





The water industry is a major energy user. In the UK, 3% of all energy used powers water treatment plants, pumping stations, and distribution networks. Despite advances in efficient and greener energy use, utilities remain under pressure to cut energy consumption and costs.
The solution? Real-time optimisation: the future of water sector energy management. It enables utilities to optimise energy use, slash carbon footprint, and cut costs.
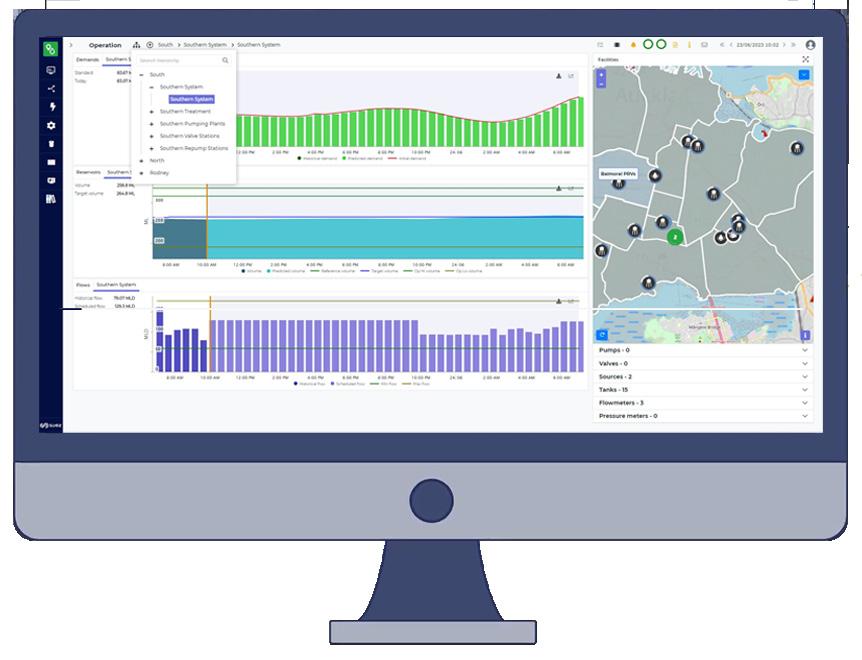
AQUADVANCED® Water Supply, the industry leading real-time optimisation software for water distribution, offers 6%-8% reduced energy consumption and emissions, and a 12%-20% energy cost reduction. This advanced digital innovation empowers water utilities to seamlessly manage energy providers and tap into renewable energy sources, contributing to a better, cleaner future.
Discover more and contact us at SUEZ.COM/UK



At H2O Global News, we stand at the crossroads of knowledge and change, empowered to highlight the issues that we face globally. Traditionally, I offer insights into our editors’ features and interviews, but in this issue, I’m shifting the lens. This editorial extends beyond mere commentary; it is a call to every water utility for transformation.
The digital revolution has swept over numerous industries, yet the water sector lags behind, despite accessible solutions. In Buckinghamshire, England where I live, water costs have soared by an overwhelming 12.3% as of April 1—an uptick notably steeper than the UK’s 6% average. It’s not just water—our everyday costs, from taxes to personal care, are climbing while salaries stagnate, far removed from keeping pace with inflation.
My growing concern on the price surge of essential utilities is matched only by my exasperation. Just outside my home childhood home, water wastefully spills from a drain—a single episode in a series of infrastructural failings that reflect a broader narrative of negligence. Instead of preventing monetary and resource wastage, we are witnessing a reckless drain of both.
Our publication champions innovations designed to staunch such loss, to refine management practices, and to accomplish so much more—take our cover story, which profiles iVapps, a visionary UK enterprise. Their smart cartridge technology provides insights and solutions to preemptively tackle water network issues to curtail water mismanagement.
The imperative to prevent water loss is monumental—it transcends mere economics; it is existential. Water is the lifeblood of Earth, yet we squander it, while in numerous regions, it remains a lifesaving commodity. It’s time we accord it the reverence it deserves.
I extend my heartfelt gratitude to global innovators working tirelessly to aid water networks, and to utilities integrating groundbreaking technologies. Your commitment to stewardship of our most vital resource is commendable. May the stories within these pages sow seeds of inspiration and propel a concerted drive towards enduring progress.
With appreciation and hope for a rejuvenated future.
Abby Davey Publisher and Co-Founder


Publisher and Co-Founder
Abby Davey abby@h2oglobalnews.com
Creative Director and Co-Founder
Louise Davey louise@h2oglobalnews.com
Editorial Team
Darby Bonner darby@h2oglobalnews.com
Martyn Shuttleworth martyn@h2oglobalnews.com
Natasha Posnett natasha@h2oglobalnews.com
Advertising
+44 (0)7817 105 258 marketing@h2oglobalnews.com
FOLLOW H2O ON @h2oglobalnews
H2O Global News delivers news from around the world covering the Drinking/ Potable Water, Hydropower and Wastewater industries incorporating technology, companies, legislation, the environment and case studies. The H2O Global News Magazine is published four times a year (Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter) by Blue Manta Media Limited, Buckinghamshire, England, UK.
H2O Global News t/a Blue Manta Media Limited has used utmost care to ensure and maintain the accuracy, completeness and currency of information published on this site. We, however, take no responsibility for any errors or omission, though if notified of any we will endeavour to rectify such.
CGN is an innovative platform that bridges the gap between industry, research and policy in a modern climate conversation. We enable our users to engage in meaningful conversations about the future of our planet and strive to create an open space where collaborators from all sectors can work together for sustainable progress.


Welcome to IFAT Munich—the world’s leading trade fair for environmental technologies
More sustainability for municipalities and industries. Being the most important driving force in the global environmental industry, IFAT Munich offers innovative solutions and best-practice examples for modern water management. With a focus on resource conservation and cost efficiency.
May 13–17, 2024 | Messe München
Get your ticket now: ifat.de/tickets/en Information: Pattern Limited Tel. +44 20 3375 8230 info@pattern.co.uk












igital transformation is becoming a major topic across the water industry as businesses and organisations adopt the exciting new technologies defining the 4th Industrial Revolution. A sector often accused of techno-conservatism is now accelerating into AI, the Internet of Things, and cloud computing, which will help face the challenges of promoting sustainability and protecting the environment while lowering costs. While this is a huge step forward, it isn’t just a matter of adopting the latest technologies because digital transformation needs very careful planning.
A couple of decades ago, the electric industry began its own digital transformation to cope with the growing demands for renewable energy and smart grids. This process happened at exactly the right time, taking advantage of high-speed communications and sophisticated enterprise software. Now, electrical systems are increasingly responsive and efficient, and
the sector learned the importance of an approach to digitalisation that layered each technology carefully, gradually building upon these strong foundations.

While the water industry is still some way behind the electrical industry in terms of digitalisation, it also has the opportunity to transform at the right time and take advantage of the rapid changes occurring in the digital realms. Now, as the world undergoes a new industrial revolution, AI, big data, cloud computing, and sophisticated apps are shaping the water sector. Utilities can use digital twins to gain detailed views of their system; sensors can help to monitor resources; and sophisticated apps help customers track water use.
Naturally, efforts tend to focus on digital transformation for large utilities, but the impact on small/medium companies and NGOs is just as important. They can create their own apps, use the cloud, and benefit from technology like sensors, drones, and AI. This is supported by the advent of open-source software and shared data resources, which they can use to innovate and develop solutions. Anyone in the water industry can access this

technology and become part of the digital transformation.
However, with all of these new digital technologies, there is some danger, and it is very easy to fall into the trap of implementing them without a coherent plan. After years of facing criticism for being too slow and conservative when adopting new technologies, the industry now faces the opposite issue. The sector risks overcompensating by going full speed and forgetting about the importance of careful integration: it is always about implementing the right technology at exactly the right time.
For example, developing smarter processes with the use of sensors, AI, and IoT requires breaking down any data siloes, while integrating different technologies and sources of data can be particularly problematic with older legacy systems. All of these technologies need the ability to communicate with each other through interfaces, and new systems need to be installed with the overall goal in mind. In terms of human resources, embracing the digital transformation needs skilled employees with the ability to work with these new technologies, from workers in the field using apps to the IT specialists ensuring that everything runs smoothly.
Another important foundation, which is often overlooked, is the importance of communications, because the new age of big data and real-time control needs quick, reliable systems that transfer information quickly and accurately. This does not just include communications within a company but connections in the field that help workers access cloud computing
services remotely. These communications need to be in place long before looking at smart meters, AI, digital twins, or any other new digital technology.
Finally, and possibly the most important issue to take into account from the start is cybersecurity. Complex, interconnected systems can leave weaknesses for hackers to exploit, compromising sensitive data and potentially disrupting services. Any plan for digital transformation needs robust cybersecurity solutions that can evolve and adapt to neutralise present and future threats with layered defences. No company is too small to think about this because any app holding customer data needs to be cybersecure or risk falling foul of increasingly strict data protection regulations.
The water industry is buying into the idea of the digital transformation with exciting new technologies to promote sustainable water management and help face the growing issues of water shortages and climate change. This is always an ongoing process and requires focusing on the final destination and establishing what technologies are needed to get there, with careful planning to make sure the important pieces are in place.
Fortunately, as is shown in this issue, many companies in the sector are finding the right balance between taking advantage of the new digital revolution and doing so in a measured fashion. Gradually, they are building upon their existing systems and processes to implement efficient, sustainable, and secure solutions that will help them navigate the digital transformation.

As someone who thoroughly enjoys spending time in and near the water, I understand the importance of monitoring water quality. No one wants to surf in sewage or swim between bits of floating rubbish! I would like to know that I am enjoying nature at its best.
It is also much more than just our recreational enjoyment that is important. Monitoring water quality is vital in maintaining healthy ecosystems. So, shouldn’t we be seeing a digital transformation in our current era of technological advancement to achieve the greatest success?
Water pollution is a massive issue in the UK and around the world. We know that a range of contributing factors, including urban runoff, agriculture and plastic pollution, cause high pollution levels. But is enough being done to manage it? And are we making the most of new advancements in technology?
Monitoring water quality helps scientists predict, learn, and determine the human impacts on these sensitive ecosystems. Taking measurements can also determine if restoration projects need to be undertaken or if the water quality meets environmental standards. Monitoring our water quality is essential to combat our pollution issues. But we are still (on the whole) using the methods we first adopted years ago. The water sector needs
to transform how it monitors water quality, benefiting from the integration of cuttingedge technologies and revolutionising how we conserve this precious resource.

