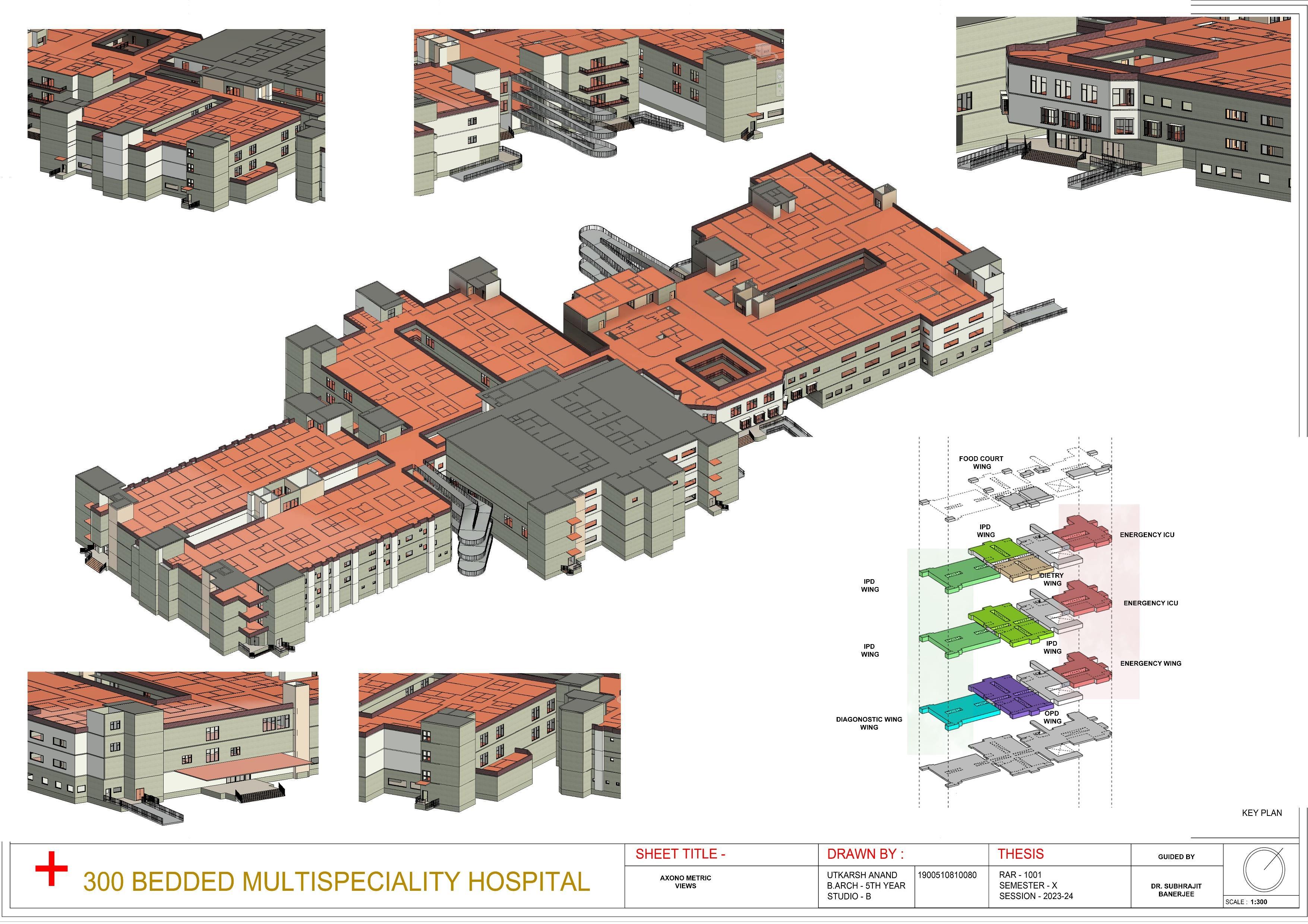
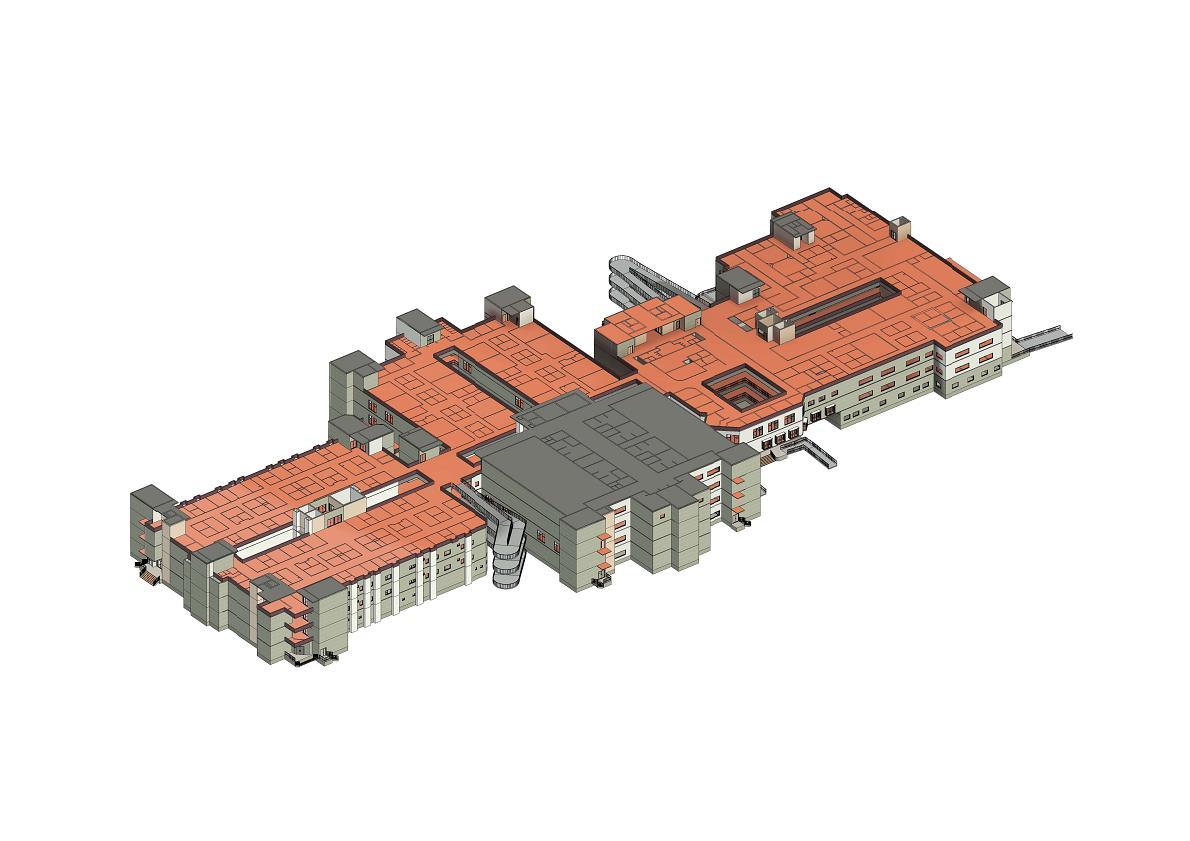
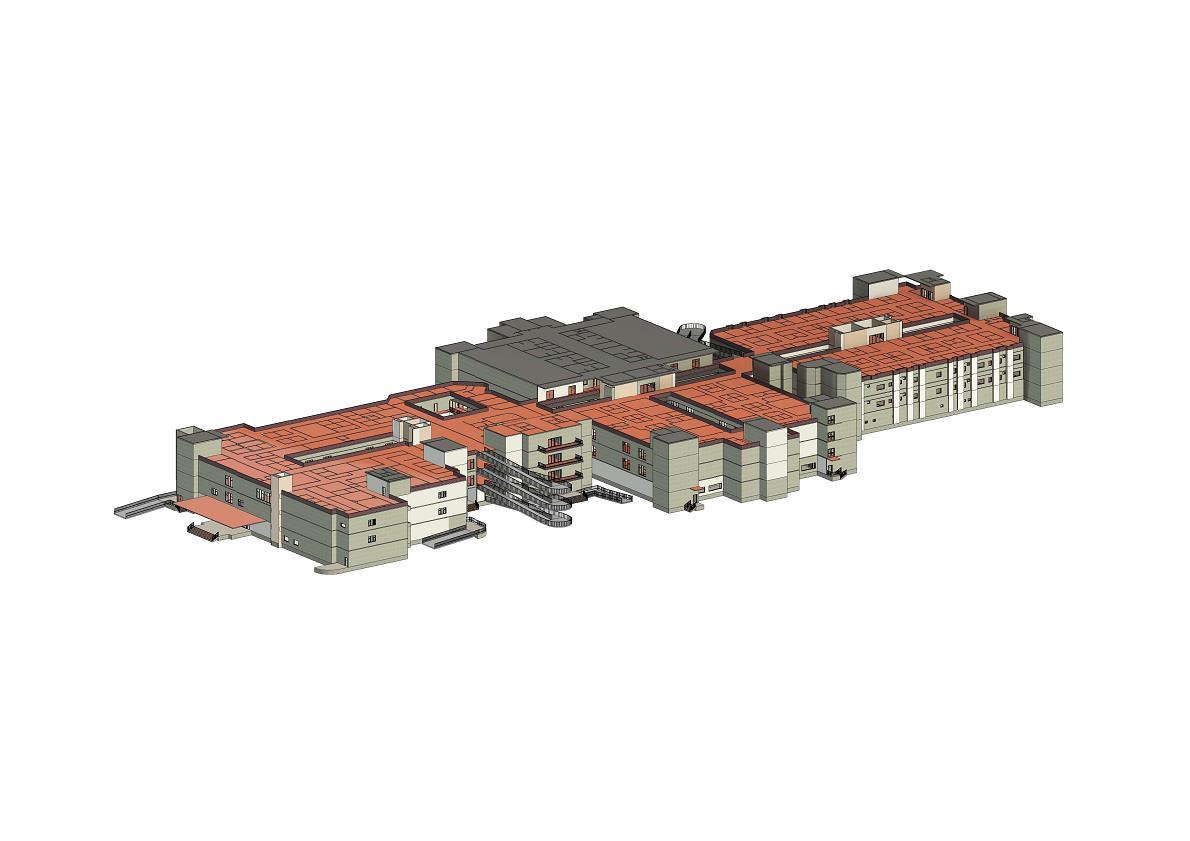
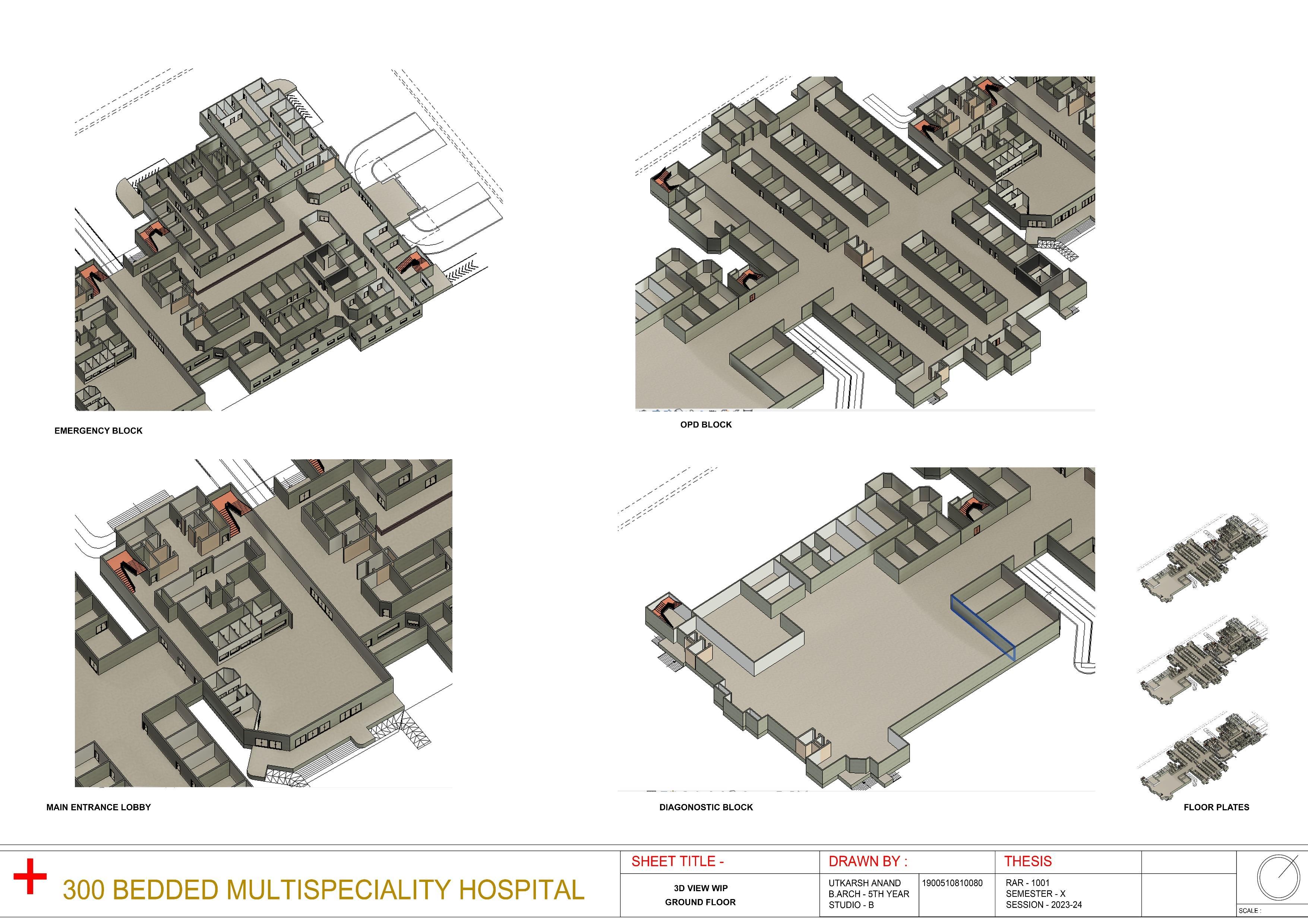
GENERAL PORTFOLIO
FINAL YEAR ARCHITECTURE PORTFOLIO PROJECT 300 BEDDED MULTISPECIALITY HOSPITAL
BACKGROUND STUDY :
• A hospital is a place where people go to get medical treatment for illnesses, accidents, and pregnancies.
• It offers services including diagnosis, therapy, and recovery.
• Outpatient care is also provided by some hospitals.
• A hospital is an essential healthcare facility that offers the community both curative and preventive treatment.
• In addition to conducting bio-social research, it provides outpatient services to families in their homes and acts as a training facility for medical staff.
• Multispecialty hospitals provide basic medical, surgical, and other services.
• They offer both primary and secondary care. Each hospital department need its own identity inside its own private, semiprivate, and public amenities, making planning a difficult proposition.
• Aside from that, in today's hospital, the engineering department and technological assistance are more important than ever. Hospitals are among the most massive and complex modern institutions.
• Hospital architecture is a component of this complication. Unlike other institutions, which can be created in a variety of ways, hospital buildings have fewer options.
• Medical architecture must support the adoption of new technology while also improving process efficiency and transparency. It must integrate clinical requirements with building planning and design challenges in a seamless manner.
• Designers create hospitable settings by using natural light, calming hues, and comfortable furnishings.
• In order to meet the needs of both patients and their families, private patient rooms are designed to provide solitude and reduce noise.
