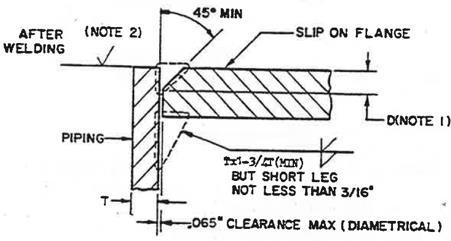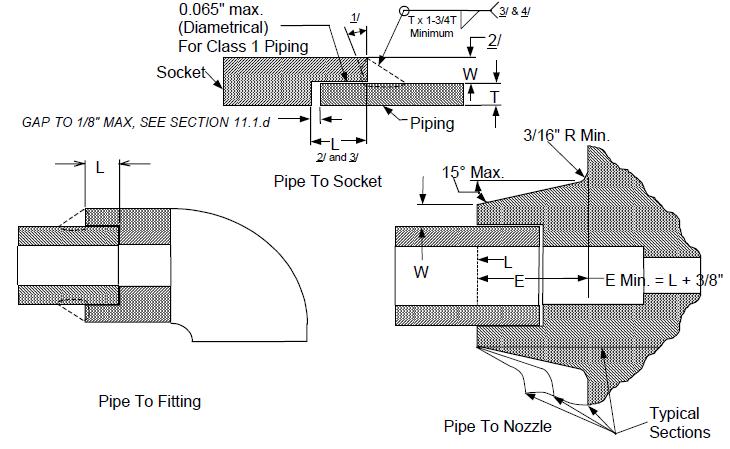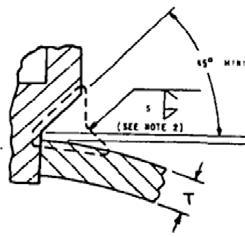
14 minute read
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
Advertisement
WI-Q-3030
ENCLOSURE E – Workmanship Inspection Methods & Inspection Tools
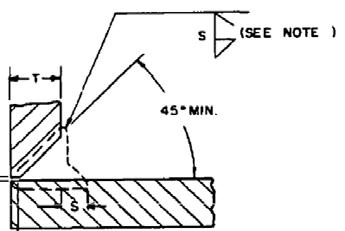
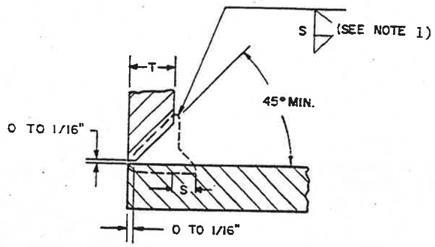
NOTE: Notice the profiles of the fillet reinforcements (S) both figures. S is what is being measured for the reinforcement.
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions
Term ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
Aligned Rounded Indication
Four or more indications in a line, where each is separated from the adjacent indication by less than 1/16 inch or D, whichever is greater, where D is the major diameter of the larger of the adjacent indications. Ambient Temperature A work piece is considered to have cooled to ambient temperature when it is cool enough to place a hand on the material (typically less than 125°F). Angular Misalignment The amount in degrees that two joint members (pipe or plate) are misaligned from a common plane.
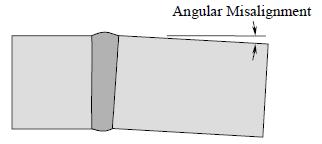
Arc Strikes Any localized heat affected zone or change in the surface contour of a finished weld or adjacent base metal resulting from an arc or heat generated by the passage of electrical energy between a finished surface and a current source. As-Welded The condition of a weld, after welding, without any surface modifications such as grinding.
Page 77 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
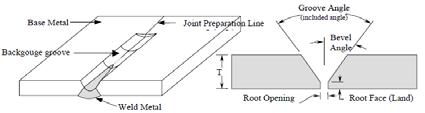
Back Gouge (back gouging) Back gouge is the preparation of the second side of full penetration welds welded from both sides to the extent necessary to permit proper deposition of weld metal and complete joint penetration.
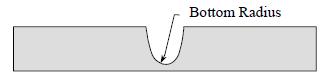
Bottom Radius Dimension representative of the bottom of an excavation.
Burn Through A void or open hole that extends through a backing ring or strip, fused root, or adjacent base metal resulting from fusion completely through a localized region. Buttering The deposition of surfacing metal on one or more surfaces to provide metallurgically compatible weld metal for the subsequent completion of the weld. Usually associated with dissimilar metal welds.