New technologies are being seen on a small scale, but the next step is to get them on a national and even global scale.
The UK ranks last out of 30 European countries for the state of its water quality. Only 70% of bathing waters are classified as ‘excellent,’ meaning 30% need to be improved in some way. Rivers are also in a bad state, with only 14% meeting good ecological status. This is worrying, considering that the Government’s target is to reach 75% by 2027.
Water quality is tested throughout the bathing season, which is only from May to September, and samples are taken weekly. Why is water quality only important during those months? People use the water all year round, and aquatic ecosystems still need to be protected no matter the time of year.
These statistics are why advanced technology needs to be widely adopted to provide more efficient and accurate data readings.

One key advancement in digital water pollution monitoring is the use of remote sensors and monitoring stations. These sensors are deployed in water to continuously measure various parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen, temperature, turbidity and the presence of pollutants. By collecting real-time data, these sensors provide valuable insights into the health of water bodies and enable prompt intervention in case of pollution events.
The Canton of Geneva in Switzerland has deployed a network of digital sensors in Lake Geneva to monitor water quality parameters. These sensors transmit real-time data to a centralised monitoring system, enabling authorities to track changes in water quality and respond promptly to pollution events or environmental concerns. The technology has facilitated more proactive management of Lake Geneva’s water resources, helping to protect the lake’s ecosystem and ensure safe drinking water for surrounding communities.
The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (GBRMPA) has established a remote monitoring system equipped with digital sensors to track water quality and coral health in the Great Barrier Reef. These sensors collect data to help researchers and marine managers assess the reef’s condition and detect signs of degradation. Through digital technologies, the GBRMPA can monitor vast areas of the reef more efficiently, identify threats such as coral bleaching or pollution, and implement targeted conservation measures to protect this iconic ecosystem.
Advances in data analytics and machine learning have changed the way we interpret and analyse water quality data. Algorithms can now process vast amounts of data, detect patterns and even identify trends that may indicate pollution sources. This proactive approach allows authorities to take preventive measures and implement targeted interventions to mitigate pollution and protect water resources. This is game-changing because it gives people more time to find solutions.
The integration of digital technologies also facilitates better communication and collaboration among stakeholders involved in water management. Data collected from remote sensors can be shared in real-time with the government, scientists, NGOs and the public through online platforms and mobile apps. This transparency allows greater awareness and engagement in water conservation efforts, empowering communities to take action to protect their local environments.
The Safer Seas & Rivers Service app was created by the charity Surfers Against Sewage. It alerts water users when untreated sewage is discharged into waterways and logs the water quality in real-time at 370 locations nationwide.
Similarly, the digitalisation of water pollution monitoring enables predictive modelling and scenario analysis, allowing people to anticipate future trends and plan accordingly. By simulating various scenarios, people can assess the potential impact of policy decisions, infrastructure projects or climate change on water quality and then develop appropriate strategies to mitigate risks and ensure sustainable water management.
The journey towards digital transformation will come with challenges, but the momentum behind this movement continues to grow.
It is an exciting time in the world of water. The digital transformation holds great promise for revolutionising how we monitor pollution and what we do with the data we receive. By harnessing the power of technology, we can maintain healthy water for everyone to benefit from, now and in the future.
I hope to continue surfing, scuba diving and wild swimming in pollution-free environments. I believe the digital transformation will help us achieve this and enjoy nature at its best.

New York is sinking. So are Venice, Bangkok and Rotterdam. But no city compares to Indonesia’s capital city - Jakarta.
Jakarta, located on the northwest coast of the island of Java, is sinking at a truly alarming rate—a rate that varies around the city but is up to an average of 11 inches a year in the northern areas. This makes Jakarta the fastest-sinking megacity in the world. Scientists warn that by 2030, most of Jakarta will be uninhabitable as 40% of Jakarta is below sea level, so the city has until 2030 to figure out a final solution, or it will be too late to hold back the Java Sea. However, Indonesia has grand plans for Jakarta—a new capital on Borneo, a giant bird-shaped sea wall to protect Jakarta itself—but they don’t solve the underlying problem.
All around the world, coastal cities are flooding, and even sinking. Sinking is caused by subsidence, and today, this geological process is happening at a rate that’s making scientists start to sweat! If these sinking areas of land didn’t have some of the most important cities and megacities, hardly anyone would notice, or in many cases, they wouldn’t be sinking in the first place.
With over 140 million people, Java is filled to the brim, making it the most populous island in the world, plus freshwater is scarce and groundwater is a hot commodity. The illegal boring of wells in and around Jakarta is understandable in a city where the local government can’t provide fresh water for its 11+ million residents, not to mention the millions of others who commute to work in the city. But the island’s wetlands are being drained by illegal wells, leading to the subsidence of the entire landscape, submerging the capital one day at a time.
 Darby Bonner Staff Writer at H2O Global News
Darby Bonner Staff Writer at H2O Global News
In a bid to tackle the sinking issue, in September 2021, Joko Widodo (Indonesia’s long-time president), proposed that the capital city be moved to a location 800 miles (1,300 kilometres) away in Indonesian Borneo. The new city of Nusantara is set to be completed by 2045.
While moving the capital city may reduce traffic in the area (one of the main reasons for relocating), those who are unable to relocate businesses and their homes, are still grappling with a sinking city. There is some good news, as in 2022, the Jakarta Government won a WSIS (World Summit of the Information Society) Prize for the flood control

system innovation which helps to predict potential disasters before they happen, and optimise control when a flood disaster occurs.
For decades, Jakarta has been battered with floods, and so far, the Flood Control system in Indonesia’s capital only involved monitoring river flow and level, based on manual human observations which is not very accurate, plus it takes a long time.
However, with rapid digital technological developments in the water industry, technology is contributing to saving lives in Jakarta. The latest Flood Control System includes the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This flood risk management was developed in collaboration with Jakarta Smart City and the Jakarta Water Resources Service (DSDA).
Utilising Internet of Things (IoT) technology, a network of 178 sensors has been strategically deployed across pump houses in the Jakarta region. These sensors are capable of measuring various parameters such as rainfall, vibration, temperature, water level, and water flow. Integrated with Artificial Intelligence (AI), this IoT sensor network facilitates seamless data processing and analysis.
A real-time monitoring system that is fueled by continuous data produced from these detectors also acts as a supervision and flood control system. This
innovative setup offers a comprehensive overview of potential flood conditions in Jakarta, resulting in the development of a robust flood prediction model.
Apart from being a proactive measure towards public early warnings, it also lays the groundwork for data-informed flood management policies in Jakarta. Beyond preemptive measures, the technology extends its utility during flooding events by autonomously adjusting flood gate and pump operations based on prevailing real-time conditions. Finishing the system - a box panel that contains key processing tools into this system. These instruments, including I/O logic, play a pivotal role in recording and transmitting analogue data gathered from the sensors. Processed data is converted into raw format which is then uploaded via a connected data logger to the Flood Control System dashboard.
The implementation of Jakarta’s Flood Control System empowers stakeholders to monitor key parameters such as water level and rainfall in realtime, streamlining coordination efforts in flood management. Plus, the 178 IoT sensors deployed throughout Jakarta represent a long-term investment, capable of accumulating historical flood data over time. By collecting this data, future policymakers can utilise the data to enable targeted policy formulation and action plans.
Despite being in its developmental phase, Jakarta’s Flood Control System is a beacon of hope. The sensors hope to tackle future flood challenges and protect those who reside in the sinking city.

iVapps is a UK-based innovation-driven smart engineering company that has created a sustainable engineering system which provides digital monitoring, via accessible sensors, and valve functionality, both located within one easy access point in a pipeline network.
To learn more about iVapps’ ability to help organisations create digital networks that can predict potential future issues, we spoke to Simon Humphreys, the CEO. iVapps was born when the team behind the technology had a eureka moment - ‘why not engineer a mechanical valve enabling it to hold a sensor or a valve. This will allow organisations to
monitor their networks, and when an issue is identified, they can simply swap out the sensor for a valve’ - and that is exactly what it did!
At its core, iVapps provides a novel mechanical design—a valve body, or PORTAL which holds a sensor carrying cartridge, or SMART Cartridge, capable of detecting multiple changes in the asset flowing through the pipeline.
Now, the really impressive bit is that the mechanical and digital solution enables water system operators to monitor their networks via a remote dashboard,

mitigating the need to travel to the location of data loggers. The sensor agnostic SMART Cartridge that monitors the systems can also be removed and replaced with a VALVE Cartridge to create control or isolation points when required, removing the need to install new gate valves. This can be achieved in minutes, rather than hours, something no other technology can do, making this digital innovation a remarkable breakthrough in the water-monitoring industry.
The iVapps team’s vision is to gather accurate data and provide it to utility companies so they can make informed decisions. The SMART Cartridge is able to measure multiple parameters including flow, pressure, and temperature,. “Our data’s real value is what our customers can do with it, allowing them to understand their entire network better,” says Simon. The information can be delivered in one of two ways, via iVapps own easy-to-use dashboard, or delivered directly to the network operator’s own system via API.
When it comes to the iVapp dashboard the team have created a traffic lights system. "Whereby green means all systems go; amber indicates possible problems; while red implies some urgent attention," Simon added.
The iVapps cartridge system is different from anything else on the market. We asked Simon about the type of sensors that can be housed in the SMART Cartridge, his response was “pretty much anything”. He continued, “And we can transfer the data via a range of different systems from 2G to the more advanced Lora Wan, pretty much however the client requests.” This technology enables the iVapps system to detect issues even in the most remote of locations.
There are a range of ways to power sensors that sit in water networks, some run on traditional batteries that need replacing at regular intervals, and some are hard-wired into a power source. Both these options bring with them their own particular challenges.
iVapps has opted to add self-charging capabilities to its system, whereby the water flowing through the pipe, turns a generator which re-charges the integral batteries. This system is a more user-friendly option and goes a long way in assisting water utilities in their net zero challenge. Less maintenance visits equals less time on the road.
As iVapps has evolved, it has partnered with key organisations. One being the Binnies Group. Binnies and iVapps are working collaboratively to deploy the solution across water networks and have run multiple events at the WRc (Water Research Centre) in Swindon, UK, to showcase the iVapps system’s functionality and ease of use.
The events have been led by Simon, and Stuart White, Binnies Head of Network Services (Asset Management). Simon said: “It was encouraging to see how well received our partnership was, and how positive the audience was with regard to our collaborative approach and knowledge sharing. Combining firstclass mechanical engineering with leading technology all supported by software that brings valuable information to life was perceived as a high-value proposition.”
In addition to operational efficiency, iVapps is Continued on page 12
committed to sustainability and environmental responsibility. The flow of water powers the system making it selfsustaining and reduces carbon emissions— proof of the company’s dedication to sustainable innovation.
Simon often gets asked how the system is powered. “I’ve always been keen to not go down the traditional battery route or wiring”. Instead, iVapps has utilised one of the best sources of power - the flow of water. iVapps has engineered energy harvesting capabilities into the SMART Cartridge. It takes just four hours of flow to fully charge the integral batteries Simon said, “By installing a selfpowering piece of equipment, it minimises maintenance and the carbon element”.
iVapps was keen to ensure any environmental credentials it shared were independently verified so turned to sustainability consultants, Tunley Environmental. Tunley carried out a whole life-cycle analysis of the system comparing it to traditional data loggers and valves – the two pieces of technology effectively replaced by the iVapps system. Following their analysis Tunley stated, “Incorporating iVapps products in water utility networks provides a substantial advantage in facilitating water utility companies’ transition towards Carbon Neutrality (Net Zero)”.

