
an integrated smart green wall
Capstone S40: Ron Kaufman - The Green Wall: A Residential Lifestyle and Energy Maximising Event
Artiaga Samantha Bless (EPD)
Song Cheong Cheong (EPD)
Kong Mei Jia (ASD)
Phua Rui Yi Sarah (ASD)
Nicholas Gandhi Peradidjaya (CSD)
Under the mentorship of:
Ron Kaufman
Jen Kaufman
Michael Alexander Reeves
Tay Zi Dong Patrick
About the Project
How might we design a large-scale, self-sustaining residential green wall that is accessible and easy to maintain?
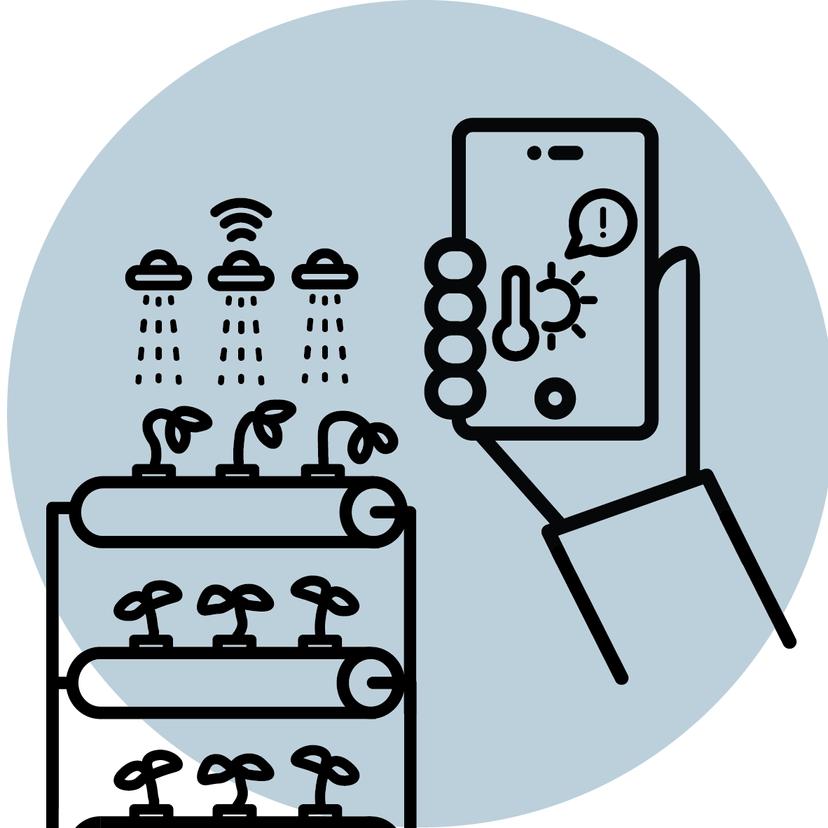
AgroReach is a technologically integrated biophilic wall that is accessible and self maintainable, designed for the residential home of Ron and Jen Kaufman.
The wall is designed to be modular and adjustable. Automated irrigation systems and smart tech monitoring are incorporated into different planting systems that form a cohesive sustainable green wall. AgroReach aims to set a precedent for self-sufficient vertical urban farms on a residential scale.
User manual
This user manual aims to help the reader gain a better understanding of the following:
The overall solution & user process
How the pull-down mechanism works
The functions of the web application
How to use the web application
The workings of the voronoi design
How to maintain the planters and greens
I
o d u c
i o n
n t r
t
1
User process Voronoi design Maintenance On Gardening 25 C o n t e n t 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3 7 9 11 15 21 23 27 29 2 AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall
Solution Overview Mechanism Explanation Moving the Mechanism Web Application Overview Web Application Usage Growth Mechanism
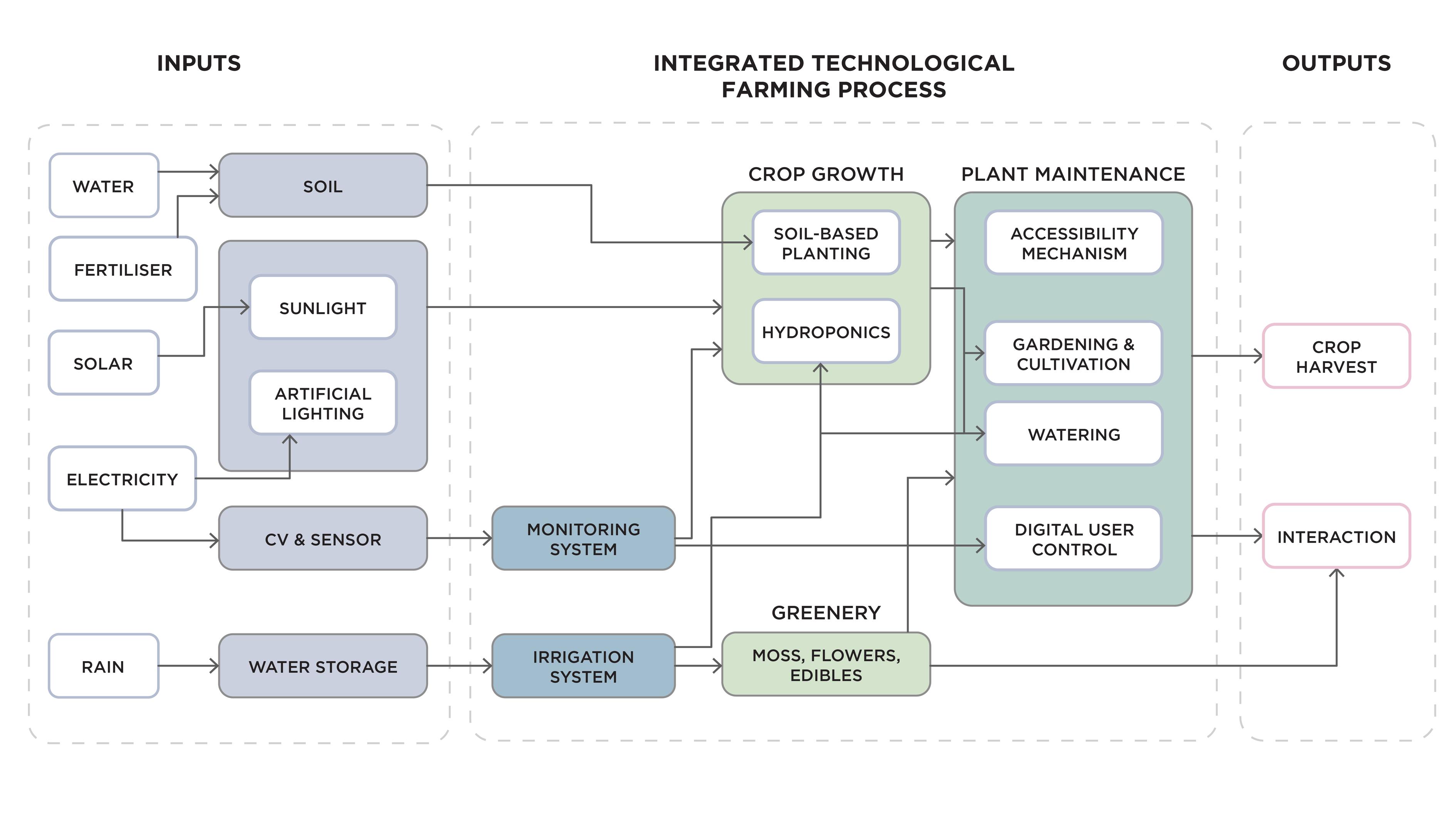
Overview of solution
The inputs into the smart green wall are on the left while the middle segment illustrates how our technological farming process looks like.
i
w 3
S o l u t i o n O v e r v
e

