1.1 Literature review
byDengChaoyang
What is Health?
‘Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity’ (World Health Organisation [WHO], 1948: 100).
What is Health Care
Health: Physical Social Mental Spiritual health
Health
Care:
Prevention Dianosis Treatment
Amelioration
Types: primary Secondarycarecar
Tertiary care
Public health
Quaternary care Home and community
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. The term includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, tertiary care, and public health.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5911255_Antonovsky’s_sense_of_coherence_scale_and_its_relation_with_quality_of_life_A_systematic_review

Global concentrations of health care resources, as depicted by the number of physicians per 10,000 individuals, by country. Data is sourced from a World Health Statistics 2010, a WHO report.[needs update]
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK584067/
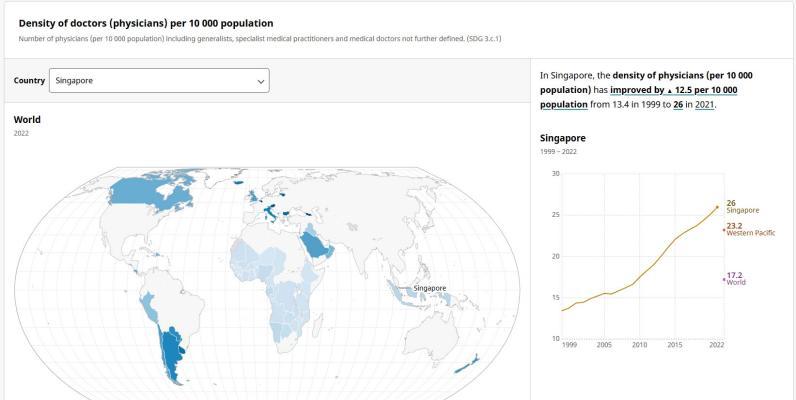
In 2023, Singapore’s density of doctors reached approximately 28 doctors per 10,000 inhabitants. This indicates an increase from the previous years as well as marks an all-time high within this timeframe.
https://data.who.int/indicators/i/CCCEBB2/217795A
ProbeA: Literature& Background research
The patient experience in Singapore
People in the ministry of public health are caring about the health experience in health care system.