· Burning 46,216 kg of coal.
“The PORTAL and SMART cartridge combination can result in carbon emissions savings of up to 1.83 tCO2e over 100 years per system compared to a data logger alone. OR 5.68 tCO2e over 100 years per system when compared to a Standard Gate Valve + Data Logger. The need for a datalogger is eliminated, which emits 4.25 tCO2e over its lifetime, thus eliminating 4.25 tCO2e per data logger purchased”.
Put simply, assuming 50 valves are required over 100 years. The use of 50 PORTAL & VALVE cartridges combined with 50 PORTAL & SMART cartridges would save between 73.63 tCO2e and 108.28 tCO2e instead of using 50 Standard Gate valve + Data Logger. This is estimated to be a mean saving of 90.96 tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents over 100 years!
This is equivalent to:
· Driving 233,180 miles in an average diesel vehicle.
· Charging 11.06 million smartphones.
· Sequestered by 108 acres of forest in a year.
· Sequestered by 1,504 tree sampling that are grown for 10 years.
Many parts of the UK, particularly inner cities, are serviced by Victorian water networks. With an increasing population, comes increasing demand and water utilities are aware their networks simply cannot take the additional workload. This is where they are experiencing leaks and bursts leading to substantial water loss. In the UK alone, around three billion litres of water are lost every day.
Another issue in the water industry is water theft. While
it doesn’t occur much in the UK as legally everyone in the UK has a right to water. However, many parts of the world are grappling with the issue. To prevent water theft, the iVapps PORTAL system can be used to identify drops in flow indicating that the line has been tapped.
One of the challenges to introducing new technology is the simple reluctance to try something new. The old adage ‘If it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” comes to mind. There is also the assumption that new technology requires additional installation training. However, the iVapps system is based on an industry-recognised valve body, meaning no additional training is required to install.
Simon said, “One guy last week said to me, ‘I don’t even need to change the tools in my van’, and that’s absolutely true. For professionals who have been installing valves for decades, the amazing thing is, that they already know how to install the iVapps PORTAL”.
iVapps looks ahead for international expansion, with plans to move into the US, South American, European and East Asian markets. Simon understands that there must be a connection between iVapps’ work and what the industry needs as well as partnerships that will

foster innovation. He elaborates, "Our relationships with university institutions, utility firms and research institutes reflect our technology-driven interest in global challenges."
Learn More: ivappstech.com


Smart water management systems stand at the forefront of revolutionising the water sector, promising enhanced efficiency and sustainability in water supply systems by leveraging high-technology solutions like smart water meters and sensors. These intelligent systems transform conventional water management approaches by integrating digital meters, sensors, and advanced control systems, setting the stage for smarter solutions in water resources management.
The grappling challenges of global warming and drought on communities have made the need for smart water meters an absolute necessity. This is a critical technology in the face of decreasing sources of water and urgent calls from the government - reducing leakage by 50% by 2050 and following The National Framework’s (Environmental Agency, 2020) advice of reducing customers’ daily usage (PCC) to 110 litres per head (person) per day (L/h/d) by 2050.
Smart meters provide accurate near real-time data about consumption thereby enabling local authorities and water services to monitor use more closely. These minute details enable them to detect high levels of water usage, prompt identification of leaks, and help people reduce their consumption, and therefore design precise programs on
how to conserve water and energy.
With SUEZ leading the charge, smart water management is poised to redefine how water resources are managed, offering benefits such as improved water allocation, increased security, and reduced operational costs.
ON’connect metering from SUEZ has been used over the last 15 years as a key tool for efficient management of water, and so far it has been implemented on more than 6 million water meters around the globe. In times when we are faced with climate emergency and global drought effects, such capabilities are priceless when it comes to ensuring sustainable development in terms of water resources.
Smart water management refers to the use of advanced technologies and strategies to effectively manage water resources. One important aspect of smart water management is smart water metering - this involves the use of digital meters that provide near real-time data on water usage. These meters can be installed in homes, businesses, and even on a larger scale, such as in urban areas, which is where the term ‘smart cities’ comes from. By providing accurate and up-to-date information on water consumption, smart metering allows for better monitoring and control of water usage.
With smart water metering, individuals and organisations can have a clear understanding of their water consumption patterns. This information not only helps in identifying potential leaks or wastage but also enables users to make informed decisions about their water usage habits. By tracking their usage in near real-time, individuals can adjust their behaviour to conserve water and reduce their environmental impact.
On a larger scale, smart water metering can play a crucial role in managing water resources in cities and municipalities. By collecting data from various meters across the area, authorities can gain valuable insights into overall water consumption patterns. This information can then be used to identify areas where water conservation measures are needed or to pinpoint potential leaks or infrastructure issues. By addressing these problems promptly, smart metering can help reduce water loss and optimise the efficiency of the overall water distribution system.
One of the primary applications of smart sensors is in the early detection of leaks. Underground water leaks can be notoriously difficult to identify and can result in significant water loss and infrastructure damage. However, with the installation of smart sensors, cities can detect leaks as soon as they occur, allowing for prompt repairs and preventing further wastage. This proactive approach not only saves valuable water resources but also minimises the need for costly and disruptive repairs.
In addition to leak detection, smart sensors can also monitor water quality. By continuously monitoring parameters such as pH levels, turbidity, and chemical contaminants, cities can ensure that their water supply meets the highest standards of safety and potability. Near real-time data from these sensors can be used to detect and address water quality issues promptly, safeguarding the health of residents and reducing the risk of waterborne diseases.
SUEZ, a global leader in water and waste management, has developed an innovative smart water metering solution called ON'connect. This advanced metering system combines smart meters with an online-based platform to provide near real-time data on water consumption and quality.
So far, ON'connect coach has been used by 25 municipalities
and water utilities, monitoring the consumption of 2 million households, resulting in reduced volume consumption. Thanks to the ON'connect coach, individuals can track their daily water usage costs and observe consumption trends over time.
This information helps tailor conservation efforts to the specific needs of each household. By following personalised recommendations, such as reducing hot water usage, individuals can conserve energy. The ON'connect coach has numerous benefits, including meeting environmental demands, promoting ecological transformation in communities, empowering users, and creating new benefits for residents and businesses, ultimately increasing the value of water services provided.
The ON'connect coach also helps modernise water services and improve the environmental impact of communities. In Valenciennes, nearly half of the residents were unsure how to analyse their water consumption or determine if it was excessive for their household size.
The water utility of Valenciennes (Syndicat des Eaux du Valenciennois) partnered with SUEZ to develop a mobile application, which includes ON'connect coach, to provide personalised instructions and practical tips. By following these recommendations, 80,000 Valenciennes users can save up to €200 per year on their water and energy bills.
ON'connect fluids offers digital tools that allow users to monitor their water, gas, and electricity consumption from one place. The modular design of this platform guarantees ease of use, providing access to various indicators that support green initiatives within companies. The system collects data from different sources, including various distributors, connected devices, internal software, and Excel files. Some of the key benefits of this system include global insights into consumption trends, generating key performance indicators for action plans, streamlining information sharing for teams, reducing water and power losses at whole sites, ensuring compliance with regulations, and potentially earning certification points and financial assistance. Users can track multiple water, gas, and electric meters simultaneously, compare performance on field actions, optimise electricity tariff calculations, and receive alerts for leaks with distinct operational priorities.
Additionally, the SUEZ team is involved throughout the project's lifecycle, assisting with efficient savings strategies
Continued on page 16
and installing additional IoT sensors, such as CO2 sensors or smart thermometers, upon request.
ON'connect switch effectively manages resources and prevents potential messes by promptly responding to water leakage. This system gives managers the ability to remotely close taps, allowing them to monitor and control water consumption on their premises. Users can manually shut off the flow of water through an online platform or set automatic limits to prevent excessive usage.
The ON'connect switch offers various benefits, including improved facility security, as it minimises potential losses and instantly detects leaks. Users can also have a positive impact on their water bills by effectively managing resources and earning points towards certifications or financial aid. Key features of this system include near real-time monitoring of multiple water usage points, immediate alerts of leaks via SMS or email, and options for manual or automatic opening and closing of supplies. Users can also program specific times for opening and closing supplies, which improves efficiency and mitigates risks. Consumption reports provide detailed information on water usage, making it easier for facility managers to schedule valve operations and prevent leaks, especially during holidays and weekends.
The success of the ON'connect switch can be seen from notable cases, such as the detection of 11 leaks in two equipped networks at the Bontaz assembly plant, resulting in significant savings of 4201m3 in just three months.
Similarly, in the Grand Est region, the system helped detect 26 leaks, saving 23,407 m3 in less than four months. In summary, the ON'connect switch reflects forward-thinking actions taken by individuals to manage water resources and ensure sustainability in various sectors of the economy worldwide.
ON'connect trends serves as a dynamic dashboard for water service operators, enabling them to oversee and manage water consumption in urban areas. This system enhances knowledge about consumption patterns through data analysis from remote meter readings, facilitating informed decision-making for tailored public policies.
ON'connect trends is essential for optimising network efficiency and reducing environmental impacts as it contains performance indicators and thematic analyses related to leaks and irrigation. It also allows for the examination of
regional trends in water usage, which helps in implementing measures such as drought action and preventing disputes with water services by anticipating consumption changes. When used at a consumer level, it can reduce household losses by up to 3%, decrease carbon footprints, and result in potential annual savings of £170 (€200) per household.
SUEZ was actively involved in the replacement of old water meters with smart meters to improve efficiency in meter management and enhance customer service in Armagnac, France. The Syndicat des eaux Armagnac Tenareze (SAT32), responsible for drinking water supply and wastewater disposal, covers 15 municipalities serving 11,000 inhabitants connected by a 730 km long drinking water network. The ON’connect smart metering system installed allows for remote reading and billing based on actual consumption. Customers are promptly alerted in case of excessive water usage, and leaks are detected and resolved quickly. The deployment of smart metering has significantly improved the reliability of data received from measurements, minimising rebate requests and financial losses for the Syndicate. It has also contributed to improving network efficiency, with a notable increase from 62% in 2021 to 66% in 2022, representing a 4% enhancement. This has resulted in better water volume counts and reduced misattributed water leaks.
According to Nicolas Bourdiol, the Director of Technical Services for SAT32, smart metering has made it easier for everyone to work, from billing to the quality of service delivered to customers, and has received positive feedback from customers. It has also helped identify and resolve many leaks in private homes and farms in the area.
Smart water management, including smart metering, is a key tool in ensuring the sustainable use of water resources. Providing near real-time data and insights into water usage helps individuals and organisations make more informed decisions about their consumption. ON'connect technology provides innovative solutions for efficient water management that enable local authorities as well as individuals to monitor consumption effectively and address environmental concerns accordingly. Being widely applicable to metering monitoring and management, ON'connect significantly contributes to sustainability efforts and cost savings across various sectors.
As a global leader, SUEZ continues to drive advancements in water management technologies, contributing to a more sustainable future for communities worldwide.
Learn more at: suez.com


The water industry isn’t always the first sector coming to mind when you think of cyberattacks, but its attractiveness to cybercriminals is clear. Multiple US water utilities and an Irish water utility were breached last year and, just last month, Southern Water in the UK and Veolia North America faced ransomware attacks that resulted in data breaches. According to analysis from GHD, about a quarter of global water systems could experience a cyber-security breach by 2025.