• The design of hospital rooms should promote smooth patient movement and efficient staff operations.
• Improved operations and wait times result from efficient layout. In hospitals, infection prevention is essential.
• Cross-contamination risk is decreased through materials, ventilation, and segregation.
AIM : TO DESIGN A 300 BEDDED MULTI-SPECIALTY HOSPITAL
OBJECTIVE :
• To provide a therapeutic environment that is both comfortable and user-friendly.
• To put patient-centered design strategies into action.
• To understand how different parts of a hospital, like departments, equipment, operating rooms, and shared spaces, are connected, is important. This helps in designing hospitals effectively.
• To create plans for situations when there are more patients than usual, like during a pandemic or a widespread flu outbreak, or after a big accident, is important.
SCOPE :
• Understanding different aspects of designing the hospital buildings with respect to site.
• An important aspect would be to study about the healing environment for patients which affects the patient’s health.
Need for Multi-Specialty Hospitals
Flexibility
Design spaces that can easily adapt to changing medical needs and technological advancements.
Patient Experience
Create a warm and welcoming environment that enhances the well-being of patients.
Thrust area :
LIMITATIONS :
• The study will concentrate mostly on the category of General Hospitals.
• The project will be limited to 300 hospital beds.
• The project will not take into account the cost of execution
Collaboration
Promote interdisciplinary collaboration and communication among healthcare professionals.
Efficient Workflow
Optimize the flow of patients, staff, and resources to minimize delays and improve efficiency.
