comet





Space is defined as the vast, seemingly infinite expanse that exists beyond the Earth’s atmosphere, encompassing all celestial bodies, including stars, planets, moons, and galaxies. It is characterized by a near vacuum, where matter is sparse and the laws of physics operate differently than on Earth. Space consists of our solar system, galaxies, stars.

Space can also refer to the three-dimensional continuum in which objects and events occur, allowing for the measurement of distance and volume. This concept is essential in fields such as astronomy, physics, and cosmology, as it provides the framework for understanding the universe and our place within it.

Our understanding of space has expanded remarkably, revealing a complex universe that encompasses billions of galaxies, each containing billions of stars and potentially countless planets. Advances in telescope technology, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, have allowed us to observe distant celestial phenomena and gather data on the origins of the universe, the formation of stars and planets, and the characteristics of exoplanets in habitable zones. There has to be aliens out there ngl.
Theoretical frameworks such as the Big Bang theory and dark matter research continue to shape our comprehension of cosmic evolution, while ongoing missions to Mars and the outer solar system enhance our knowledge of the conditions necessary for life beyond Earth. Despite these strides, many mysteries remain, including the nature of dark energy and the potential for extraterrestrial life, driving the quest for deeper understanding in this vast and enigmatic expanse.
Studying space is essential for numerous reasons, as it expands our understanding of the universe and our place within it. Knowledge gained from space exploration can lead to technological advancements, inspire innovation, and drive economic growth through the development of new materials and methods. Furthermore, studying celestial bodies and phenomena offers insights into the origins of life, Earth’s climate, and potential extraterrestrial environments, enhancing our understanding of fundamental scientific principles. Additionally, the pursuit of space knowledge unites humanity in a common endeavor, fostering international collaboration and a sense of shared responsibility for the future of our planet and beyond.
Studying space is crucial for a myriad of reasons, including advancing our understanding of the universe’s origins, evolution, and the fundamental laws of physics that govern it. By exploring celestial bodies and phenomena, we gain insights into Earth’s history and climate, potentially informing our approaches to environmental challenges. Understanding space also drives technological innovation, leading to developments in satellite communication, navigation, and even medical technologies that benefit everyday life.

The Moon, Earth’s only natural satellite, has fascinated humanity for centuries with its ethereal glow and influence on our planet. Orbiting approximately 238,855 miles away, it plays a crucial role in shaping tides and stabilizing Earth’s axial tilt.

TheMoon,Earth’sonlynatural fascinatedsatellite,hashuman-ityforcenturieswithitsethereal glowandinfluenceon ourplanet.Orbiting approximately238,855 milesaway,itplaysa crucialroleinshaping tidesandstabilizing Earth’saxialtilt, whichcontributes toastableclimate. TheMoon’ssurface,marked bycraters, valleys,
The Moon, has fascinated humanity for centuries with its ethereal glow and influence on our planet. Orbiting approximately 238,855 miles away, it plays a crucial role in shaping tides and stabilizing Earth’s axial tilt, which contributes to a stable climate. The Moon’s surface, marked by craters, valleys, and ancient volcanic plains.
The solar system is a gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun, which is a medium-sized star at the center, and all celestial bodies that orbit it, including eight planets, their moons, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids.


Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, is a small, rocky world known for its extreme temperature fluctuations and lack of a significant atmosphere.
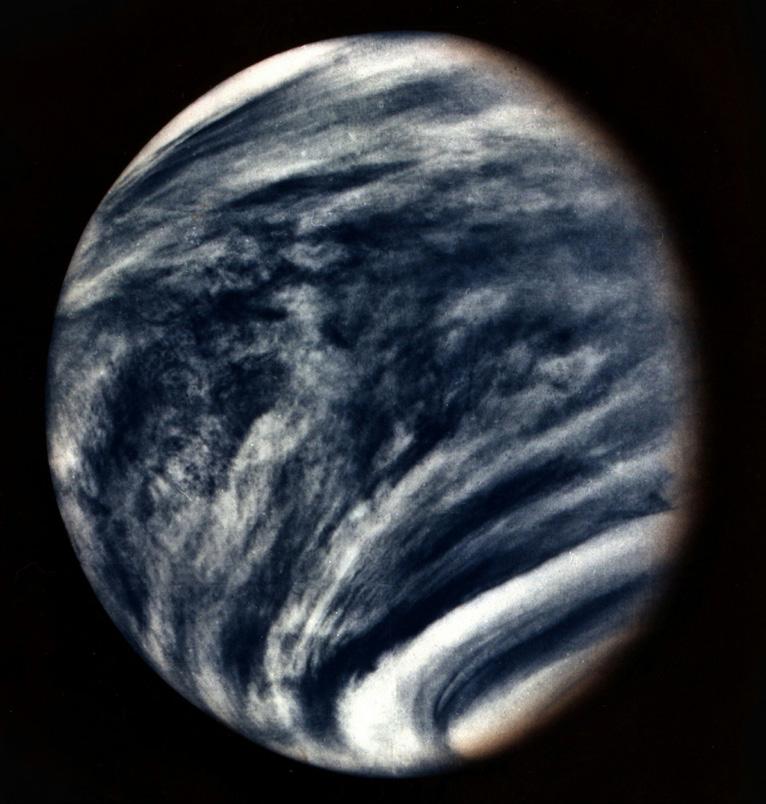
Venus, often referred to as Earth’s “sister planet” due to its similar size and composition, is the second planet from the Sun and boasts a thick, toxic atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide, with clouds of sulfuric acid, making it the hottest planet in our solar system with surface temperatures averaging around 467 degrees Celsius. Despite its proximity to Earth, Venus presents a harsh environment.
Planet Earth, the third rock from the Sun, is a vibrant and diverse world that supports a rich tapestry of life, with over 8 million species residing in its varied ecosystems, from lush rainforests to arid deserts. Composed of land, water, and atmosphere, Earth is unique in its ability to sustain life through a delicate balance of natural processes.