A recent investor report by Moody’s warned of an ‘elevated’ risk of attacks targeting UK drinking water. The report attributes increased cybersecurity risks to the growing use of data-logging to monitor water consumption and leverage digital smart meters. Data has become crucial in maintaining and improving public infrastructure - the water industry is no exception.
Water companies hold vast amounts of information that contain crucial insights into service use and impact. Now, Ofwat calls on water companies to adopt open data
practices that better utilise this information: data sharing boosts transparency and consumer trust, helps establish new business models and services (especially benefiting vulnerable customers), improves decision making, and helps meet environmental challenges.
Data insights and innovation should never sacrifice the safety and security of critical national infrastructure. So, how can water companies utilise data whilst protecting it from cybercriminals?
Cybercriminals use tactics that trick employees into giving access to the organisation. Phishing scams, used to attack 8 in 10 UK companies last year, are just one example. Once inside, they search for sensitive information, such as customer card details. To reduce the risk of employees inadvertently giving hackers access, cyber-hygiene training and robust security tools (like perimeter defence) are vital. But, since roughly a third of employees could be susceptible to phishing scams, it’s not always possible to prevent hackers gaining entry. Reducing the risk of data loss if defences are breached needs good data governance.
To practise good data governance, water companies should run a data audit to fully understand the extent and nature of the information they hold. Data can be lost or forgotten as companies grow, employees come and go, and technology systems change. Data that is unaccounted for or incorrectly labelled cannot be appropriately protected.
Next comes cleaning and classifying data. Documents and files must be reviewed so they can be organised, labelled, and properly stored - with security measures for files identified as ‘sensitive’. Classification means the right data gets the right protections, with proper permissions and retention policies ensuring that personal data or sensitive IP is managed and destroyed responsibly.
The classification process also helps businesses run more smoothly. Recent Gartner research shows that 47% of digital workers struggle to find information needed to effectively perform their jobs. This data disconnect can be fixed by properly labelling data so that information is easier to discover and access. Of course, access shouldn’t be granted indiscriminately, and users should only have access to information they need.
Finally, smart organisations automate data governance processes, recognising that keeping data secure manually is virtually impossible. Water companies deal with data enmasse and a one-time data overhaul won’t cut it: new
data constantly flowing in also needs to be classified, labelled, and protected - whatever system or file type it resides in. AI helps automate this process to increase both security and efficiency in a changing security landscape.
Specialist AI tools flag any duplicate or similar versions of files, processing unstructured information so that it can be governed just as effectively as structured data, enabling greater accessibility and easier discoverability. This might involve converting sound files into text, which can be ‘read’ by AI, classified, and protected. Automating data governance means companies can automatically understand the data they have, where it lives, its sensitivity, what it’s used for, who has access, and who really needs access. From there, sensitive information is instantly protected against hackers and complies with data protection laws.
Automatic data management doesn’t just defend datait’s the key to AI transformation.
A strong data governance strategy gives water companies more control over their information and helps them prepare for an AI-enabled future. AI offers transformative possibilities for the water industry, and Ofwat’s £200 million Innovation Fund backs several AI projects. Amidst global challenges such as the climate crisis, AI is crucial for effective and sustainable water management.
Behind any safe, secure, and successful AI application is well-governed, high-quality data. Water companies who automate data cleaning, so that the correct information is rapidly accessible in the right form for AI models to understand, can move more quickly and safely to adopt emerging applications of the technology.
The recent flood of cyberattacks against water companies is a worrying trend, and the sector should ensure its data practices don’t increase their vulnerability. Improving data governance needn’t be viewed as a chore and, using automation, companies can sort and shore up their data against present-day threats, embracing the digital and AI innovations shaping the future of water management.
The MetriNet telemetry bollard provides street level water quality monitoring for distribution networks.
Our ultra low powered, multi-parameter, MetriNet smart water quality monitor delivers a modular solution for generating reliable and continuous data within distribution networks. With 16 parameters to choose from, the MetriNet telemetry bollard offers a secure and serviceable street level monitoring solution with less hostile environmental conditions, prolonging the life of the monitoring asset.
Creating intelligent, optimised, smart water networks of the future with MetriNet. analyticaltechnology.com
 M-Node digital water quality sensors
Q52 multifunctional controller
M-Node digital water quality sensors
Q52 multifunctional controller

Revolutionising how we live, work and interact with our environment, smart cities are set to be a crucial part of our urban future. They are areas that leverage technology and data-driven solutions to improve efficiency, sustainability and overall quality of life for their residents. The goal is to maintain a healthy planet for everyone to enjoy!
With an ever-increasing strain on our water resources, transforming the way we manage our water is one key aspect of sustainable development. Smart cities and their technology can pave the way for efficient conservation strategies and sustainable solutions.
A lot of exciting work is being done around the development of smart cities, including the wide range of projects at BABLE Smart Cities. BABLE is a facilitator for smart cities across Europe. Working to accelerate change for a better urban life, they provide data, knowledge and expert insights to the public and private sectors. They use real-world experience to help make the transitions to smart cities attainable and smooth.
I spoke with BABLE’s Tamlyn Shimizu to find out more
about their mission and some of their work around water management and conservation:
“Moving towards smart cities is essential for fostering sustainable urban development, improving the quality of life for residents and protecting the planet. It also means taking an innovative and holistic approach to our cities and world’s biggest challenges…”
Smart cities use a combination of digital technology, IoT and data analytics to make infrastructure and services more efficient, responsive and adaptive to the needs of their residents. They can optimise the use of resources, including water, reduce waste and minimise environmental footprints.
By offering smart mobility solutions, efficient public services, safer communities and healthier environments, smart cities enhance the overall wellbeing of their residents. They are also better equipped to respond to climate change challenges, ensuring long-term sustainability and security for urban populations.
Continued on page 22
Furthermore, smart cities’ innovation and technologydriven approach promotes economic development, creating new jobs and attracting investments in sectors like clean technology and sustainable construction.
However, it is crucial to note that smart cities no longer solely focus on technology. Tackling our world’s toughest challenges requires a holistic, human-centric approach, aiming for a better life for all.
One key area that BABLE supports cities and other areas with is smart water management.
“Smart water management plays a pivotal role in fostering sustainable cities by optimising the use of water resources, reducing waste and enhancing the resilience of urban water systems. By integrating advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, AI and data analytics, smart water management solutions enable real-time monitoring and control of water distribution, quality and usage.“
This leads to several key benefits:
Efficiency and Conservation: Smart systems can detect leaks and losses in the water distribution network in real-time, significantly reducing water waste. They can manage water use more efficiently, ensuring that the demand for water in cities is met without overexploiting natural water sources.
Enhanced Water Quality: Through continuous monitoring, smart water management systems can quickly identify contamination or quality issues, ensuring safer drinking water and reducing health risks.
Resilience and Adaptation: These solutions enable cities to better adapt to climate change impacts, such as droughts or floods, by optimising water storage and distribution based on predictive analytics and weather forecasts.
Engagement and Awareness: Smart water management fosters greater awareness about water conservation by providing data and insights to policymakers and the public, promoting sustainable usage patterns among residents.
Glasgow Smart Canal Project
In Glasgow, the Smart Canal Project uses weather
predictions and IoT technology to dynamically manage the Forth & Clyde canal water levels, preventing urban flooding by allowing it to become a drainage route for excess surface water during high rainfall events. With early warning of wet weather, the water level in the canal can be lowered by up to 100 mm, isolating the North Glasgow section and moving excess water into the nearby River Kelvin.
Essen’s trees suffer from drought stress and must be watered intensively to prevent them from dying. In the past ten years, the city has lost around 34,000 trees. The solution has been using TreeCop sensors to monitor the trees’ watering needs, allowing the city to optimise their water use while supporting urban greening. The combined soil moisture and drought stress data provide all the information needed to determine watering requirements.
These examples highlight the benefits of smart water management, including reduced water wastage, improved water quality and enhanced urban resilience and sustainability.
“Smart rainwater harvesting is critical in addressing the current climate crisis due to its potential to mitigate water scarcity, reduce urban flooding and adapt to changing weather patterns.”
Here’s why it’s so important:
Water Scarcity Mitigation: As climate change exacerbates drought conditions in many regions, harvesting rainwater provides an alternative water source, reducing dependence on groundwater or surface water and alleviating stress on these resources.
Flood Risk Reduction: Smart rainwater harvesting systems can help manage stormwater runoff, reducing the risk and severity of urban flooding by capturing and storing rainwater, especially in urban areas with impermeable surfaces.
Sustainable Urban Development:
Incorporating smart rainwater harvesting in urban planning contributes to greener, more sustainable cities. It supports the replenishment of local aquifers, reduces the energy footprint associated with water treatment and transportation, and can be used for non-potable purposes like irrigation and flushing toilets, further conserving potable water.
Climate Adaptation: These systems offer a flexible and
adaptive approach to water management, allowing cities to better cope with the unpredictability and extremity of weather patterns caused by climate change.
“Over the next ten years, BABLE’s objective is clear and grounded: to evolve from being Europe’s leading facilitator for smart cities into the world’s leading facilitator for entire forward-thinking urban projects. Having already facilitated more than €2 billion in smart city initiatives, our ambition is to expand our impact globally.”
The Smart City market faces significant challenges, notably the slow pace governments procure essential technologies like smart water management systems, which averages 22 months. BABLE is working to change this, aiming to cut procurement time by at least 50% for both the public and private sectors. Another critical issue is the inefficiency in the market, where a staggering 80% of funds spent fail to create a lasting impact.
“Our mission is to partner with thousands of cities and companies worldwide, enhancing the speed and efficiency of smart city projects. By focusing on practical, impactful collaborations, we plan to make the smart city market more dynamic, faster and impactful. Our work isn’t just about leading the change; it’s about making meaningful, lasting improvements in how cities adopt and implement smart technologies, ensuring they deliver real benefits to communities around the globe.”
There is a great allure around smart cities and an idealistic view of the future—a vision of sustainability, community, and resilience. Cities across Europe are committing to being smart and climate-neutral by 2030. Time will tell how successful we are with this transition towards a more sustainable urban future, but smart cities will play a crucial and positive role in transforming our urban landscapes for the better.