Crops can be grown using both hydroponics and soil based systems which are monitored by sensors and computer vision, as well as having a smart irrigation system. An accessibility mechanism and web application allows the user to interact with the garden and cultivate the plants.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 4
About AgroReach
One key limitation to integrating vertical farming into residential areas is the issue of accessibility. How may one reach higher areas without mobility devices such as ladders and scissor lifts? These devices poses safety concerns and their use is limited by space constraints in the case of houses.
With our pull down farming concept AgroReach, more crops can be grown in higher areas and easily maintained without any additional accessibility aid.
AgroReach stacks hydroponic planters above reachable areas, the planters are attached to a roller system that allows them to be brought down to reachable height for easy access.

o l u t i o n O v e r v i e w 5
S

House model at 1:50 scale, design as of Feb 2024
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 6

Safety Precautions
Remember to exercise these cautionary measures when controlling the moving mechanism:
Ensure no hoses or wires are tangled
Check for leaks and loose water connections
Pull the planters down gently, parallel to the wall
If step-stools are necessary, test stability before climbing
Ensure the metal wire rope is not tangled before usage.
7
M e c h a n i s m E x p l a n a t i o n

How the Mechanism Works
The hydroponic planters are attached to a frame with rollers. The system uses a mini electric rope hoist attached to the hydroponic planters’ frame via a pulley system.
The position of the hydroponic planters can adjusted and placed at the desired height by using the hoist's remote control. Simply press and hold the up or down button to adjust the height.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 8
Using the hydroponic planters
1. Lowering the wall
Access each pipe via remote control. The movement is motorised, allowing the hydroponics wall to descend in a steadily until the wall has fully reached the ground.
2. Planting crops
Plant seeds or place saplings within the supporting cup holders within each hole in the hydroponics pipe.
3. Raising the wall
Raise the hydroponics panel back to original placement via the same remote control.
4. Harvesting crops
Begin harvest on a weekly basis once matured.
Time taken till maturity is on a case-by-case basis for the type of plant to be harvested.


M o v i n g t h e M e
9
c h a n i s m




AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 10
1. Lowering the wall
3. Raising the wall
2. Planting the crops
4. Harvesting crops
Purpose of Web Application
1.Ease of maintenance
The app aims to allow one to monitor the green wall through data and leverage on technology for efficient plant care
2.Remote accessibility
The app brings convenience for users to monitor and manage the green wall from anywhere with internet access
3.Data Visualization
The app presents data and advice on plant health, water levels, and environmental conditions through intuitive charts and graphs, improving readability
Accessing the Application
The web application may be accessed using either of the following methods:
1.
Using the website link: https://agroreach.netlify.app/
By scanning the QR code below: 2.

i o n
e r v i e w 11
W e b A p p l i c a t
O v
Features of the Application
1.Real-time Weather
Users can access up-to-date weather information in the area within the application.
2.Coloured Status Indicators
Each row of plants has indicative statuses that are represented with intuitive colors, making their interpretation straightforward.
3.Live Plant Video Feed
Users can view a live feed video, captured by cameras, of the plants directly from the application.
4.Past Statistics
The app provides historical data on plant performance over 30, 90, and 180-day intervals, depicting them on graphs that are easy to navigate.
5.Remote Control
Users are able to activate the irrigation and fertilisation system for each row of plants through the app with the push of an in-app button.
6.Harvest tracker
Notification reminders and a schedule tracker assist the user to keep track of harvesting times.
7.Data Security
The app securely stores all information in the database, including live plant feed and past statistics, ensuring its safety and recoverability.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 12
W
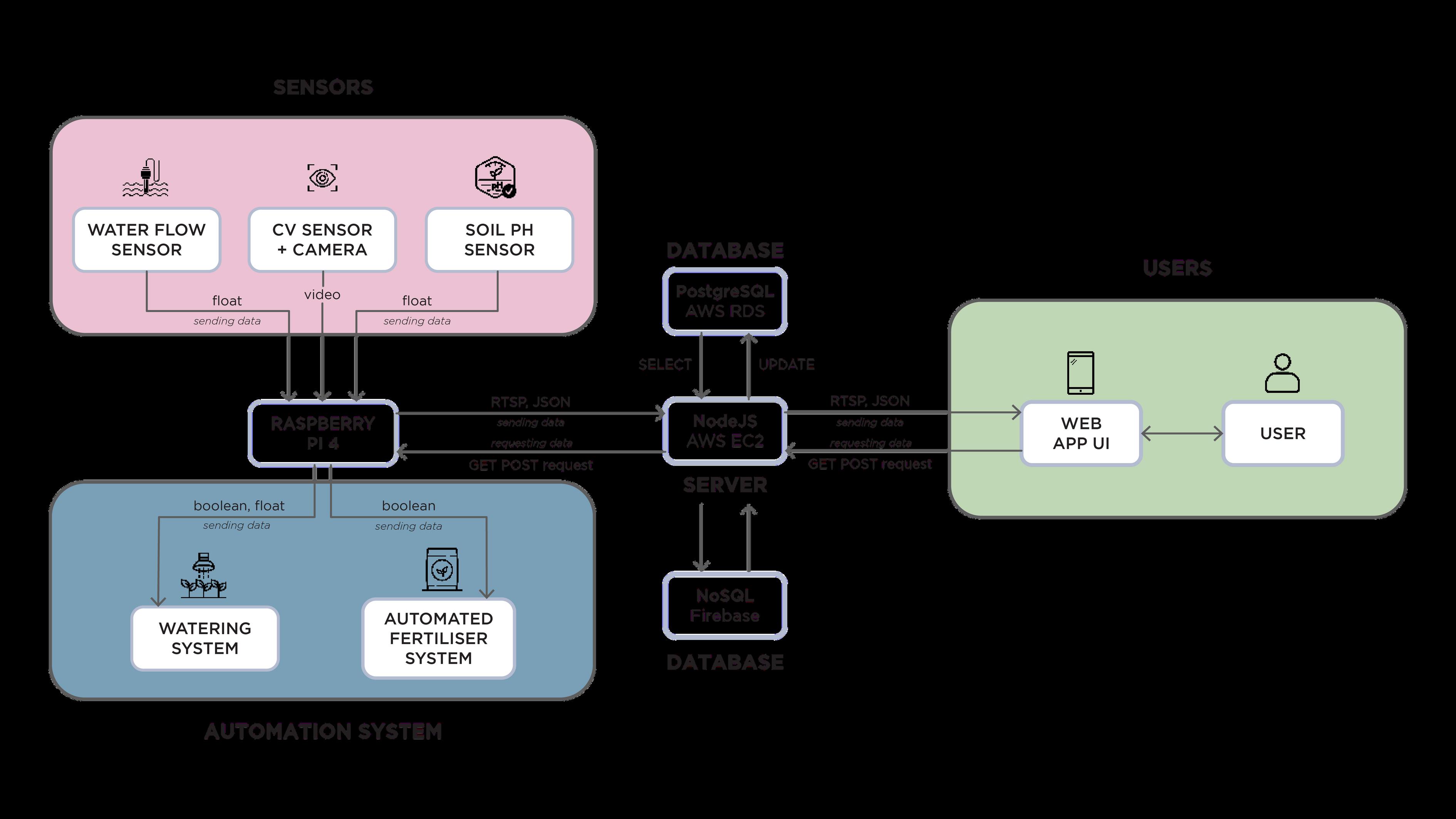
Overview of System Architecture
The application integrates Internet of Things (IoT) technology, with a Raspberry Pi as the central hub. Data is stored in a PostgreSQL database, and sent to the web application.
13
e b A p p l i c a t i o n O v e r v i e w

