
• EVOLUTION
• CORE
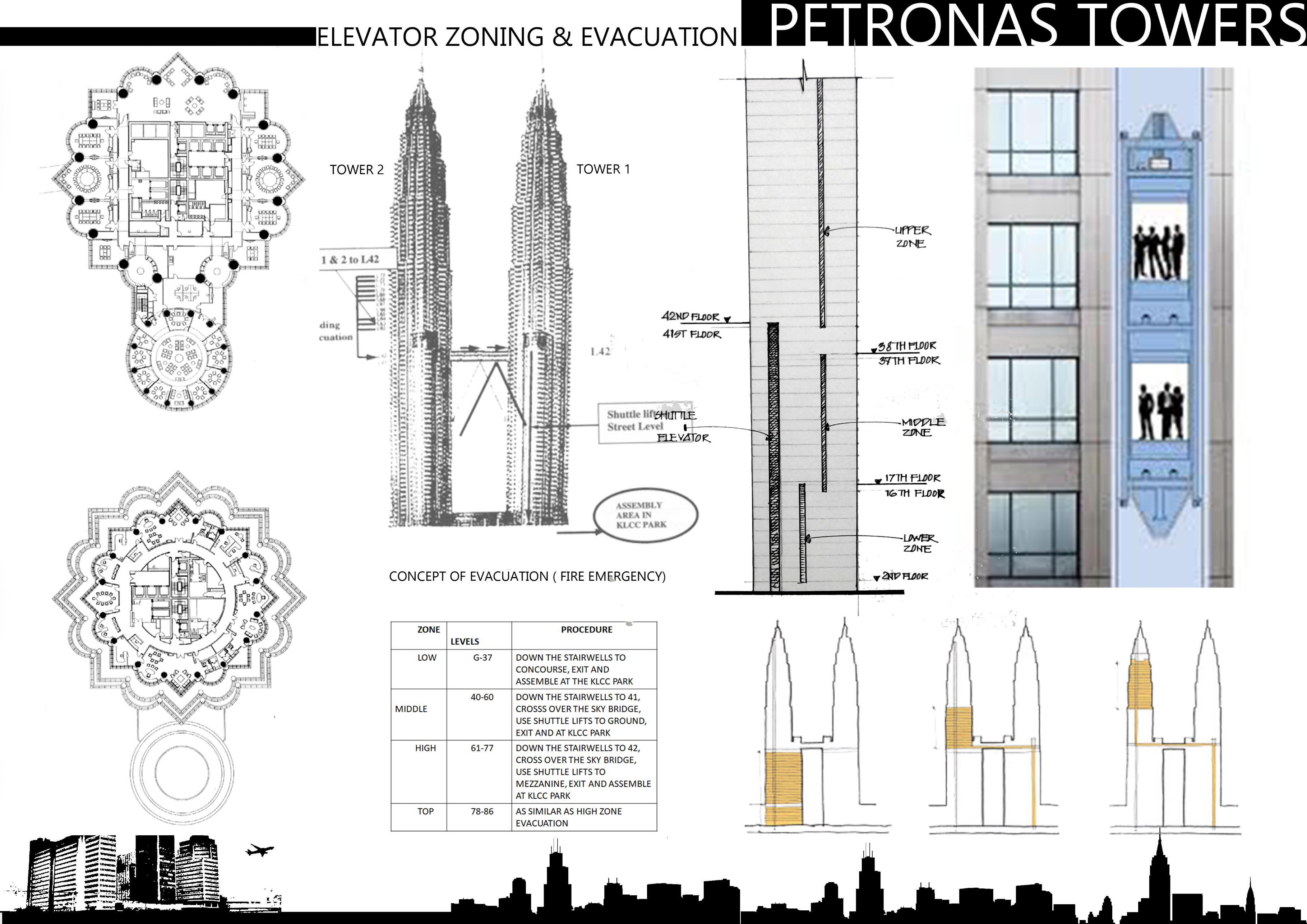
• ELEVATOR
• ESCALATOR
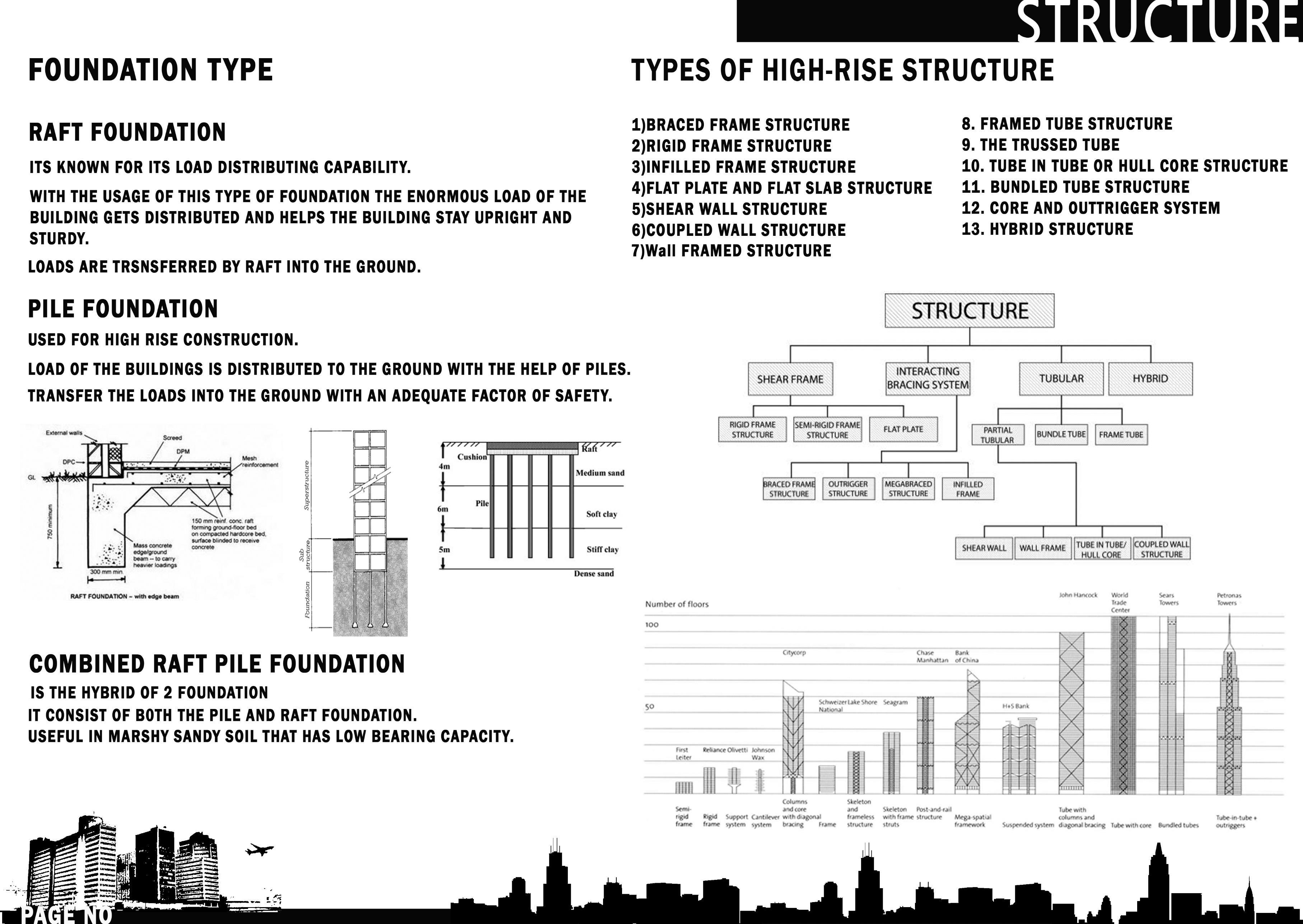
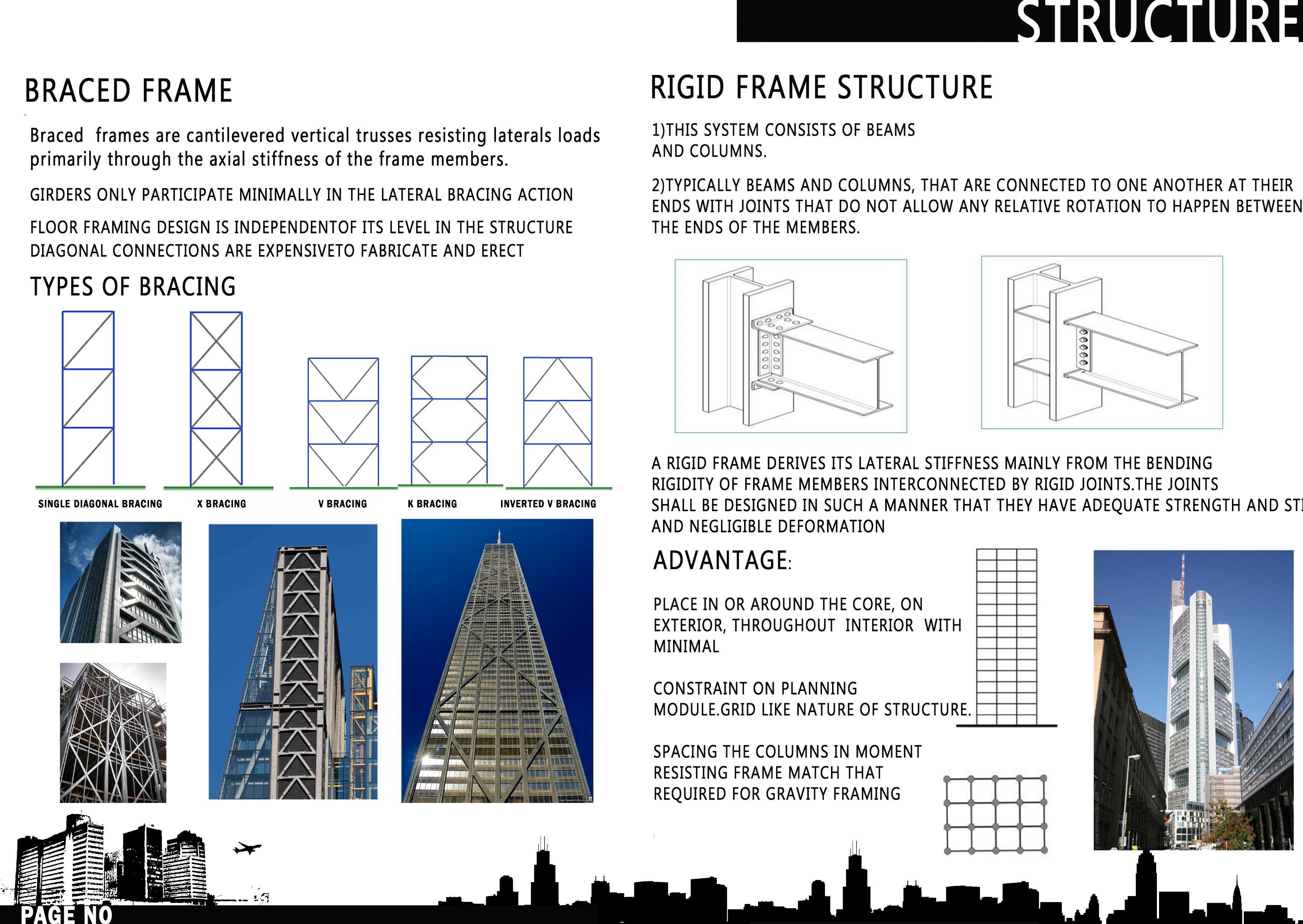
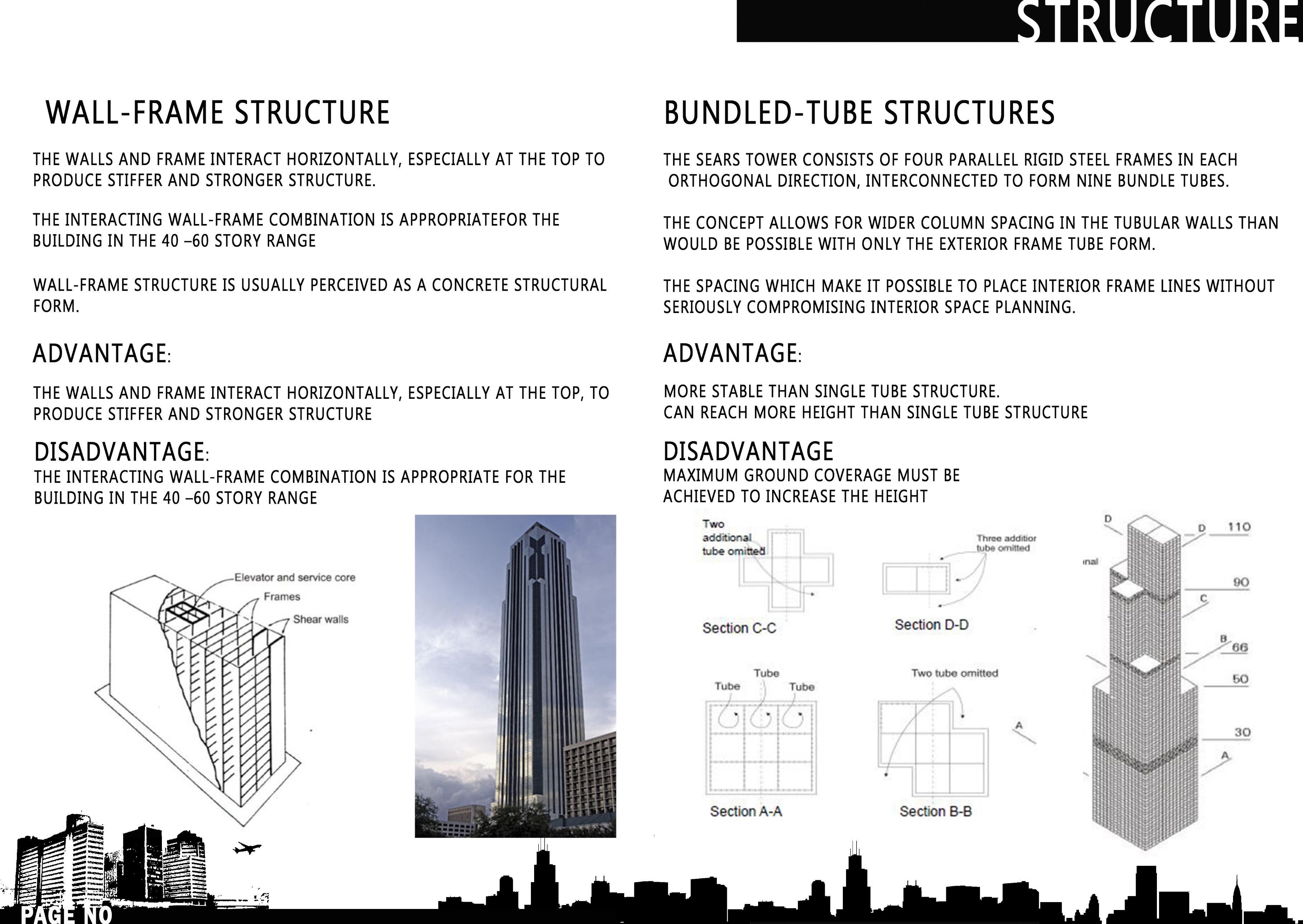
• STRUCTURE
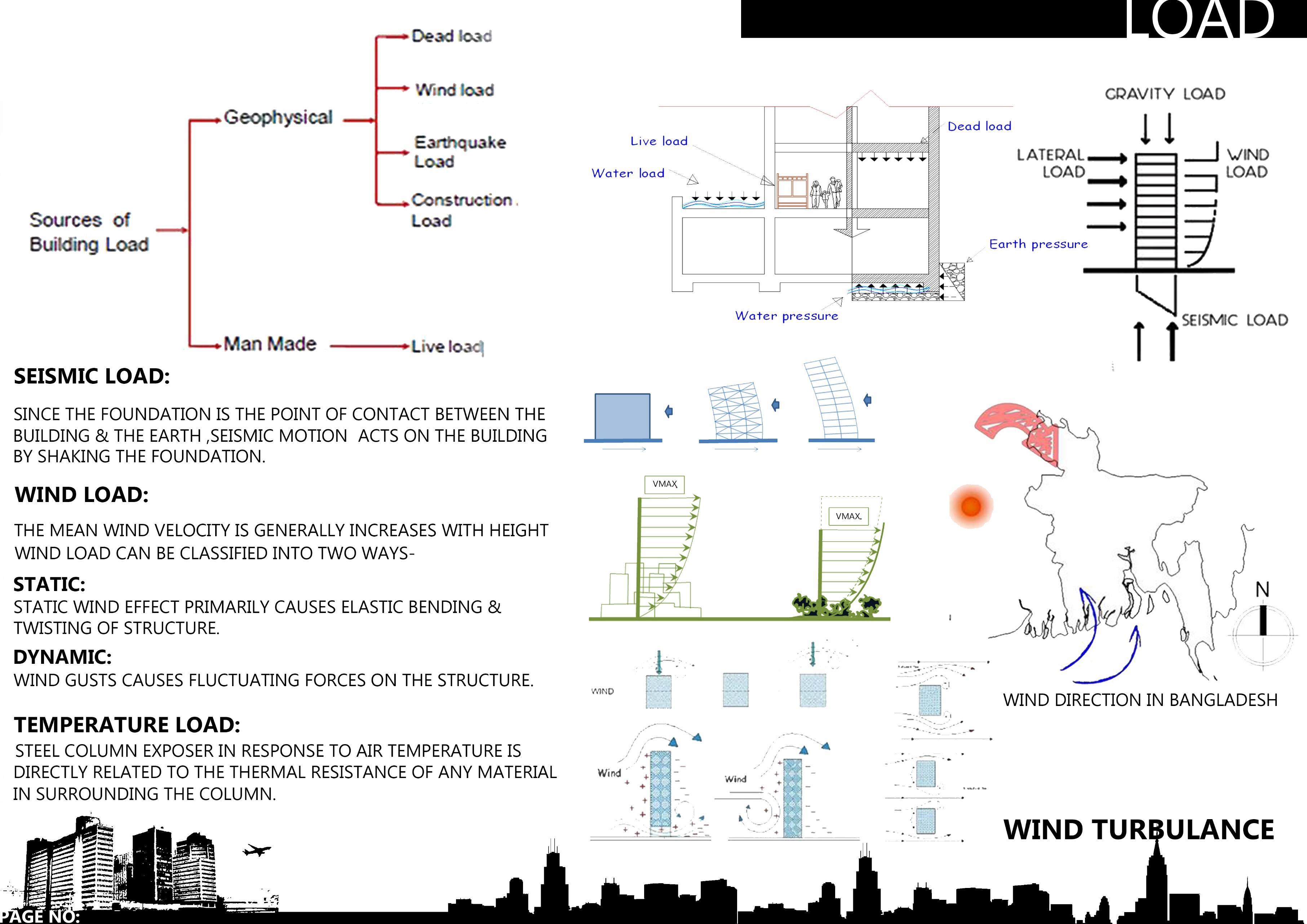