Kozani is a quiet and unassuming town in West Macedonia, Greece, a centre of Greek culture known for producing wine and saffron. Nestled between the Vérmio and Voúrinos mountains, this municipality is leading the country’s digital transformation by adopting digital twin technology to tackle the perennial problem of water leaks. We dive deeper into this interesting project, including an interview with Dr Konstantinos Gkonelas, a specialist who proved instrumental to its successful implementation.
In the economic struggles after the EU’s austerity measures and the COVID-19 pandemic, the Greek government developed a National Recovery and Resilience Plan. With this, it intends to bring digital transformation to the country’s infrastructure,
including water and wastewater. At present, Greece’s public water supply loses over a quarter of its water to leaks, so households use more drinking water than any other European Union country. In the face of climate change, the country needs use its water resources much better.
The Municipal Water Supply and Sewerage Company of Kozani (DEYAK) is receptive to new technologies and recently undertook programs to segment district metered areas (DMAs) and improve pressure management. Now, working with Greek company, Tech-Go-Round, they are adopting a digital twin powered by Bentley Systems OpenFlows technology. The cloud-based software uses a virtual, real-time model of the water system to replace many manual processes and reduce water leakage.
Installing a digital twin needs some preparation, including a fully-mapped system, but DEYAK lacked information about where some of its older pipes were buried. After mapping its network, the utility installed a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system supported by Bentley’s water distribution analysis software, OpenFlows. The utility could now use digital sensors to monitor water pressure, flow, and quality in detail.
With preparations complete, the utility was ready to install Bentley’s water infrastructure digital twin software, OpenFlows WaterSight, making it easy to view data from SCADA on a unified platform. DEYAK can now identify and locate problems quickly, replace inefficient manual processes, and make betterinformed decisions based on data.
DEYAK has seen the digital technology transform its approach, and now spends an astonishing 40% less time on managing pressure, while locating and repairing leaks much more quickly. Wastage has dropped dramatically, with 20% less water flowing through the network, so consumers benefit through lower bills.
Not only does the digital twin future proof the system, but it brings Kozani’s water system in line with a number of EU directives that focus on cleaner water and leakage rates.
Konstantinos Gkonelas, technical manager of TechGo-Round, which partnered with DEYAK to implement the digital twin, tells us more about the program.

I am 46 years old and father of 3 children. A Civil Engineer specializing in hydraulic engineering, with a PhD in the management of water supply networks using hydraulic simulation software with the aim of optimal water and energy use. For the last 20 years I have been active in the field of water supply and irrigation utilities but also perform specialized
Continued on page 26
"missions" such as simulating firefighting scenarios in a military air unit and simulating water hammer in a desalination water pipeline in the Persian Gulf.
I am the founder and co-owner of ReonHydor, a company active in the field, and also technical manager in Tech-Go-Round a software service provider. We were the first to implement the digital twin of water supply network at Kozani Water Utility with Bentley’s Openflows WaterSight and we are already working as a company on the digital twin of the rain/stormwater network and flood management, something very promising in an era of climate change.
Why do you think that water usage is so high in Greece?
Urban water is managed by municipal companies and despite the honorable efforts of their employees, they cannot keep up with the pace of evolution of the sector. The main reasons for the high water use are the large volume of water lost in leaks and bursts, the feeling of consumers that water is cheap, the lack of recording and maintenance of the networks, the lack of personnel of the utilities, etc.
What advantages do you think technology, such as digital twins, could bring to Greek water utilities?
The main advantages (till now) that water utilities can benefit from DT are:
• Aggregation of various network data on one platform
• Perception of the hydraulic characteristics of the network in real time
• Improvement of management of emergencies (breakages, leaks) resulting in water savings
• Ability to use tools that use big data, such as finding new unreported leaks, a form of Active Leakage Control (ALC)
• Compliance with the EC directives to be implemented in the following years (risk analysis, failure management, etc.)
• Better monitoring of water quality, resulting in better sanitary conditions
What are the main barriers to implementing the technology, especially for larger utilities?
Most of the problems in large utilities are the multiple decision centers within the utility, the incomplete cooperation of the different departments of the company and also the greater bureaucracy. Very figuratively I will tell you that in small utilities, decisions
are made quickly (in 2-3 weeks) by a small team of 2-3 people, while the same decisions take years to be done by large ones. The transition to digital twin technology is best piloted in a part of a large utility’s network, while full commitment to a specific technology and the unknown future is a concern for decision makers. They feel insecure with such a fast-moving industry and fear that control might slip out of their hands.
more utilities to adopt the technology?
The real-time connection of the network simulation model to the sensors in the field and its automatic calibration fully illuminates all levels of network operation. This means a better and faster understanding of the causes of problems, and also the possibility of using new technologies to solve them. Without the use of the digital twin, the utilities cannot move into the new era. It is definitely the evolution in the field of water.
What were the main lessons from the project in Kozani?
Vigilance is required at all levels of the water utility. The operation of the digital twin is dynamic and for there to be benefits and results for the utilities, all data communication infrastructures must remain operational 24/7. Ensuring the sensors (flow and pressure meters, etc.) are connected to the hydraulic model in real-time (rather than after a day's lag) requires effort from technicians and overcoming issues such as code-locked SCADA. At first many will face the transition with suspicion, but it takes consistency in our choices for the benefits to appear and be accepted by all. Maintaining the digital twin for years to come is maybe more difficult than trying to install it initially.
I believe that managing water utilities has become complex and the use of tools such as the digital twin is one way. However, it should be understood that in order to exploit the potential of this technology, it is necessary to involve scientists who can unlock its benefits. Therefore, the provision of digital twin services of water supply networks is the comprehensive response to modern infrastructure requirements. The combination of new technologies and specialized human resources is the key to success.

iVapps helps water pipeline network operators detect leaks and other asset issues with the smart cartridge. When an issue is identified, the cartridge is extracted and a valve cartridge installed to create a control point where it’s needed.

Visit our website or drop us a line to learn more
Leading The Charge In Water Pollution Clean-Ups of Ports, Harbours And Marinas
Written By | NATASHA POSNETT"In our pursuit of a cleaner, more sustainable future, battery-driven autonomous surface vessels (ASVs) are emerging as invaluable tools! They're transforming water pollution clean-ups on a grand scale,"
Richard Hardiman, CEO of RanMarine.
Water pollution significantly threatens ecosystems, biodiversity and human health worldwide. From industrial or agricultural runoff to oil spills and plastic waste, pollutants contaminate water bodies, endangering aquatic life and compromising vital resources.
Traditional clean-up methods often fall short due to limitations in workforce, resources and efficiency. However, the rise of autonomous technology presents a game-changing opportunity to tackle this pressing and ever-growing issue.
All water bodies are impacted by pollution, but as busy centres of trade and travel, ports, harbours and marinas have become key locations that require attention to address their pollution concerns. Ports are hubs for global trade and are crucial for the world economy. Sadly, their operations often come at a significant cost to the environment, generating high pollution levels. Commercial and fishing harbours are notorious for leaking waste into surrounding seas. Plastic is a huge concern and requires regular removal to prevent its accumulation. Wind also poses a big challenge for harbours as it quickly and easily blows waste into the water.
RanMarine Technology is a cleantech company that designs, manufactures and distributes emission-free ASVs such as the WasteShark, MegaShark, and soon-to-bereleased OilShark.
RanMarine’s Patrick Baransky was able to tell me more about what they do and how their technology is making a difference to pollution clean-up efforts.
“We want to empower people and organisations to restore the aquatic environment back to its natural state. Our initiatives help to clear-up debris, plastic, algae and other biomass from water bodies. We combine this with water-quality data acquisition, with the overall aim of safeguarding aquatic ecosystems.”
RanMarine is perhaps best known for its robotic WasteShark. Inspired by the whale shark, which uses its broad mouth for filter feeding, this ASV houses a central waste collection basket between its hulls to scoop up floating rubbish. It is equipped with depth and temperature readings and an array of optional extra sensors for oxygen, pH and turbidity levels. The WasteShark was designed to reach areas that are tough to get to. It is small enough to fit into tight spaces yet big enough to make a difference!

The MegaShark is a scaled-up version of WasteShark designed with a larger storage compartment to handle larger volumes of waste and biomass. Its size allows for extended operation periods without the need for frequent emptying. It is used in bigger water bodies and industrial areas where waste accumulation is more substantial, making it a perfect fit for ports, harbours, and marinas.
Excitingly, RanMarine is also in the advanced stages of

research and development, with a goal of bringing the OilShark to fruition in 2024.
“Built on a platform similar to the MegaShark, this innovative vessel harnesses industry expertise to transform oil spill clean-up. Its optimal size allows for swift deployment and safe and sustainable resolution of oil spill challenges, particularly in harbours and ports due to engine or pump spillages.”
The modernisation of ports and harbours into digital hubs, often termed Port 4.0, has numerous benefits in addressing environmental concerns and advancing sustainability. Digital transformation also brings many other advantages: improved waste collection techniques, increased efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Digitalising port operations and introducing smart and clean energy operations minimises environmental impact, while IoT enables real-time data exchange and informed decision-making.
“The WasteShark offers both remote-controlled operation and full robotic autonomy, minimising human intervention while performing waste collection and environmental monitoring tasks. This capability optimises operational efficiency, reduces costs and promotes cleaner port waters. Additionally, these agile vessels excel at navigating hard-to-reach areas in marinas, ports, or harbours, intercepting water pollution before it disperses into the open ocean.”
Using the RanMarine ASVs, ports and harbours can leverage customisable onboard sensors and cameras to gather data on waste accumulation patterns and water quality conditions. This data empowers port authorities to pinpoint pollution hotspots, prioritise clean-up efforts, and enact targeted interventions for
maximum efficacy.
Scalability and adaptability are further benefits of this digital shift, as RanMarine's ASVs can be integrated into existing port infrastructure. This flexibility allows for tailored responses to evolving waste management needs, ensuring continuous protection of marine ecosystems in a dynamic environment.
With global trade expected to continue growing, the environmental pressures associated with port activities are likely to intensify. Maritime users and boat owners are increasing, pushing up the number of marinas and people frequenting these facilities. Addressing these challenges will require concerted action from governments, industry stakeholders and individuals to develop and implement innovative solutions that balance the needs of maritime trade, recreation, and tourism with environmental sustainability.
The pollution of ports, harbours and marinas represents a complex and pressing environmental issue with far-reaching consequences. As we navigate these waters, we must raise awareness and advocate for cleaner, more sustainable operations to protect the health of our planet and its inhabitants for generations to come.
Baransky was able to shed light on the situation further with some statistics:
“The United Nations Environment Programme forecasts that plastic waste in aquatic ecosystems will almost triple, ranging from 8-15 billion kg annually in 2016 to an estimated 24-40 billion kg by 2040. Aggressive agricultural practices and nutrient runoff are fuelling an increase in Harmful Algal Blooms, adversely affecting marine ecology and economies. The National Academy of Sciences also reports approximately 4 million metric tons of oil entering global oceans annually from 2010 to 2019. The US Coast Guard estimates around 30,000 minor to moderate oil spills annually in the US, primarily from fuel bunkering and salvage operations, requiring legal protection and cleaning protocols in major ports and harbours.”
RanMarine is providing the technology to aid people in the digital transformation transition—harnessing the power of ASVs to keep our aquatic environments pollution-free. RanMarine’s technology already spans 27 countries, and they aim to achieve widespread global adoption within the next decade.
“Ultimately, our goal is for our Autonomous Surface Vessels to become as ubiquitous as robotic vacuum cleaners or street sweepers. Innovation, crafted for nature.”