The cameras and different types of sensors placed in the planters capture numerical and video data. These are sent through a Raspberry Pi for storage in the PostgreSQL database, allowing for efficient organization and retrieval. The user interface presents relevant insights to users, and allows user interaction with the wall.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 14
W e b A p p l i c a t i o n U s a g e
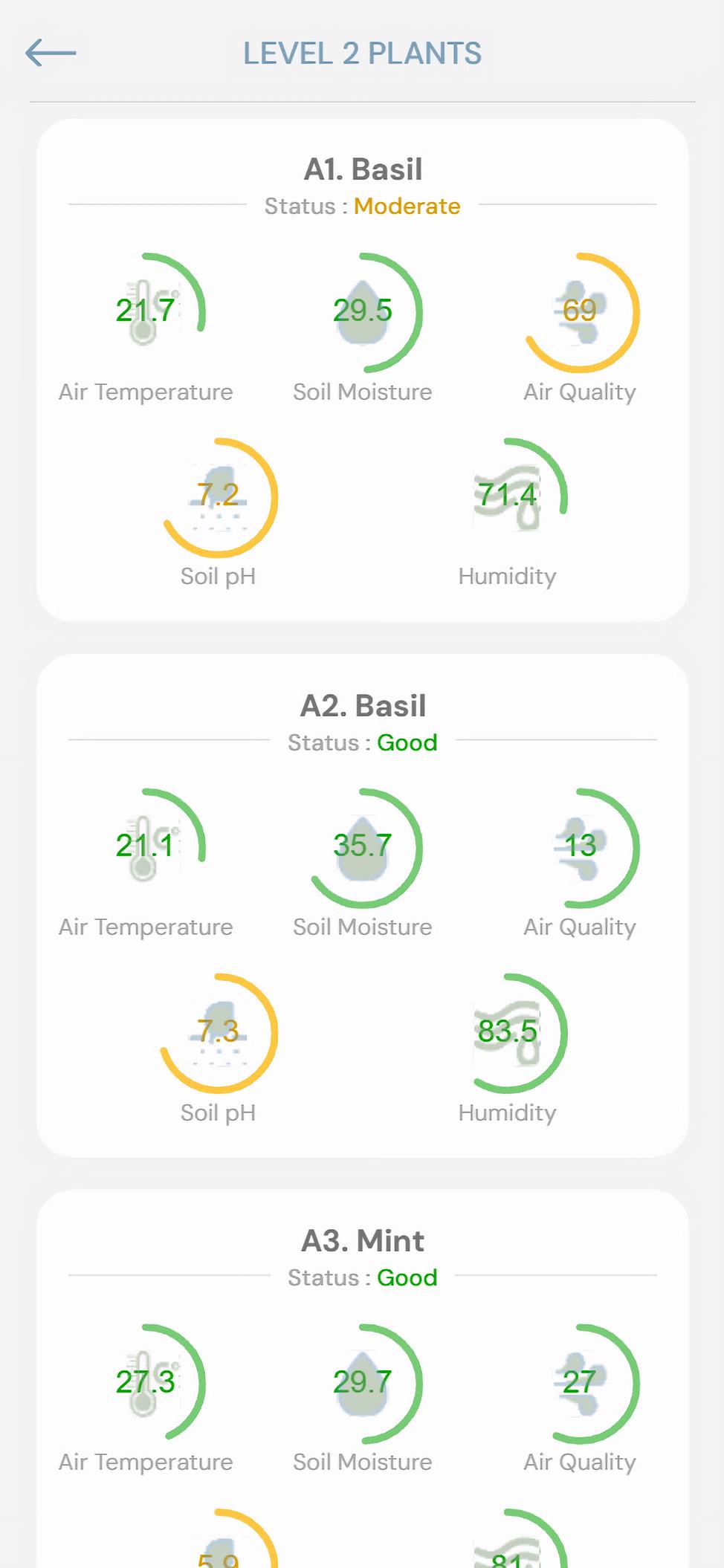
View details of individual rows
Control grow lights
Average statuses by level
For each floor, the measured quantities are displayed numerically with their different units. The condition of the level of plants is visually represented using colours: Red indicates poor, yellow indicates moderate, green indicates good.
The grow lights are automated to turn on for 4 hours daily. The user may also remotely control the grow lights.
15

Data is collected and coloured for each row
Yellow and red colours indicate the plants that require attention
The webpage presents the status of plants arranged in rows according to a specific level. By planting a single type of crop in each row, the conditions should result in consistent crop status across the row.
The condition of the row of plants is visually represented using colours: Red indicates poor, yellow indicates moderate, green indicates good.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 16
WRemotely controllable functions

Users can also visually inspect the plants through a live feed directly embedded on the page to confirm the plants’ health. Camera vision analyses the video feed for pixel colour differentiation, contributing to the status of the plant health. Users may remotely water or fertilize the plants should they deem it beneficial, depending on the planter.
17
e b A p p l i c a t i o n U s a g e
Live video feed of current selected row

