

Critical analysis & evaluation
Careers information, advice and guidance (CIAG)

Part of the BPN Boost provision



Careers information, advice and guidance (CIAG)

Part of the BPN Boost provision
(PowerPoint will be shared & a Podcast is available)





www.bestpracticenet.co.uk/safeguarding
Aim
To develop skills in critically analysing and evaluating workplace projects and decisions, using evidence-based reasoning and structured reflection.
Objectives
•Differentiate between evaluative and critical writing.
L5: K6, K15, S9
L7: K5, S3, B3
•Apply structured approaches to critical analysis and evaluation.
L5: K6, K12, S10
L7: K7, S3, S7
•Recognise how critical analysis and evaluation support End-Point Assessment (EPA).
L5: K8, S10, B3


L7: K2, S2, B2
A. Fully confident; have extensive knowledge & experience & applied both consistently.
B. Fairly confident, can define them both and have applied the approaches successfully, several times.
C. I have limited understanding and could not confidently apply both approaches.
D. I feel I have no understanding and would not be able to confidently apply either approach.


Aim
To develop skills in critically analysing and evaluating workplace projects and decisions, using evidence-based reasoning and structured reflection.
Introduce yourself to the group
• Discuss what you already know about critical analysis and evaluation.
• Any examples you have produced/received from others?
• What KSBs might you need to develop?
• Any particular challenges?


Introduce yourself to the group
• Discuss what you already know about critical analysis and evaluation.
• Any examples you have produced/received from others?
• What KSBs might you need to develop?
• Any particular challenges?



1. Differentiate between evaluative and critical writing.
Resource 1 contains more detail for each of these headings
Questions assumptions and explores meanings Makes a judgement based on criteria
Considers what worked and what did not
Explores why it worked or did not
Common in reflective reports
Supported by evidence and reasoning


Common in academic or strategy-focused work
Supported by interpretation and deep analysis
The data shows that the incidence (new cases) of asthma rates in children under 15 years old increased rapidly from 1977, peaking in 1993 and then declining, though rates remain significantly higher than pre-1976 levels.
The trend, from 1977 until 1993, of a rapid rise in rates of asthma diagnosis in children under 15 years, suggests that one of the causal factors was particularly prevalent during this time, but has since declined in importance or effect.


Evaluate the role of mobile phone technology in creating a globalised world.
Descriptive/explanatory writing
There are more than 7 billion mobile phones - more than one per person. This number has risen rapidly in recent years. Just ten years ago, there were less than one billion mobile phones. Mobile phones and other technologies are an important factor contributing to globalisation. By having a mobile phone, people can experience ‘the shrinking world’ and so become more globalised.
Commentary: this answer is largely factual. The only place where it becomes evaluative is in the final sentence, but it is basic.


There are more than 7 billion mobile phones - more than one per person. By having a mobile phone, people may experience ‘the shrinking world’ and become more globalised. However, many mobile users, such as those in North Korea, do not have full access to the internet and are ‘excluded’ from external influences. So, in some places, mobile phone growth may not necessarily be linked with globalisation.
Commentary: as in the previous answer, the first sentence is factual. The rest of the paragraph is evaluative.


Critical analysis is about examining ideas in depth - questioning assumptions, exploring alternative perspectives and identifying implications.
Evaluative writing, on the other hand, is about making reasoned judgments based on clear criteria, assessing strengths and weaknesses and drawing conclusions. Both are essential, but they serve different purposes in professional and academic writing.