• LOAD
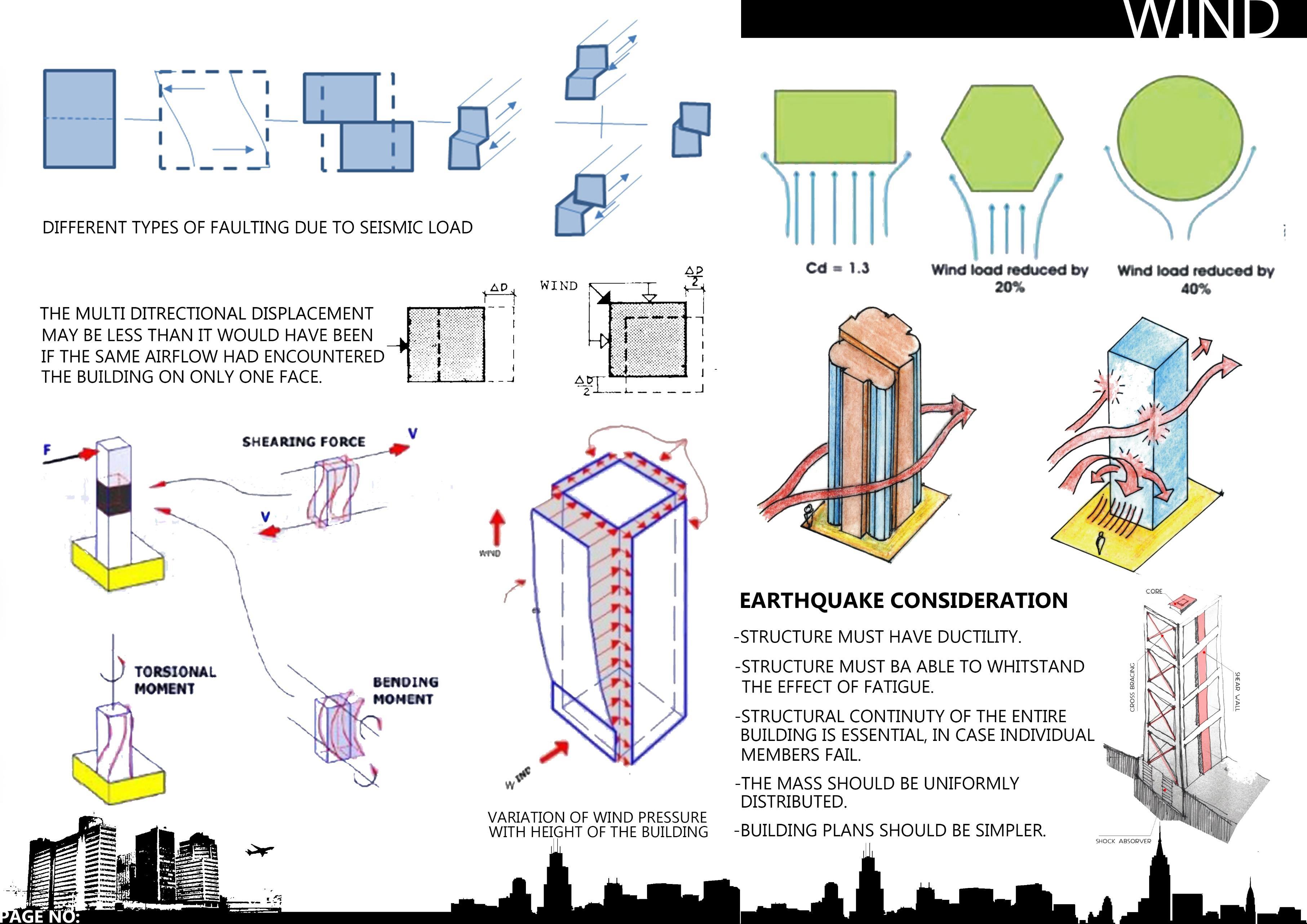
• WIND
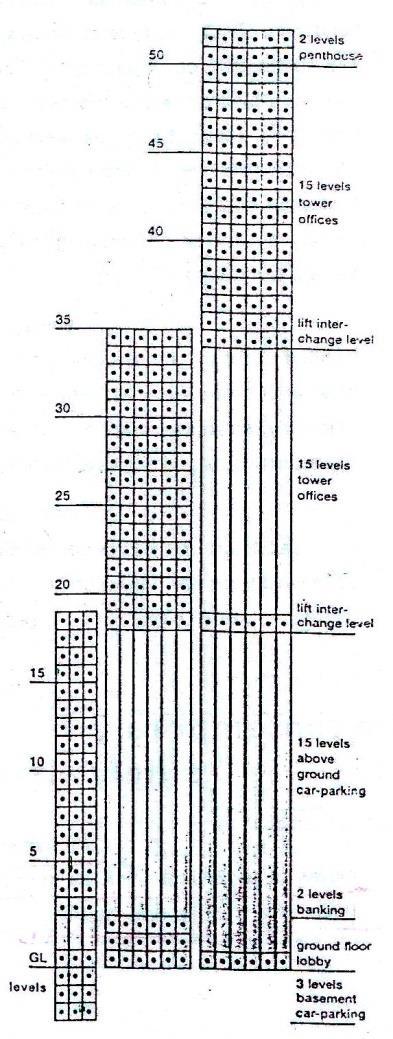
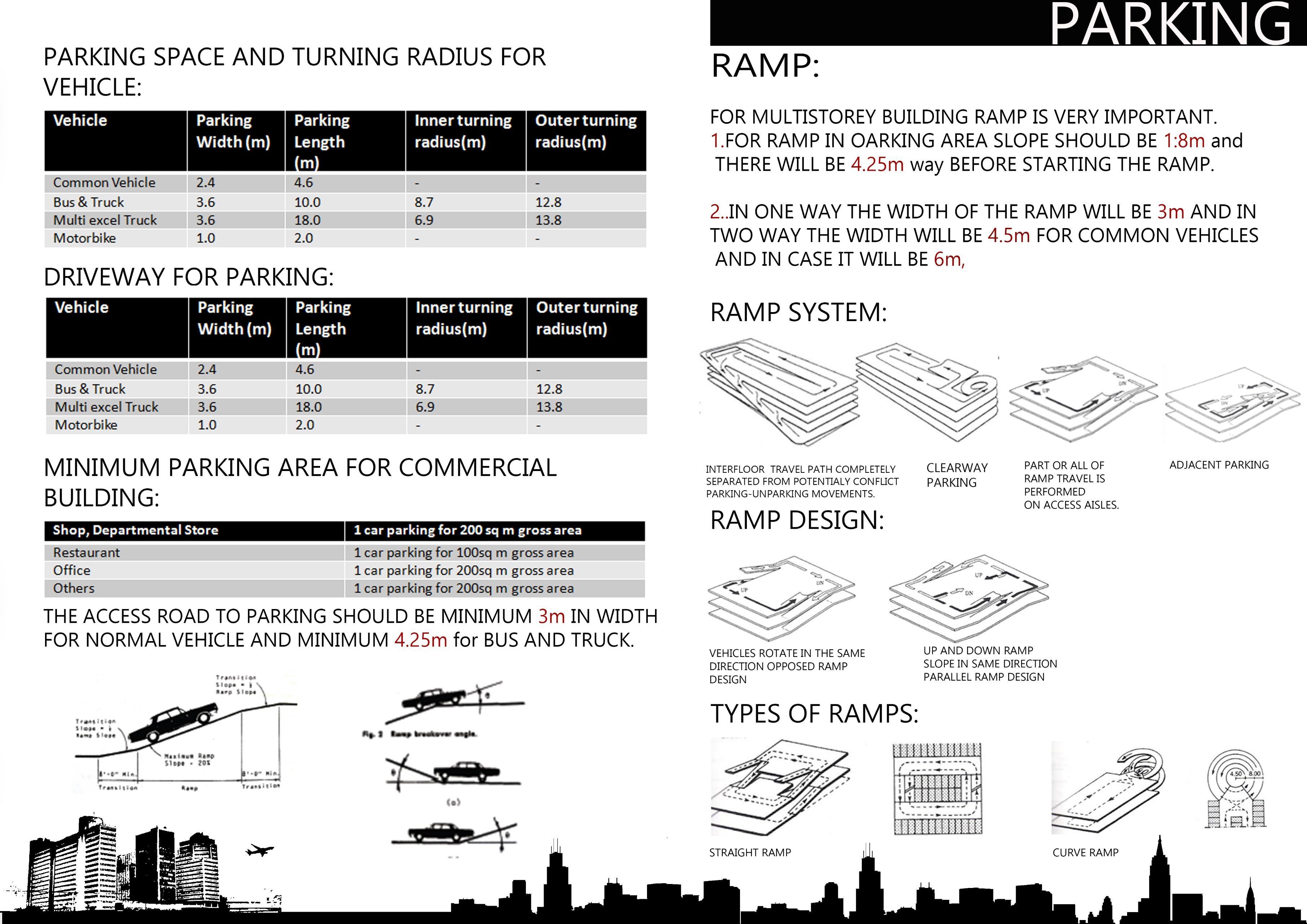
• PARKING
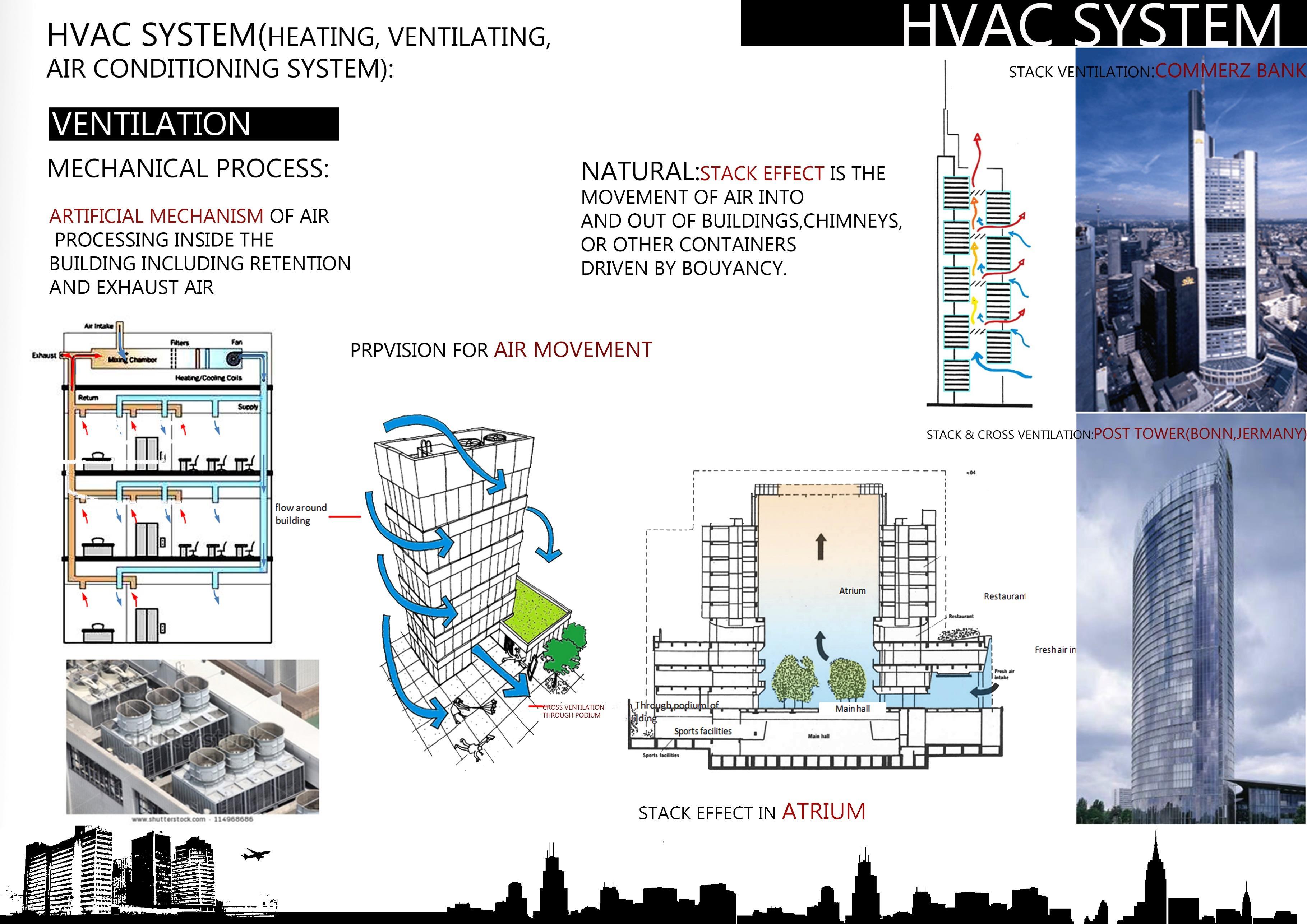
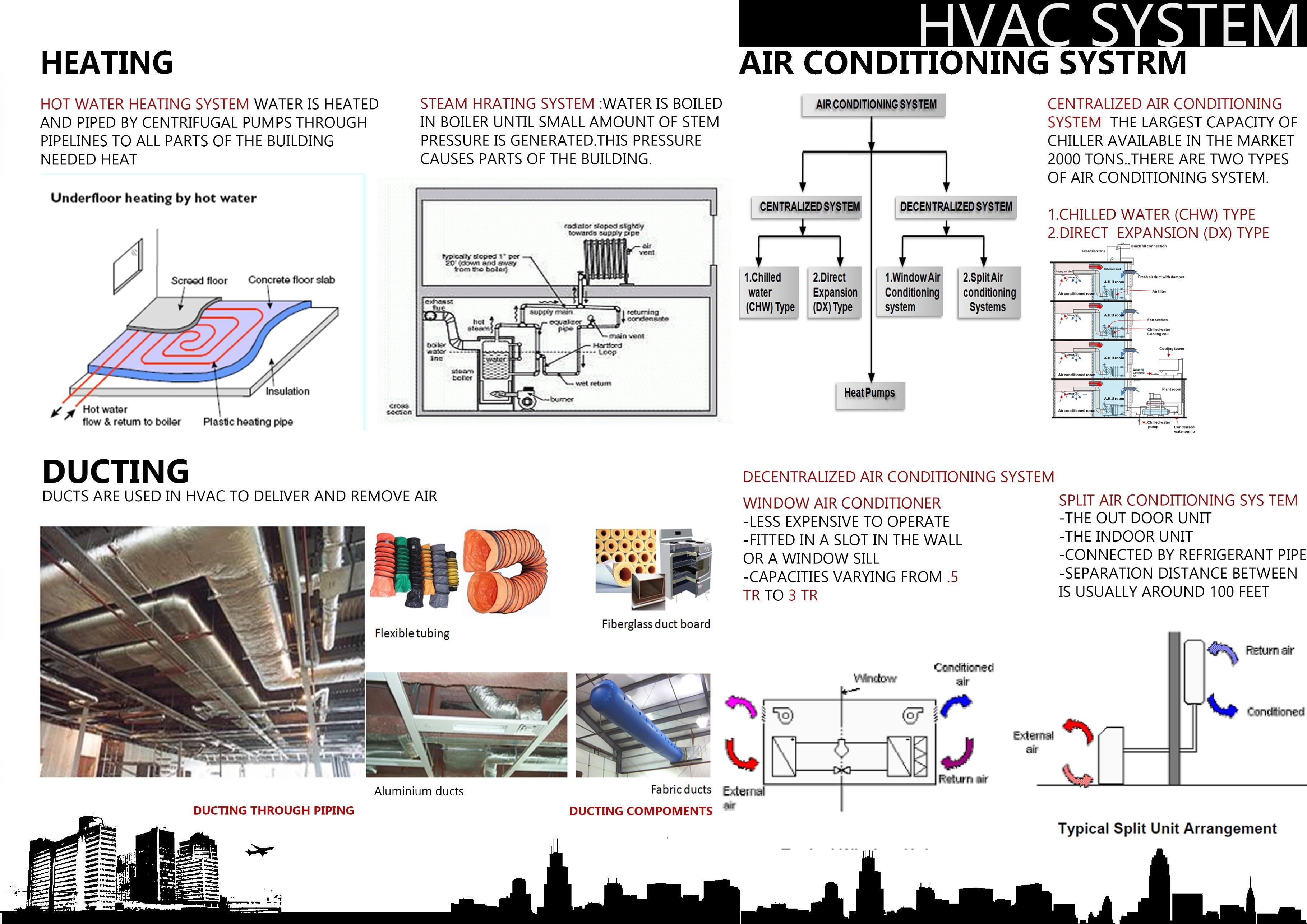
• HVAC SYSTEM