In this world where every drop of water counts, there has been an industry that has been splashing its way through unnoticed - car washes. Did you know that over 1.3 million gallons of fresh water are being flushed down the drain daily for people to drive around in squeaky-clean cars? Yes, you heard it right. That is enough to fill up a small lake or an Olympic-sized swimming pool!
While the car wash industry is extremely popular worldwide, little do people know that the average car wash slurps a staggering 246-303 litres (65-80 gallons) of water per car in doing so. One company that hasn’t allowed this industry to go unnoticed, is FlowStat.
In the bustling world of car wash businesses where water efficiency is essential, the establishment of FlowStat in November 2022 was a turning point. To learn how FlowStat became an innovation icon amidst an industry plagued by high water bills and lost revenues, we spoke to FlowStat co-founder Viran Nana.

Viran said that after struggling to consistently resolve issues with high water bills while operating 11 Express Tunnel Car Washes, things got serious in July 2022 when Dilan Nana, his son, came home from University to hear him complain about the $330,000 in lost cash flow due to high water bills and the over $6M in lost valuation in their sale of the 11 car washes. FlowStat’s digital revolution in this sector of the water industry, allows operators to receive real-time alerts about their water use, preventing losses and saving money.
FlowStat is headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas but has already expanded its footprints targeting four other locations in Nashville and eighteen others throughout Texas. This however is only just a beginning. Viran said that their goal is to have 100 systems installed by


December this year, and 2000 units installed by December 2028.
At its heart lies revolutionary technology –the “Instant Water Usage Data & High Usage Alert System.” With FlowStat’s technology, car wash operators can resolve issues long before the water bill arrives. The experienced team at FlowStat have worked hard to keep it simple and easy to use, as they know that car wash managers & operators have many challenges every day. Their SMS Text Alert system sends messages when high usage is experienced, so operators can be alerted immediately. This alert system has contributed to operators saving over $30,000 per location per year and 50% of water usage and costs.
Viran said that FlowStat is much more than saving costs. He said: “All car wash operators experience water leaks, malfunctions, mistakes, and other wasteful situations that may be due to timing, worn-out tips, etc. These situations could easily be fixed but are often unseen or missed, leading to high water bills. With FlowStat operators will know immediately when usage is higher than expected.”
FlowStat simplifies monitoring usage data by offering a user-friendly interface that provides easy access to key performance indicators like Gallon Count, Car Count, Gallon Per Car, and Location Health Status on an hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly basis.
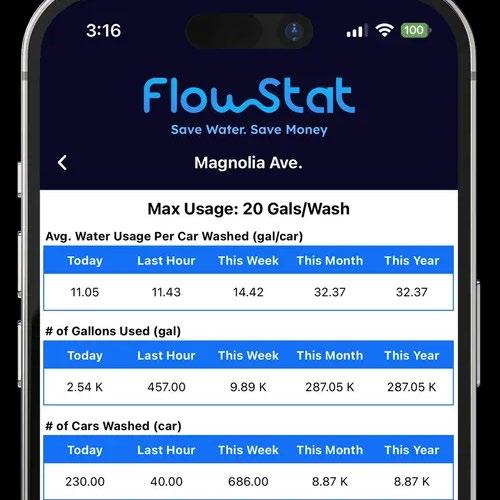
While FlowStat is focused on helping car wash operators by capturing and providing important data about chemicals and other areas of the business, FlowStat is a flexible system that could potentially open up new opportunities for future growth.
Viran is excited to see where FlowStat goes. He said they are looking forward to achieving ambitious goals in five years. Their goal is for 2000 operators to save approximately 6 billion gallons of freshwater per year and experience 50% savings in their water costs.
With FlowStat, operators can now identify water conservation opportunities, optimise water usage, and ultimately reduce costs, contributing to both environmental sustainability and economic savings!
Learn More: FlowStat.com













Dive into the digital revolution of water management with expert insights. Discover our readers views on how technology is shaping the future of this vital resource.






Transcend Software Inc.
Founder and CEO

Compared to other industries, what are some of the unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in the water sector?
I don’t think the water industry faces different challenges vs. any other regulated, infrastructure-driven industry (e.g. power, transportation, etc). I actually think the biggest challenge is that these businesses (like many others) don’t have good processes for business process transformation well, and to get the most out of digital transformation a business must deal with non-digital part first. For example, considering how workflows, pricing, and org structure will change to effectively get the most value from a software implementation is critical, yet its usually an afterthought when evaluating digital technologies.
As digital transformation accelerates in the water sector, what role do you believe partnerships and collaborations play in driving innovation and overcoming sector-specific challenges?

Partnership is critical to accelerating digital transformation in the water sector in a couple of ways. First, when water companies collaborate with one another and share their experience and best practice implementing digital technologies it helps to remove barriers and accelerate adoption. Second, implementations are much more effective when viewing work with the technology provider as a partnership where both parties learn from one another, as opposed to a vendor-client relationship.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
Transcend is already helping impact many water businesses through its generative design platform, Transcend Design Generator. Tangible benefits include de-risking capital investments by evaluating more options, with more detail, during the budgeting stage of a project; accelerating adoption of new treatment technologies by simplifying the ability to assess these technologies in a capital planning process; and speeding up the preliminary design process to help accelerate time to value for a wide variety of projects.
Foresight Canada Program Manager, waterNEXT and agriNEXT

Compared to other industries, what are some of the unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in the water sector?
Foresight’s waterNEXT initiative tackles the water sector’s unique digital transformation challenges by fostering collaborative solutions. We help ventures understand how to navigate the regulatory landscapes in the water sector (which are notoriously known to be complicated) and maneuver through the ecosystem as their innovative solutions look for pilot and customer testing opportunities. Through industry discovery and partnerships, we understand data privacy concerns and interoperability issues are being addressed through all aspects of the sector by leveraging advanced technologies for secure data handling. By aligning with regulatory bodies and industry leaders through consistent knowledge sharing, Canadian water tech ventures that are part of the ecosystem are pioneering digital innovations that meet both regulatory mandates and societal needs.
As digital transformation accelerates in the water sector, what role do you believe partnerships and collaborations play in driving innovation and overcoming sector-specific challenges?
In the constantly evolving landscape of the water sector, partnerships and collaborations serve as the cornerstone for increased innovation as we face new challenges around water scarcity. Leveraging our expertise in activating and maintaining the dynamic ecosystem through acceleration, strategic support, and industry matchmaking programming, waterNEXT collaborates with government agencies, research institutions, technology innovators, industry players and investors to accelerate innovative water tech solutions that support the present and future needs of technology end-users and society as a whole. Digital transformation gives the sector a chance to have a deeper outreach than previously seen before.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
As a water professional, it has been intriguing to see the growth and development of AI in the water sector. I have seen an uptick of ventures innovating more technological solutions utilizing AI in ways that will revolutionize the water industry sector’s current practices, sustainability and resiliency. While a regulatory aspect needs to be maintained regarding AI and its use, there will be a profound impact on the industry. AI has the potential to optimize water management, from predictive maintenance to smart water distribution. With the meshing of AI algorithms with data analytics, we will see more efficiency, less resource wastage, and smoother risk mitigation in water infrastructure.

How is the water sector leveraging digital revolutions to address key challenges such as ageing infrastructure, water quality management, and sustainability goals?
Digital platforms like SCADA and GIS have long played a crucial role in utility operations. However, amid mounting economic, environmental, workforce, and regulatory pressures, smarter use of data and cutting-edge digital technologies are enabling utilities to better serve customers and stakeholders, maximize operational performance and efficiency, and safeguard assets and natural resources as never before. For example, digital metering systems are being used to great effect across North America, Europe, and beyond to simultaneously improve customer service and engagement, reduce leaks and non-revenue water, cut fleet emissions and fuel costs, and bridge labor gaps.
Compared to other industries, what are some of the unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in the water sector?
Water utilities have traditionally been conservative in their approach to technological change, and with good reason: utilities’ primary responsibility is to provide an essential public good, protect public health, and safeguard natural resources and ecosystems, all while maintaining reasonable costs for their ratepayers. The utility sector is also highly fragmented, with only 1.5% of all global water and wastewater utilities serving populations greater than 100,000 people, creating financial and technical barriers to adoption particularly among smaller, under-resourced utility organizations. Circumventing these roadblocks will require continued innovation and collaboration between utilities, solutions providers, and regulators to ensure that digital water solutions are effective, affordable, scalable, secure, and fit-for-purpose to address the industry’s most pressing challenges.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
There is a great deal of fear both in the water industry and beyond that artificial intelligence will lead to large-scale job loss. But the truth is that AI cannot fully replace human intelligence, and AI should be harnessed as a tool rather than looked at as a threat. Notably, water utilities are responsible for managing large networks of remote assets, which in turn generate significant quantities of valuable data, much of which is currently underutilized. AI can help to process and analyze that data far more efficiently than human operators, providing real-time insights to support human decision making, identify potential problems and blind spots, and ultimately improve operational performance and customer service. AI will augment rather than replace the critical work already being done by utility workers, and free up staff time for more high-value, creative, and innovative tasks.
Flowserve
Global Product Leader Strategic Planning & Initiatives