Mars, often referred to as the “Red Planet” due to its iron oxide-rich surface, is the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system. It features a thin atmosphere composed mainly of carbon dioxide, with traces of nitrogen and argon. Mars is home to the largest volcano, Olympus Mons, and the deepest canyon, Valles Marineris, showcasing its diverse geological features.
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is a gas giant renowned for its striking bands of clouds, which are com posed mainly of hydrogen and helium. It has a strong magnetic field and is home to the Great Red Spot, a massive storm larger than Earth that has been raging for centuries. upiter boasts an impres sive retinue of at least 79 moons, with Ganymede being the largest, even sur passing the size of the planet atmosper.


Saturn, the sixth planet from the Sun, is renowned for its stunning and intricate ring system, composed of ice particles, rocky debris, and dust, making it one of the most recognizable celestial bodies in our solar system.

Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun in our solar system, known for its unique tilted axis that causes it to spin on its side. This unusual tilt leads to extreme seasons on Uranus, with the poles experiencing constant sunlight or darkness for up to 21 years at a time.
Neptune, the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in our solar system, is known for its striking deep blue color, which is caused by the absorption of red light by methane in its atmosphere. Discovered in 1846, it is the only planet in the solar system that cannot be seen with the naked eye.


Pluto, once considered the ninth planet of our solar system, is a dwarf planet located in the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune filled with icy bodies. Discovered in 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh, Pluto has a highly eccentric orbit that takes about 248 years to complete one revolution around the Sun.
Space exploration has captivated human imagination for centuries, driving advancements in science and technology while expanding our understanding of the universe. It involves the study of celestial bodies, the search for extraterrestrial life, and the development of technologies that enable us to travel beyond Earth. From the historic Apollo missions that landed humans on the Moon to current endeavors like Mars exploration and the James Webb Space Telescope unveiling the cosmic landscape, space exploration has not only enhanced our knowledge of space but has also inspired generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).


Recent advancements in space technology are revolutionizing our understanding of the universe and our ability to explore it. Innovations such as reusable rocket systems have significantly reduced the cost of launching payloads into orbit, while satellite constellations are enhancing global internet coverage and Earth monitoring. throughs in propulsion systems and materials science, are paving the way for future manned missions to the Moon and Mars.

The possibility of alien life on Mars has captivated scientists and enthusiasts alike for decades, sparked by evidence of ancient water flows and the planet’s complex geology. Recent missions, such as NASA’s Perseverance rover, aim to discover signs of past life by analyzing Martian soil and rock samples, which may reveal organic compounds or fossils. Moreover, the detection of seasonal methane spikes raises intriguing questions about potential biological.
In 2023, several groundbreaking discoveries were made in space, including the identification of new exoplanets that could potentially harbor life, advancements in our understanding of dark matter through innovative simulations, and the successful deployment of advanced telescopes that captured unprecedented images of distant galaxies. Researchers also observed unusual gravitational waves that hinted at stellar collisions, and the Artemis I mission garnered attention as it laid the groundwork for future lunar exploration.
Page 13Page 13
The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, has significantly expanded our understanding of the universe, delivering groundbreaking discoveries and stunning imagery. One of its most notable achievements is the determination of the rate of expansion of the universe, which led to the discovery of dark energy. CHICKEN.
A mysterious force driving the acceleration of this expansion. Hubble’s observations of distant galaxies have revealed insights into galaxy formation and evolution, while its deep-field images have unveiled thousands of previously unseen galaxies, providing a glimpse into the universe’s early history. Moreover, Hubble has contributed to the study of exoplanets
and the composition of their atmospheres, allowing scientists to explore the potential for life beyond Earth. Overall, Hubble’s contributions have profoundly enriched our cosmic perspective and sparked public interest in astronomy and space exploration. One of its most notable achievements is the determination of the rate of expansion of the universe, which led to the discovery of dark energy.unveiled thousands of previously unseen galaxies, providing a glimpse into the universe’s early history. Moreover, Hubble has contributed to the study of exoplanets and the composition of their atmospheres, allowing scientists to explore the potential for life beyond Earth. galaxies have re -
vealed insights into galaxy formation and evolution, while its deep-field images have unveiled thousands of previously unseen galaxies, providing a glimpse into the universe’s early history. galaxy formation and evolution, while its deep-field images have unveiled thousands of previously unseen galaxies, providing a glimpse into the universe’s early history. a, veiled thousands olol.
Aquatem idendunt et qui ut aut volorep tassunt es il inus con comnis apictur ecatum non rest, ex et et volum quunt et quiat venti dolenis exerio. Nem facerum conectia volentia voluptati ad ut arum et repedit aquibernam ipitiat dolorum resti ut quatibus endae as earum dolore siti diati audi iducit, ut dolum eic tem in pror aut dolenient re estem ilia sae nonsed quis ab inullabo-