Graphical plot of data collected, by category and duration (30, 90, 180 day intervals)
Indicative line bar with description of category measured
The statistics are plotted in a graph for better readability and comparison in data. The current status of each category (bad, moderate, or good) is clearly represented in a line bar, allowing for easy comparison. The addition of simple instructional text allows for better understanding each category.
The webpage is able to provide historical statistics of the row of plants, showing their performance over intervals of 30, 90, and 180 days.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 18
Status bar corresponding with harvest countdown
WTrack harvest times by resetting the harvest timer


Users are able to keep track of different harvest cycles by pressing “harvest” to reset the countdown. The application sends a notification on the user’s phone when a row of plants are ready to be harvested. The harvest duration corresponding to the type of plant in that row.
Users may tap the grey button twice to reset the tracker, if they harvest the plants out of the recommended cycle.
19
e b A p p l i c a t i o n U s a g e

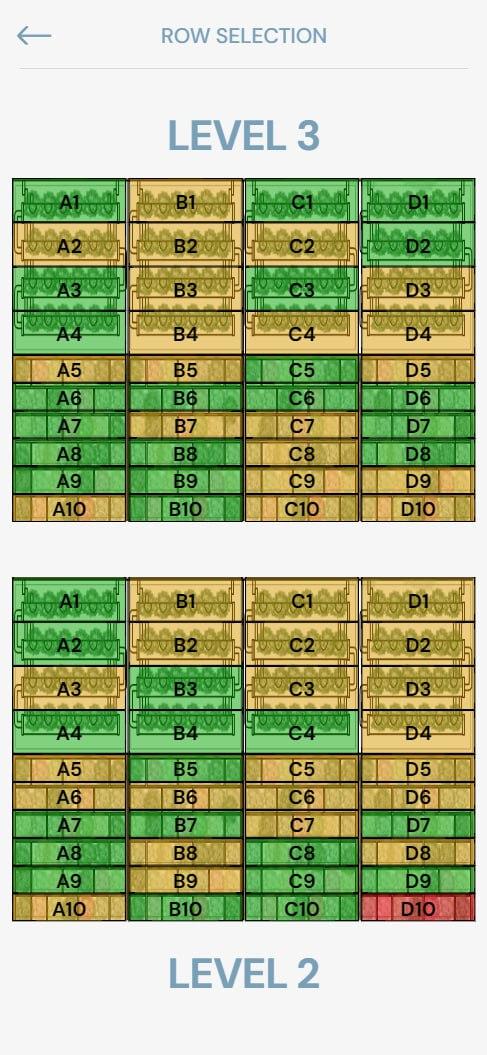
Coloured indicator graphics corresponding to each row’s health