How do you see data analytics and IoT technologies transforming operations and decisionmaking processes within the water industry?
Data analytics and IoT are revolutionizing water management by enabling predictive maintenance, which anticipates repairs before failures occur, and optimizing resource allocation through datadriven insights. This leads to more efficient operations and informed decision-making. By monitoring equipment and predicting behaviours with digital internet of things (IoT) technologies like RedRaven, focused on asset monitoring, Flowserve is equipped with sensors, algorithms and insights to optimize flow control equipment performance for our customers, allowing them to safely and efficiently operate. In desalination plants, for example, where pumps represent 90% of the total electricity consumption, adopting a solution like RedRaven is crucial.
Given the increasing importance of resilience and adaptability in water infrastructure, how do you integrate digital twins, real-time monitoring, and AI-driven predictive modelling to enhance system reliability and response capabilities?
Digital twins - virtual replicas of physical infrastructure - combined with real-time monitoring and AI-powered predictive modelling, are boosting system resilience. By simulating various scenarios, these technologies identify potential weak points and predict infrastructure behaviour. This allows for proactive maintenance and rapid response to disruptions, minimizing downtime and ensuring water system reliability.
However, limitations exist. Complexities in modelling real-world systems and the vast amount of data required for accurate predictions are ongoing challenges. For example, for just one pump, with a measurement taken in real-time we can have more than one million measurements in a year. The client who uses this technology will most likely be in an awkward position, because although it may receive all these data, it will not be reliable, and the number of false positives reported could jeopardize the implementation of predictive maintenance. So it’s fundamental to use the right algorithms together with the right data.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
AI is poised to significantly impact the water industry by enhancing data analysis for better decision-making, automating treatment processes, and improving customer service through chatbots and virtual assistants. It can also aid in environmental protection by predicting pollution patterns and optimizing resource use. However AI is Data dependence: AI systems are heavily reliant on data to learn and make predictions. The quality and quantity of data available can significantly impact the performance of AI models, so the AI should be always implemented by smart sensors and algorithms based on decades of experience of designing, upgrading the asset or the systems.

How is the water sector leveraging digital revolutions to address key challenges such as ageing infrastructure, water quality management, and sustainability goals?
It’s a delicate balancing act; ensuring the right investments are made that will bring our aging infrastructure up to modern standards, whilst also investing in technology and digitising our workforces to ensure smooth, efficient operations. Delivering improvements in the maintenance and operation of existing assets should go hand in hand with infrastructure upgrades, ensuring long-term sustainability and efficiency.
The industry is gathering pace in the uptake of AI and machine learning to streamline operations, generate predictive insights, and optimise emergency response. These optimisations allow water companies to prioritise critical issues, create more efficient workflows, and reduce response time to mitigate issues such as leakage and pollution. Improving data collection through ‘field-first’ AI tools can improve operational decision-making in emergencies, and deliver efficiencies in work completion, allowing more robust and cost-effective maintenance of assets to reduce likelihood of failure. FYLD’s workforce optimisation tools have given our partners 8-12% productivity uplift and helped them improve safety and environmental outcomes in parallel.
Compared to other industries, what are some of the unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in the water sector?
Implementing digital transformation in the water sector presents several unique challenges. One primary challenge is the need for highly reliable and resilient systems. Water is essential for public health, sanitation, agriculture, and various industrial processes so any service disruption can have significant consequences. Therefore, digital transformation initiatives must prioritize system reliability and uptime to ensure uninterrupted water supply.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
We’re seeing the rise of AI across core areas in the water sector. Firstly, using asset data and AI-based modeling to predict where failures will occur allows teams to intervene faster. For example the rapid uptake in smart sewer level monitoring across most water companies.
But the more recent rise and development has been in the execution of fieldwork. Seeing our workforce as a critical resource, we can use AI to support data capture and decisionmaking. By streamlining the workflow and data flow between different parties, and helping operators and fieldworkers assess and prioritise their daily objectives, we can increase the utilisation and quality of work delivered, allowing stretched resources to go further. The growth of AI will allow the industry to improve operations, reduce incidents, and create better outcomes for their customers.
How is the water sector leveraging digital revolutions to address key challenges such as ageing infrastructure, water quality management, and sustainability goals?

Knowing how to manage a water network obliges the operator to constantly monitor the network while having full data management capabilities.
This step requires enormous effort and this is where AI can be of support. Through technologies that exploit artificial intelligence, it is possible to monitor the network faster, plan predictive maintenance, forecast demand more accurately and optimise distribution processes.
For example, among the technologies for locating leaks, the innovative CRNS non-contact neutron monitoring technology emerges, which fuses a particle sensor with the use of AI and surpasses traditional noise logger methods and predictive algorithms.
How do you see data analytics and IoT technologies transforming operations and decision-making processes within the water industry?
Having robust and reliable data is crucial for water operators. In detail, the technologies that exploit AI to provide targeted information are:
- CRNS probes, which make it possible to pre-localise water leaks thanks to the use of Environmental Neutrons, allowing for a reduction in network inspection time, obtaining an output, to be analysed later with traditional techniques, of only 10% of the route covered!
- Noise loggers that allow, with the use of intelligent algorithms, to identify and locate the point of leakage
- The predictive algorithms that analyse the demand/ distribution history, optimising its management.
- The Digital Twins that make it possible to simulate the behaviour of the water system according to different scenarios.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
An effective knowledge of the state of one’s assets allows one to promptly direct investments where they are needed. With this in mind, technologies based on cognitive analysis enable value to be derived from data, directing choices towards the best action, by means of predictive and prescriptive algorithms, predicting potential failures, automating processes and choices.
Continuous mapping of the water network, using non-contact technologies, which can be carried out by normal moving vehicles and even untrained personnel, allows the mapping of the water network to becontinuously even 2 or more times a year.

How is the water sector leveraging digital revolutions to address key challenges such as ageing infrastructure, water quality management, and sustainability goals?
The water sector is embracing digital technology to address critical challenges in innovative ways. At Red Sea Global, we have taken a step in this direction by providing the residents of Turtle Bay Village, a residential and commercial area at The Red Sea, with advanced digital technology to monitor their water consumption. The destination is located in an area with no significant water infrastructure, so we have implemented permanent structures, including RO plants and constructed wetlands. This helps to meet the needs of the destination and reduces the burden on the wider national infrastructure. The integration of these digital technologies addresses the immediate challenges and demonstrates our commitment to sustainable water use.
As digital transformation accelerates in the water sector, what role do you believe partnerships and collaborations play in driving innovation and overcoming sector-specific challenges?
We draw on collective expertise and resources to effectively drive digital initiatives and overcome sector-specific challenges. By partnering with external and independent organizations, we gain access to different perspectives and implement industry-wide best practices to ensure we operate to the highest standards. This collaboration also allows us to implement various digital monitoring systems that enable real-time analysis of water quality around our production facilities. This capability ensures that our operations have zero impact on the surrounding environment.
Given the increasing importance of resilience and adaptability in water infrastructure, how do you integrate digital twins, realtime monitoring, and AI-driven predictive modelling to enhance system reliability and response capabilities?
We have developed a detailed infrastructure model and carried out feasibility studies to accurately determine the requirements for our operations. This planning ensures that our system does not put pressure on existing national infrastructure and includes areas such as water and power generation, waste management and wastewater treatment.
We have also created digital twins of sensitive habitats such as coral reefs. By using this data, we can ensure that our operations do not impact these habitats. We integrate this data into the same system as our live water quality measurements, allowing us to proactively manage our environment in the best way possible.
These technologies have many benefits, including the ability to better manage water consumption. However, it’s important to note that they rely heavily on the ability to integrate diverse technologies and data sources Despite these challenges, the integration of digital technologies remains critical to improving the resilience of water systems.

Compared to other industries, what are some of unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in water sector?
One of the unique challenges is the breadth of data types. only what can be measured (across physical and chemical parameters) but also geographic, process, and network information, and how the readings, be it a sensor with a location or in an area of influence, interact with each other.
The security concerns are also multifaceted, from operational technology data and its critical importance to privacy/GDPR concerns. Many have been hampered rather than aided security and the perceived value of sharing not being greater than the risk of failure, leading to the question is interoperability implicit or should it be reiterated?
Another unique challenge for the water sector is the pervasive problem of ageing infrastructure and the quality of data available relating to that as many inputs are prone to technical and human error. This of course hampers both application, quality of results, and interoperability. This is where the selling point of the InfoTiles PipeFusion technology comes as it connects, corrects and validates utility network data 99%+ accuracy, continuously in real-time from any data network device.
How do you see data analytics and IoT technologies transforming operations and decision-making processes within the water industry?
While the potential of analytics and IoT is great, interoperability and integration have seen the available solutions often adding new silos, adding to interoperability issues, often requiring manual maintenance in keeping track of metadata becoming an insurmountable task. While many are valuable in their niche, the real value and big picture understanding to answer complex questions remains.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in various sectors, how do you envision AI impacting the water industry’s digital transformation journey?
The current state of AI works wonders with language and utilise the massive volumes of text produced by humanity through the ages, but they still struggle with logic, maths structured data. Basically, the data which utilities are producing today.
Until we see the next breakthrough in AI, I believe there potential to take steps on current digital technology through clever encoding and labelling of existing data to utilise it is. But at the current rate of development we’ve seen in last few years, I’m still open to being surprised at what lies across the next watershed as it were.