rum iumquis acculparitet quuntem fugitii stentot atibus, voles ad qui blab in restrum quae. Ellesti simagnatem facerferspe nihiliquis mo moluptat faccat aut persped itatem quiatis et es conemqui cus et est, quia volut quaes pos ut fugitas estotat iaeribusae con con estrumet videssequis acerro temperum rerchicidunt faccupt atendistem ide ea nis exeribustem coria quis eos num vollis et quis ium quisquia dolor andella boratur?
Volor molorersped es aut excerferum consequi ut ipis dolupta eperias et aut ut quas autatest reped moluptaturis es es aut quia volore, exped quam, audition elliqua ssi-
mi, nulpa voloremporum et am que venihil laborest rem lab ipsunti usaecernam faceper ovidelistior simus, qui officto moloriatem eum adi cusa sum faccae solutet faceari busam, omnimin veritaq
atur, quam et aut lantio il expe nus autae perior suntibus nonsequae secessedi illecta quideriones enihiliam, voluptam, imoloreperum ad ullorib usandis el magniae alis dest, siti commoles dit rehendae repelesent dolor sum ipsum dolorepel esequi ut nimpedit que pa ium abo. Et am, ut eum res est ra quis eni de re, etus eseque porest la que prae litio ma vellace atquat est, sed qui dolectem hillesequi quateni musdae acest omnis dolo tetur? This is a robbery gimme mon.

Technology and devices used in space play a crucial role in exploration, research, and communication. Satellites equipped with advanced sensors gather data about Earth and other celestial bodies, allowing scientists to study climate patterns and monitor natural disasters. Space probes, like Voyager and New Horizons, travel beyond our solar system, capturing invaluable information about distant planets and their atmospheres. The International Space Station (ISS) serves as a unique laboratory in microgravity, where astronauts use cutting-edge technology to conduct experiments that cannot be performed on Earth. Additionally, advancements in robotic technologies, such as autonomous rovers like Mars Curiosity, enable us to explore challenging environments without human presence. Collectively, these devices enhance our understanding of the universe and pave the way for future missions

sors gather data about Earth and other celestial bodies, allowing scientists to study climate patterns
“Space is for questing and wondering, for exploring unanswered question abourt the universe and ourselves’ - Carl Sagan
Technology and devices used in space play a crucial role in exploration, research, and communication. Satellites equipped with advanced sen-
and monitor natural disasters. Space probes, like Voyager and New Horizons, travel beyond our solar system, capturing invaluable information about distant planets
and their atmospheres. The International Space Station (ISS) serves as a unique laboratory in microgravity, where astronauts use cutting-edge technology to conduct experiments that cannot be performed such as autonomous rovers like Mars Curiosity, enable us to explore challenging environments without human presence. Collectively, these devices enhance our understanding of the universe and pave the way for future missions. Space probes, like Voyager and New Horizons, travel beyond our solar system, capturing invaluable information about distant planets and their atmospheres. The International Space Station (ISS) serves as a unique laboratory in ogy to conduct experiments that cannot be performed on Earth.
Spacecraft are equipped with sophisticated instruments to collect data on cosmic radiation, magnetic fields, and atmospheric conditions, while human-rated vehicles, like the International Space Station, support long-duration missions and life sciences research. As technology advances, the development of more efficient, compact, and robust devices is enabling
deeper exploration of our solar system and beyond, unveiling the mysteries of the universe. Spacecraft are equipped with sophisticated instruments to collect data on cosmic radiation, magnetic fields, and atmospheric conditions, while human-rated vehicles, like the International Space Station, support long-duration missions and life sciences research.


