A Guide to Investment in India’s Mineral Sector
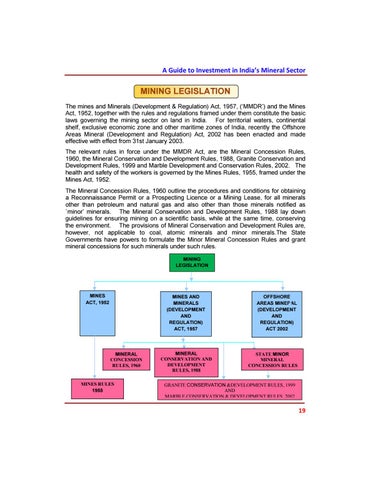
MINING LEGISLATION The mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Act, 1957, (‘MMDR’) and the Mines Act, 1952, together with the rules and regulations framed under them constitute the basic laws governing the mining sector on land in India. For territorial waters, continental shelf, exclusive economic zone and other maritime zones of India, recently the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002 has been enacted and made effective with effect from 31st January 2003. The relevant rules in force under the MMDR Act, are the Mineral Concession Rules, 1960, the Mineral Conservation and Development Rules, 1988, Granite Conservation and Development Rules, 1999 and Marble Development and Conservation Rules, 2002. The health and safety of the workers is governed by the Mines Rules, 1955, framed under the Mines Act, 1952. The Mineral Concession Rules, 1960 outline the procedures and conditions for obtaining a Reconnaissance Permit or a Prospecting Licence or a Mining Lease, for all minerals other than petroleum and natural gas and also other than those minerals notified as `minor’ minerals. The Mineral Conservation and Development Rules, 1988 lay down guidelines for ensuring mining on a scientific basis, while at the same time, conserving the environment. The provisions of Mineral Conservation and Development Rules are, however, not applicable to coal, atomic minerals and minor minerals.The State Governments have powers to formulate the Minor Mineral Concession Rules and grant mineral concessions for such minerals under such rules.
MINING LEGISLATION
MINES ACT, 1952
MINES AND MINERALS (DEVELOPMENT AND REGULATION) ACT, 1957
MINERAL CONCESSION RULES, 1960
MINES RULES 1955
MINERAL CONSERVATION AND DEVELOPMENT RULES, 1988
OFFSHORE AREAS MINERAL (DEVELOPMENT AND REGULATION) ACT 2002
STATE MINOR MINERAL CONCESSION RULES
GRANITE CONSERVATION &DEVELOPMENT RULES, 1999 AND MARBLE CONSERVATION & DEVELOPMENT RULES, 2002
19