The graphic row selection page serves as an alternative interface, enabling users to view a summary overview screen of the each row, in a table form. Upon pressing on the corresponding rectangle, the user will be brought to the status page of that row.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 20
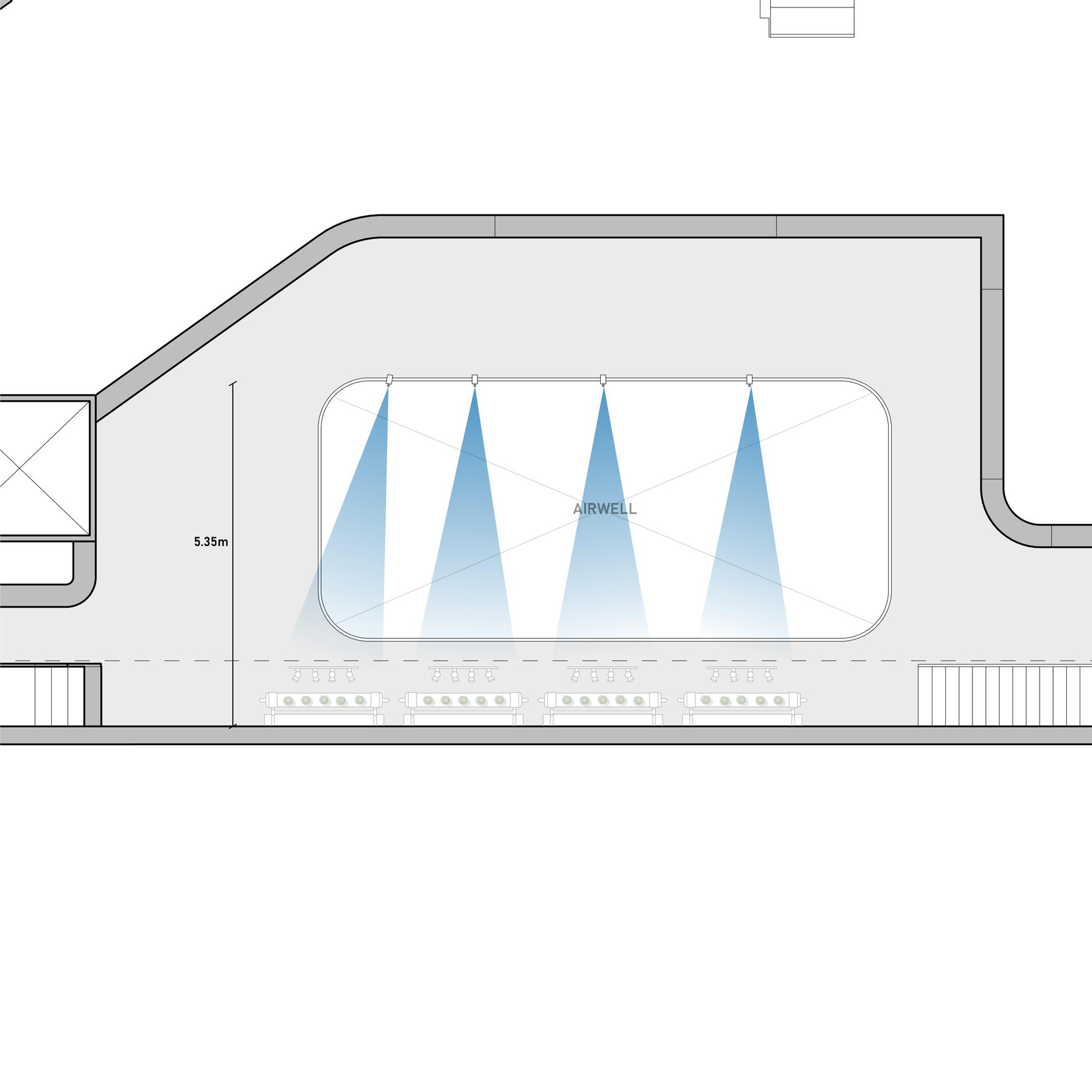
Grow Lights Placement
Automated grow lights are needed to supplement the crops with additional lighting of at least 4 hours a day for plant growth, as the amount of direct sunlight received in the area is insufficient for crop growth.
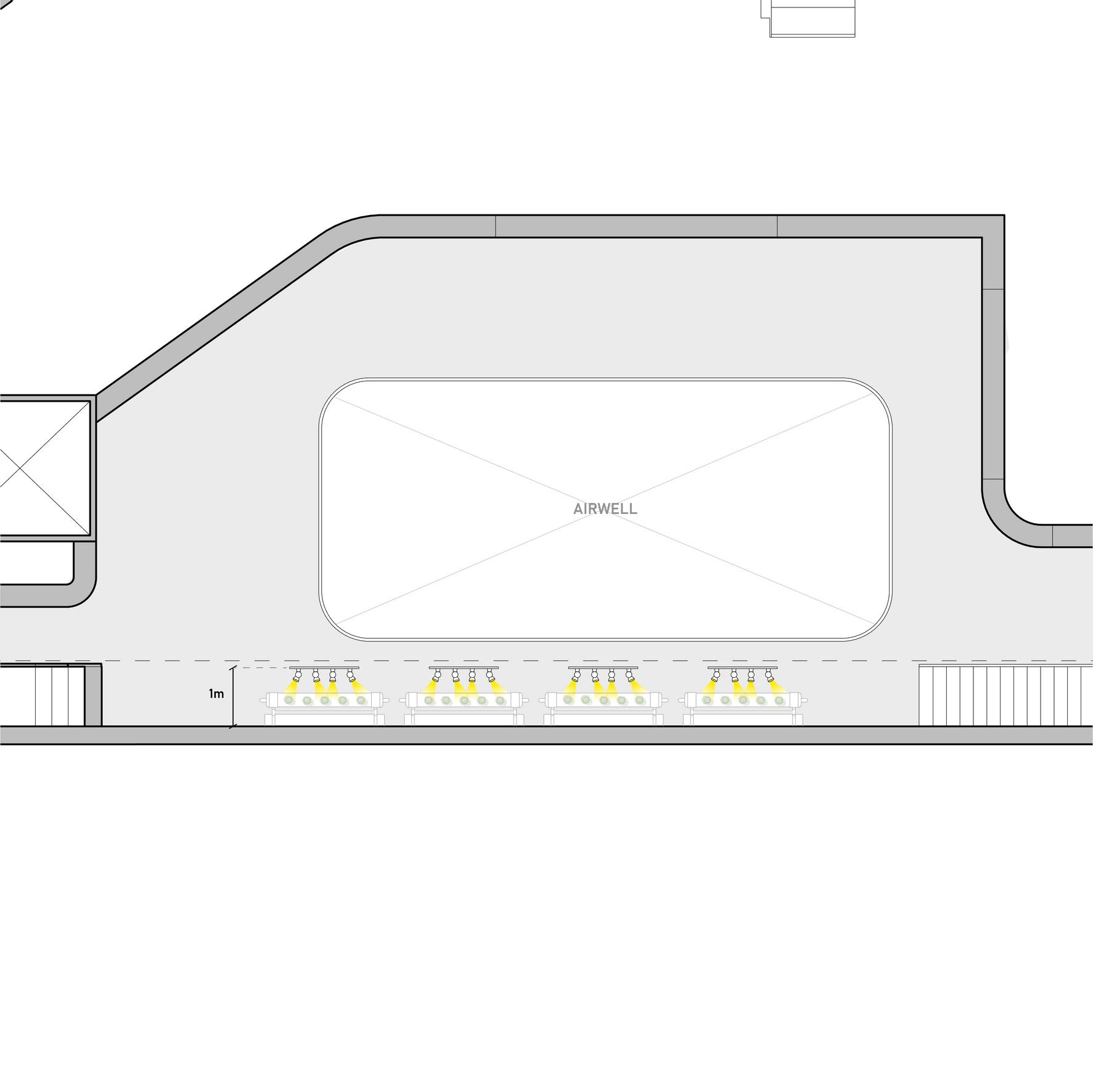
We propo lights to be the walkw 1m away backing, as view above
The sectio right show lights ma plants in t area.
Section drawing
r o w t h M e c h a n i s m s 21
G
Plan view of level 2
Camera Placement
Cameras need to be placed across the green wall to capture the video feed of the plants shown in the web application, for 24/7 monitoring of the plants.
Plan view of level 2
We propose for the cameras to be positioned on the parapet of the opposite walkway, about a 1.1m off the ground level and 5.35m away from the green wall backing, as seen from the plan view above.
The section drawing on the right shows how the plants in the top hydroponic area can be monitored by these cameras.