https://aio.nuhs.edu.sg//redcap/surveys/?s=HPCYK7CFWD&smode=2 https://www.singhealth.com.sg/news/tomorrows-medicine/better-patient-experience-and-outcomes-as-value-driven-care-expands-across-singhealth
Accouding to Survey of Patient Satisfaction with Public Healthcare Institutions data of 2015
85.9% of respondents rated their overall satisfaction levels with the public HCIs as “excellent” and “good” (compared with 79.1% in 2014).
83.8% of respondents rated the public HCIs as having met or exceeded expectations (compared with 80.6% in 2014).
84.9% of respondents were willing to recommend the public HCIs to others (compared with 82.4% in 2014).
72% of respondents rated the affordability of the services provided by the public HCIs as ‘excellent’ or ‘good’ (compared with 68.7% in 2014).
1.1 Literature review byDengChaoyang But?
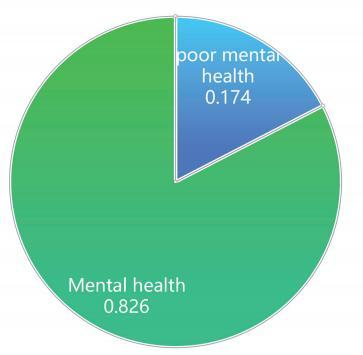
Prevalence of poor mental health increasing in Singapore; young adults have highest proportion at 25.3%
Data was collected from around 8,000 adults through self-reported household interviews and about 9,000 adults through health examinations.
The survey findings showed that the prevalence of poor mental health increased from 13.4 per cent in 2020 to 17 per cent in 2022.
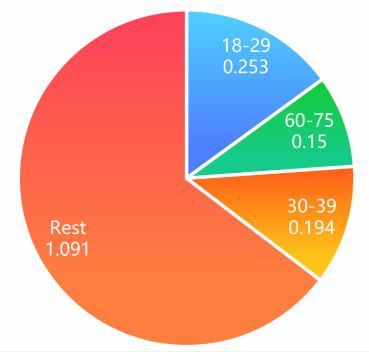
Younger adults aged 18 to 29 had the highest proportion of poor mental health at 25.3 per cent. The prevalence for other age groups was much lower, ranging from 10.5 per cent for those aged 60 to 74 to 19.4 per cent in those aged 30 to 39 years, results showed.
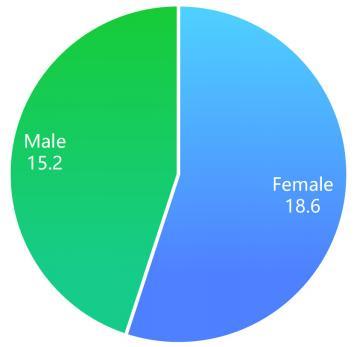
There were also more females (18.6 per cent) with poor mental health compared to males (15.2 per cent), according to the survey.
About 56.6 per cent of Singapore residents were willing to seek help from health professionals in 2022 - slightly lower than 58.3 per cent in 2021 but higher than 47.8 per cent in 2019.
Among the age groups, Singapore residents aged 60 to 74 years (48.1 per cent) were the least willing to seek help from healthcare professionals in 2022, while those aged 30 to 39 years (62 per cent) were the most willing.
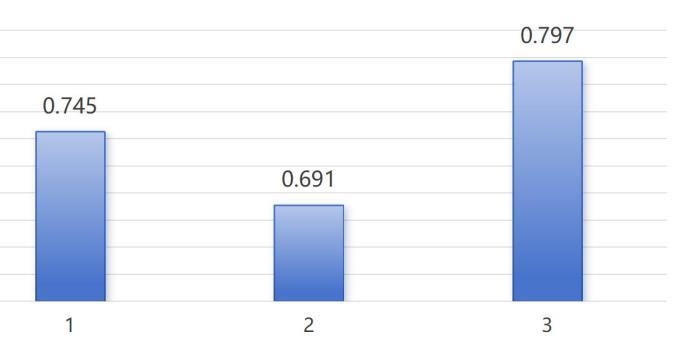
Meanwhile, the proportion of residents willing to seek help from informal support networks such as friends and family rose to 79.7 per cent in 2022, up from 69.1 per cent in 2021 and 74.5 per cent in 2019.
Younger adults aged 18 to 29 years were most willing to seek help from these networks (88.1 per cent), while older adults aged 60 to 74 years were least willing (68.4 per cent).
The increased willingness to seek help for mental health issues "reflects continued public awareness of mental health and reduced stigma around mental health conditions”, said MOH in a joint press release with the Health Promotion Board (HPB).
https://cnalifestyle.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/poor-mental-health-young-adults-seek-help-moh-survey-379391
1.2 HistoryTimeline of Health care
byDengChaoyang
Such as imitating animals by licking them with their tongues or washing away blood with stream water after being injured
No distinction between medical care and nursing. Early treatment care included delivery, wound bandaging and hemostasis, dietary adjustment
Mummies - bandage techniques, herbal, animal, mineral medicines - preparations (pastes and pills), hypnosis, hemostasis, wounds, sutures, vomiting
Claudius Galenus Creating a unique medical system like public baths, sewers, and stadiums; paying attention to environmental hygiene in preventing disease
Hippocrates introduced medicine into the scientific: explore the cause of disease.
Emphasis on diet conditioning; personal hygiene; physical therapy;
The fraternity and sacrifice influence on medical care for more than a thousand years.
Clergy built charitable institutions such as temples, relief homes, and nursing homes to spread religious beliefs;
some women who devoted themselves to religious causes participated in the care of the elderly, the weak, the sick, and the disabled, which moved nursing work from the family to the social stage.