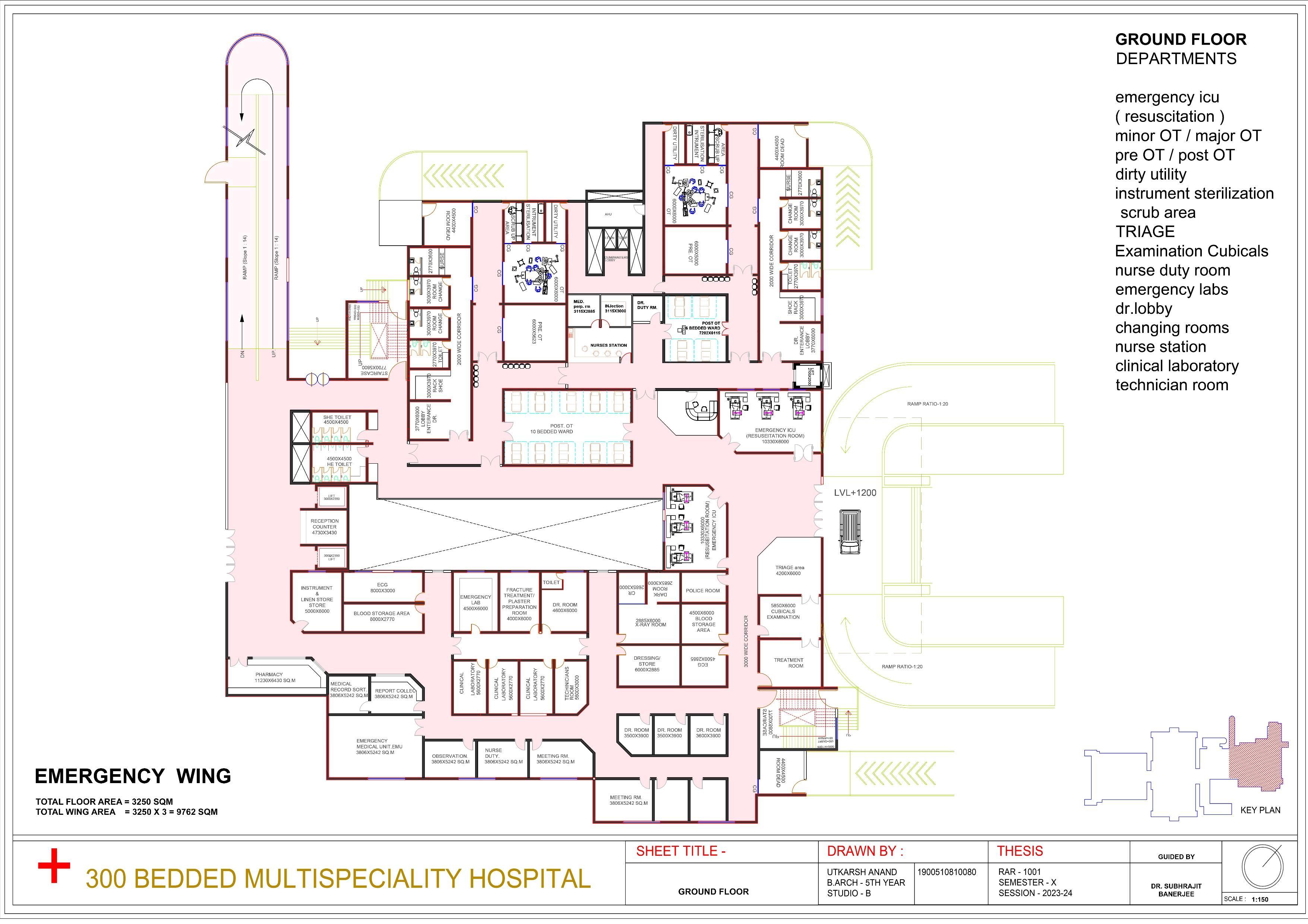
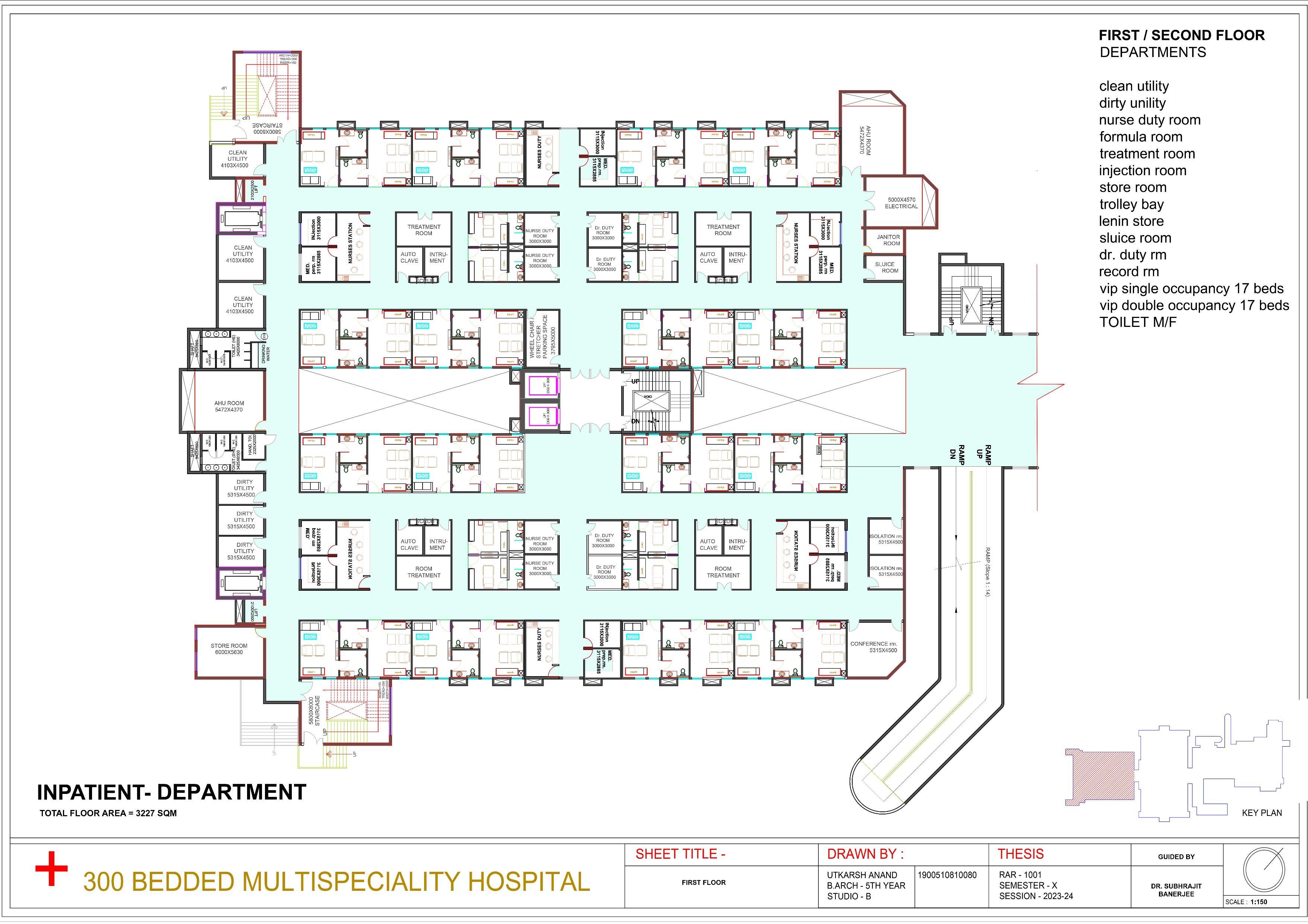
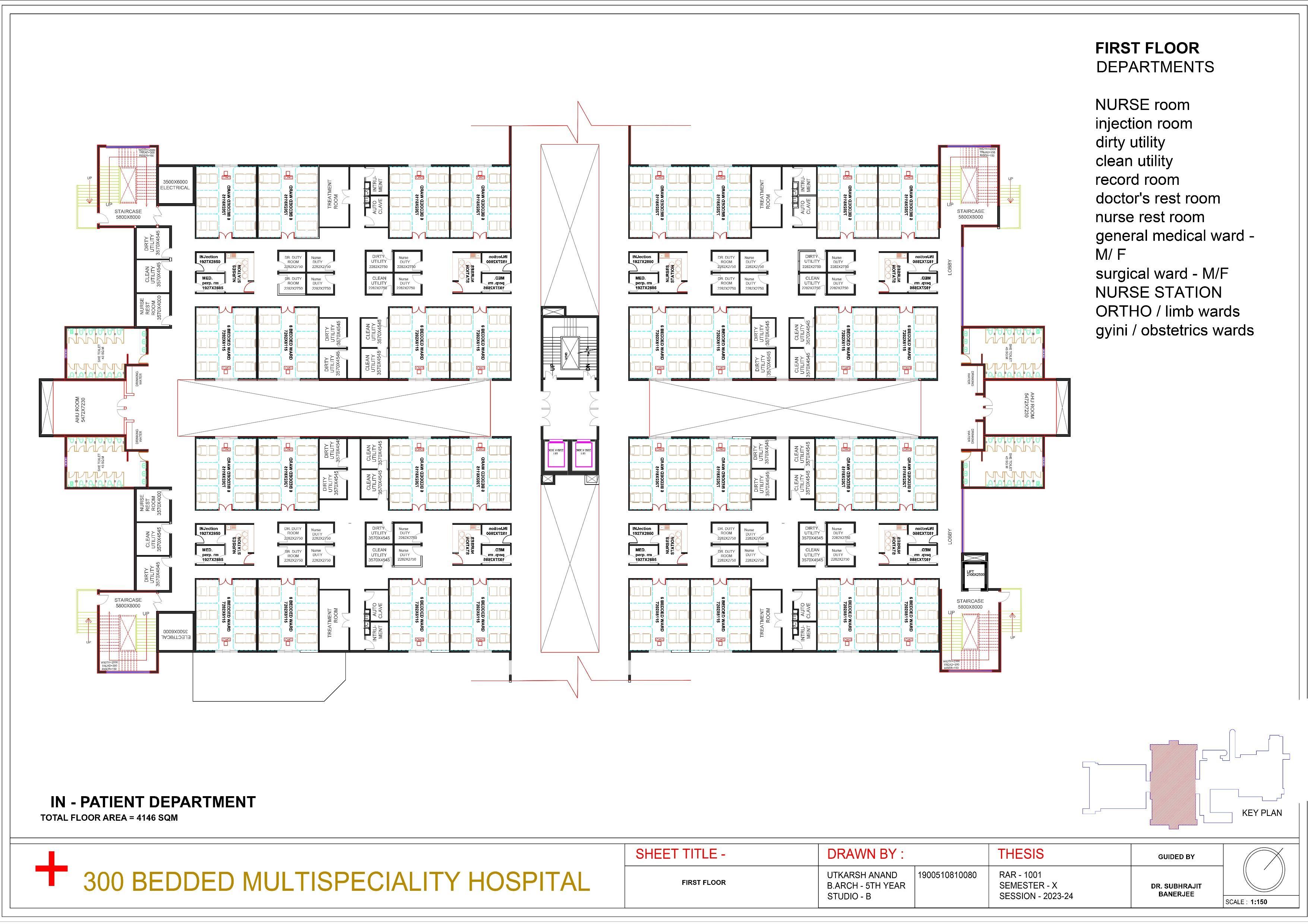
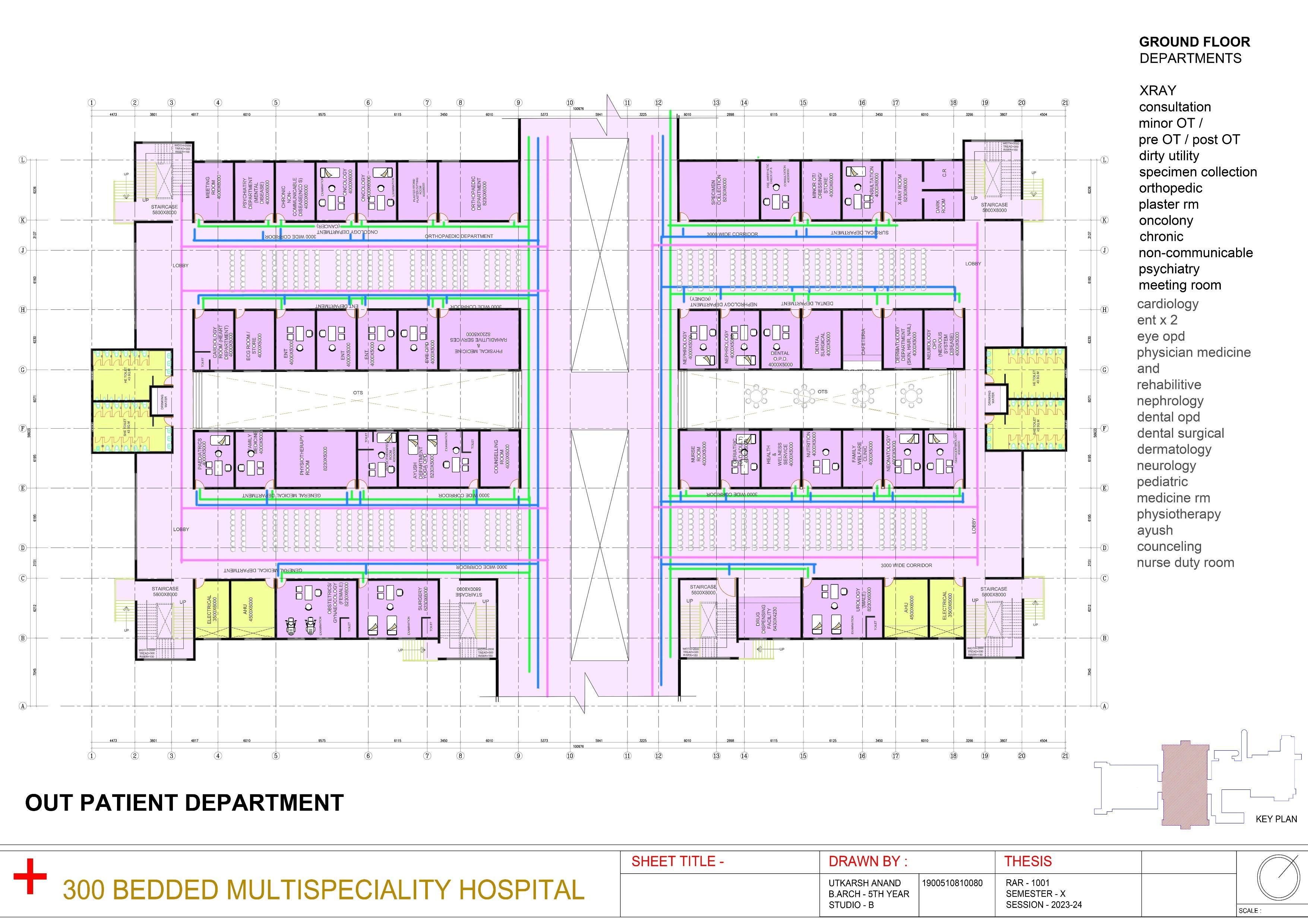
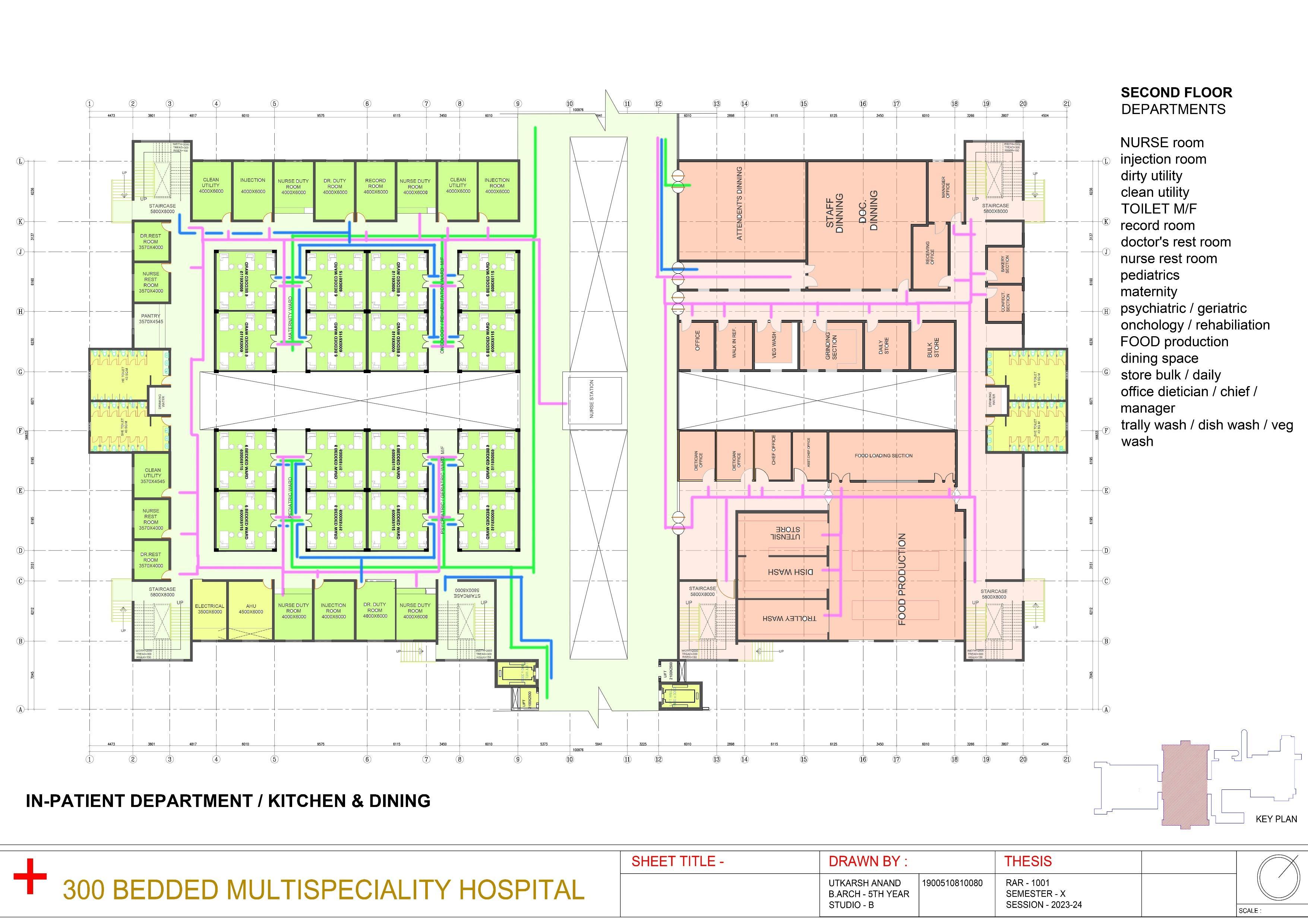
Planning of Hospital spaces and its specialized services
Functional Zoning in Hospital Design
Inpatient Areas
Design dedicated spaces for patient care, including wards, intensive care units, and operating theaters.
Outpatient Areas
Create separate areas for outpatient services such as consultation rooms and diagnostic facilities.
Support and Amenities
Include ancillary spaces like cafeterias, pharmacies, and administrative offices.
Designing for Efficiency and Workflow Optimization
Streamlined Processes
Efficient flow and seamless navigation navigation of patients, staff, and equipment ensures better patient outcomes and reduced wait times. times.
Ergonomic Design
Designing workspaces for optimal comfort and productivity can lead to to better staff satisfaction, retention, retention, and reduced errors.