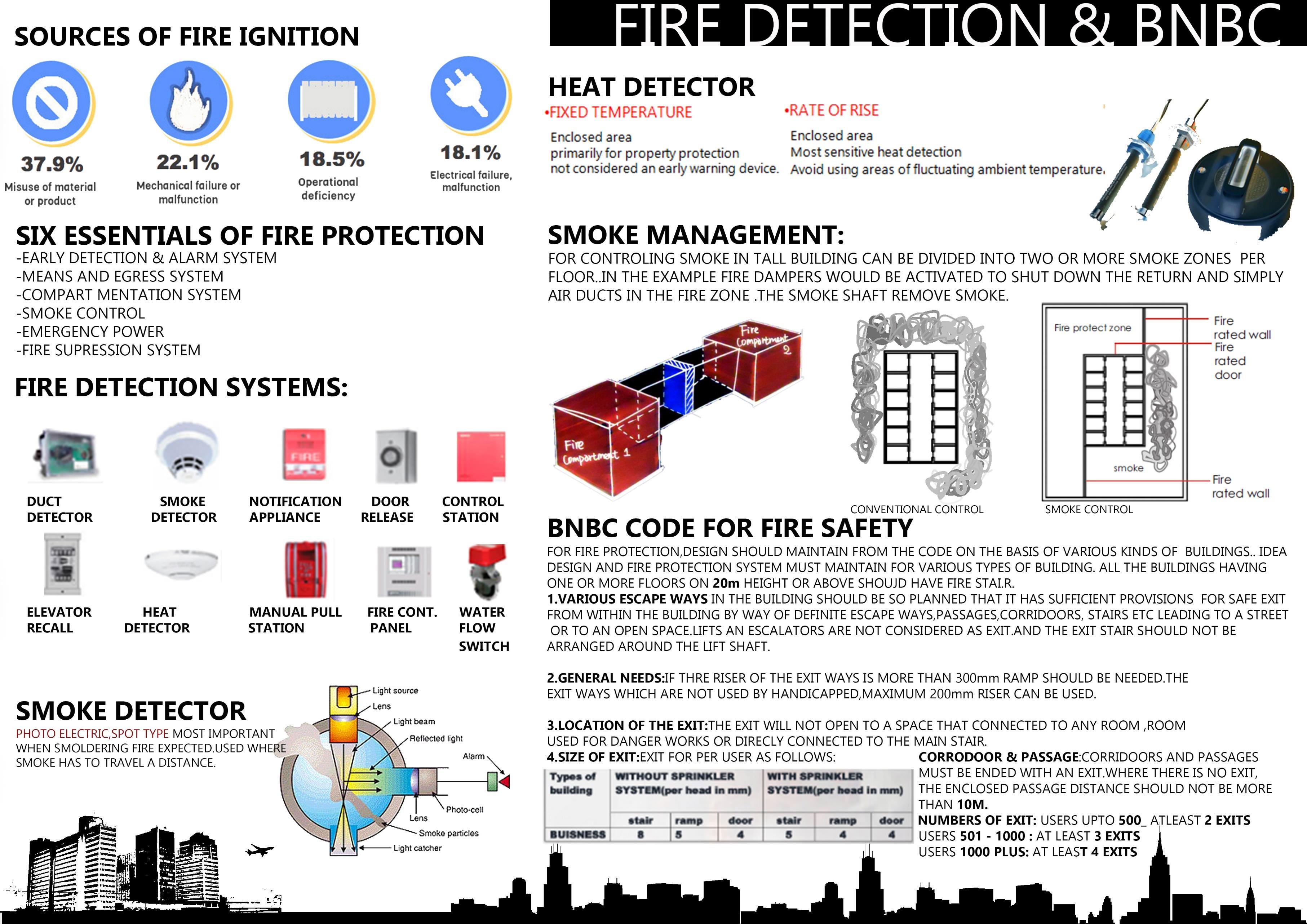
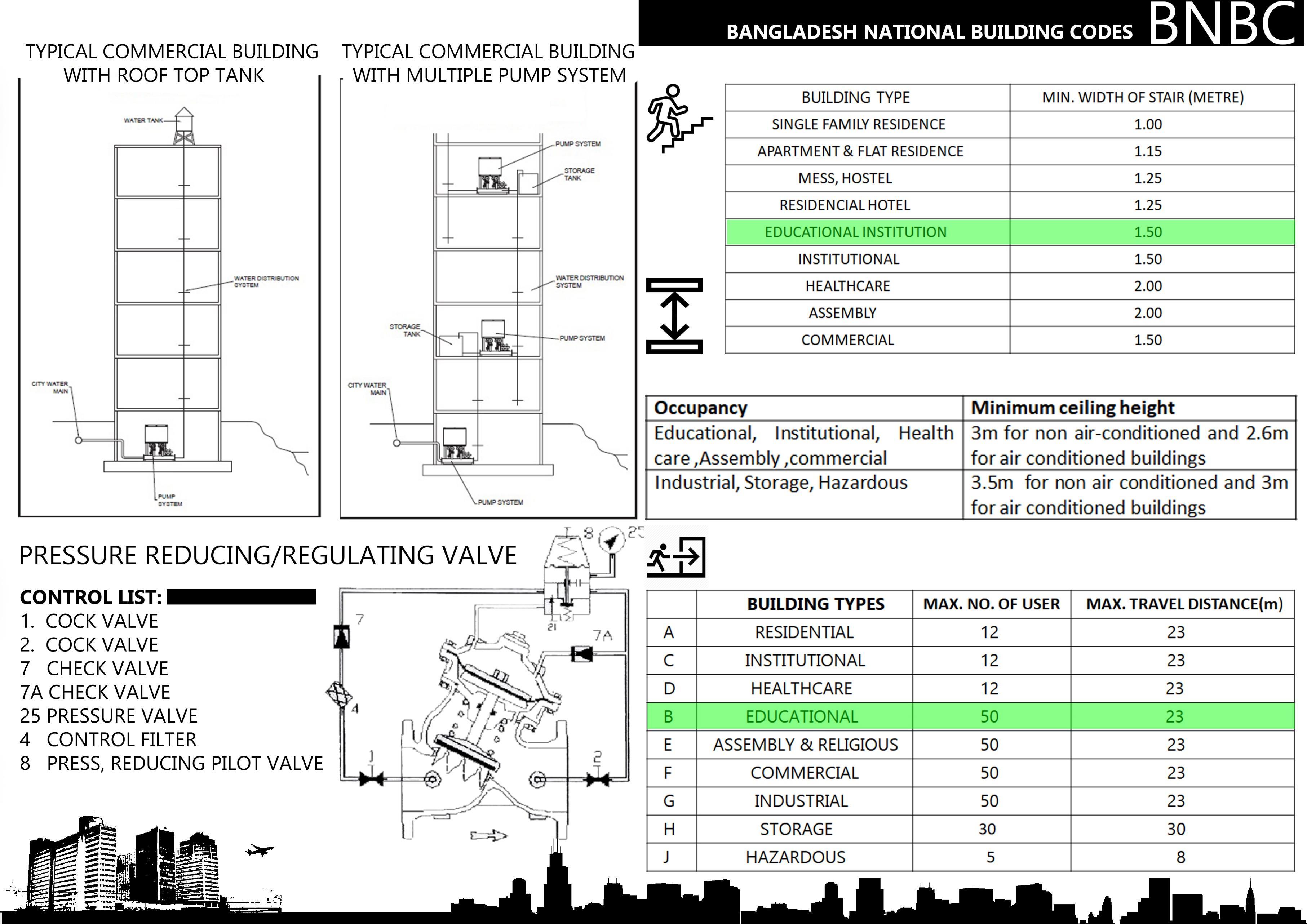
• FIRE DETECTION AND BNBC
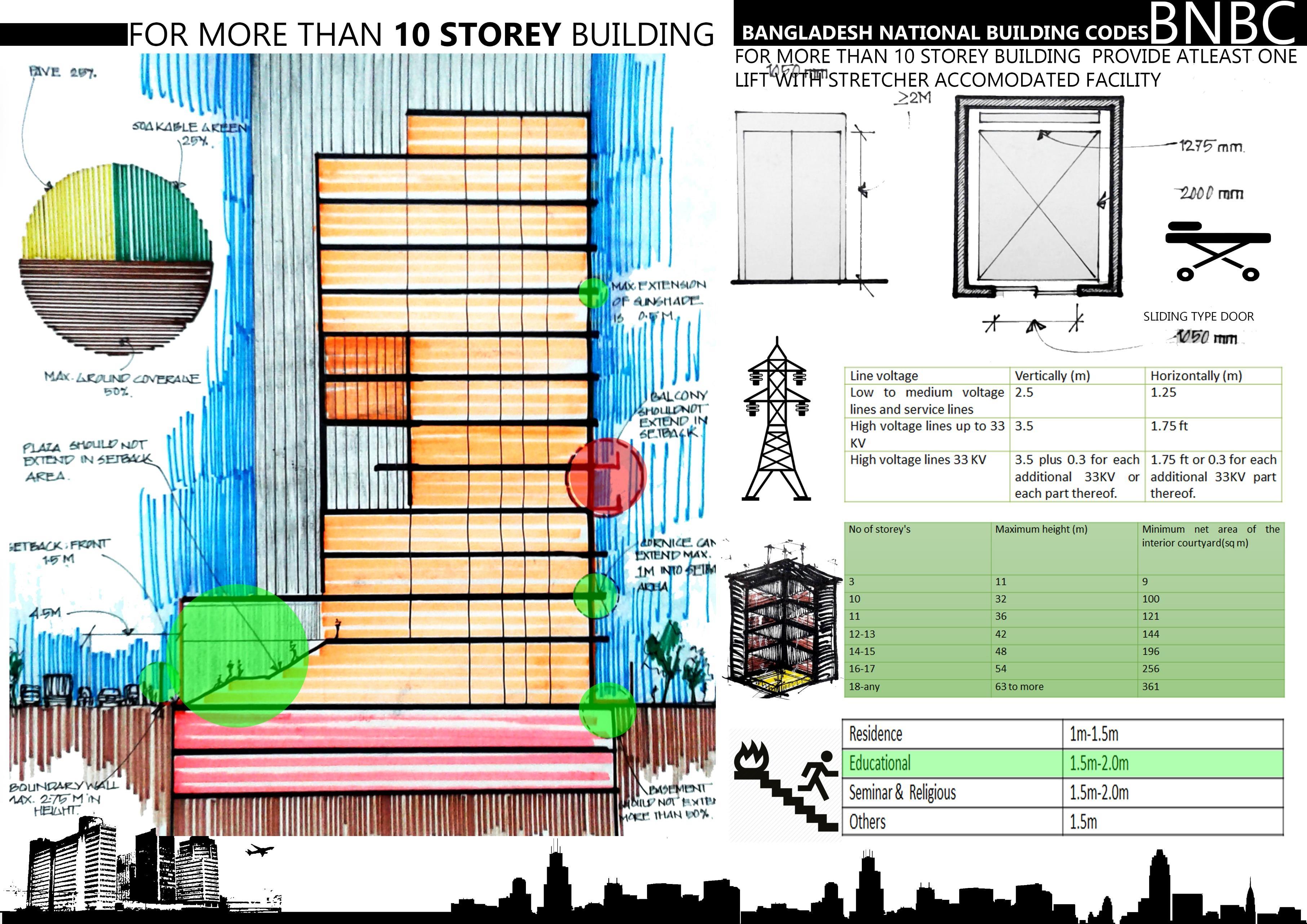
• BNBC
• CASE STUDY
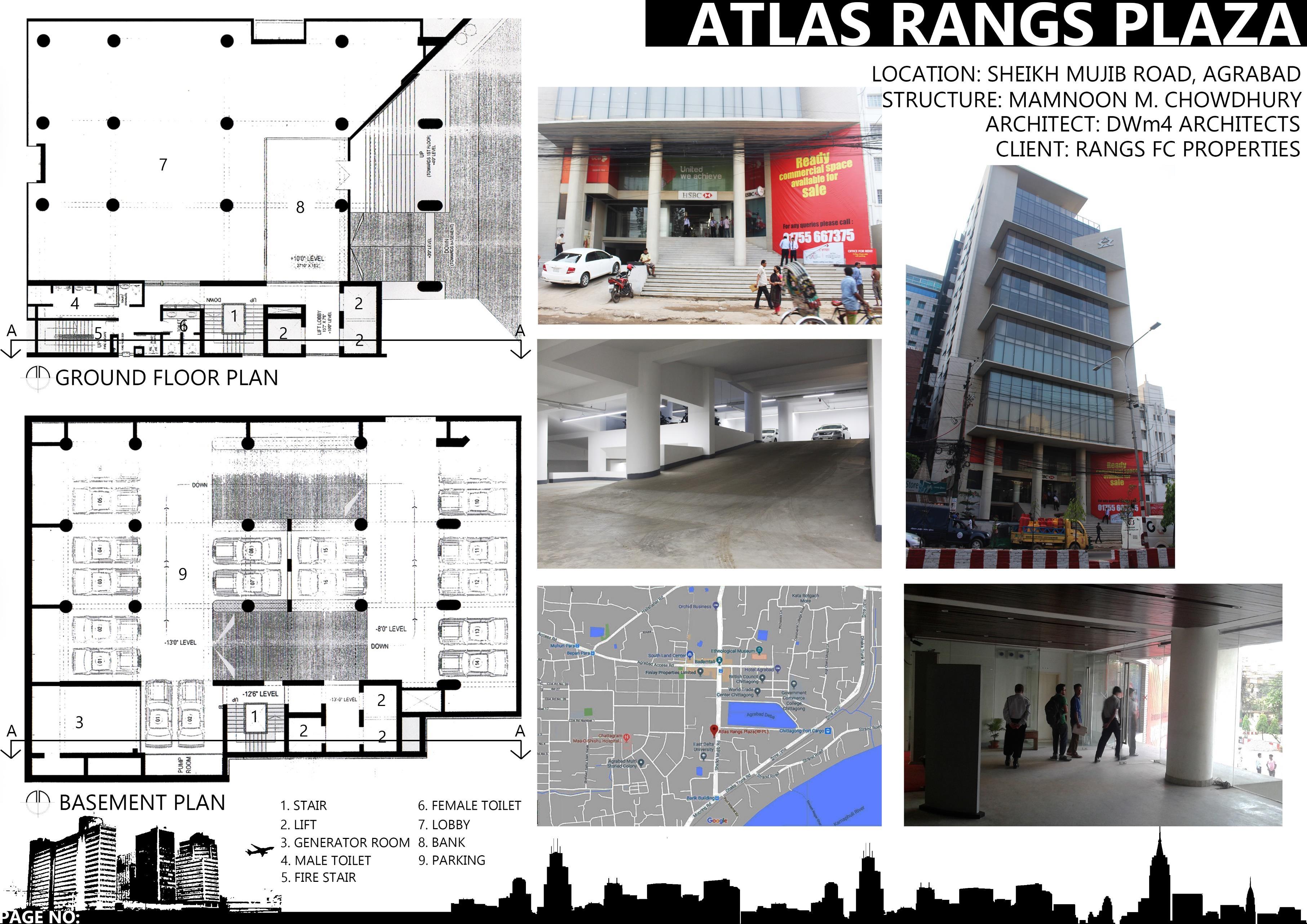
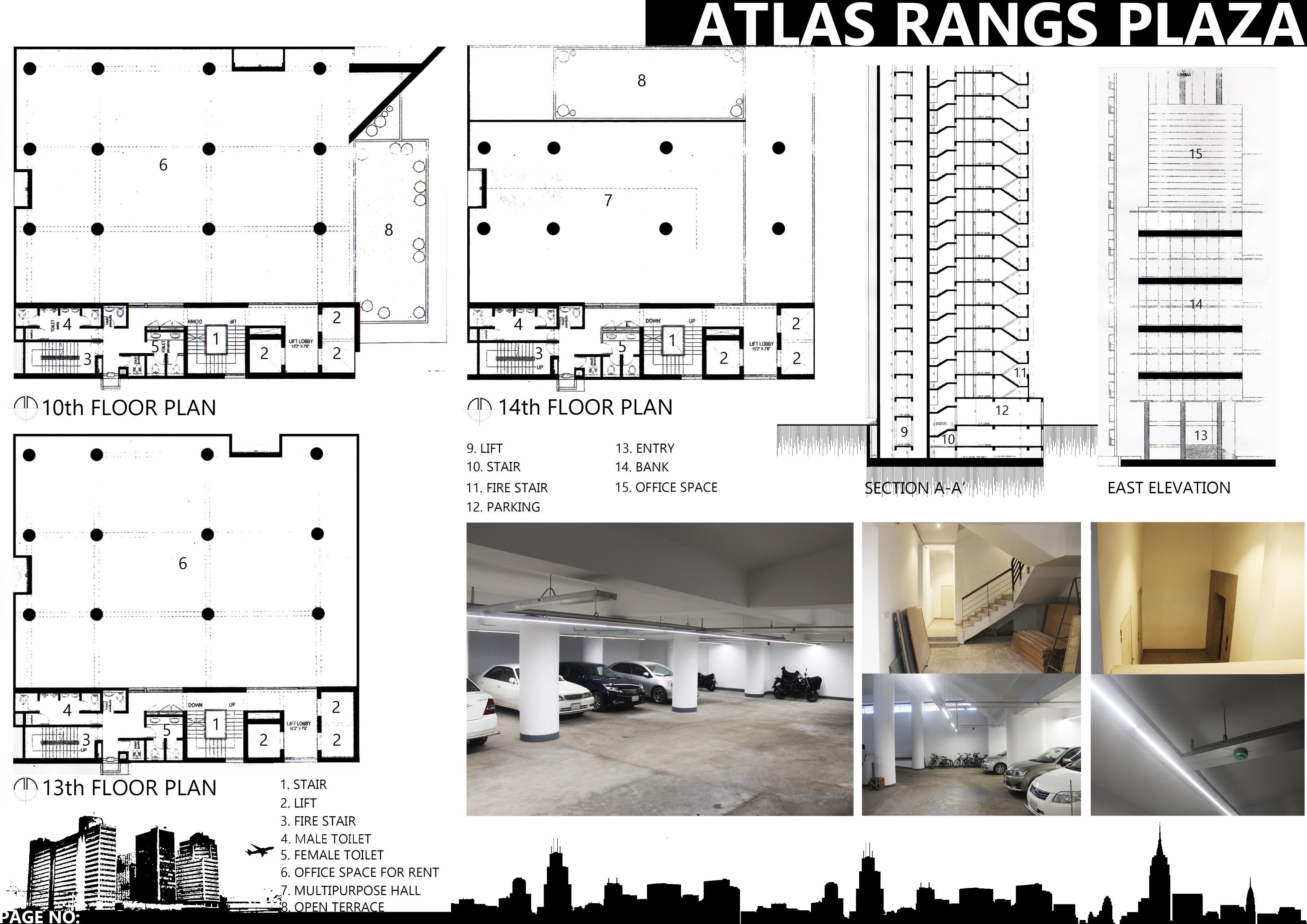