Section drawing
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 22
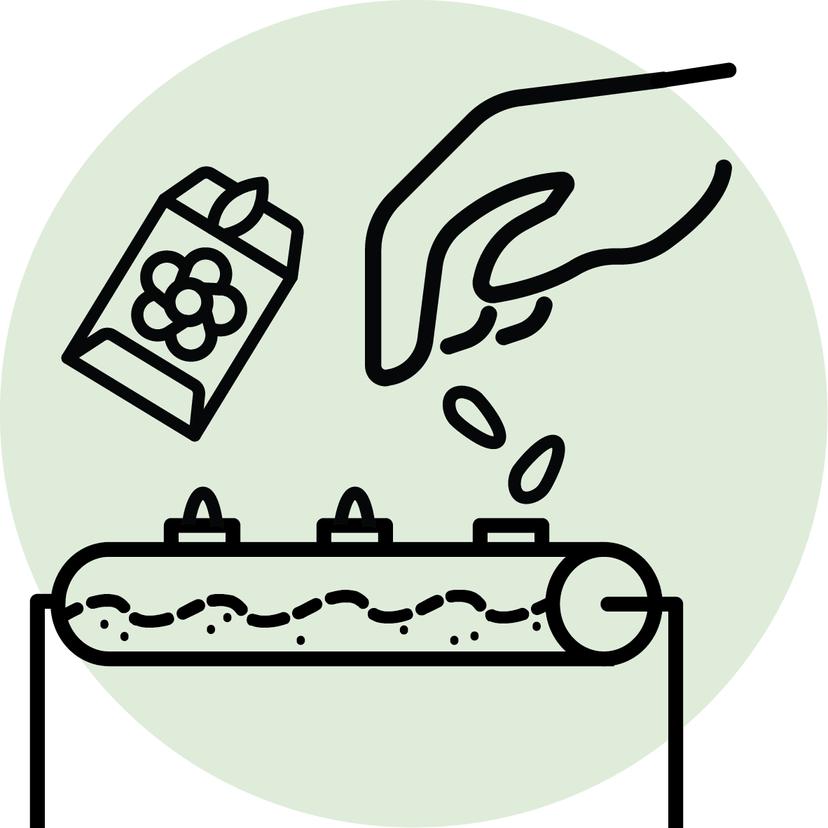
Step 1 : Sow
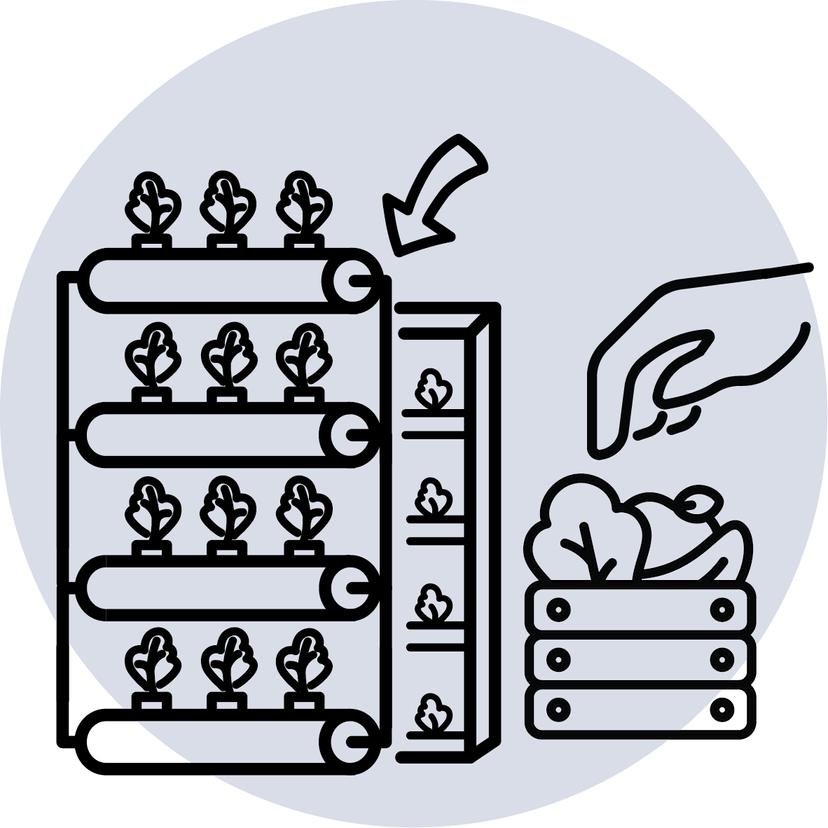
Step 4 : Harvest
23
U s e r P r o c e s s
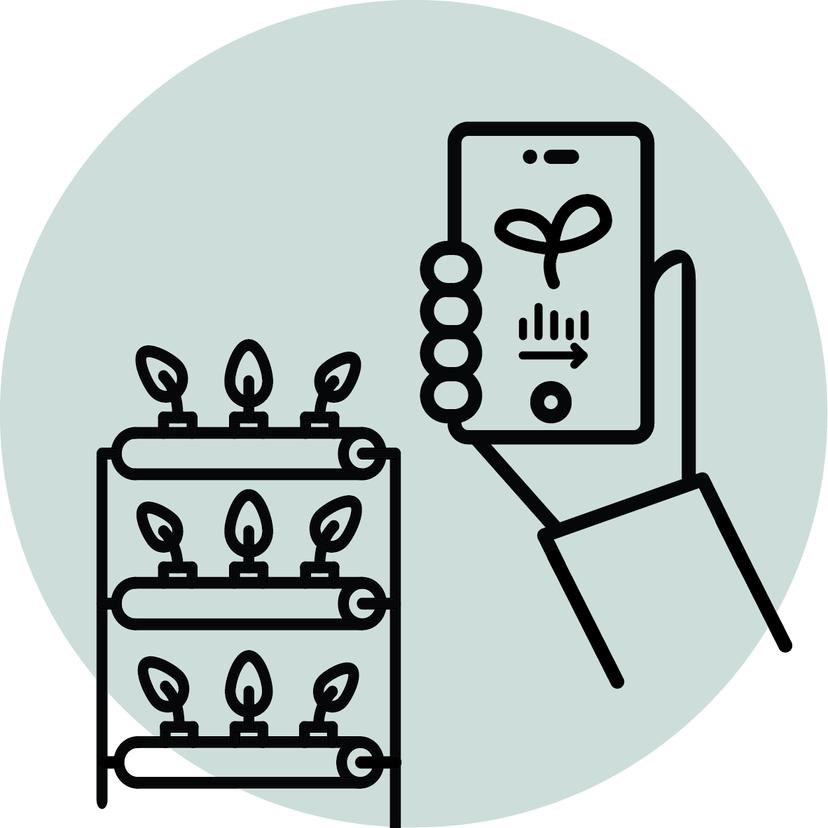
Step 2 : Grow
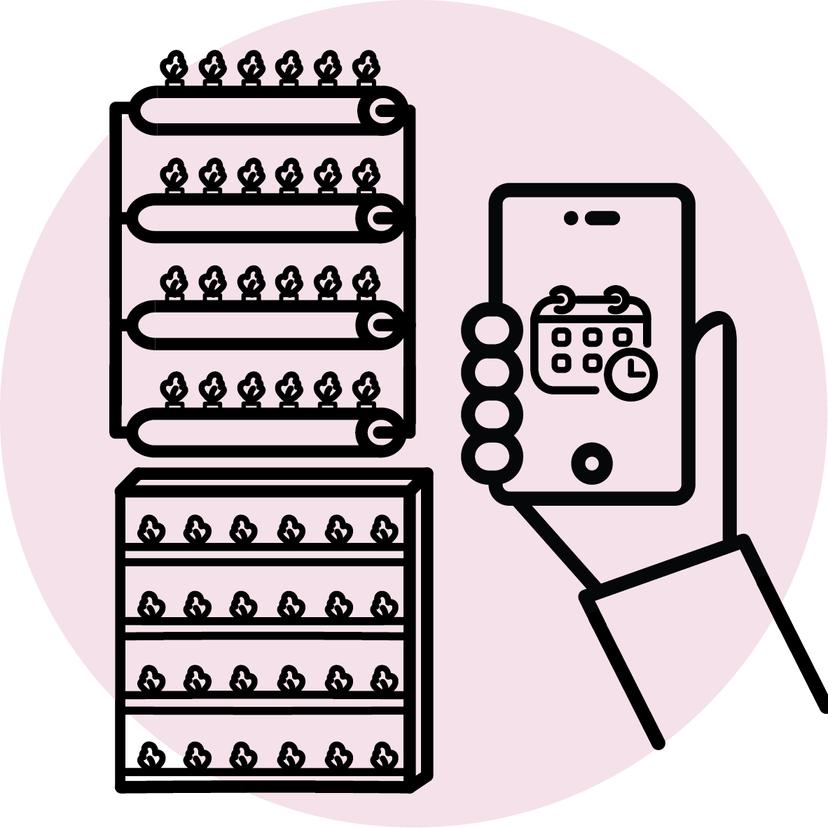
Step 5 : Track
Step 3 : Tend
User steps
1. Plant saplings & seeds into hydroponic & soil planters
2. Monitor growth of plants through the app’s video and status functions
3. Intervene if necessary, using app data to support growth
4. Lower wall to harvest fully grown vegetables and tend to crops
5. Return wall to original position & update the harvest tracker in the app
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 24
The Voronoi System
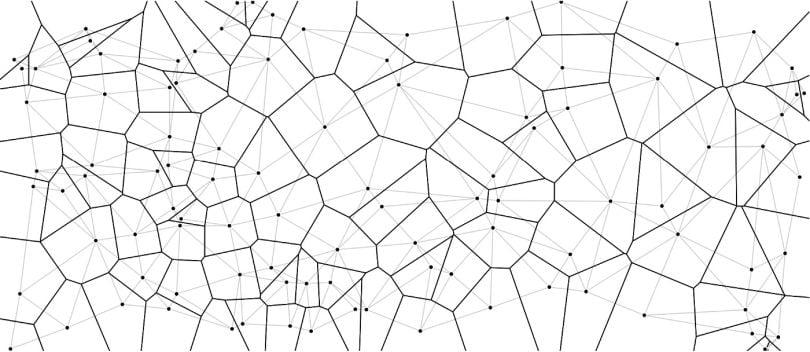
Voronoi diagram, also known as Dirichlet tessellation or Thiessen polygon, is a type of tessellation pattern in which a number of points scattered on a plane subdivides in exactly n cells enclosing a portion of the plane that is closest to each point.