Churches and monasteries generally have hospitals. Nuns' good moral qualities and rich experience have improved the status of nursing work
St. John of Christ of the cross organized the "Crusader Rescue Corps" responsible for transporting the wounded and taking emergency care measures.
In addition to taking good care of the wounded and sick, she also improved hospital management.
The mortality rate of soldiers dropped from 50% to 2.2%
1. Reform the army's health care; 2. Create the world's first nursing school; 3. Write books;
In addition, Nightingale also supported regional home care. Under her influence, Swiss banker Dunant founded the International Red Cross in Geneva in 1864
Public health campaign: Strengthening sanitation and water supply systems. Rapid advances in medical imaging technologies (such as X-rays, CT and MRI), establishment of WHO
Minimally invasive and robotic surgery. Electronic health records.
Telemedicine, artificial intelligence, and wearable device innovations.
Expanding the coverage of medical services through telemedicine and mobile technology. In-depth application of artificial intelligence in diagnosis and treatment






From unscientific to scientific, it seems that there is a fixed place for medicine, will this phenomenon be broken in the future? Realize remote diagnosis and treatment and physical monitoring when returning home from the hospital
1.2 HistoryTimeline of Health care
byDengChaoyang
Power beyond the health care
Influence of religion in healthcare
Religious teachings often emphasize compassion, charity, and the sanctity of human life. These principles motivated many religious groups and individuals to care for the sick, poor, and vulnerable, laying the groundwork for what we now recognize as humanitarian and medical care.
Mummies - bandage techniques, herbal, animal, mineral medicines - preparations (pastes and pills), hypnosis, hemostasis, wounds, sutures, vomiting
Hippocrates introduced medicine into the scientific: explore the cause of disease.
Emphasis on diet conditioning; personal hygiene; physical therapy;
The fraternity and sacrifice influence on medical care for more than a thousand years.
Clergy built charitable institutions such as temples, relief homes, and nursing homes to spread religious beliefs;
some women who devoted themselves to religious causes participated in the care of the elderly, the weak, the sick, and the disabled, which moved nursing work from the family to the social stage.




Churches and monasteries generally have hospitals. Nuns' good moral qualities and rich experience have improved the status of nursing work
St. John of Christ of the cross organized the "Crusader Rescue Corps" responsible for transporting the wounded and taking emergency care measures.
Medieval Military nursing


Consistent Goal of Healing:
From ancient mummification practices (using bandages, herbal and other remedies) to Hippocrates’ scientific exploration of disease, and later the charitable care provided by religious institutions, every era has aimed to treat illness and ease suffering.
Blending Empirical Techniques with Spiritual/Charitable
Early treatments often mixed practical techniques (like suturing, wound care, and even hypnosis) with beliefs and rituals. Hippocrates introduced a more systematic, evidence-based approach, yet the compassionate, community-centered care continued—often driven by religious organizations and dedicated individuals.
1.3 Conclusion of Holistic health byDengChaoyang

-Culture. What is one’s cultural inheritance? What values and traditions — including art, performances, ceremonies, rites, crafts, and ways of life — would one like to bring into the present and preserve for the future? What can one’s culture teach us about living healthily and well?
-Body. What are the body’s needs for nutrition, sleep, exercise, and rejuvenation? What are the underlying causes of physical pain, and what steps can be taken to ameliorate this pain — or live with it? What actions can be taken to prevent bodily injury, illness, and disease?
-Mind. What are the mind’s needs for stimulation, curiosity, wonder, and creative expression? What information and lessons do our emotions provide? What is an embodied account of the mind and spirit? What are its interdependent connections with others and the environment?
-Spirit. What practices and rituals connect us with something larger than ourselves? How can we connect with the divine, with nature, with ancestors, and with other sources of deep purpose and meaning beyond oneself?
-Environment. What are the unique features of the space one lives in — the neighborhood, geography, flora, and fauna? Who lives nearby, and how has this place changed over time? What is the history of this place? How does this place affect one’s health — is it clean, welcoming, loud, harsh, disruptive, joyful, or peaceful? What healing and help does this environment need to be healthy?
3.1 Location of the site