2. Apply structured approaches to critical analysis & evaluation.
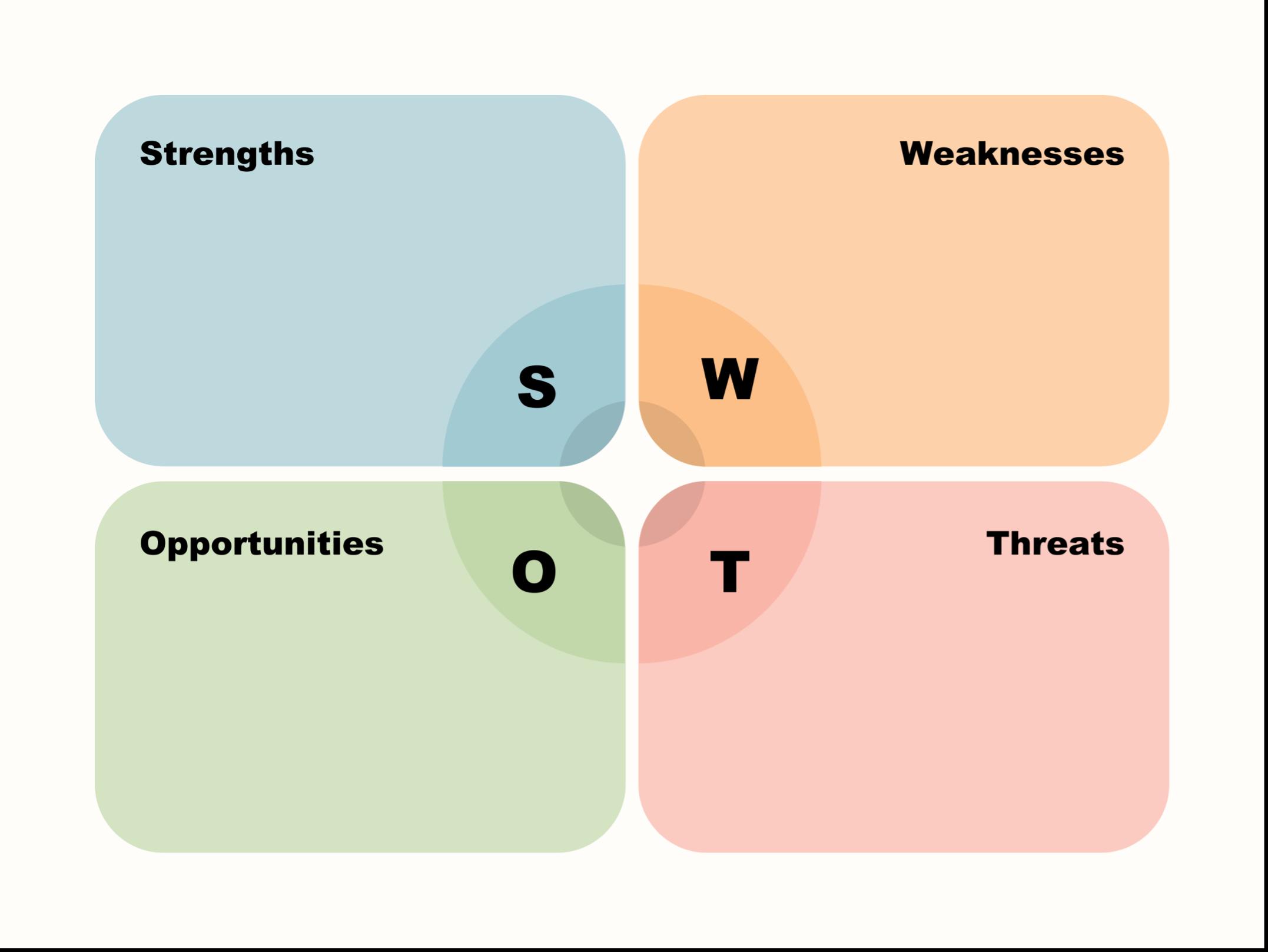
SWOT analysis: Helps evaluate an idea, decision, project or situation by exploring internal and external factors.
The 'So What?’ test: Promotes deeper reflection by pushing the learner to consider the relevance and impact of each point made.
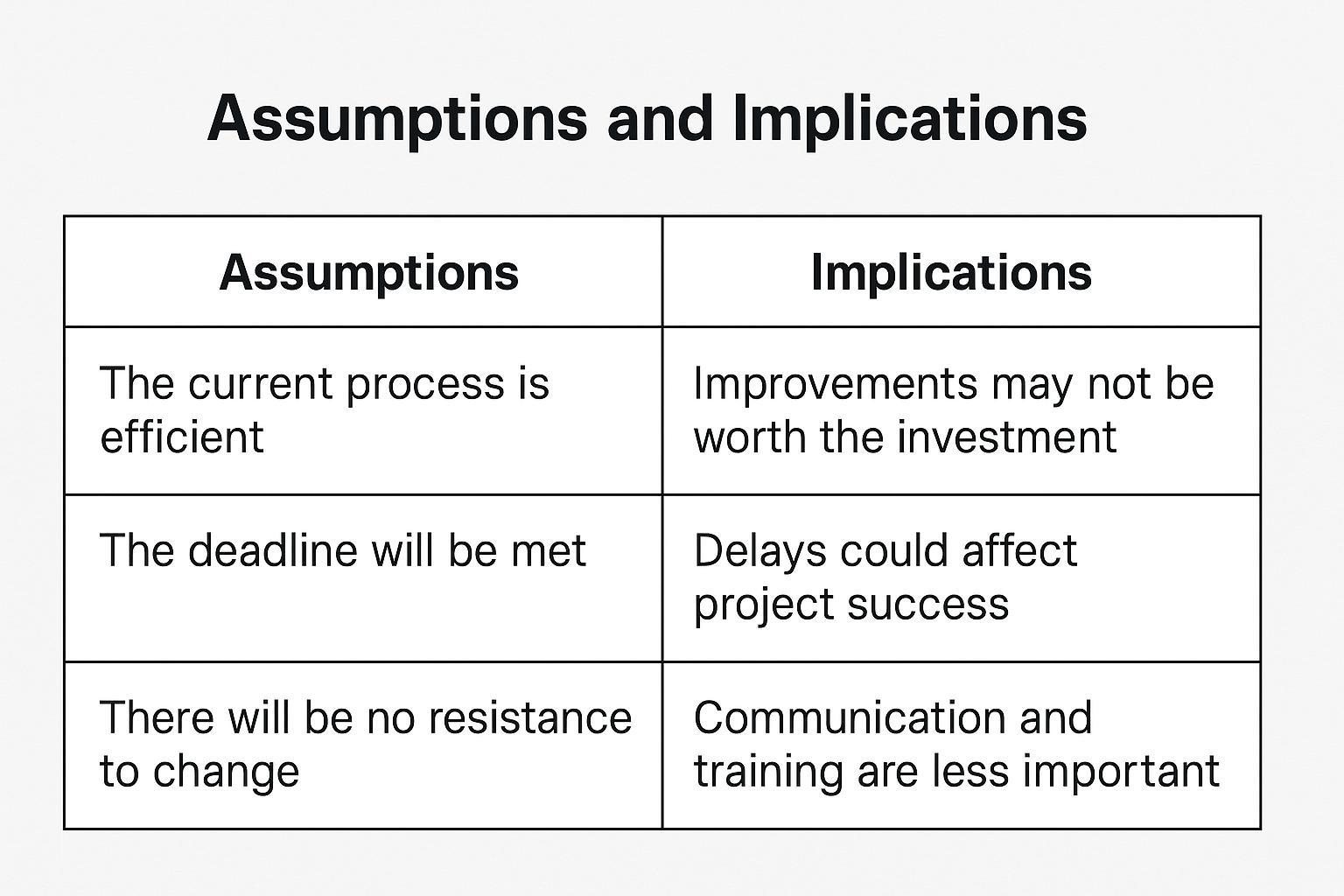
Assumptions & implications analysis: Encourages learners to challenge what is being taken for granted and anticipate the consequences of a decision or belief.
Alternative perspectives grid: Broadens analysis by forcing the learner to adopt multiple stakeholder views.