PLANING ASPECTS
• Intelligent buildings
• Create a healing architecture
• Aesthetic - an essential requisite
• Hospital architecture
• Go green
• Accessibility to transportation & communication lines
• Parking facilities
• Availability of public utilities
• Proper elevation for drainage & general sanitary
• measures
• Freedom from smoke, noise, vapours & other annoyances
• Future expansion
ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS
(i) Area must have clear sun shine, avoid big buildings, trees near by.
(ii) Climate should be moderate.
(iii) No near by noise or smoke emitting industries.
(iv) Flow of fresh air.
(v) Away from roads with heavy traffic.
ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS
(i) Area must have clear sun shine, avoid big buildings, trees near by.
(ii) Climate should be moderate.
Smart Rooms
Integrating technology into patient patient rooms can improve safety, comfort, and communication while while reducing costs and energy consumption.
(iii) No near by noise or smoke emitting industries.
(iv) Flow of fresh air.
(v) Away from roads with heavy traffic.
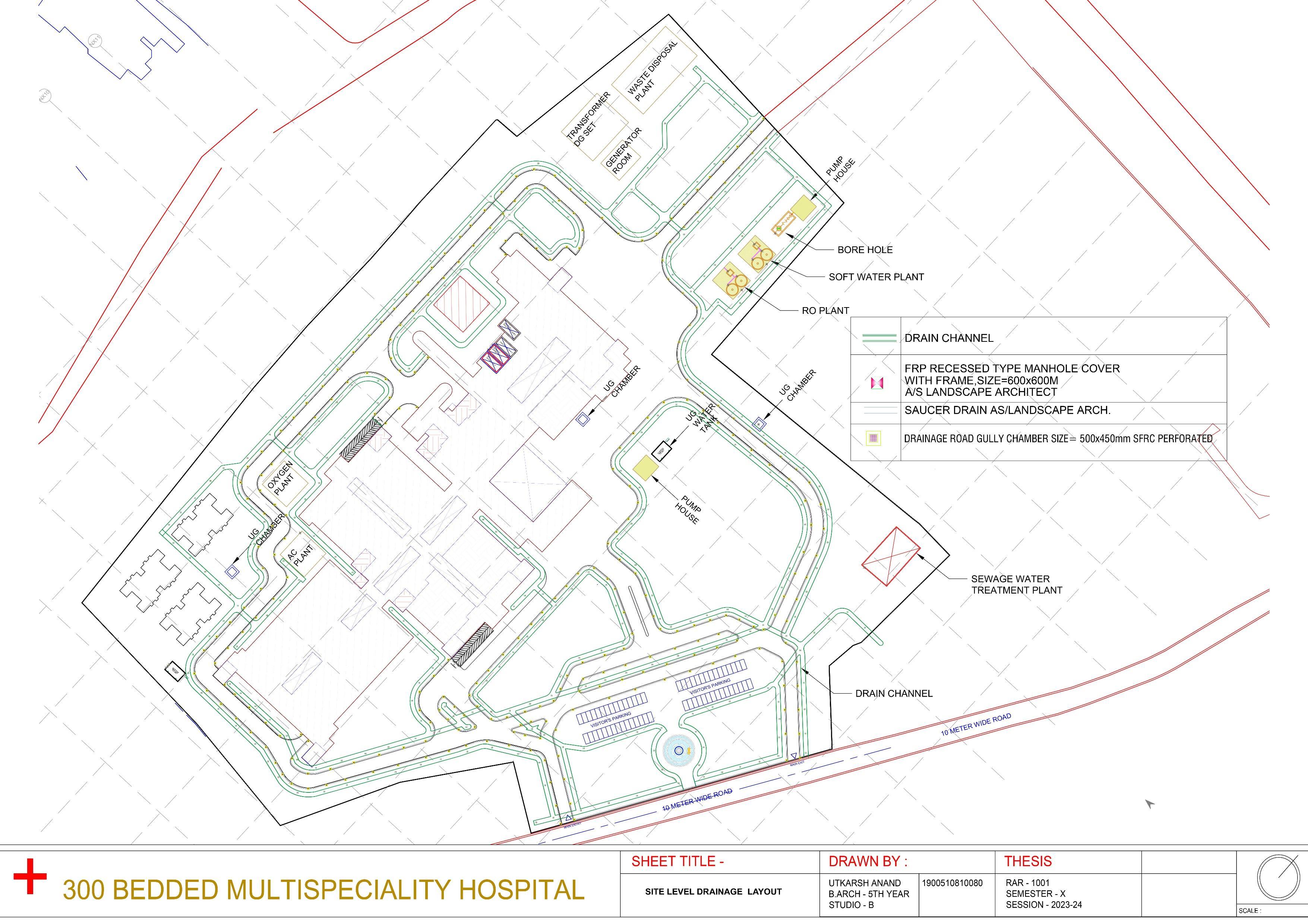
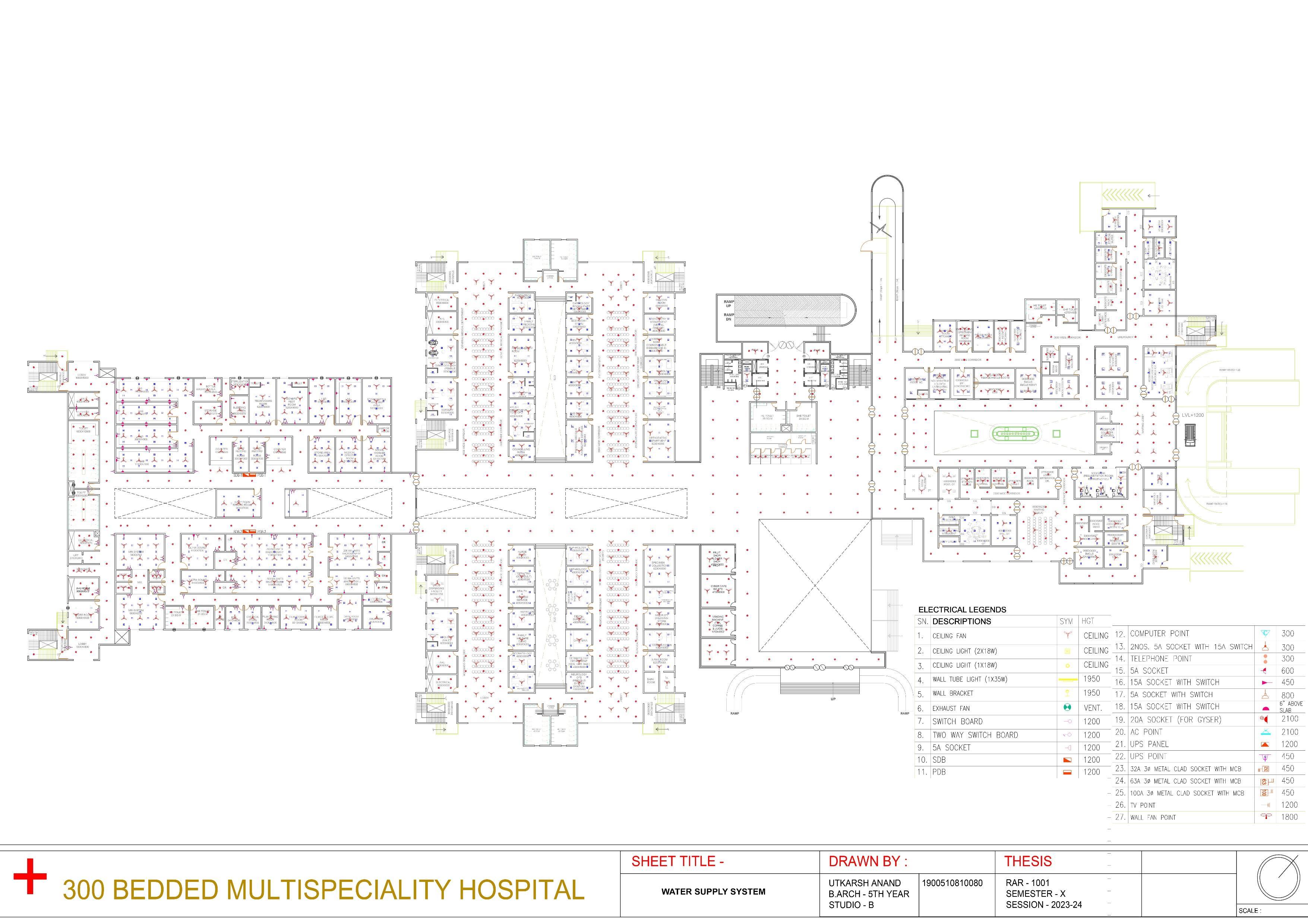
WATER SUPPLY AND SANITATION
-Availability of deep table subsoil water.
-Adequate water supply (400 liters/ bed/ day.
-Good maintained sewerage system (300-400 liter/ bed/ day)
- Easy access to sewerage treatment plant.
-Facility for Bio-Medical Waste Disposal near by.