Centerline Crease or Shrinkage
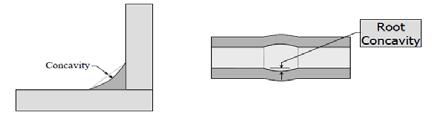
An intermittent or continuous peripheral centerline concavity formed on the root surface. Cladding The deposition or application of surfacing material usually to improve corrosion or heat resistance. Completed Weld Completion occurs when all weld metal has been deposited, required weld soaks are completed, preheat is removed, weld has cooled to ambient temperature, and the weld is ready for other nondestructive test (NDT) inspections. Concavity The maximum distance from the face of a concave fillet weld perpendicular to a line joining the weld toes. For pipe butt welds, concavity is a root contour condition.
Contour See weld contour.
Page 78 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
Convexity The maximum distance from the face of a convex fillet weld perpendicular to a line joining the weld toes. For pipe butt welds, convexity is a root contour condition.
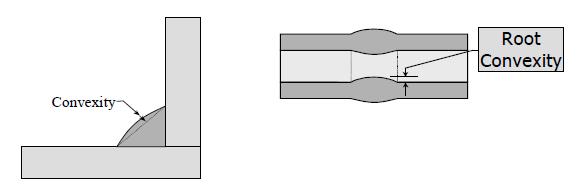
Corner Crack A crack occurring in weld metal in way of a temporary access snipe, a drain or vent opening, or at the intersection of three members. Crack A linear rupture of metal under stress. Crater Pit An approximately circular surface condition extending into the weld in an irregular manner, such as from the inside diameter surface of a fused root insert. If the depression appears to have more depth than diameter of the opening, or if you can’t determine if the opening has an end it is considered irregular. By contrast, a small depression that you can see the entire volume of the opening and has an obvious radius on the bottom is not irregular. Crevice A narrow opening between two pieces of metal in which liquids or particles can be trapped (e.g., backing straps, partial penetration welds, lap joints, etc.).
Defect
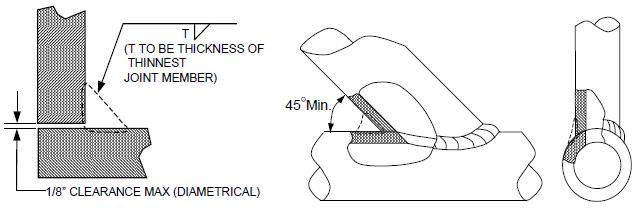
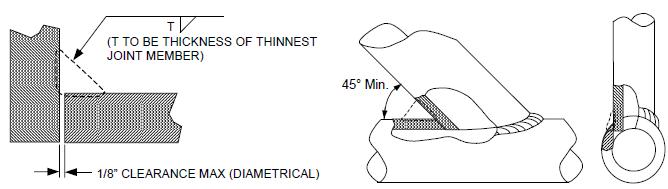
Design material Thickness (TM) A discontinuity or discontinuities that by nature or accumulated effect (for example total crack length) render a part or product unable to meet minimum applicable acceptance standards or specifications. The term designates rejectable condition. The nominal or average thickness of material of the strength member, exclusive of reinforcement or backing rings and strips, as follows: For groove welds, the TM shall be the groove depth including the root land thickness. For fillet, partial penetration and socket type welds, the TM shall be the nominal pipe wall thickness. For weld deposited pads, butter, cladding, hard-surfacing or wear-surfacing, the TM shall be the average height of the deposit thickness measured from the original base metal surface. For tapered welds, the TM shall be the average weld thickness. For base metal repairs, the TM shall be the maximum depth of repair exclusive of reinforcement.
Page 79 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
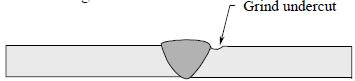
Discontinuity An interruption of the typical structure of a material that affects its mechanical, metallurgical, or physical characteristics (e.g., slag, spatter, porosity, etc.). A discontinuity is not necessarily a defect (rejectable). Dissimilar Metal Weld Welds between two metals that differ sufficiently in metallurgical and physical properties to require special consideration in welding qualification and inspection. Welds made by either direct joining of the dissimilar metals or by use of weld deposited buttering are considered dissimilar metal welds. End Melt A form of weld undercut at the end of welded members that are 1/4 inch thick or less. Face of Weld The exposed surface of a weld on the side from which welding was done. Fillet Weld A weld of approximately triangular cross section joining two surfaces approximately at right angles to each other in a lap joint, tee joint, or corner joint. Finished weld Finished weld is a weld which has received all required final inspections and has been accepted. Globules Ball or globe shaped metal formations commonly associated with melt through. Grind Undercut The resultant groove after grinding to fair weld undercut smoothly into the base metal.