I. ATLAS RANKS PLAZA
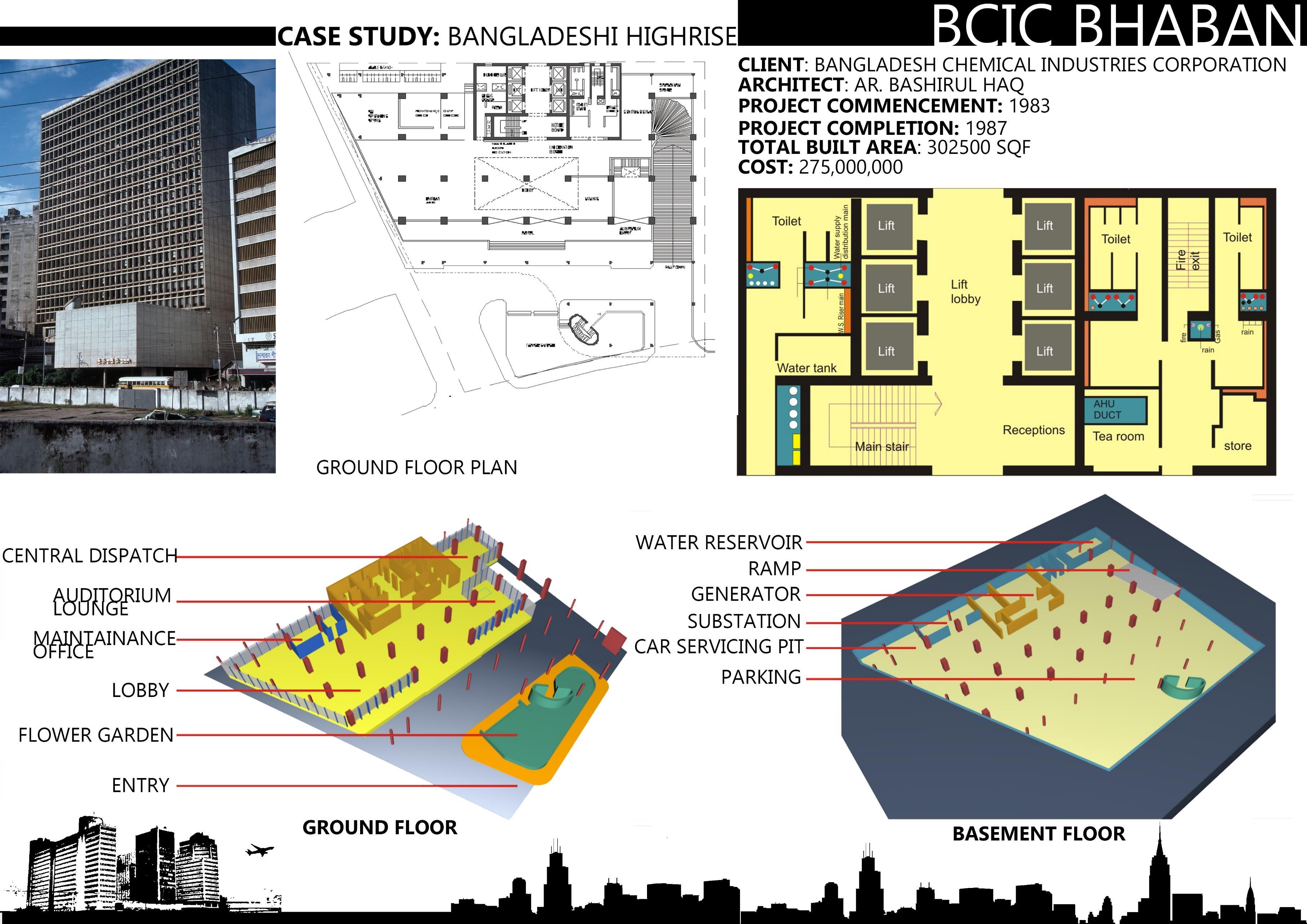
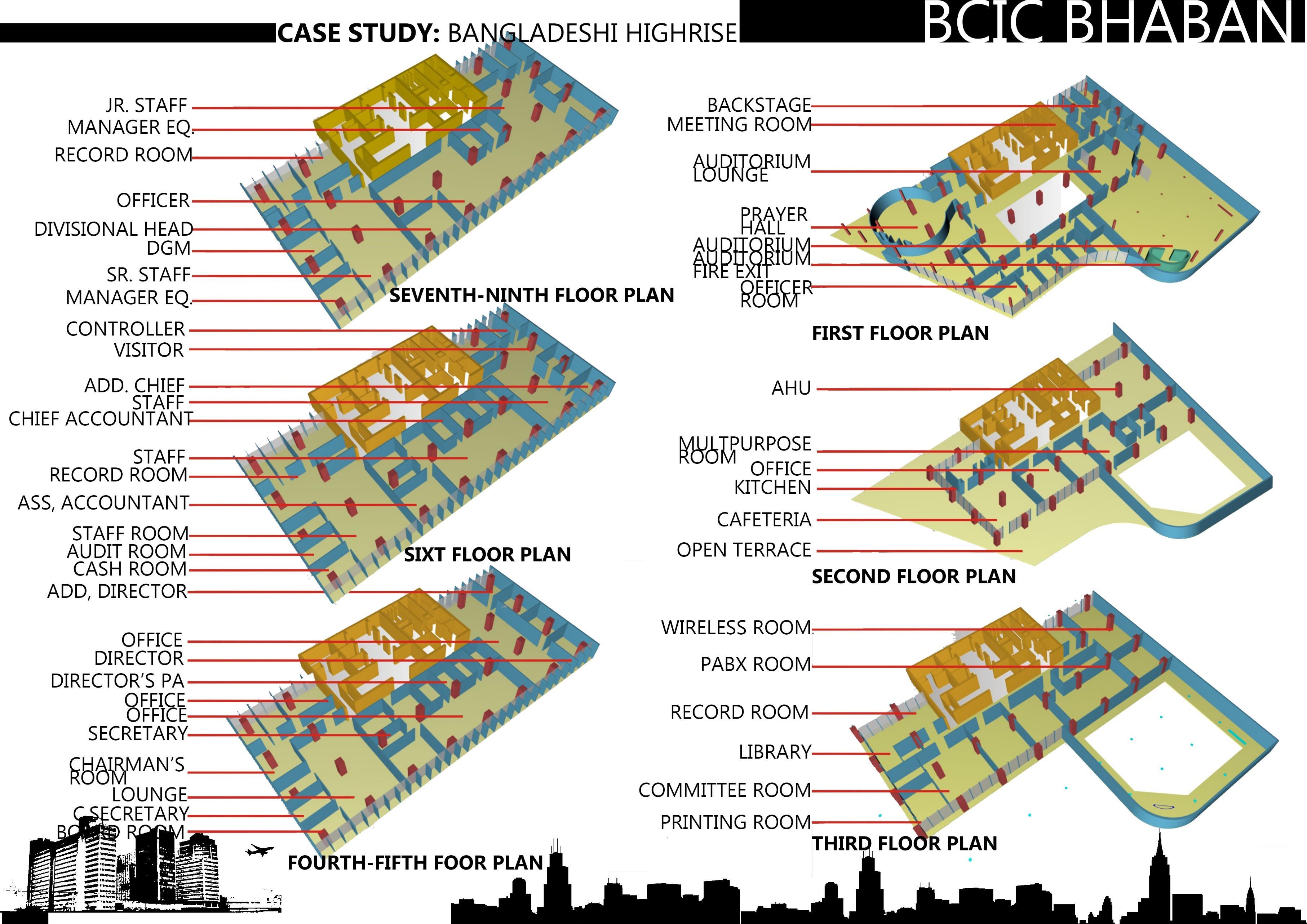
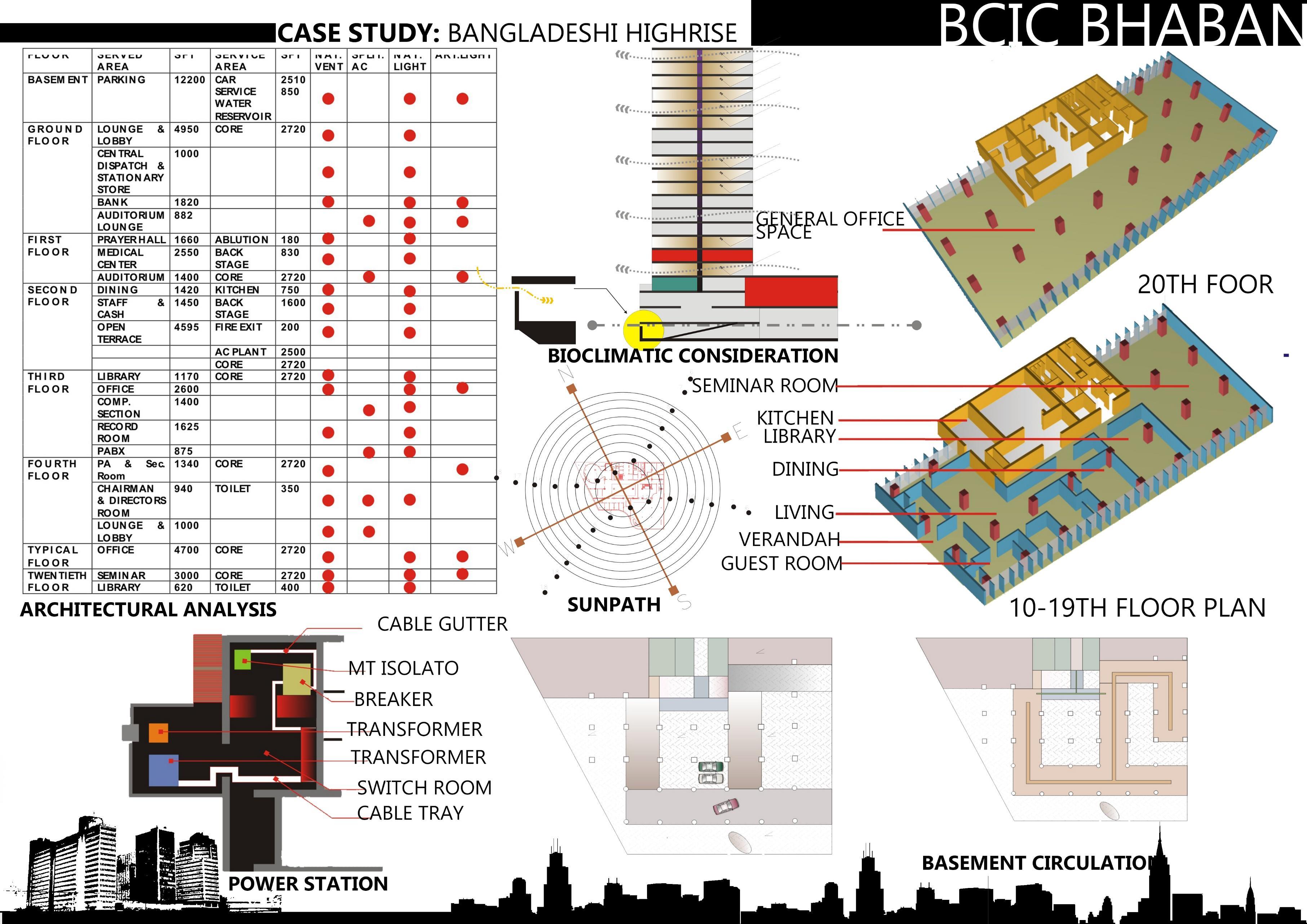
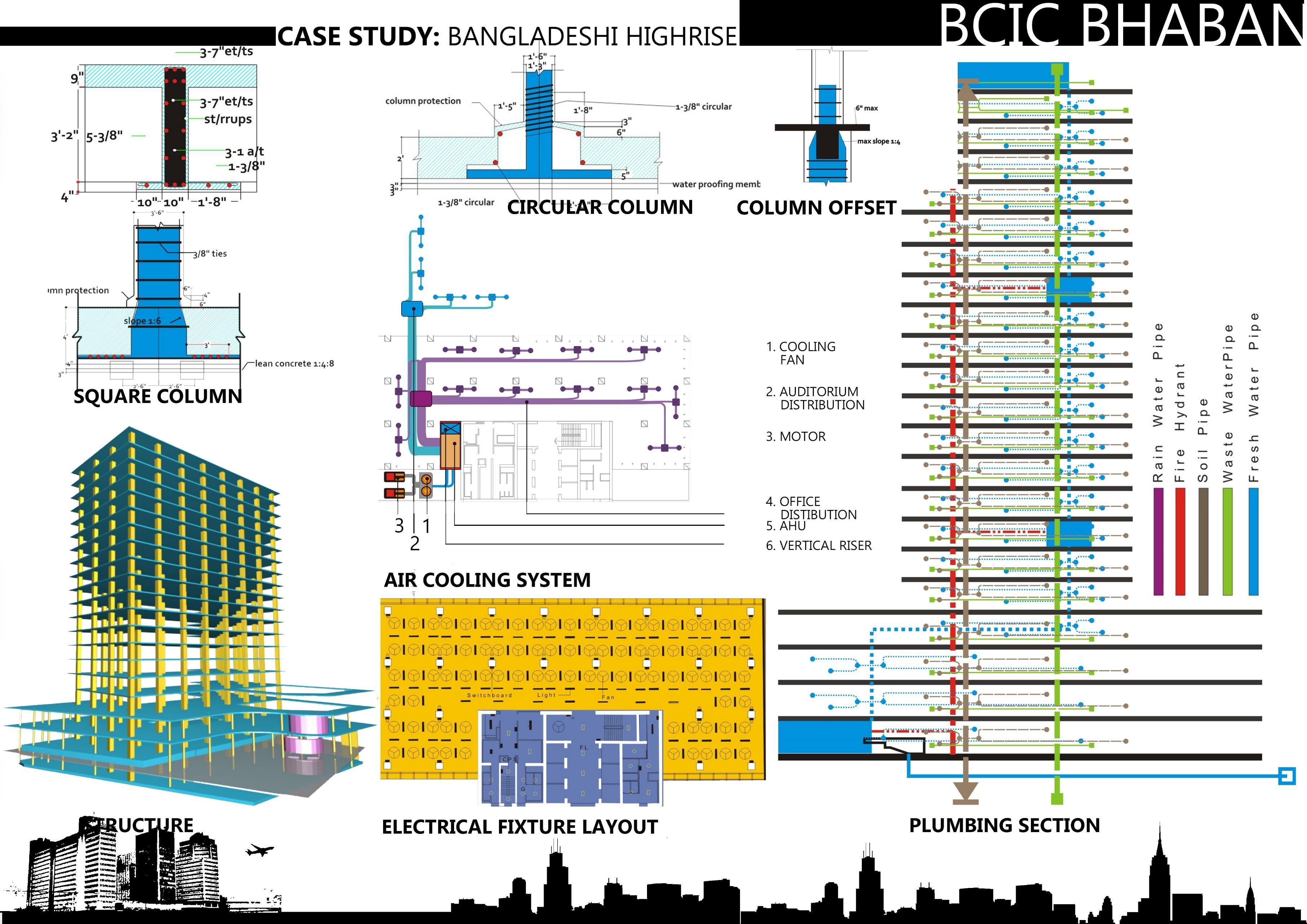
II. BCIC BHABAN
III. SHAGHAI TOWER
IV. PETRONUS TOWER