INTRODUCTION/
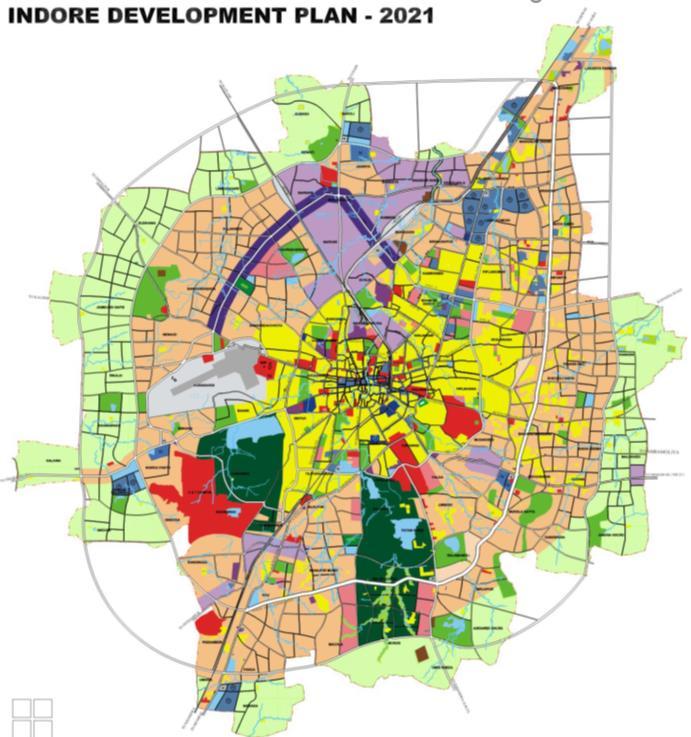
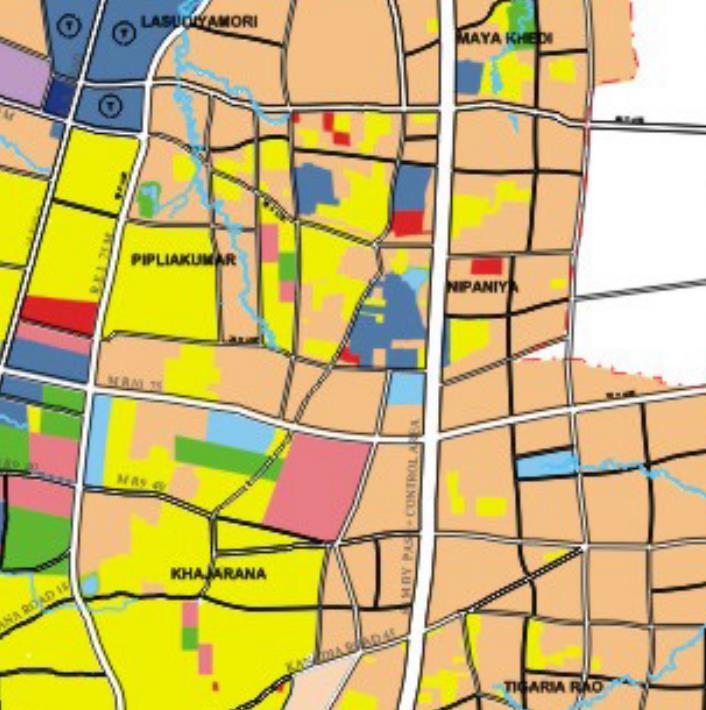
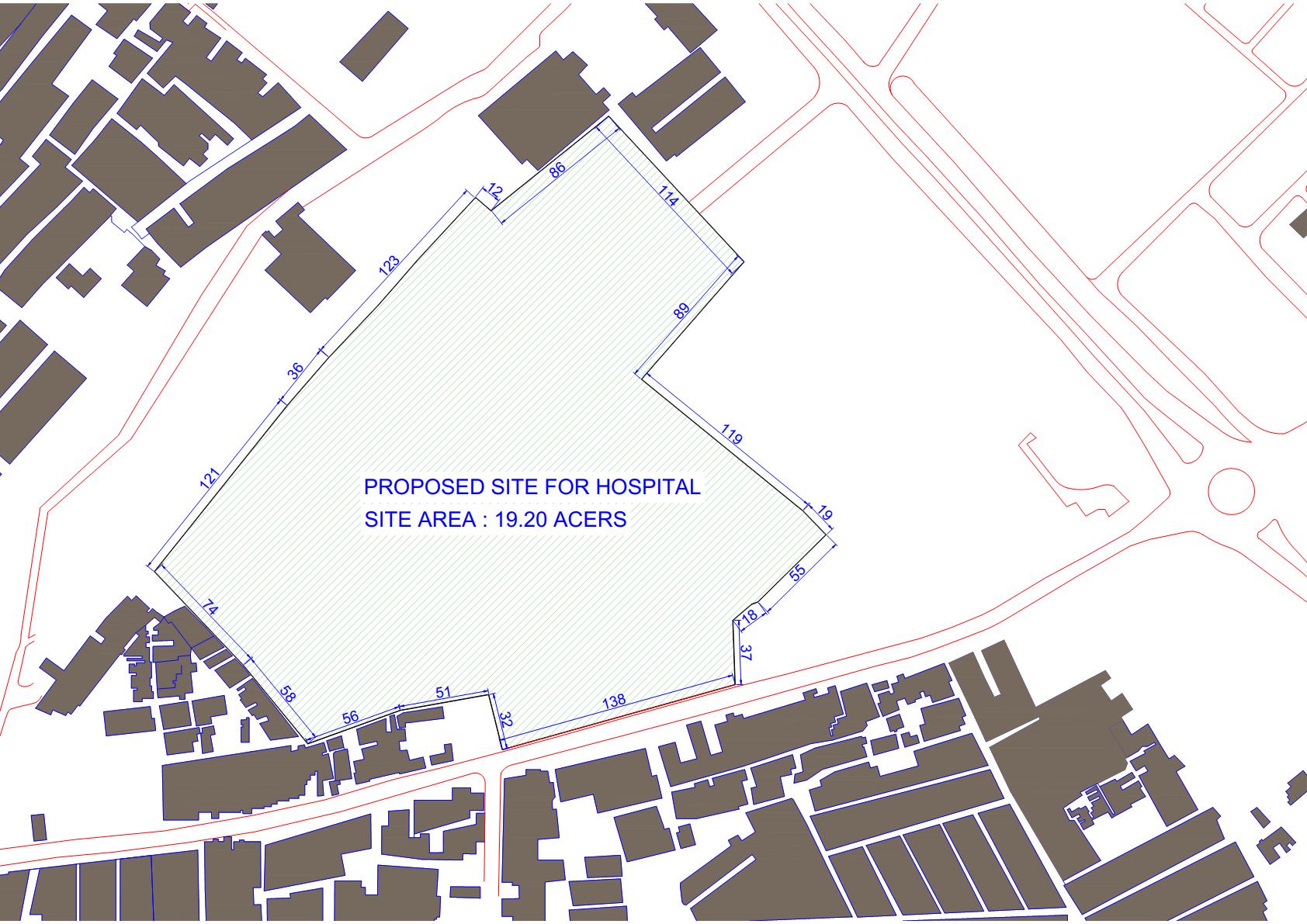
PROPOSED SITE
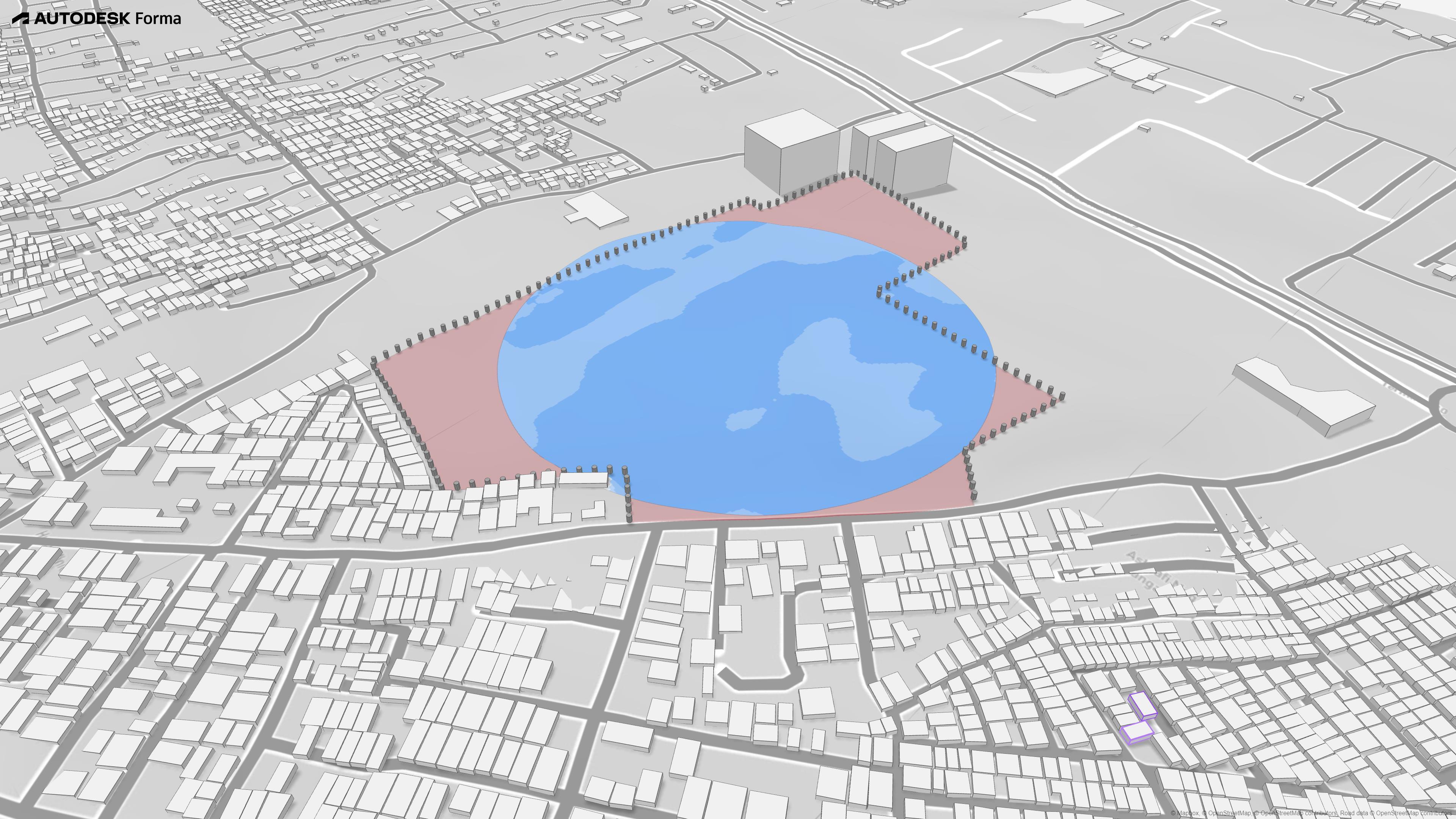
Site area: 19.20 acers
Site location: near Star Chouraha on MR 10 Main Road , Indore , Madhya Pradesh
INDIA MADHYA PRADESH
Main Road networks & various types of amenities connected to site site
Arterial road networks
MR 10 ROAD
Phinex citadel mall
Khajrana temple
NIPANIA marg Bombay hospital
SSTRENGTHS
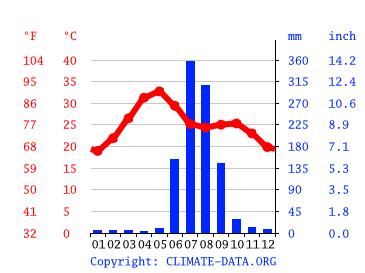
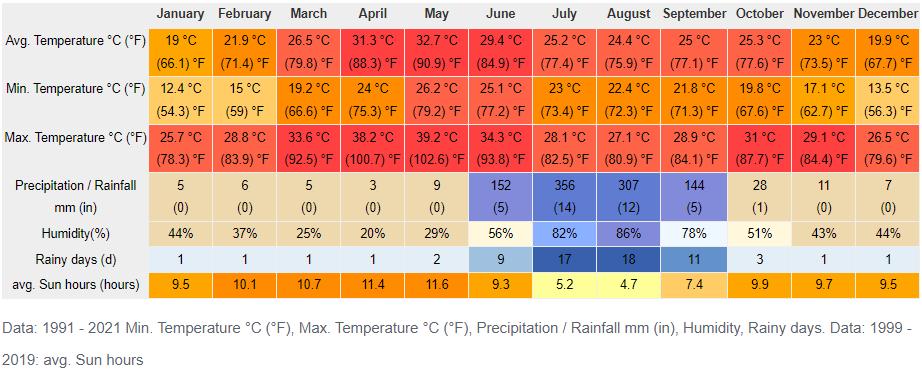
CLIMATIC STUDY OF INDORE DATA AND GRAPHS FOR WEATHER & CLIMATE IN INDORE
WEAKNESSES O OPPORTUNITIES T THREATS
▪ SITE IS WELL CONNECTED WITH TRANSPORT
▪ SITE IS WELL CONNECTED WITH AMINITIES OF ALL THE TYPES
▪ WELL CONNECTED WITH PUBLIC TRANSPORT
▪ THERE IS LOTS OF GREENERY AROUND THE SITE WHICH REGULATES THE MICROCLIMATE
▪ SITE IS SURROUNDED BY RESIDENTIAL AND COMMERCIAL SPACES LIKE MARKET , APPARTMENTS
▪ SITE IS SURROUNDED WITH RESIDENTIAL DEVELOPMENT
▪ CURRENTLY, SITE IS USED AS ABANDONED CAR PARKING BY DWARKA AND CATTLE GAZZING
▪ WASTE MANAGEMENT CAN BE BIG TASK FOR THIS PARTICULAR SITE
▪ SINCE SITE SURROUNDED WITH RESIDENTIAL AREA THEREFORE HOSPITAL INFRASTRUCTURE WILL BE VERY BENIFICIAL FOR POPULATION NEARBY