Groove Angle The total included angle of the groove between pieces to be welded. Hardfacing Surfacing metal deposited to reduce wear. Heat Checks Fissures or tears in the weld heat affected zone of material containing low melting point alloying elements Incomplete Fusion Lack of complete fusion of some portion of the metal in a weld joint with adjacent metal. The adjacent metal may be either base metal or previously deposited weld metal, or consumable insert.
Incomplete Penetration
Lack of penetration through the thickness of the joint, or penetration which is less than specified. A portion of the weld preparation has been left in its original state. Indication Visual evidence that indicates a discontinuity may be present. For example, magnetic particles may align to form an indication during performance of magnetic particle inspection.
Page 80 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
Keyholing A rejectable condition that exists when the base metal overhangs on the side wall(s) of an excavation preventing accessibility for welding. Keyholing results from grinding or air carbon arc gouging.

Lamination A type of discontinuity with separation generally aligned parallel to the work surface of a metal.
Lap
Folding of metal on the surface of the forging, usually when some of the forging metal is squeezed out between the two dies. Layer A stratum of weld metal, consisting of one or more weld beads. The thickness of a layer shall not be greater than the thickness of a pass. See also weld layer or root layer. Leg (fillet weld) The distance from the joint root to the toe of the fillet weld.

Linear Indication An indication in which the length is equal to or greater than three times the width. Nominal Thickness That thickness specified on plans or drawings without application of any allowed tolerance.
Non-linear or Rounded Indication Indication whose length is less than three times its width.
Melt Through A convex or concave irregularity on the surface of a backing ring or strip, fused root, or adjacent base metal resulting from fusion completely through a localized region, but without development of a void or open hole.
Minimum Allowable Thickness For fit-up purposes, piping thickness not exceeding 10% below the nominal pipe thickness shall be acceptable. Thickness exceeding 10% below the nominal pipe thickness will have the minimum allowable thickness researched (notify the Welding Engineering Department for assistance) prior to acceptance.
Page 81 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
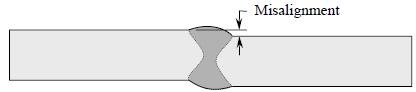
Misalignment The distance two members butted together are misaligned.
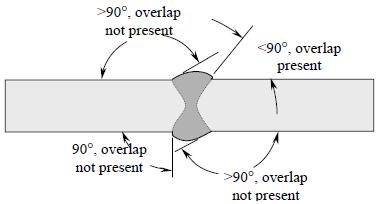
Overlap The protrusion of weld metal beyond the weld toe or weld root. The weld metal protrusion extends over the base material surface but is not fused to the base material. This condition occurs when the reentrant angle is less than 90°.
Oxidation A condition resulting from partial or complete lack of inert gas shielding of a surface which is heated during welding, resulting in the formation of oxide on the surface. This condition may range from slight oxidation evidenced by a multicolored or tightly adhering black film to the extreme of a very rough surface having a crystalline appearance. For purposes of this procedure, iridescent temper films and tightly adhering films are not considered oxidation. Pass A weld bead which extends the entire length of a longitudinal weld or a maximum of 360° of a circumferential or spiral weld. A pass may include several starts and stops. Peening The mechanical working of metals using impact blows to reduce distortion and stress. Porosity Gas pockets or voids in a weld or casting.
Page 82 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
P-1 System Class P-1 includes fabrication welds for design pressures exceeding 300 pounds per square inch or design temperatures exceeding 650°F, or both, and all piping systems for conveying oxygen, gasoline, and lethal gases or liquids regardless of pressure and temperature. This class also includes fabrication welds in piping systems which transmit oxygen, helium, mixed gases, air, water and exhaust of diving life support systems. Also included are any structural welds made to the internal or external surfaces of a fluid boundary subject to system pressure but which do not form a part of the fluid boundary. This includes any weld made to a weld deposit pad or cladding on the fluid boundary as well as the weld deposited pad or cladding beneath the weld itself. This does not include welds which join clips, nameplates, insulation supports, or other nonstructural members to the fluid boundary. P-2 System Class P-2 includes fabrication welds for design pressures and design temperatures not exceeding 300 pounds per square inch and 650°F. Also included are fabrication welds in all open ended vent, drain, and steam escape piping that has no isolation capability from its origin to its terminus regardless of the design temperature or pressure. Re-Entrant Angle The angle formed between the base plate and the toe of the weld.