CONTENT

Contains:
• ELEVATOR SHAFTS
• ELEVATOR Lobbies
• STAIRCASES
• FIRE PROTECTED LOBBIES
• TOILETS
• ANCILLARY ROOMS eg. PANTRY,SPACE FOR CLEANING MATERIAL
• RISER DUCTS
• M&E SERVICES PLANT
• WALLS
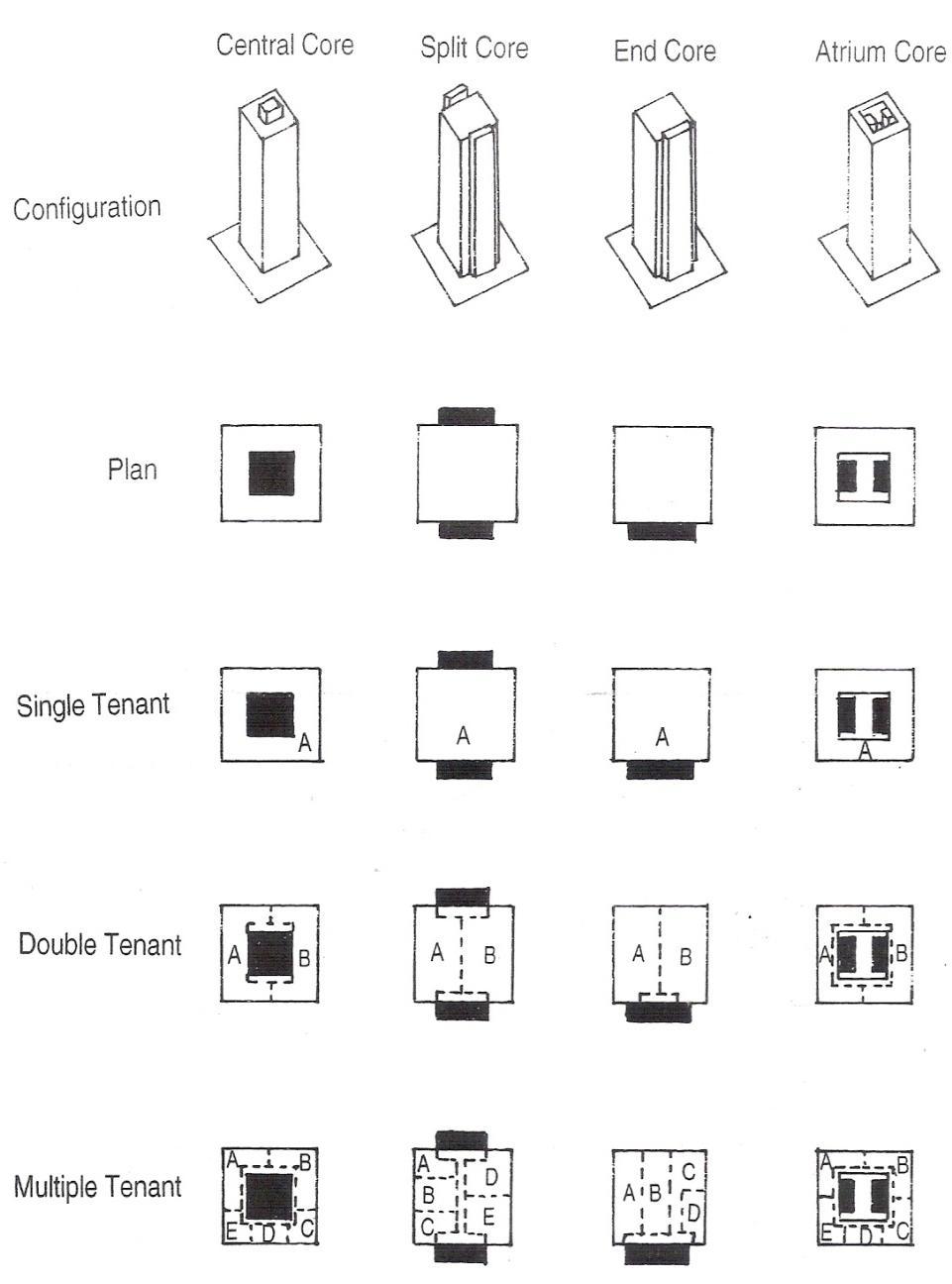
A CORE IS A VERTICAL SPACE USED FOR CIRCULATION AND SERVICES. IT MAY ALSO BE REFERRED TO AS A CIRCULATION CORE OR SERVICE CORE. A CORE ALLOWS PEOPLE TO MOVE BETWEEN THE FLOORS OF A BUILDING, AND DISTRIBUTES SERVICES EFFICIENTLY TO THE FLOORS.
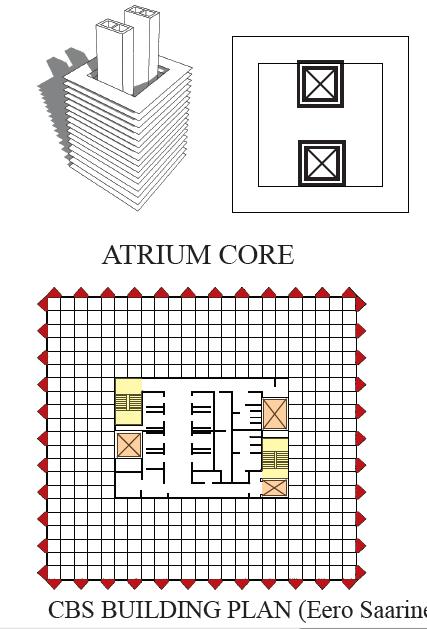
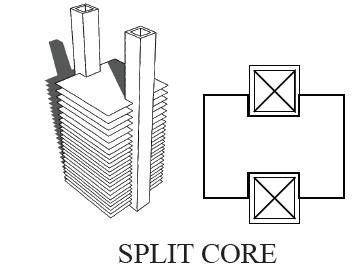
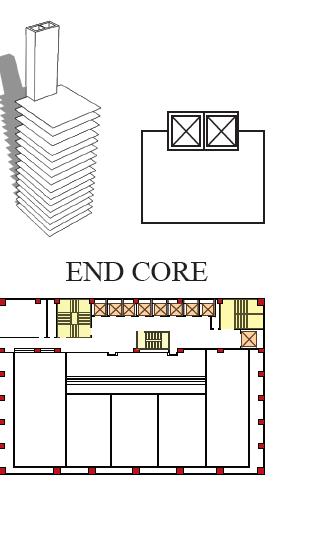
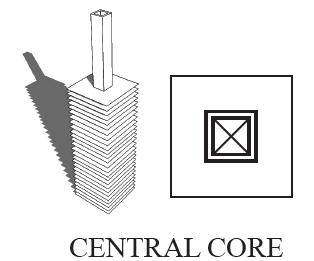

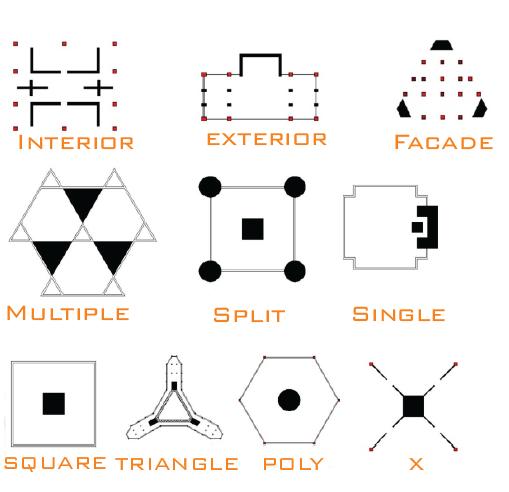
THE PLACEMENT OF THE SERVICES CORE STEMS FROM FOUR GENERIC TYPES
IBM Headquarters,Tokyo
Landmark Tower, Yokohama
Mitsui Marine Insurance, Nagoya
CORE
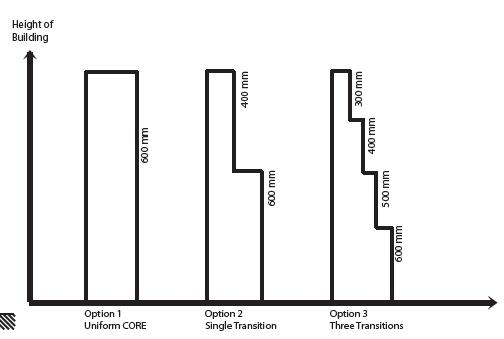
TENANT DISTRIBUTION CORE TRANSITION
HIGHEST COOLING LOAD
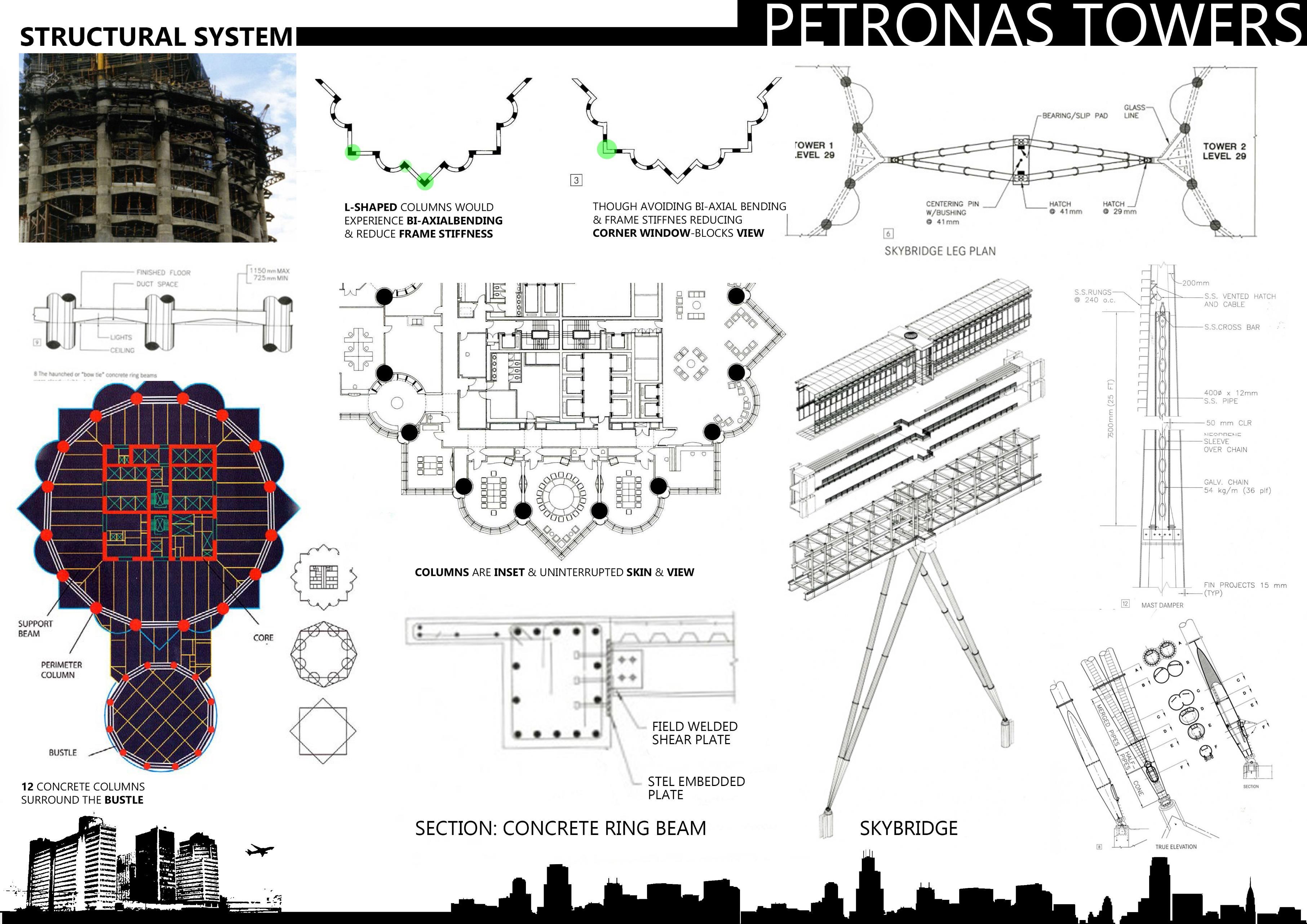
Slender ratio for tower maximum is 1:10 or 1:12

LOWEST COOLING LOAD
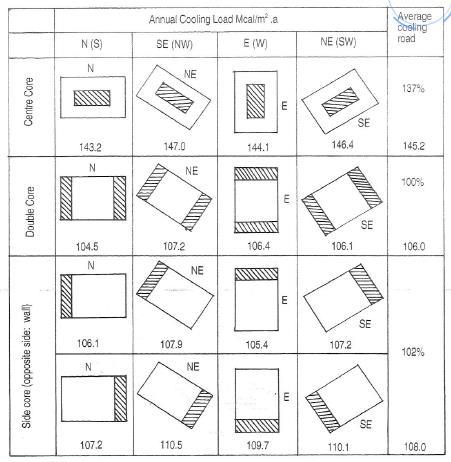
DESIGN SYSTEM SHOULD AVOID THE HIGHEST COOLING LOAD
CORE
CORE
M & E SERVICES