SWOT analysis helps structure both evaluative and critical writing by guiding you to consider strengths and weaknesses (internal evaluation) and opportunities and threats (external analysis). It encourages objective judgment (evaluation) while prompting deeper questioning about cause, context and future implications (critical thinking).


The ‘So What?’ test supports evaluative and critical writing by encouraging deeper reflection on the significance of each point. It moves beyond description and towards impact and meaning.
By asking ‘So what?’, you clarify consequences, relevance and strategic importance. This strengthens analysis and ensures writing demonstrates insight rather than simple reporting.



An assumptions & implications analysis supports evaluative and critical writing by exploring hidden risks and encouraging you to question what is taken for granted. It helps identify weaknesses and reflect on consequences, promoting forward-thinking and deeper insight in your writing.


An alternative perspectives grid encourages critical analysis by helping you consider a decision or issue through multiple stakeholder viewpoints. It highlights different priorities and concerns, strengthening the depth, balance and insight of evaluations and written analysis.



Introduce yourself to the group
• Consider each of the three, short writing extracts
• Which style do you think best suits each one?
Evaluative, critical or descriptive?
• Why?
How might you rewrite/improve them?
(Make a note of your choices (for a poll after the breakout rooms)


Introduce yourself to the group
• Consider each of the three, short writing extracts
• Which style do you think best suits each one?
Evaluative, critical or descriptive? Why? How might you rewrite/improve them?
• Make a note of your choices (for a poll after the breakout rooms)





3. Recognising the importance of critical analysis and evaluation for end point assessment (EPA)
Written project: report/proposal/ coaching records
Assessors expect reference to research, analysis of evidence, evaluation of outcomes and drawing wellreasoned conclusions.
Look for critical analysis and evaluation, not just description. Pass/distinction
Credibility
Critical
and evaluative writing reflects the ability to think
strategically,
which is essential for leadership roles.


3. Recognising the importance of critical analysis and evaluation for end point assessment (EPA)
Top tip
…describe. A good project might….
…explains, evaluates and challenges. But a great project…


Pop a comment in the chat or click the ‘raise hand’ button





Aim
To develop skills in critically analysing and evaluating workplace projects and decisions, using evidence-based reasoning and structured reflection.
Objectives
•Differentiate between evaluative and critical writing.
L5: K6, K15, S9
L7: K5, S3, B3
•Apply structured approaches to critical analysis and evaluation.
L5: K6, K12, S10
L7: K7, S3, S7
•Recognise how critical analysis and evaluation support End-Point Assessment (EPA).
L5: K8, S10, B3


L7: K2, S2, B2