1. Adaptable shapes
Allows for controlled flexibility of the design to suit individual aspirations of the voronoi biophilic system.



. Low maintenance nables low-maintenance plants to be grown with his system, for unreachable parts of the green wall.
3. Lightweight panels
Skeletal voronoi modules with cladding allow for panels to be lightweight, facilitating maintenance


4. Mimics natural forms
Spontaneous, natural patterns that mimic natural phenomena is guided by meticulously calculated formulae
o r o n o i D e s i g n 25
V

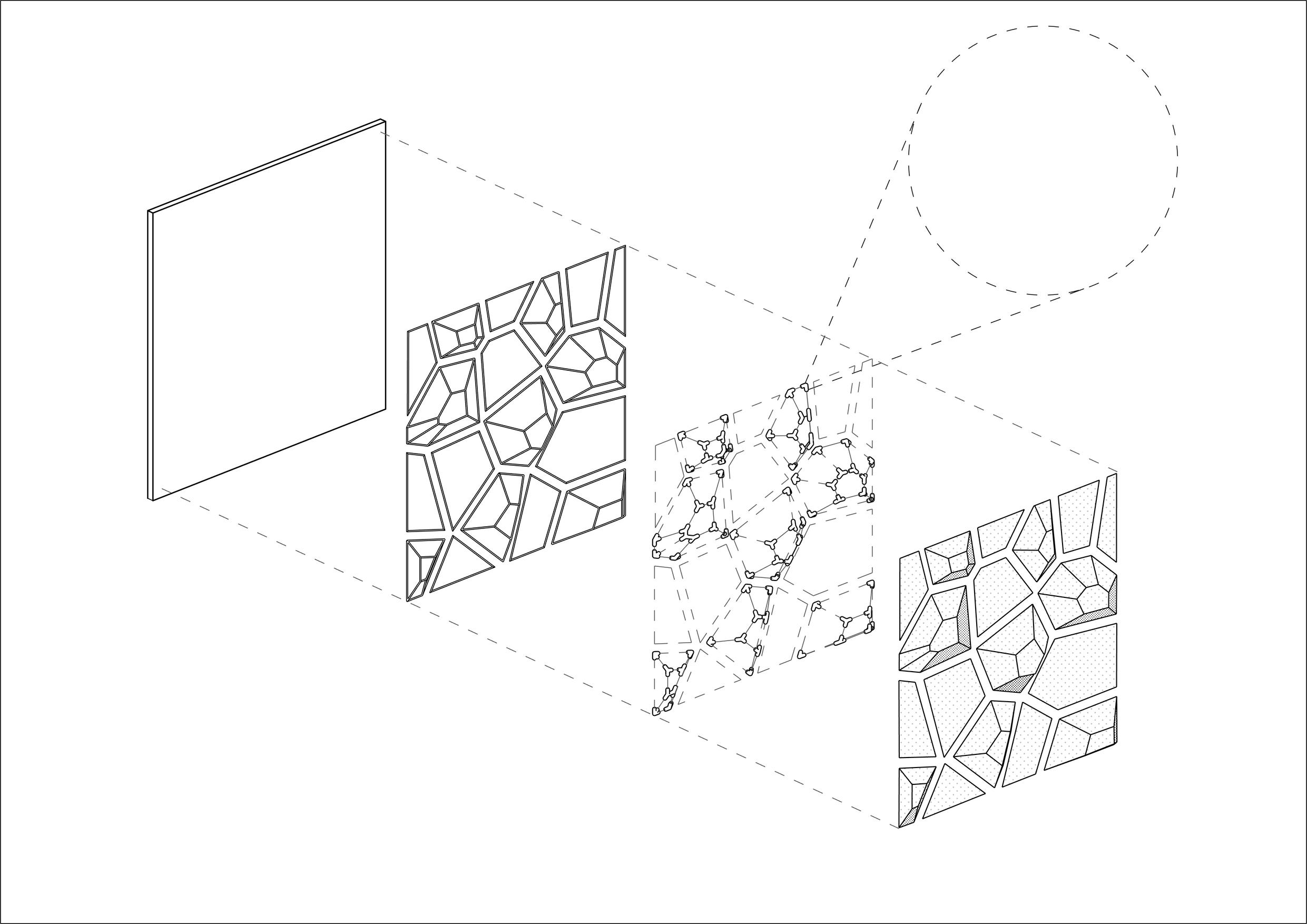



AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 26
Voronoi prototype Backing Rods Connections
Foliage
Using the soil-based planters
1. Prepare pots for planting
Make sure that the pots used are at maximum ~16cm in diameter, and ~135mm in height. Prepare soil and nutrients as preferred.
2. Planting crops
Plant and harvest crops in the soil-based pots placed within each row as per usual farming processes.
3. Maintenance of planters
Inspect the planters on a weekly basis for moulding and/or warping of the supporting shelves, moving or removing the pots if necessary
4. Maintaining watering system
Ensure that the drip irrigation system is located at a suitable height above the pots such that water is able to flow smoothly into the dirt.