THE SERVICE CORE PROVIDES MEANS OF ACCOMODATING VERTICAL M&E SERVICES RUNS, SUCH AS
• DUCT RISERS
• MECHANICAL PIPE RISES
• HYDRAULIC STACKS
• ELECTRICAL AND COMMUNICATIONS CABLING
• AIR HANDLING UNIT (A.H.U)
TOILETS
IN THE EVENT OF SINGLE OCCUPANCY OF THE FLOOR
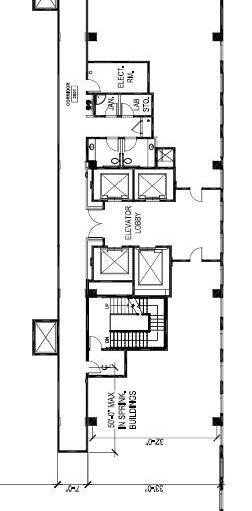
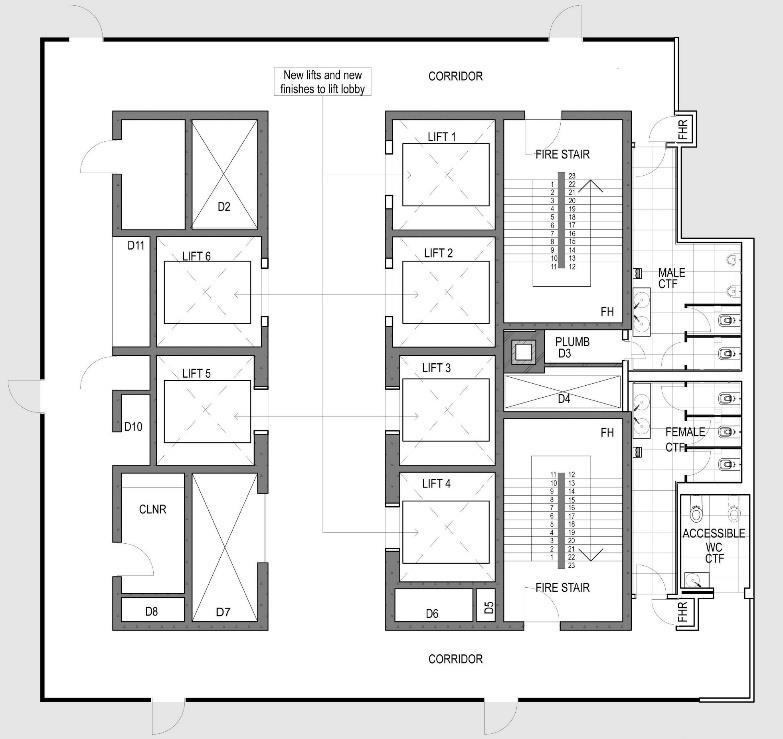
PLATE ENTRY TO THE TOILETS
MIGHT BE ORGANISED SO THAT USERS ARE ABLE TO ACCESS THEM WITHOUT GOING
THROUGH THE ELEVATOR LOBBY
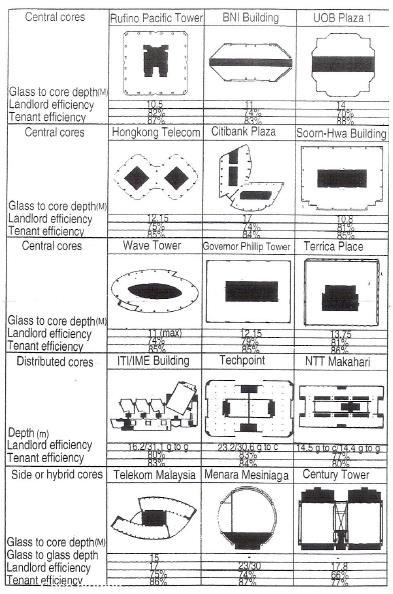
CORE TO GLASS DEPTH AND ITS EFFICIENCY
TYPOLOGY
Major Types of elevator Definition advantage disadvantage
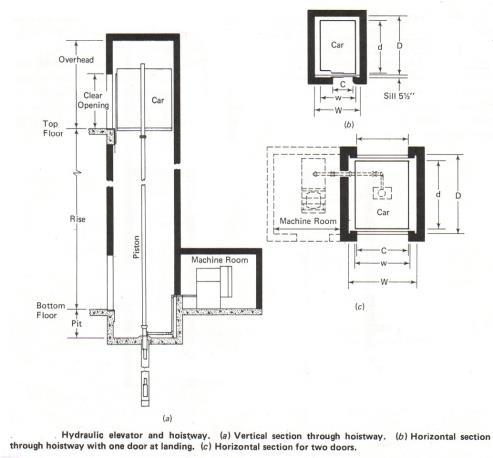
a.Hydraulicelevator: 1.powered elevator
2.energy is applied by a liquid under pressure in a cylinder equipped with a plunger or piston.
1. efficient, safer, and friendlier to the environment.
2. Does not require brakes,
3. Can use very small motor to pump fluid .
4. Very powerful
1. if there is a catastrophic oil line failure (it has happened) the elevator will drop uncontrolled 2. limited to about 6 or 7 floors max.
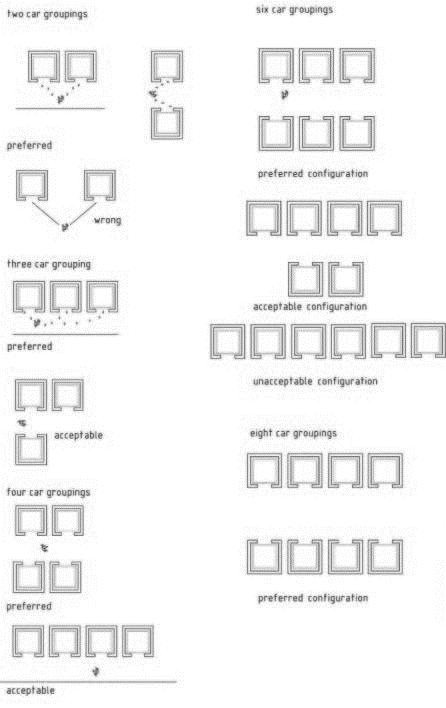
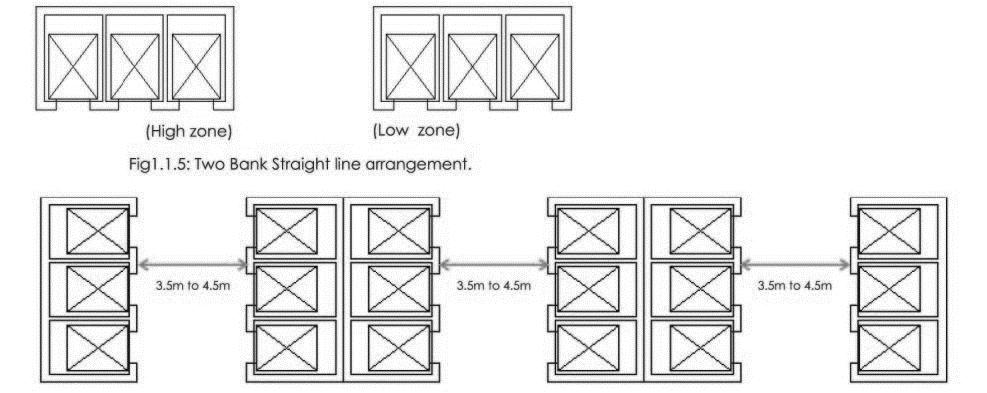
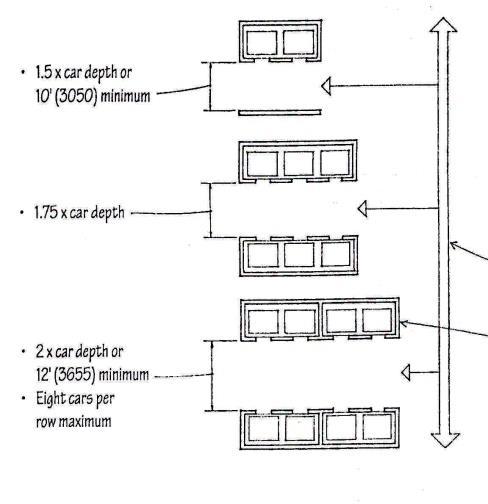
CAR ARRANGEM ENT:
CORE ELEVATOR

b.Electricelevator: 1.energy is applied by electric driving machine .
2.used in tall buildings

1.Electric elevators consume less energy than hydraulic elevators.
2.no. of floors are not limited
Failure of electricity creates panic
•Capsulelift: similar to electric elevator. Machine room is not essential largest version of electric elevator.
Hydraulic elevator Electric elevator Capsule lift
Lobby depth

Are used for fire safety
help firefighters to get to the fire and to permit people evacuation
elevator landing must be min. 5m² wide for a gurney to be brought out of the elevator.
required to display a written notice in the car that the passengers are prohibited.
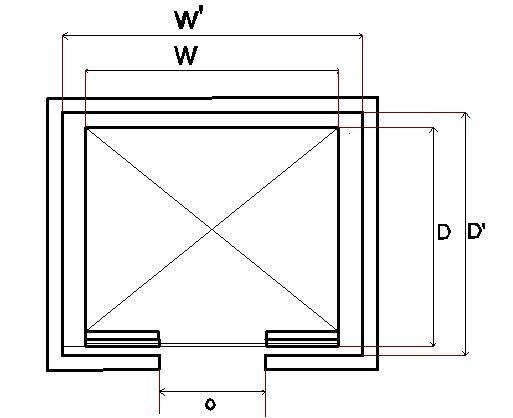
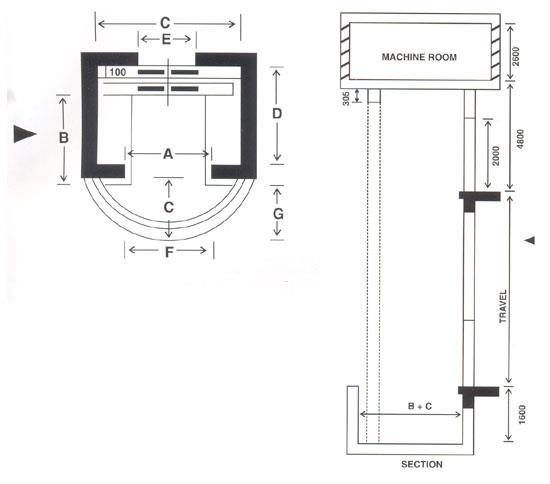
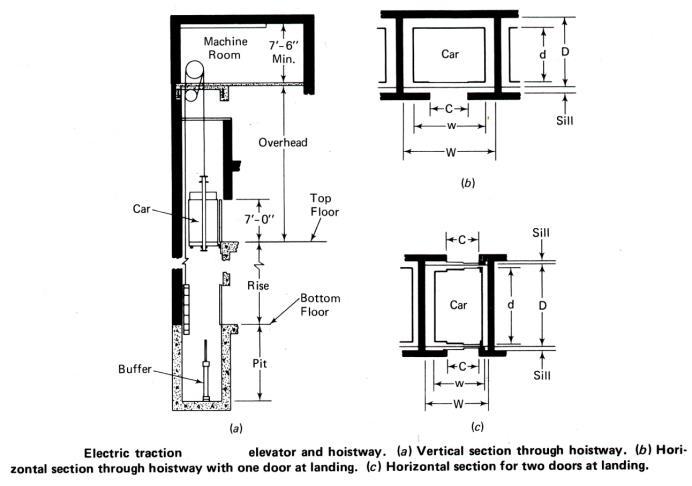
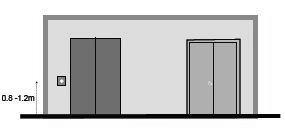
Capacity (lb) Passe ngers Width, w Depth , D Clear width .w’ Clear depth , D’ Doors clear openings ,o Over head Max. rise 1500 10 5’-0” 4’-6” 6’-8” 4’-11” 2’-8” 10’-9” 29’ 2000 13 6’-4” 4’-5” 7’-8” 4’-10” 3’-0” 11’-0” 41’ 2500 16 7’-0” 5’-0” 8’-4” 5’-5” 3’-6” 11’-3” 42’ 3000 20 7’-0” 5’-6” 8’-4” 5’-11” 3’-6” 11’-3” 42’ 3500 23 7’-0” 6’-2” 8’-4” 6’-7” 3’-6” 11’-3” 42’ 4000 26 8’-0” 6’-2” 9’-4” 6’-7” 4’-0” 11’-3” 42’ Height of call button= .8-1.2m According to BNBC= 3.12’- 3.9’ 3.125’3.9’ZZZ
elevators
ELEVATOR STANDARDS Firefighter
•1.10m wide
deep
the
at least
wide •minimum
capacity
630kg.
by 1.40m
with
door entry
800mm
loading
is regulated at
elevator
Freight
Is designed to carry goods. capable of carrying heavier loads than a passenger elevator, generally from 2,300 to 4,500 kg. The number of LIFT PxtxHC 300x100xq N=
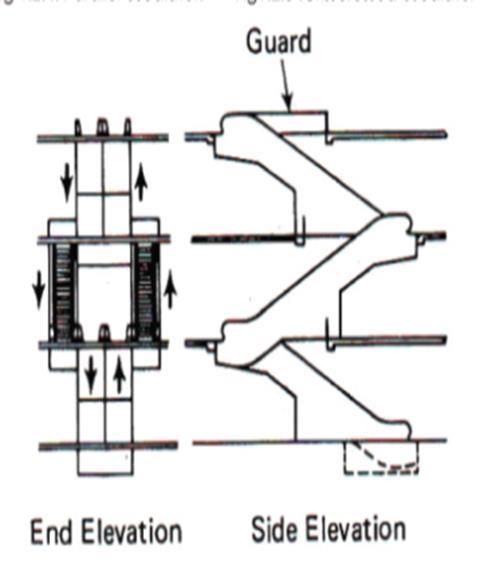
COMPONENTS OF ESCALATOR
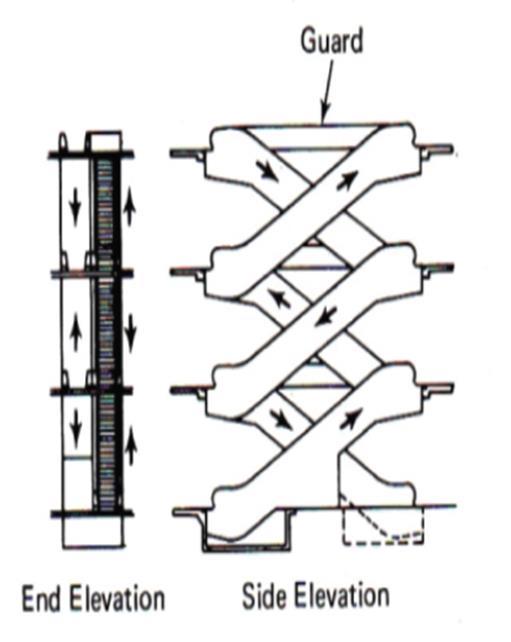
• Top and Bottom Landing Platforms
• The Tracks
• The Steps
• The Handrail
• Anti-slide devices
• Complete impact switches
• Deflector brush

• Emergency Stop button
• Extended balustrades
• Flat steps
• Handrail inlet switches
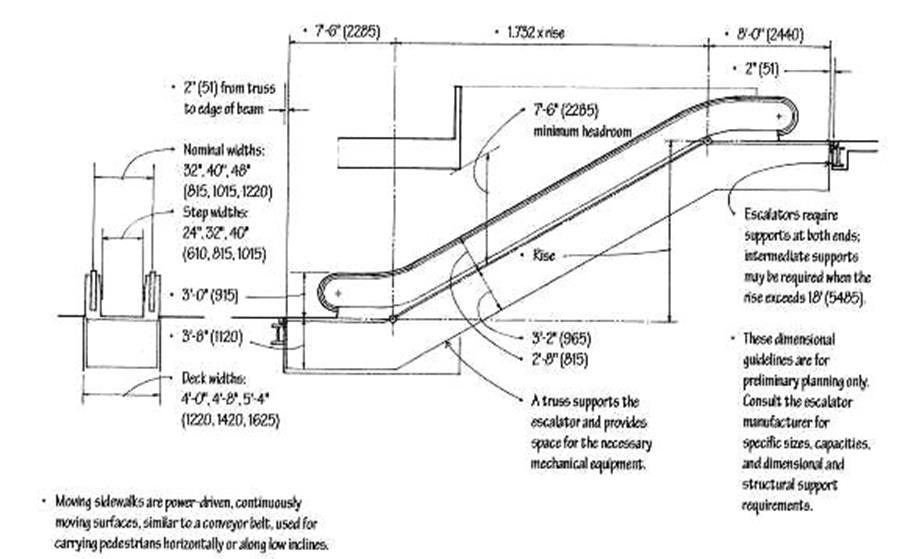
STANDARDS FOR ESCALATOR
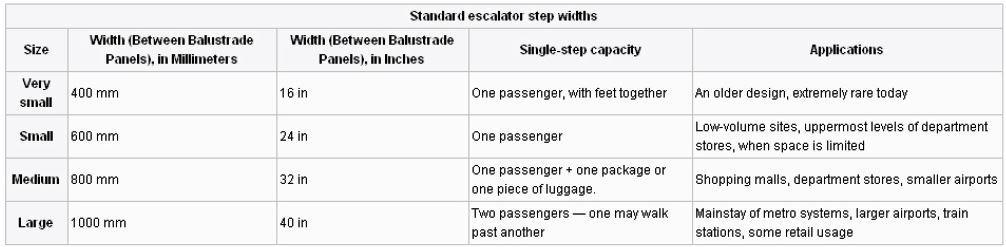
• Speed is usually 90 or 120 fpm
• Standard widths are 32 to 48 in. between handrails.
• A 32-in. escalator operating at 90 fpm can transport between 5000 and 8000 persons per hour.
• A 48-in. escalator operating at 120 fpm can transport as many as 10000 persons per hour.
• The maximum angle of inclination of an escalator to the horizontal floor level is 30 degrees with a standard rise up to about 60 feet (18 m).
TYPES OF ARRNGEMENT:
• PARRALLAL
• CRISSCROSS
ESCALATOR





GENERATOR ROOM


WATER PUMP


PLACE FOR AC EQUIPMENT



STAIR
FIRE EQUIPMENT
General information

Status: Topped-out
Location: Lujiazui, Pudong,Shanghai
Architectural: 632 m (2,073 ft)

FIRM: Gensler
Architect: Marshal Strabala, Jun Zia and Aurthur Gensler
Floor count: 121
Floor area: 380,000 m2 (4,090,300 sf ) above
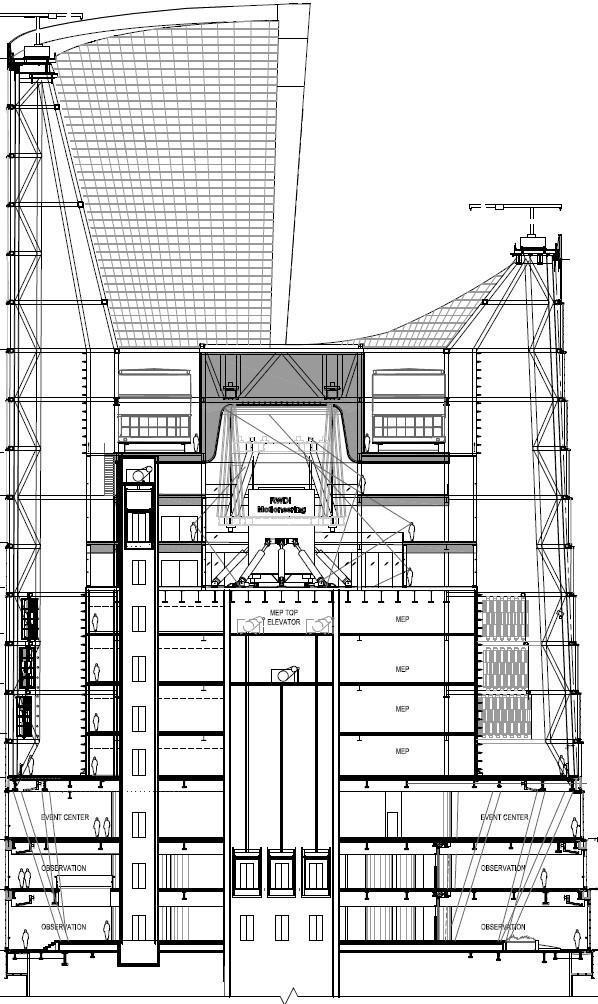
CASE STUDY
SHANGHAI TOWER CASE STUDY






SCULPTED FOR EFFICIENCY
The wind tunnel test is used to find the most beneficial scaling factor of about 55% and rotation at 120°, which is account for the 24% savings of the wind load working on the structure.
TECHNICAL INNOVATION
The concrete core acts with outriggers and super columns are the advances science of super-high rises.
VERTICAL COMMUNITY
Shanghai tower embodies a new concept of super-tall building by emphasizing public spaces at the atrium levels.