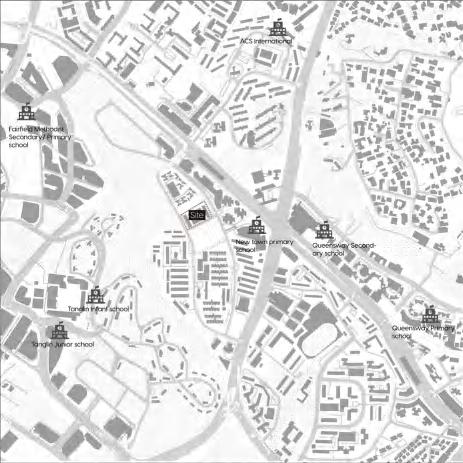
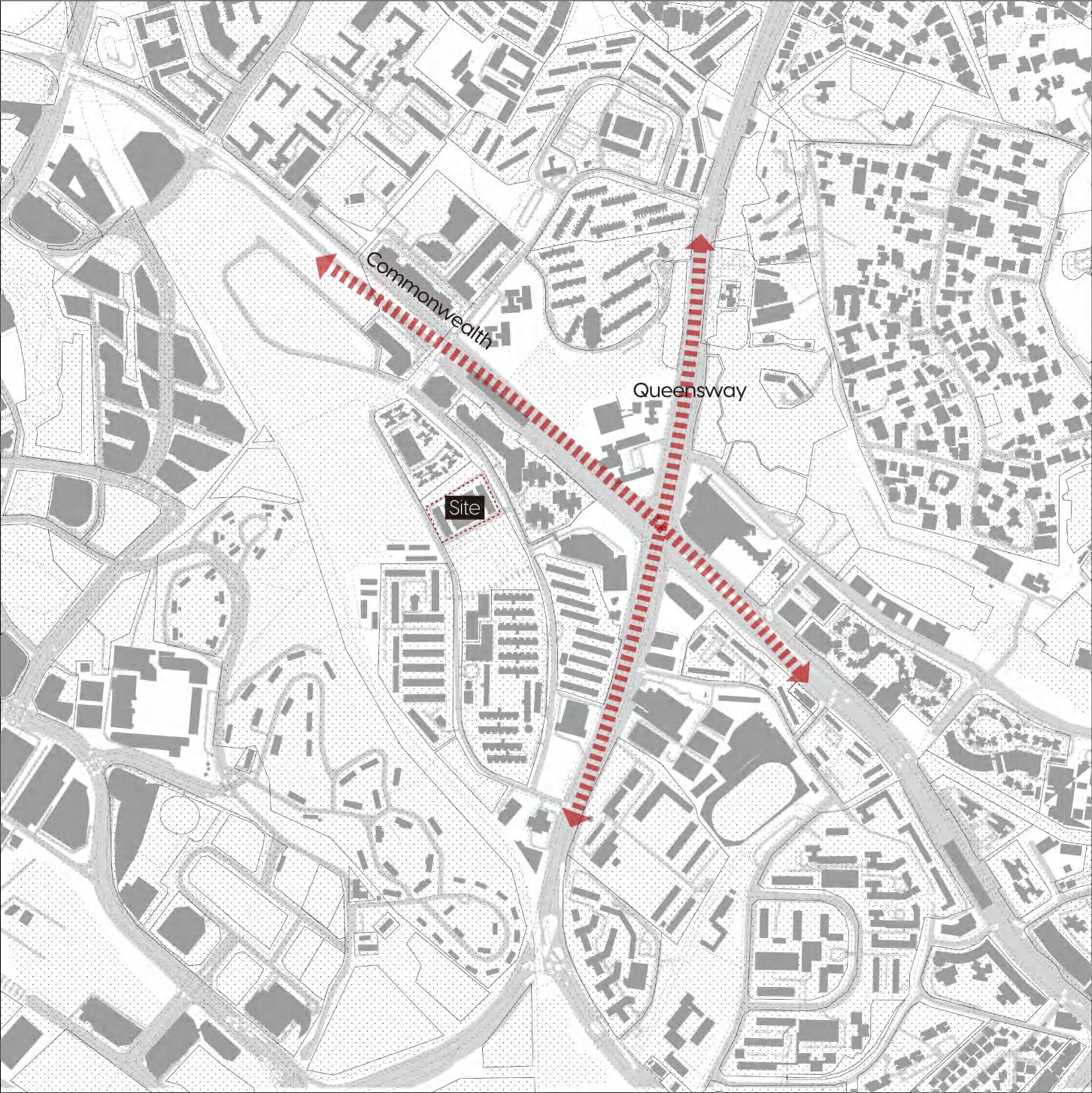
3.2 Historical memory of the site
byDengChaoyang
Tanglin Hawker center
Tanglin Halt Neighbourhood Centre, which housed the former Commonwealth Drive Food Centre and existing Tanglin Halt Market. Most stallholders from the former Commonwealth Drive Food Centre have relocated to the new Margaret Drive Hawker Centre sited within the SkyResidence @ Dawson development, while Tanglin Halt Market is still in operation.