▪ THE HOSPITAL CAN BE SEEN AS A BEST GREEN AND SUSTAINABLE INFRASTRUCTURE IN INDORE
▪ THE PROJECT CAN CREATE LOTS OF EMPLOYMENT DURING ITS CONSTRUCTION PERIOD
▪ THE HOSPITAL CAN ALSO REFLECT DIVERSE THINGS BY MEANS OF ARCHITECTURAL ELEMENTS AND BUILT FORM ▪ DIFFICULTIES RELEATED TO BIO WASTE GENERATION CAN BE SEEN
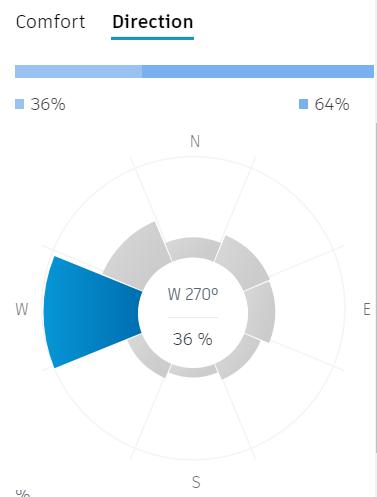
MICROCLIMATE ANALYSIS
In the region of Indore, it has been observed that May is the month which experiences maximum daily sunshine hours, with an average duration of approximately 11.65. The total number of sunlit hours during this period amounts to a staggering sum of about 361.04.
SUN PATH DIAGRAM
The location of Indore experiences the least amount of daily sunshine hours during January, with an average duration of only 9.71. The total number of sunlight hours recorded in this month is equal to 291.32.
It has been estimated that the total annual sunshine duration in Indore is approximately 3312.05 hours. This translates to an average monthly value of roughly 109.04 hours for each month, on a consistent basis.
ZONES CONNECTIVITY FLOWCHART
• CARDIAC CATCH
• LAB.
• ANGIOGRAM
• GAMA RAY
• ECG
• ETT
• ECO
• RADIOLOGY & IMAGING DEPT.
• X-RAY
• ULTRASONOGRAM
• CT ANGIOGRAM DEPT.
• MICROBIOLOGY DEPT.
• BIOCHEMISTRY DEPT.