SUSTAINABLE ACIEVEMENTS
There are two lays of skin wrapping the entire building. The atriums created by the skins features as an insulation which keep the temperature stable.








CASE
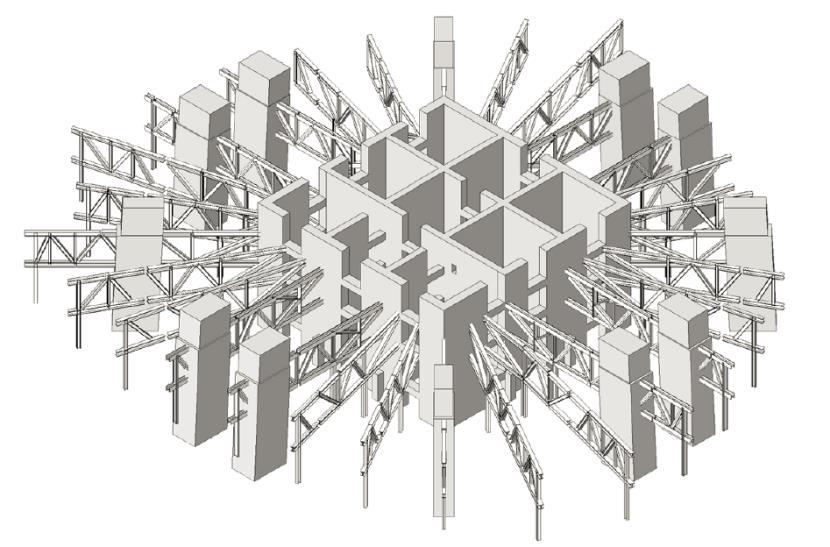
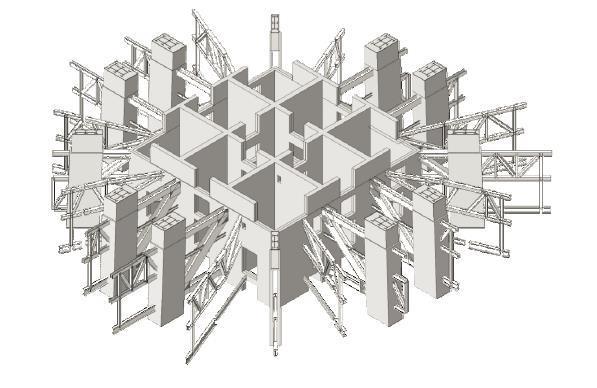
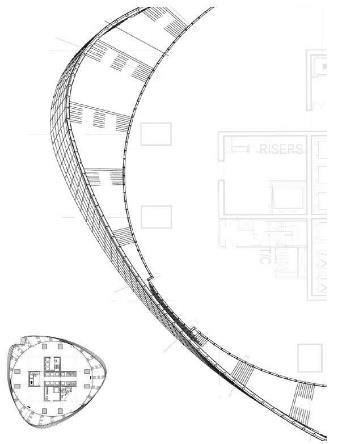
SHANGHAI TOWER PLANDETAIL TWO STOERY OUTRIGGER TRUSS ONE STORY RADIAL TRUUS CORE WALL DIAGONAL CORNER COLUMN SUPER COLUMN BELT TRUSS BUILDING
INNER CYLINDICAL TOWER • CORE • OUTRIGGERS • MEGA FRAME: SUPER COLUMN SYSTEM AND BELT TRUSS
STUDY
SYSTEM MAINSTRUCTURE
CASE STUDY
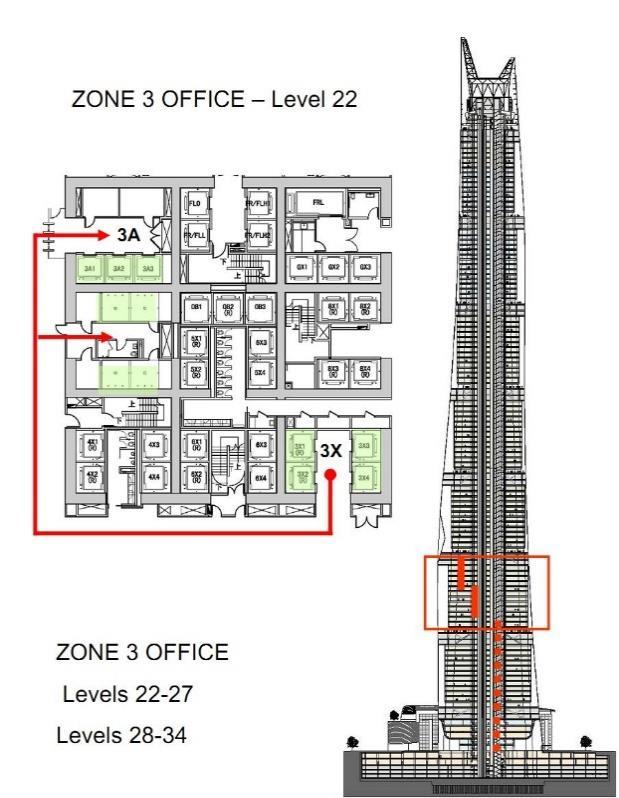
CAR ARRANGEMENT
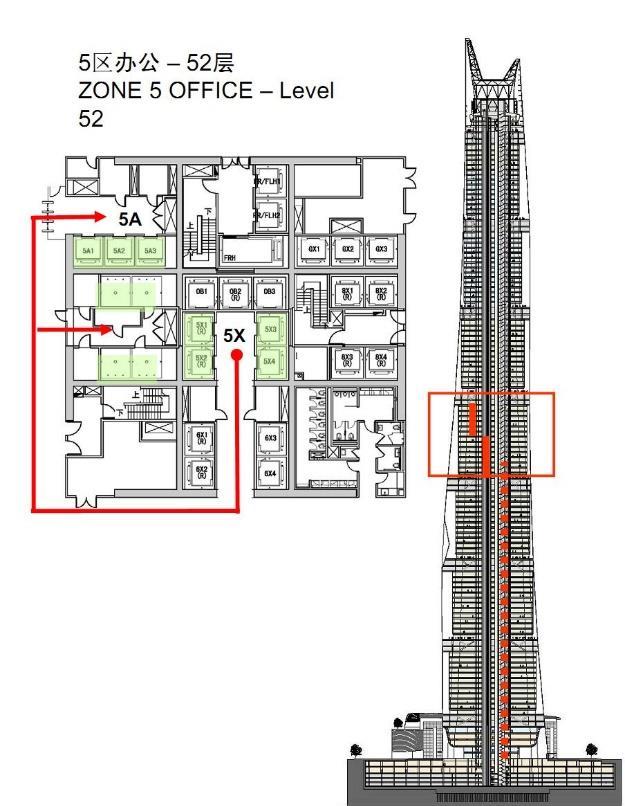
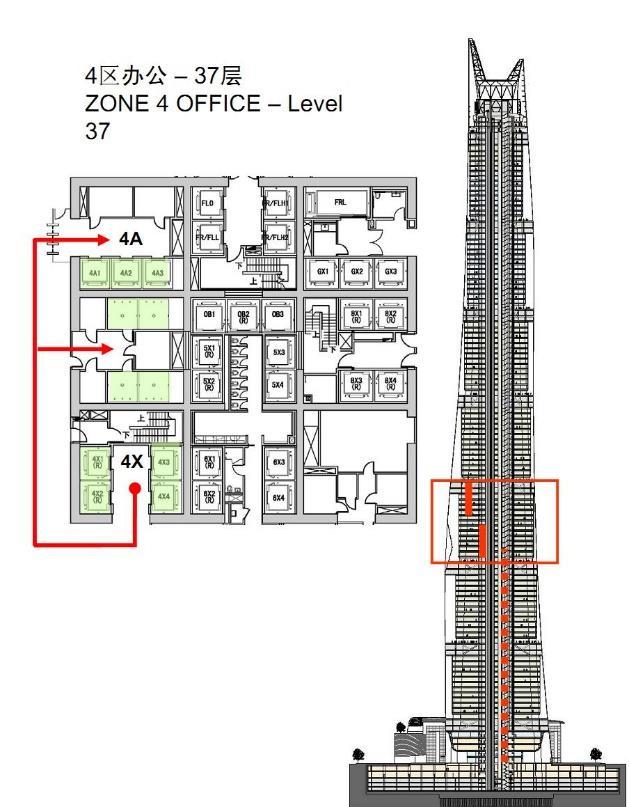
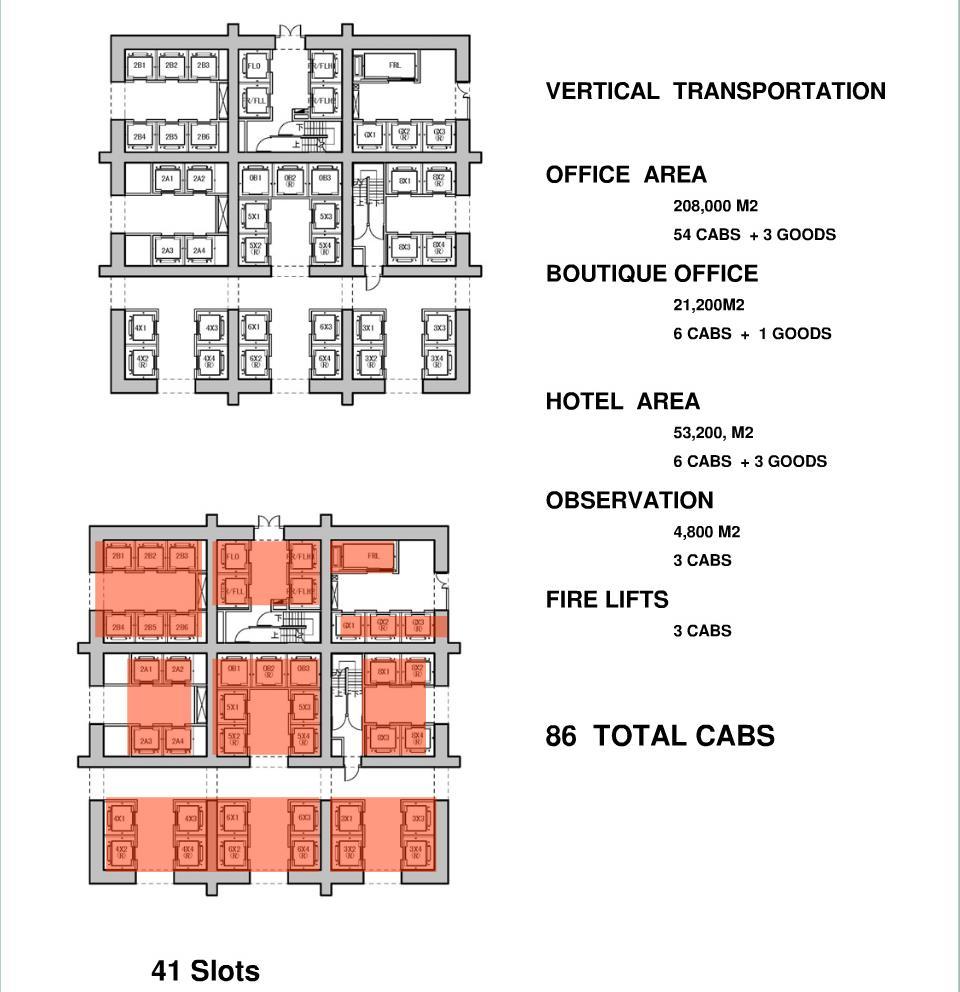
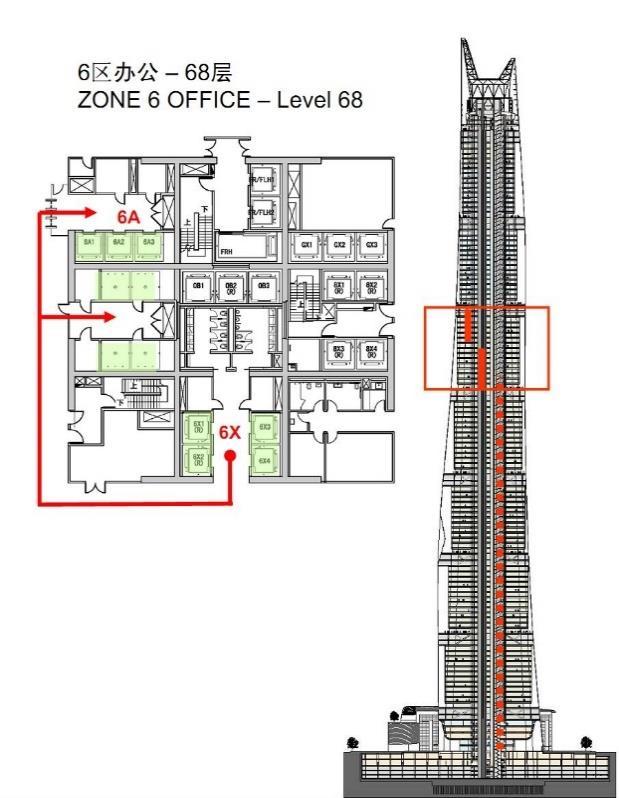
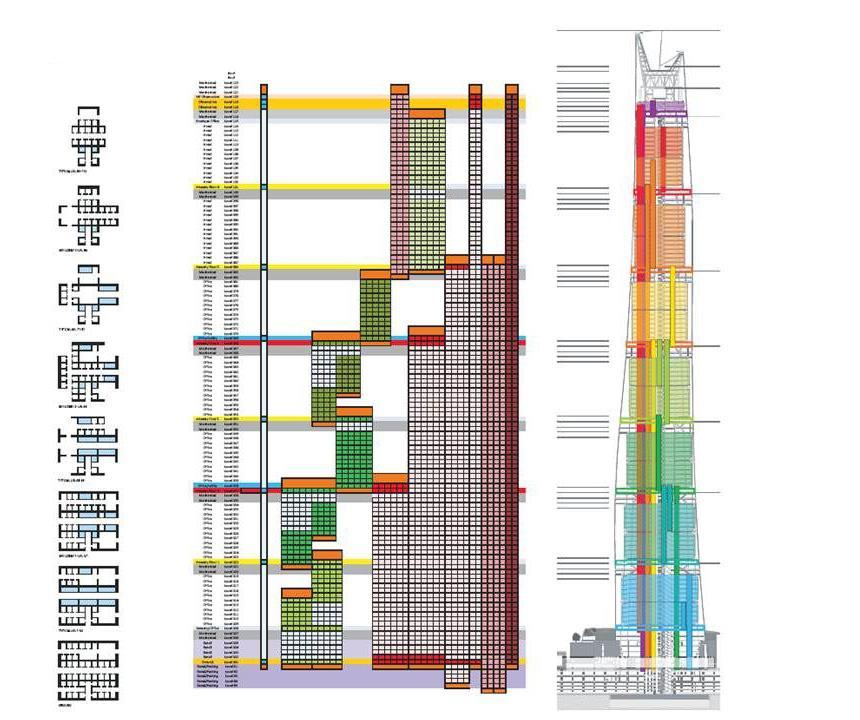
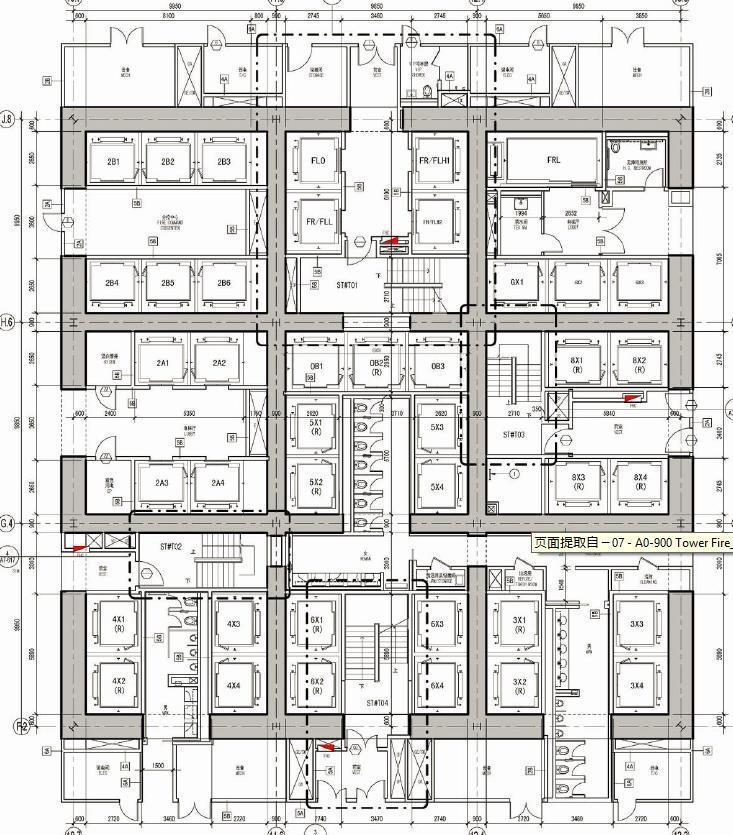