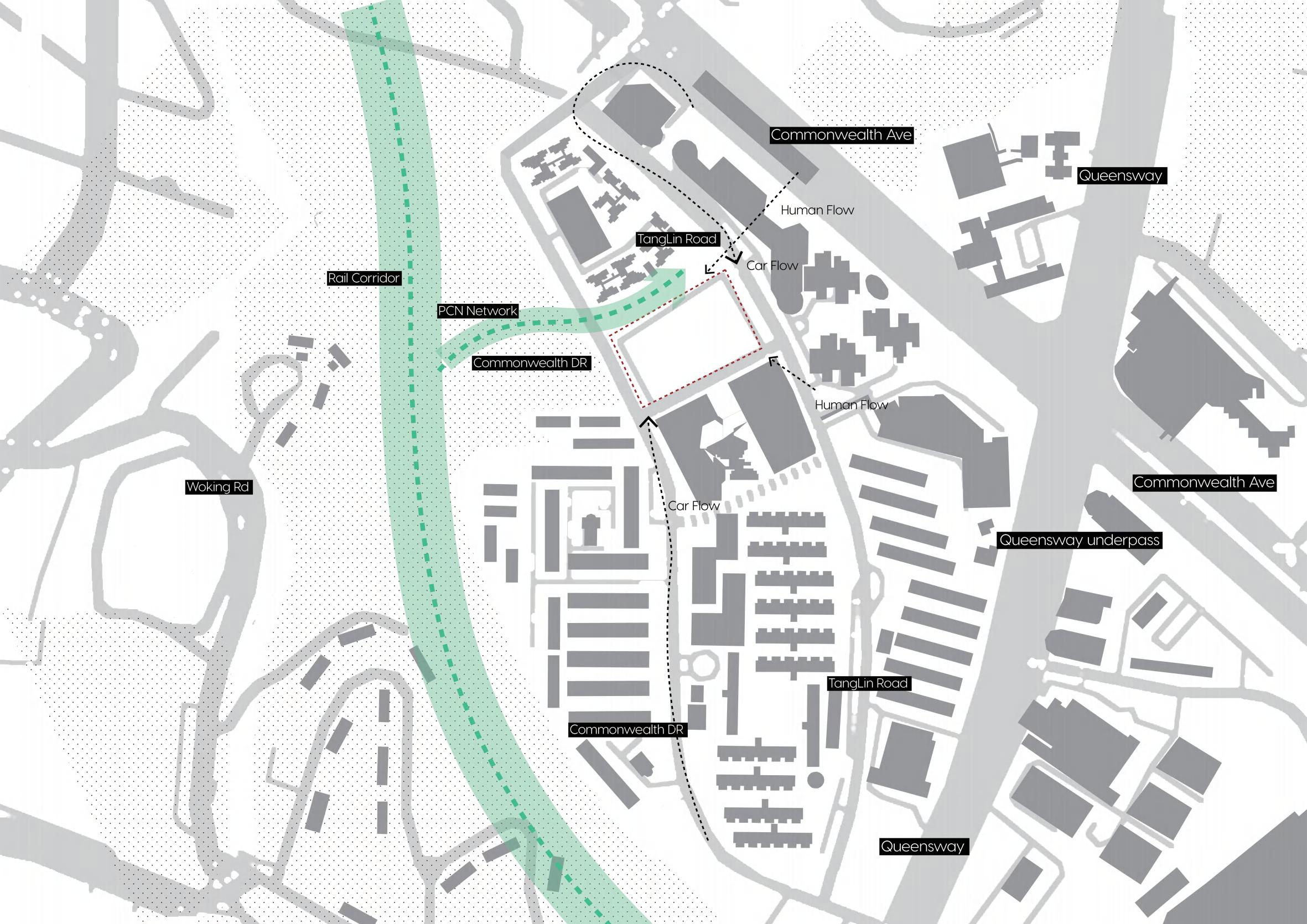
byDengChaoyang
Redeveloped Tanglin Halt Estate to Have New Hawker Centre and Market, and Polyclinic
HDB will progressively redevelop Tanglin Halt to ensure that it stays vibrant and attractive.The redevelopment plans will focus on introducing new amenities and facilities for existing and future residents, and improving connectivity for pedestrians and cyclists between Commonwealth MRT Station and the Rail Corridor. Additionally, the greenery will be enhanced, and as much of Tanglin Halt’s history and heritage will be retained as possible.
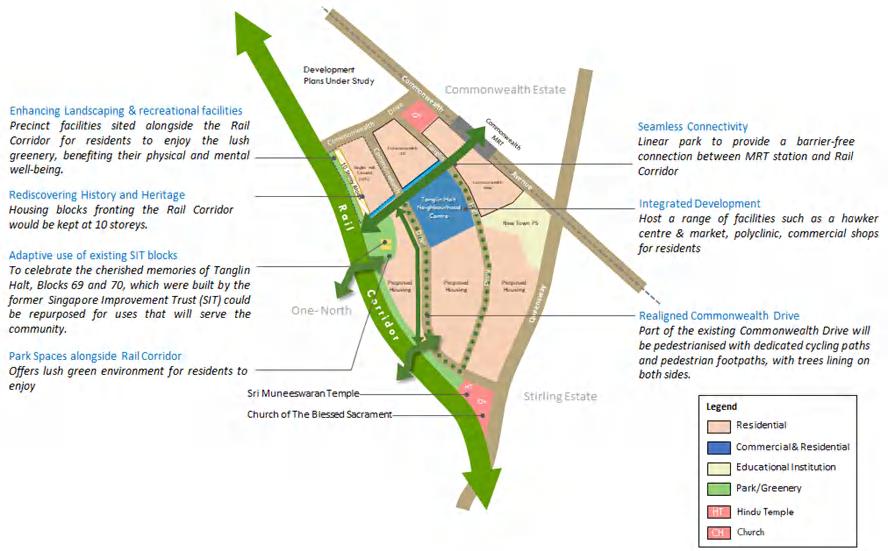
https://www.hdb.gov.sg/cs/infoweb/about-us/news-and-publications/press-releases/19102023-Redeveloped-Tanglin-Halt-Estate-to-Have-New-Hawker-Centre-and-Market-and-Polyclinichealth--at-the-22nd-asia-pacific-medical-education-coneference-2025