the in the types. Not chemical a fixed other. operational privacy/GDPR by greater pervasive technical application, unique comes in data to data set or technologies interoperability adding requiring becoming their own answer various water and can humanity maths and is through it as it the lies
Matthew Langdon Veolia Water Technologies Business Development Manager
How is the water sector leveraging digital revolutions to address key challenges such as ageing infrastructure, water quality management, and sustainability goals?
Digital is rapidly being adopted in the Water Sector and is set to continue to grow as the challenges of AMP8 come into play. Utilising a digital Platform such as Veolias Hubgrade can help the water sector in many areas such as OPEX reduction through energy optimisation, reduction of CSOs through network and WWTP management, reducing chemical reduction and reducing the carbon footprint through CAPEX avoidance solutions that essentially allow you to do more with less.
Compared to other industries, what are some of the unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in the water sector?
Data privacy concerns are a huge challenge in the water sector compared to other sectors, quite rightly its sensitive and has always been managed in house. Veolia have vast experience globally with implementation of our digital platform Hubgrade and have a substantial IT and Cyber security team to work alongside clients to ensure we meet all of their requirements. Ultimately with Hubgrade Performance the client remains in control and is able to set the parameters for use and access levels ensuring a robust system.
How do you see data analytics and IoT technologies transforming operations and decision-making processes within the water industry?
Remote access to performance and alerts set within Veolias Hubgrade allow optimised resource allocation and enhanced efficiency in water management systems. Automated real time control ensures the plant and network are operating at their optimum at all times, this gives operators, engineers and managers confidence in performance whilst not on site, meaning resource can be allocated to areas that require immediate attention, reducing wasted time travelling or not being at the right site at the right time.
Neal White Rusco & Vu-Flow Filtration CEO
How is the water sector leveraging digital revolutions to address key challenges such as ageing infrastructure, water quality management, and sustainability goals?
We are fortunate in most of North America to have very good water quality supplied by municipalities and private water companies but to provide quality water takes a lot of time effort and expertise. Technology is being used to aid in real-time monitoring and testing both at the water plant and along the distribution route. Technology is having a growing impact on the assurance of water safety.
Compared to other industries, what are some of the unique challenges or considerations faced when implementing digital transformation initiatives in the water sector?
The landscape for public water is indeed complicated and there are many stakeholders, often with different goals, objectives, and ideas on the many challenges involved in developing and implementing digital solutions for water. The water industry has several trade organizations (Water Quality Association, Water Systems Council, AWWA, etc) that have taken the lead. They do a lot of work at the legislative level to create awareness on Capitol Hill and among myriad government agencies of water concerns, treatment technologies, and the use of data to aid municipal water authorities and private water companies in supplying clean, safe water to consumers.
How do you see data analytics and IoT technologies transforming operations and decision-making processes within the water industry?
Consumers, in general, expect clear, safe, great-tasting water when they turn on the tap. The reality is that a lot goes into providing that experience and maintaining systems and infrastructure is a large component of this. Information technologies and IOT are gaining a lot of traction in this area. IoT technology embedded in treatment systems and along the vast water distribution pipelines can alert when contaminates are detected or when there has been a breach in water mains. This allows for rapid, sometimes proactive response before any catastrophic failures occur. It is still early, and we are just scratching the surface. Still, it is safe to say that there will continue to be a revolutionary innovation in technology that will play an increasingly important role in the water industry.

Breaking the glass ceiling on water technology Technology and Innovation
Website URL: Emerson.com
Product Name: Movicon NeXT
Product Details:
Movicon.NExT™ is a state-of-the-art software technology for secure, scalable interconnectivity throughout all types of industrial environments. An open solution that configures easily to your requirements and protocols, Movicon.NExT™ allows quick, easy design of any project, and generates enhanced graphics and data capture that improve efficiency, energy usage and machine performance.

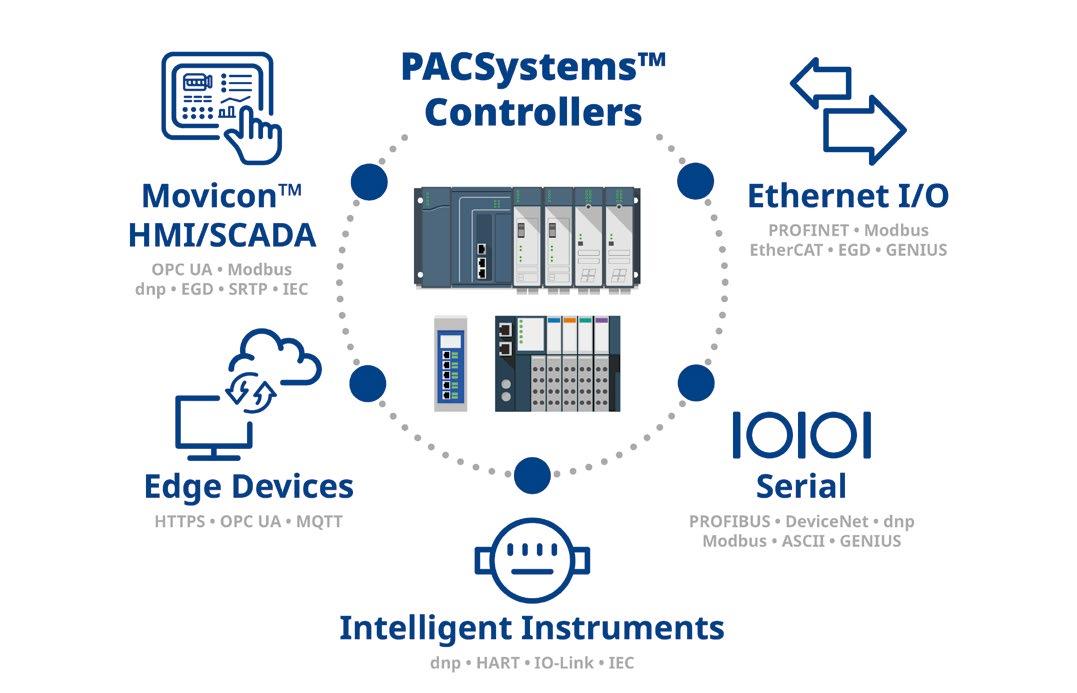


Website URL: Emerson.com
Product Name: PACSystems
Product Details:
PACSystems RX3i controllers provide the foundation for Industrial Internet connectivity. It is a powerful, modular Programmable Automation Controller with a focus on high availability. The RX3i features a single control engine and a universal programming environment to provide application portability across multiple hardware platforms.
Website URL: e-sens.com
Product Name: e-sens ROAM
Product Details:
The e-sens ROAM is a revolutionary, portable water quality testing device, capable of testing 23 parameters with a single sample by utilizing solid-state silicon sensors and microfluidic technology. Our app allows test results to be accessed immediately, making data management easier than ever.


Website URL: finapptech.com
Product Name: Finapp
Product Details:
Finapp with CRNS technology and innovative probes makes it possible to pre-locate water network leaks. It is contactless, monitoring up to 150 km per day quickly and easily.



Website URL: fyld.ai
Product Name: FYLD
Product Details:
FYLD’s AI-powered platform is a mobile app and cloud-based browser that takes passive PDF, paper, or digital work forms for water companies and transforms them into video and voice assessments. FYLD’s generative AI can give safety and productivity guidance in real-time, while field managers can make informed decisions and improve processes.
Website URL: huber-technology.com
Product Name: HUBER CarbonWin®
Product Details:
The HUBER CarbonWin® offers a compact alternative for replacing traditional primary clarifiers, featuring increased removal rates, reduced downstream operating costs, and a significant reduction in energy utilization. This proven primary treatment solution has become the European standard and is swiftly gaining recognition as an emerging technology in the United States.



The ever-changing nature of today’s manufacturing world and the challenges it faces will make the value of measurement ever more important. By connecting the physical and digital world and unlocking the power of instrument and analyzer data, SmartMaster provides operators with the assurance that their measurement data is as accurate as possible, enabling them to make informed operating decisions that will transform the way they manage their plant.
Website URL: ketos.co
Product Name: PRISM
Product Details:
KETOS PRISM leverages AI and public data to contextualize water insights across the US. Users can define the region of interest while the innovative tool developed with extensive satellite imaging and other sources can generate Water Compliance Risk Reports for permitting, drinking water, toxic waste, superfund sites, and PFAS/PFOS.



Website URL: oldcastleinfrastructure.com
Product Name: Leak detection featuring actionable AI, powered by FIDO
Product Details:
Oldcastle Infrastructure, a CRH company, has entered the smart water market to deliver unparalleled leak detection and water management/conservation solutions in the United States using actionable AI, powered by FIDO. Leveraging real-time data, customers can optimize operations and prioritize leaks before catastrophic system failure, reducing repair costs and downtime.
Website URL: ovarro.com
Product Name: EnigmaREACH
Product Details:
A complete solution for widescale leakage detection, combining multi-correlating pinpointing loggers, tablet, app for logger deployment tools and retrieval, and access to the automated AI LeakInsight platform. One kit can monitor double the distance (14 km per day) of traditional kits with fewer loggers, and it assigns POIs directly to technicians.


Website URL: redberry.net
Product Name: Matipi™
Product Details:
For municipalities and industries. On-field microbiological results: get total flora count in two minutes for 50mL thanks to ATP measurements and the new generation of Luciferase. All is in the Matipi™ suitcase! Easy and rapid on-field controls for your waters (drinking, swimming, process) that enables quick response and troubleshooting.


Website URL: sharcenergy.com
Product Name: SHARC Series & PIRANHA Series
Product Details:


Website URL: rshydro.co.uk
Product Name: Proteus
Product Details:
For optical ammonium measurement, a calibration dataset of 2000 consecutive ammonium readings (every 15-minutes) over 18 days used an Ion Selective Electrode correlated to a Proteus optical output. The ISE had not drifted, confirmed by routine calibration and Environment Agency samples, showing the optical sensor only required a 12-monthly calibration.

Harness wastewater for sustainable heating and cooling, reducing energy and water use. The SHARC Series optimizes large-scale wastewater energy transfer for heating and cooling with patented filtration, perfect for district energy projects. The PIRANHA Series compact, highly-efficient water-to-water heat pump utilizes wastewater energy, ideal for multifamily and commercial buildings.


Date: 15 April - 17 April
Location: London Heathrow Airport, UK
The Global Water Summit spans three days, drawing top-tier executives from various sectors including industry, municipalities, and international water companies. This event presents a unique chance to engage with key industry figures who may not participate in any other water-related gatherings.
Date: 22 April - 23 April
Location: Hilton London Kensington, London, UK
The Smart Water Systems conference, spanning two days, seeks to facilitate collaboration among water utility companies, solution/service providers, government officials, and finance/investment firms. Together, participants can network and explore cutting-edge technologies and recent advancements, with a focus on enhancing leakage detection and management efficiency.
Date: 13 May - 17 May
Location: Messe München GmbH Messegelände, Bavaria, Germany
IFAT is a five-day gathering showcasing environmental technologies, serving as the premier platform for water, sewage, waste, and raw materials management. With an expected participation of over 3000 exhibitors from nearly 60 countries, and approximately 120,000 visitors spanning the globe, IFAT stands as the largest event of its kind.
Date: 2 June - 4 June
Location: Assembly Rooms, Edinburgh, Scotland, UK
A three-day conference, fuelled by BlueTech Research, unites top water technology firms, entrepreneurs, investors, and executives from prominent research centres for networking and informative presentations on the latest market trends and insights.
Date: 10 June - 13 June
Location: Anaheim, CA, USA
AWWA’s 2024 Annual Conference & Expo (ACE24) is a four-day conference accompanied by a three-day trade show, orchestrated by the American Water Works Association (AWWA), serving as a focal point for water sector professionals to acquire knowledge, forge connections, and gain inspiration for addressing today’s global water challenges.
Date: 16 June - 20 June
Location: Sands Expo & Convention Centre, Marina Bay Sands, Singapore
The Singapore International Water Week spans five days, gathering thought leaders, experts, and practitioners from governments, utilities, academia, and industry to collaborate and devise innovative solutions aimed at addressing urgent urban water challenges on a global scale.
AD
BC
agriculture
circular economy energy
health and science
technology and innovation transport
water and ocean

Stay Informed. Be Empowered
climateglobalnews.com