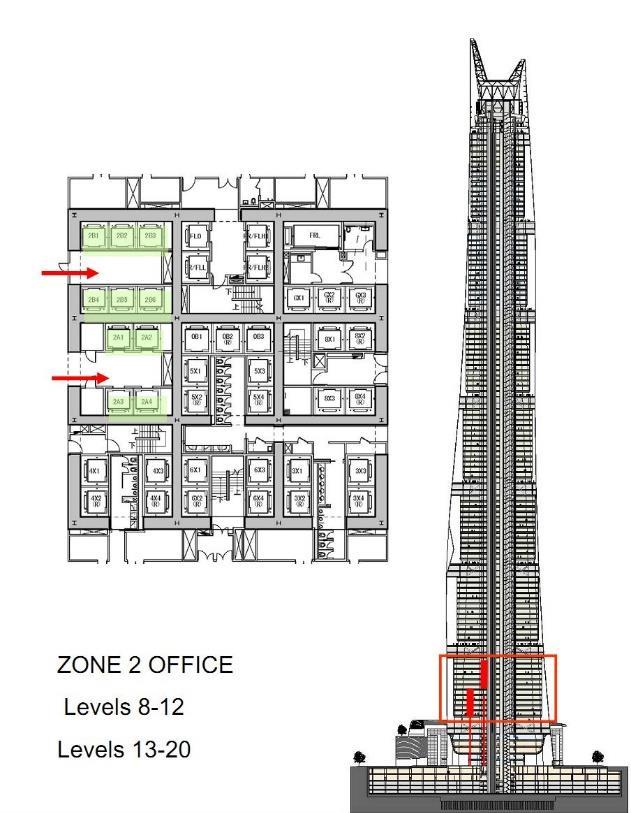
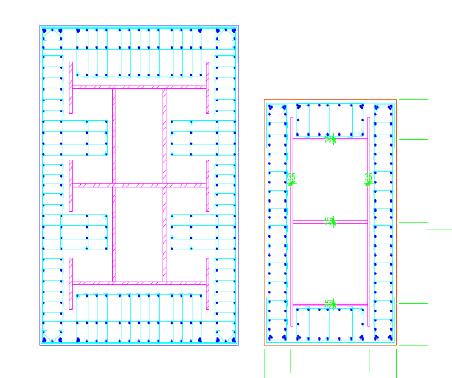
CORE ZONE 1 AND BASEMENT CORE
SHANGHAI
CASE STUDY
TOWER
Inner Cylindrical TowerMEGA FRAME
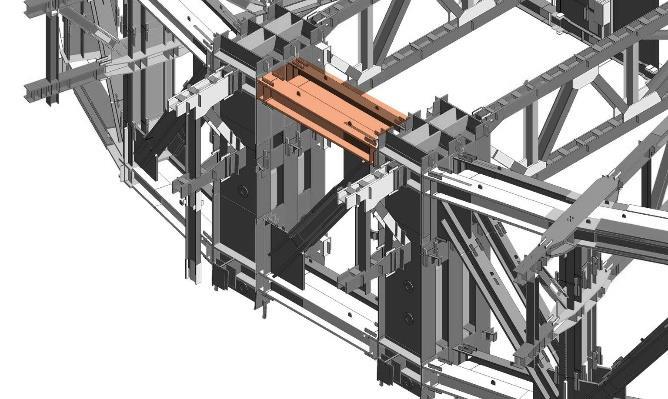
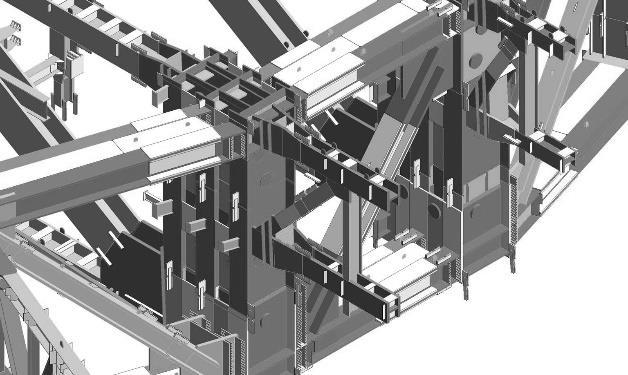
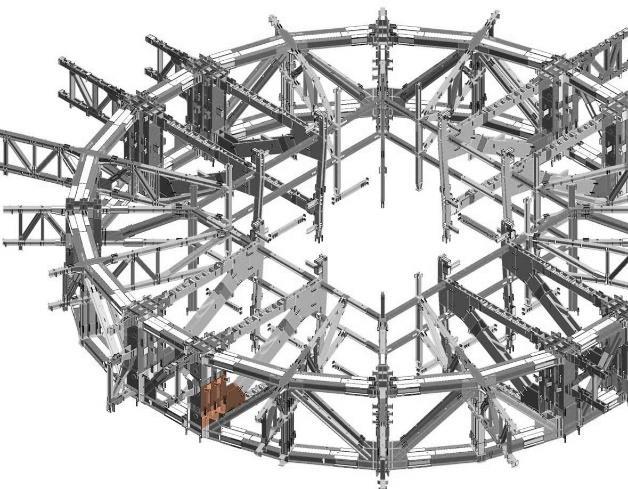
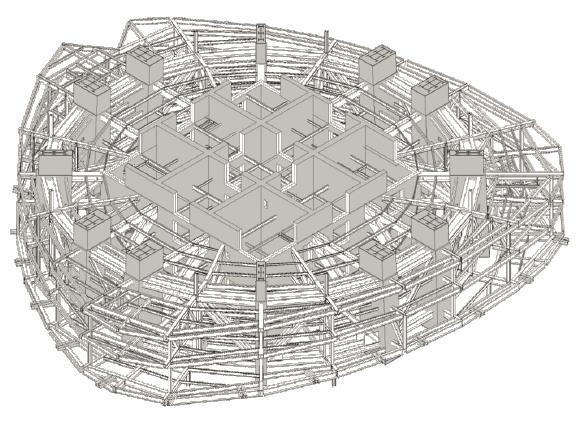

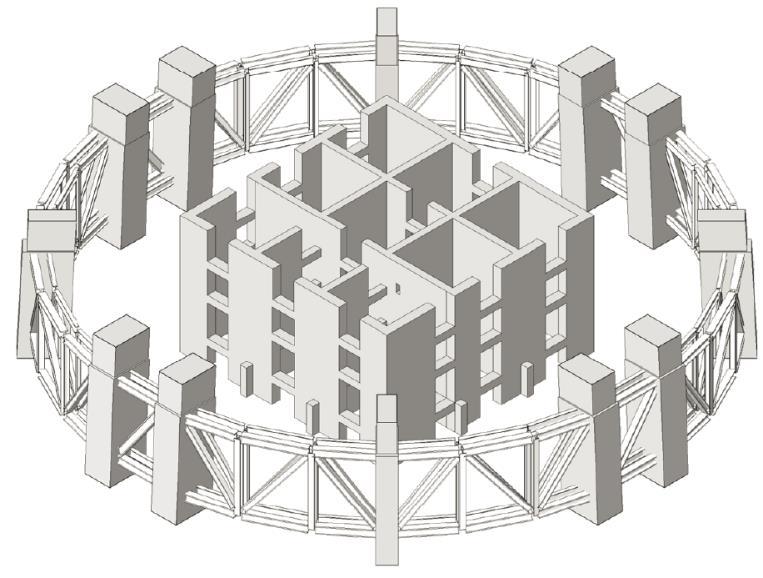

Super column System: two at each end of each orthonormal axis four diagonal super columns along each 45-degree axis
CONNECTION DESCRIPTION
• Complexity of stress state.
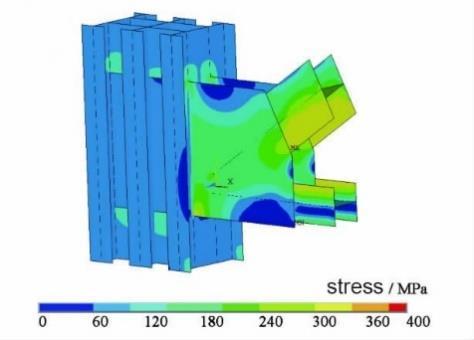
• Connections should be broken after the destructiveness of members
• Different connections have different design criteria, according to the variation of structure members.
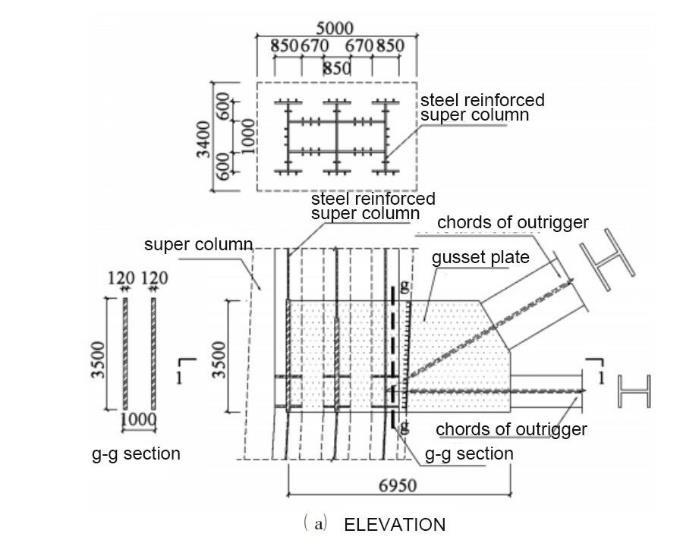
Outrigger
Double stories
In the steel section of the super columns, there are perpendicular cross ribs that align with belt trusses
TECHNICAL FEATURES
• The chords of outrigger truss
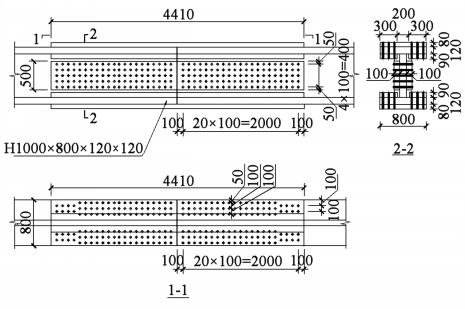
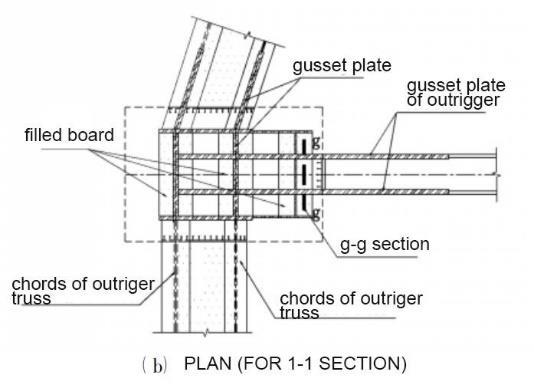
• Gusset plates, 120mm thickness, Q390GJC steel
• The steel reinforced dual web of the super-column
• The belts trusses
Radical Outrigger
One story
Technical Feactures
• Since there exist large member force of the chords in the belt trusses, there are large quantity of the bolts, and super length of the bolts set.
SHANGHAI TOWER CASE STUDY
STRUCTURAL FEATURE
1-6 ZONE 7-8 ZONE
SECTION OF THE SUPER COLUMN
Type A: The Joint of Outrigger to Super-column
Type B: The Long Bolt Joint of the Belt Truss
CASE STUDY
SHEAR MOMENT TENSION DEFLECTION
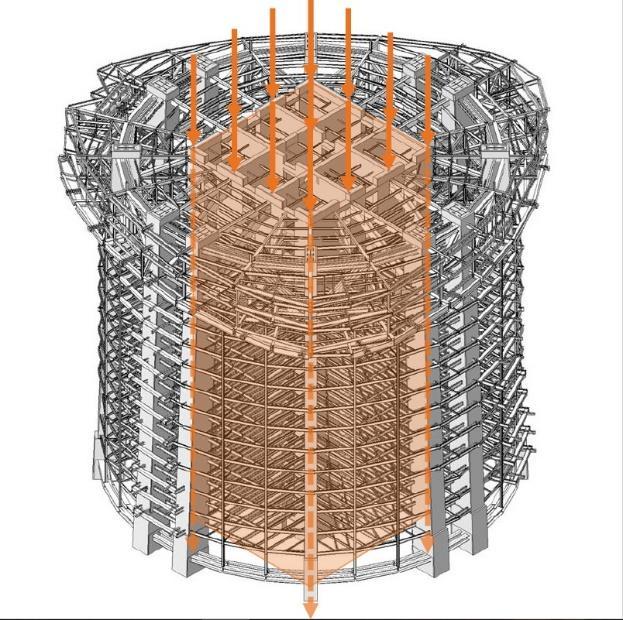
LATERAL LOAD TRANSFER
Type C: The Detail of Interior Curtain Wall Type D: The Detail of Exterior Curtain Wall LOADING ANALYSIS GRAVITY LOAD TRANSFER PATH THE MEGA FRAME 50% TUBE OF COLUMN 50% STRUCTURE COMPONENT SHEAR FORCE OVERTURNING MOMENT THE MEGA FRAME 47% 76% TUBE OF COLUMN 53% 24%
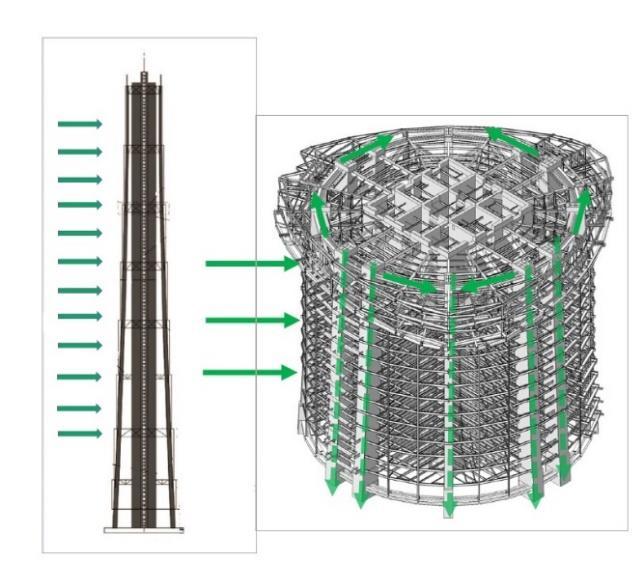




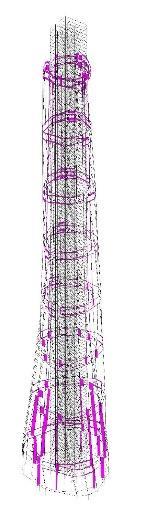
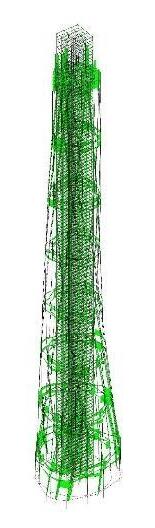
Building resist to Lateral loads through 3 layers of structure, they transfer wind and seismic load one by one, from inside to outside.
Tower Top

• Vertical fin-like truss
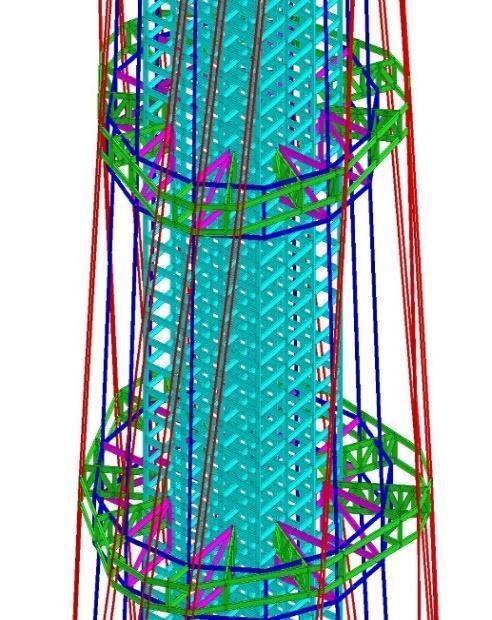



• Two-way truss
• Octagonal steel frame bracing system


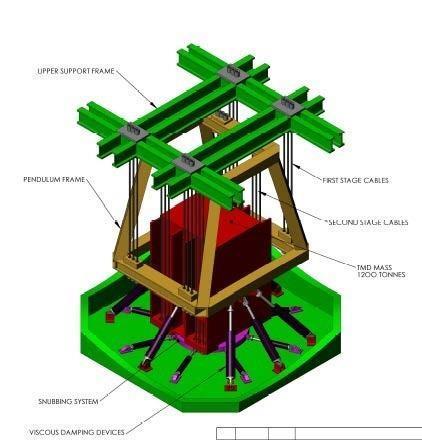
CASE STUDY SHANGHAI TOWER
The tuned mass damper
Multi-frame Analysis
The Supper core is the first layer of Resistance. The double belt truss and super column are the second layer of Resistance. The outriggers and radial trusses are the third layer.
















CASE STUDY SHANGHAI TOWER
THANK YOU
PHOTO GALLERY

THANK
YOU







































































































