3.5 Chritical thinking of the site
byDengChaoyang
Argueing: Can we improve the Phrase 2 in the redevelopment of Tanglin Halt

Community networks are disrupted:
Residents who have lived here for a long time, especially the elderly, have formed stable neighborhood relationships and mutual assistance networks. Forced relocation and the construction of new communities may make it difficult to maintain this long-established sense of community belonging, thus affecting the mental health and life satisfaction of residents.
The spirit of the place is not preserved:
As one of Singapore’s earlier public housing estates, Tanglin Halt carries a rich history and memory. Redevelopment may cause this unique historical culture to be erased in the process of modernization, thus losing an intangible urban memory.
Density of Residence:
Although the population density of Tanglin Halt has been declining in recent years, it is still very high, from 13,160 to 10,590 before the demolition. If the planned 5,900 households are added, the population density will exceed the 20,000 people in the surrounding Margenet Drive.
Small and depressing space
Although the tanglin halt center is retained in the design, the atrium and open space of the entire HDB block are too small. Although the roof garden is retained, there is a lack of large open space. Secondly, the distance between the second phase building and the adjacent buildings is too small. The east-west distance between more than 40 floors is less than 40m.
Parts of design: Home ward module,Vittual HQ and Community center
Community Vitality and Nutrition Center
Sports empowerment, cross-age social interaction
Office study and spiritual healing Ecological education, natural Therapy Strategic R&D and Physical and Mental Regeneration
3.5
































