 = 1.14sq-m
6. Strap/Shoe Footing
Strap footing is generally used for the plot where we have to construct a column attached to a neighboring wall. In this case the column cannot be constructed in the center of the footing, therefore we make use of strap footings in this scenario.

Fig.(1.12) Top view of Strap Footing
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering area of Strap Footing:
Given:
Footing length (L) = 1.2m
Footing breadth (B) = 1.0m
Footing depth (D) = 0.25m
Solution:
Area of footing = length x breadth = 1.2 x 1.0 = 1.2sq-m
Volume of concrete = area x depth = 1.2 x 0.25 = 0.3cu-m
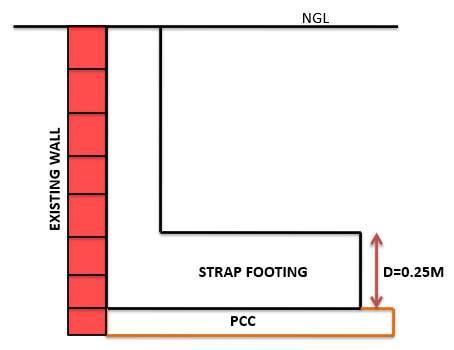
(1 13) Front view of Strap footing
Shuttering area of footing = (2(length)+ breadth) x depth
7. Raft/Mat Footing
It is provided where the bearing capacity of the soil is very low. This footing contains double mesh at full depth of raft. Generally it does not have neck column provided because the depth of the footing is till ground level. It is mostly used near sea or river where the soil bearing capacity is very low.
Calculation of concrete quantity and shuttering area of Raft Footing: = (2(1.2 )+1.0) x 0.25 = 0.85sq-m

Fig.(1.14) Top View of Raft footing

Given:
Footing length (L) = 3.5m
Footing breadth (B) = 3m
Footing depth (D) = 0.5m
Solution:
Area of footing = Length x Breadth = 3.5 x 3 = 10.5sq-m
Volume of concrete = Area x Depth = 10.5 x 0.5 = 5.25cu-m
Shuttering area of footing = 2(length+breadth) x depth = 2(3.5+3) x 0.5 = 6.5sq-m
Did You Know?
Why PCC (plain cement concrete) work is done below footing?
Concrete is the mixture of cement, sand, aggregate and water. When the concrete of footing is poured directly on soil ,the soil soaks the slurry of concrete and then the concrete looses its strength. Therefore, PCC work creates a barrier between the concrete and the soil, thus avoiding their direct contact.