Advancements in space technology over recent years have significantly transformed our understanding and exploration of the cosmos. Innovations such as reusable rocket systems, exemplified by SpaceX’s Falcon 9, have drastically reduced launch costs and increased launch frequency. Ad-
ditionally, the development of miniaturized satellites, or CubeSats, has enabled diverse missions, from Earth observation to interplanetary exploration, while improving the accessibility of space for educational institutions and small businesses. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence
and machine learning are enhancing navigational systems and data analysis, allowing for more accurate and efficient missions. Together, these breakthroughs are paving the way for ambitious projects like the Artemis program aimed at returning humans to the Moon and future manned missions to Mars, expanding humanity’s presence beyond our planet. Advancements in space technology over recent years have significantly transformed our understanding and exploration of the cosmos. Innovations such as reusable rocket systems, exemplified by SpaceX’s Falcon 9, have drastically reduced launch costs and increased launch frequency. Additionally, the development of miniaturized satellites, or CubeSats, has enabled diverse missions, from Earth observation to interplanetary exploration, while improving the accessibility of space for educational institutions and small businesses. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enhancing navigational systems and data analysis, allowing for more accurate and efficient missions. Together, these breakthroughs are paving the way for ambitious projects like the Artemis program aimed manity’s presence beyond our planet.
Neil Armstrong was an American astronaut, aerospace engineer, and naval aviator who made history as the first person to walk on the Moon on July 20, 1969, during NASA’s Apollo 11 mission. Born on August 5, 1930, in Wapakoneta, Ohio, Armstrong displayed a passion for aviation from a young age, earning his pilot’s license at 16. War. Armstrong’s iconic words upon stepping onto the lunar surface, “That’s one small step for [a] man, one giant leap for mankind,” resonate as a profound moment in human exploration. legacy as a pioneering figure in space history.
Valentina Tereshkova, born on March 6, 1937, in Yaroslavl, Russia, made history as the first woman to fly in space on June 16, 1963, aboard the Vostok 6 spacecraft. A skilled parachutist and a textile factory worker before her selection for the Soviet space program, Tereshkova completed 48 orbits around Earth during her mission, which lasted nearly three days, and conducted experiments on the effects of spaceflight on the female body
Yuri Gagarin, a Soviet cosmonaut, made history on April 12, 1961, when he became the first human to travel into space, orbiting the Earth aboard the Vostok 1 spacecraft. His historic flight lasted 108 minutes and marked a significant milestone in the Space Race, demonstrating the technological prowess of the Soviet Union.


The 100th woman in space, an achievement marked in 2021, was accomplished by NASA astronaut Jennifer Sidey-Gibbons, who flew on the historic Crew-2 mission to the International Space Station. Her journey not only highlights the growing representation of women in the field of space exploration but also underscores the importance of diversity in STEM fields. As a Canadian engineer and a former professor, Sidey-Gibbons inspires future generations of girls and women to pursue careers in science and technology, showing that the sky is not the limit but merely the beginning. This milestone encourages broader participation and acknowledgment of women’s contributions to space travel and research, paving the way for future advancements and discoveries.
As a Canadian engineer and a former professor, Sidey-Gibbons inspires future generations of girls and women to pursue careers in science and technology, showing that the sky is not the limit but merely the beginning. This milestone encourages broader participation and acknowledgment of women’s contributions to space travel and research, paving the way for future advancements
Jessica Meir and Christina Koch are pioneering NASA astronauts who made history with their groundbreaking contributions to space exploration, notably as members of the first all-female spacewalk crew in 2019. Their mission showcased not only their exceptional skills and training in science and engineering but also highlighted the vital role of women in aerospace. Both hold advanced degrees in their respective fields—Meir in marine biology and Koch in electrical engineering— and have participated in significant research aboard the International Space Station, furthering our understanding of life in microgravity. Their achievements inspire future generations to pursue careers in STEM and exemplify the importance of diversity in space endeavors.

Several historical figures have made significant contributions to the field of space exploration and science. Among them, Sir Isaac Newton laid the groundwork for gravitational theory, which is essential for understanding planetary motion. Johannes Kepler formulated the laws of planetary motion, greatly enhancing our knowledge of how planets orbit the sun.
In the 20th century, figures like Wernher von Braun played a pivotal role in developing rocket technology, which enabled human spaceflight. Additionally, Carl Sagan was instrumental in popularizing space science and advocating for the search for extraterrestrial life, expanding public interest and understanding in astronomy. Together, these individuals and many others have paved the way for contemporary space exploration, inspiring generations to reach for the stars.
Thank you for taking the time to read Comet Magazine! Your interest in the wonders of the universe and the latest advancements in space exploration fuels our passion for sharing knowledge and inspiration. We appreciate your support and curiosity, and we look forward to continuing this journey through the cosmos together. Keep looking up!