• SERIO LOGY
• COVERED SPACE FOR AMBULANCE
• LOBBY, RECEPTION, WAITING
• POLICE ROOM
• RECORD ROOM
• STRETCHER STORAGE
• EXAM ROOM
• NURSHING STATION
• MINOR OT
• EMERGENCY OT
• EQUIPMENT ROOM
• AUTOCLAVE ROOM
• DOCTERS AREA
• EMERGENCY STORE
• TOILET
• REGISTRATION AREA
• WAITING AREA
• CONSULTING ROOM
• RECORDS ROOM
• NURSE ROOM
• CARDIOLOGY CLINIC
• TOILET
• WAITING ADMISSION
• RECORDS ROOM
• NURSING ROOM
• DOCTORS ROOM
• PATIENT TRANSFER AREA
• TOILET M/F
WARD MANAGEMENT FLOWCHART
RECEPTION : Admission of the patient Outpatient service Emergency / casualty department
INPATIENT DEPARTMENT
DIAGNOSTICS LAB-TEST
- INVASIVE AND NONINVASIVE
RESEARCH DEPARTMENT
SITE CIRCULATION FLOWCHART
SHORTEST ROUTE
PROTECTION SEPERATION OF DISSIMILAR ACTIVITIES
SITE ZONING
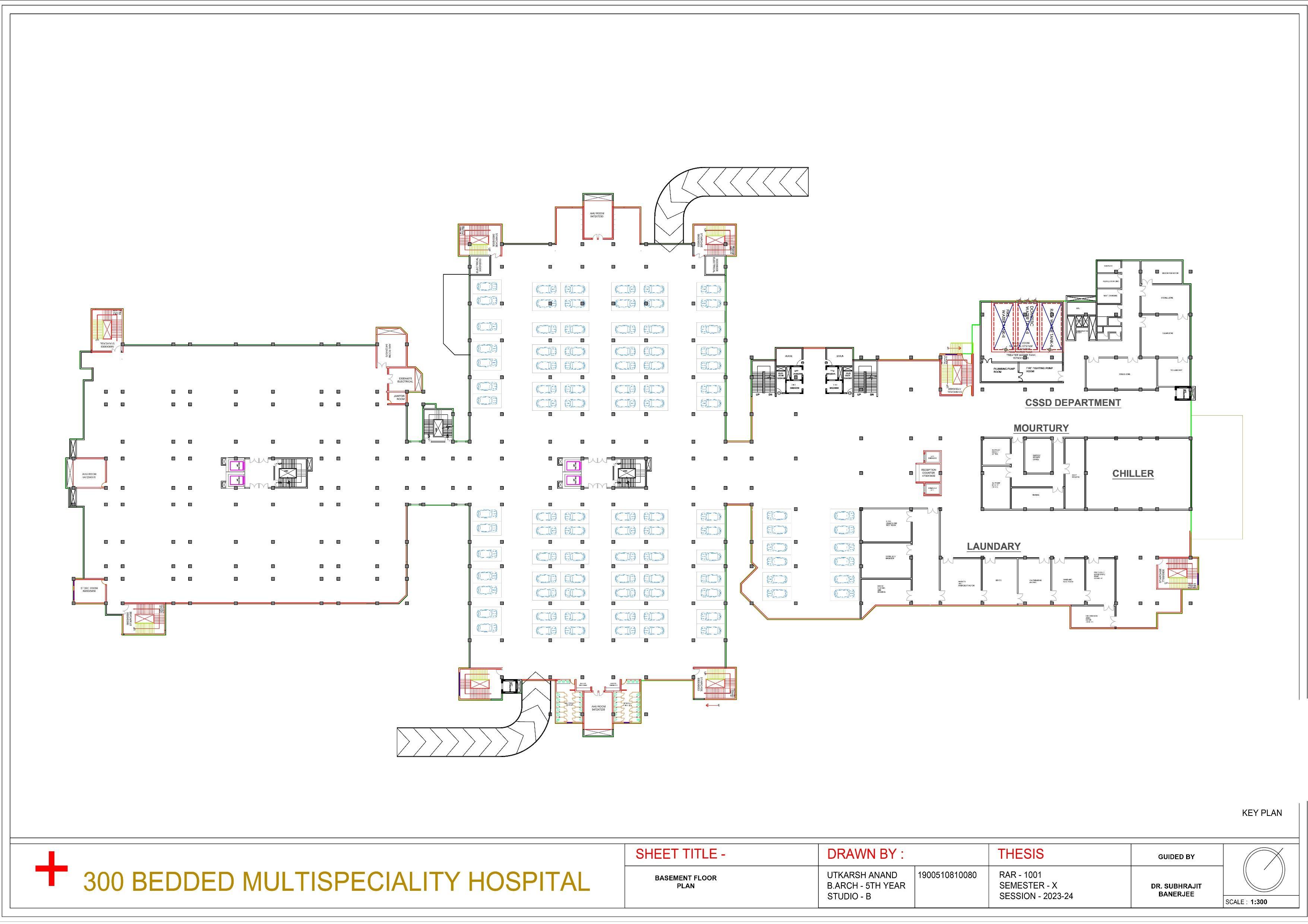
• SERVICE LOBBY
• SUBSTATION
• OXYGEN PLANT
• GARBAGE ROOM
• FIREFIGHTING EQUIP STORE
• LAUNDRY
• KITCHEN OT, ICU, CCU, WARD
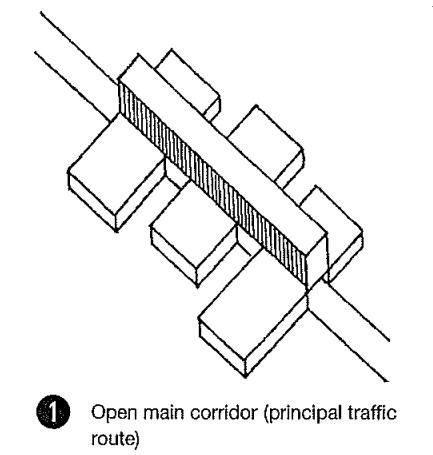
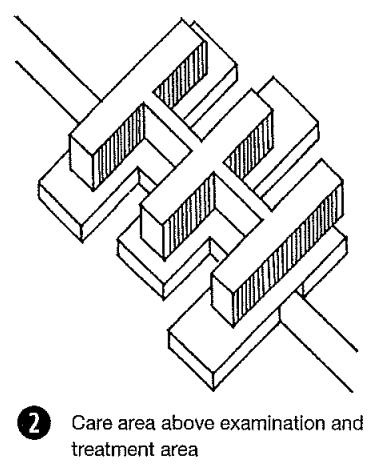
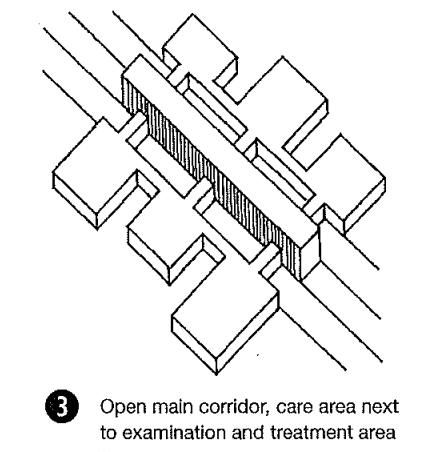
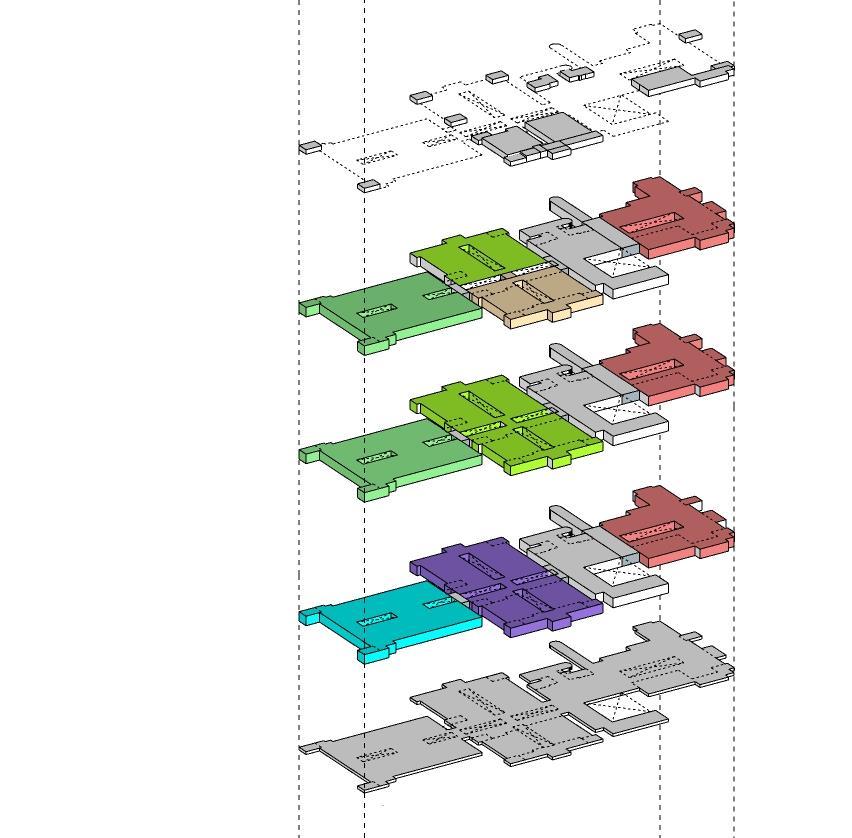
1. MODULAR ARRANGEMENT OF HOSPITAL SPACES
2. FUNCTION FOLLOW FORM
3. ELEMENTS OF HOSPITAL
Introduction to Modular Arrangement of Hospital Spaces
Modular arrangement
Modular arrangement refers to the PLANNING & DESIGNING of hospital spaces in modules which can be replaced and shifted as per the needs of changes use of pre-fabricated components that can be easily assembled and reconfigured to create hospital spaces.
Benefits of Modular Arrangement
Rapid construction and expansion
Flexibility to adapt to changing needs
Key Considerations
Space optimization
Scalability and adaptability
Integration of technology and equipment
Key Design Considerations for Modular
Hospital Spaces
Creating Efficient and Functional Healthcare Environments
Space Optimization
Efficient use of space is crucial in modular hospital design, ensuring optimal workflow, patient comfort, and staff convenience.
Scalability and Adaptability
Designing modular spaces with scalability and adaptability in mind allows for seamless expansion and integration of new technologies and services.
Advantages of Modular Arrangement in Hospitals
Reduced Construction Time
Modular construction allows for faster completion of hospital projects, reducing construction time by up to 50% compared to traditional methods.
Hospital building design concept & design consideration according to site
Flexibility and Adaptability
Modular spaces can be easily reconfigured and expanded to meet changing demands, allowing hospitals to adapt to evolving healthcare needs.
Cost-Effective Design
Modular construction offers cost savings through streamlined processes, reduced material waste, and potential for future expansion without major disruptions.
Future of Modular Arrangement in Hospital Spaces
Embracing Innovation and Advancements
Greenery and Sustainability
Advancements in technology, such as modular robotic systems and smart sensors, will further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of modular hospital spaces.
Technological Integration
Advancements in technology, such as modular robotic systems and smart sensors, will further enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of modular hospital spaces
Customization and Personalization
Modular design will continue to evolve, allowing for greater customization and personalization of hospital spaces to meet the unique needs of patients and healthcare providers.
HOSPITAL BUILDING DESIGN CONCEPTS & DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS AS standards
Integration of Technology and Equipment
Modular design should accommodate the integration of advanced medical technologies and equipment, enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
MICROCLIMATE ANALYSIS
MICROCLIMATE ANALYSIS