M
27
a i n t e n a n c e
Easy removal of pots Irrigation system pipes
Specifications of Prototype Electronics





1. DHT22 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
Model SEN0137 from DFRobot
Temperature range:- 40 to 80 °C
Humidity range: 0-100%
2. Gravity Analog TDS Sensor
Model SEN0244 from DFRobot
TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) indictes the cleanliness of the irrigation water.
TDS Measurement Range: 0 ~ 1000ppm
TDS Measurement Accuracy: ± 10%
3. Liquid pH Sensor
From Reland Sun
Detectable Concentration Range: PH0-14
Detection Temperature Range: 0-80 °C
4. USB HD Webcam
From OEM
Image Capture Resolution: 1080p
Frame Rate: 30 fps
5. Mini Electric Rope Hoist
Single hook, 110V rating
Rated lifting weight: 100kg
Lifting speed: 10m/min
30
Planting Tips
For Hydroponics
Start with easy-to-grow crops like lettuce, herbs, or cherry tomatoes before experimenting with more challenging plants.
Pointers to take note of:
Hydroponic systems use a nutrient-rich water solution to deliver essential nutrients directly to the plant roots. To ensure optimal plant growth, make sure to monitor and maintain proper nutrient levels, pH balance, and water temperature.
Regularly inspect the system for any signs of algae, mold, or nutrient imbalances, and address them promptly.
For soil-based gardening
Soil gardening allows for a wide range of plant varieties to be grown, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and ornamentals. However, the type of soil used should be catered to the type of plant grown.
Pointers to take note of:
Monitor the soil's pH and nutrient levels to ensure it's suitable for the plants you intend to grow.
Amend the soil as needed with compost, organic matter, or fertilizers.
O n G a r d e n i n g 29
Maintaining the planters
Soil-based planters
Undergo a monthly check on the following:
1. Status of shelf material
If warping, cracking, or moulding is detected, refurnish the shelving by first taking out the planter pots and unscrewing the horizontal shelf panels and replacing them with the new panels.
Use M6 size flat head screws
2. Status of drainage pipes
If clogging, leaking, or moulding is detected in any of the pipes, remove the damaged pipe section from between the two right-angle connectors on the sides and replace with a new pipe.
Use any plastic pipe with 20mm diameter.
Avoid the scheduled watering time for the particular row of plants when replacing the water pipes.
Hydroponic planters
Undergo a monthly check on the following:
1. Status of the main hydroponics system pipes
Check for leaking of pipes or any moulding.
If any damage is detected, replace the pipe for the particular row by screwing the narrow pipes attached on each side out of the right-angle connectors.
Ensure that water flow is turned off during replacement such that all water is void from the hydroponics system.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 28
Flowers are mostly sunlight-loving plants.
Below is a list of some flowers that grow well locally:
1. Bougainvillea (Bougainvillea spp.)
Bougainvilleas are known for their vibrant and colorful bracts. They thrive in full sunlight and can add a splash of color to green walls.
2. Morning Glory (Ipomoea spp.)
Morning glories produce trumpet-shaped flowers and are well-suited for sunny locations. They can be trained to climb on trellises or green walls.
3. Portulaca/Moss Rose (Portulaca grandiflora)
Portulacas are low-growing, sun-loving plants with colorful flowers. They're drought-tolerant and perfect for vertical gardens.
4. Verbena (Verbena spp.)
Verbena is a sun-loving plant that produces clusters of small, vibrant flowers. It's a great choice for adding color to green walls.




O n G a r d e n i n g 31
Recommended flowers Bougainvillea MorningGlory Verbana Portulaca
Recommended plants for less sunlight
In cases where there is less sunlight, below is a list of plants that do not require full sunlight to grow.
1. Maidenhair Fern (Adiantum spp.)
Maidenhair ferns have delicate, lacy fronds and are well-suited for shaded or partially shaded green walls. They require consistently moist soil and good humidity.
2. Nerve Plant (Fittonia spp.)
Nerve plants have striking, colorful foliage and thrive in low to medium light conditions. They prefer consistently moist soil.
3. Pothos (Epipremnum aureum)
Pothos, also known as Devil's Ivy, is a hardy and adaptable vine that can grow in various light conditions, including low light. It's an excellent choice for green walls.
4. Peace Lily (Spathiphyllum spp.)
Peace lilies are known for their attractive white blooms and glossy green leaves. They can tolerate low light but appreciate bright, indirect sunlight.




AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 32
Maidenhair Fern Nerveplant PeaceLily Pothos
Recommended crops
Food crops thrive in full sunlight.
Below is a list of some commonly grown food crops:
1. Herbs
Herbs like Basil prefer full sun and need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. They can also be grown in partial shade but may not be as prolific.
Germination
Grow time
Harvest time
Keep in mind that Singapore's climate is humid, and it's essential to provide adequate air circulation to prevent fungal diseases. Herbplants
Seeds typically germinate within 5 to 10 days
Usually reach maturity for harvesting in about 4 to 6 weeks after germination
You can start harvesting the leaves once the plant has reached a height of around 6-8 inches (15-20 cm). You can continue harvesting throughout the growing season by picking leaves from the top of the plant Regular harvesting promotes bushier growth and prolongs the harvest period.



O n G a r d e n i n g 33
Lettuce CherryTomatoes
2. Leafy Greens
Greens like lettuce can thrive in partial shade and requires about 4-6 hours of sunlight per day. It can tolerate some shade in Singapore's climate.
Germination
Grow time
Harvest time
Seeds typically germinate within 7 to 14 days
Depending on the variety, lettuce can take anywhere from 30 to 70 days to reach maturity. Some varieties, such as loose leaf lettuce, can be harvested earlier as baby greens, while others, like romaine or iceberg lettuce, take longer to develop full heads.
You can begin harvesting lettuce leaves for salads or sandwiches as soon as they are large enough to eat, typically when they reach about 4-6 inches (10-15 cm) in height. For head lettuce varieties, wait until the heads are firm and fully formed before harvesting. You can either cut the entire head or pick individual leaves as needed, allowing the plant to continue producing new growth.
2. Tomatoes
Cherry tomatoes need full sun, which means they require 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
Germination
Grow time
Harvest time
Seeds typically germinate within 5 to 10 days
Cherry tomato plants usually take about 60 to 80 days from germination to reach maturity and start producing ripe fruits. However, this timeline can vary depending on the variety. Some early-maturing varieties may produce ripe fruits in as little as 50 days, while others may take longer.
You can start harvesting cherry tomatoes when the fruits are fully ripe, meaning they have reached their full color and are firm but not hard to the touch Harvesting cherry tomatoes regularly as they ripen encourages the plant to produce more fruit.
AgroReach: an integrated smart green wall 34
.
SUTD Capstone - Class of 2024



https://capstoneshowcase.sutd.edu.sg/project /agroreach-an-integrated-smart-green-wall/























