Ridge Root (Razorback)
The formation of a relatively sharp circumferential ridge on the inside surface of a consumable insert or backing ring butt weld. Generally associated with NiCu, CuNi, and Inconel materials when there is less than optimum purge (e.g., moisture in purging gas) and is considered a form of oxidation. Root See “Weld Root”. Root Face (land) The portion of the groove face adjacent to the joint root. Root Layer The first layer of weld metal placed in a joint required to initially join the base materials. This may consist of one or more passes depending on the width of the root opening.
Root Notched Condition
A sharp surface irregularity in the weld or base material normally found in the root of insert or backing ring welds. The notch condition is a stress riser that could cause stress cracks. Root Opening A separation at the joint root between the work pieces.
Page 83 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
Root Surface Concavity A depression on the root surface of a weld which may be due to gravity, internal purge, or shrinkage.
Root Surface Convexity Reinforcement on the root surface of a weld.
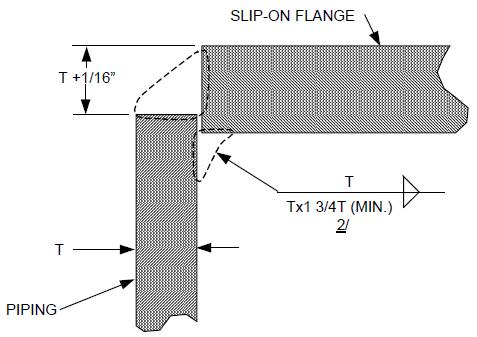
Root Undercut An intermittent or continuous groove on the internal surface of the base metal, or backing ring or strip at the fusion line between the base metal and backing. Sharp Irregularity A rejectable condition that exists when the angle formed between weld beads or weld ripples on the bead surface are less than 90°. Slag Non-metallic solid material entrapped between beads of weld metal or between weld metal and base metal or in a casting. Stress Riser Changes in contour or discontinuities in structure that cause local increases in stress (stress concentration point). T Unless otherwise specified herein or by the TWD, “T” (used alone) represents nominal thickness (TNOM). Another term used in conjunction with “T” is TMIN = minimum allowable thickness (min. wall), or minimum drawing or design thickness. Tack Welds Welds made to hold the parts of a weldment in proper alignment until the final welds are made.
Temporary Attachment Weld A weld made to attach a piece or pieces to a weldment or temporary use in handling, shipping, or working on a weldment.
Throat Thickness (fillet weld) The shortest distance from the face of the weld to the joint root of the weld.
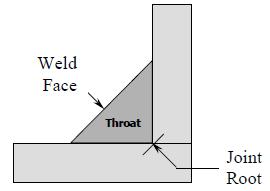
Undercut A groove melted into the base metal at the toe of the weld and left unfilled by weld metal. This is an as welded condition which can be removed by grinding. Underfill A condition in which the weld face extends below the adjacent surface of the base metal.

Page 84 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021
NIMS PIPE WELDING WORKMANSHIP & TRAINING GUIDE
Process Owner – QA
WI-Q-3030
Term
ENCLOSURE F – Welding Attribute Terms & Definitions Definition
Weld Bead An increment of a weld pass with one start and one stop. A weld bead may be a weld pass if it extends for the entire length of the joint or block length. Weld Buildup The deposition of filler material to restore base material or weld surface dimensions or to deposit a weld layer on the material surface of the joint prior to joining the material members together. Weld Contour The surface profile of a weld in the as-deposited condition or after mechanical preparation to meet workmanship or NDT requirements. Weld Contouring The deliberate shaping of weld surfaces for hydrodynamic or fatigue considerations, or as otherwise permitted in this procedure.
Weld Deposited Buttering Weld metal deposited on base metal prior to completing the weld to permit the final portion of a dissimilar metal weld to be completed as a similar metal weld.
Weld Deposited Hard Surfacing
Weld metal which is deposited for the purpose of providing wear resistance. Weld Deposited Overlay Cladding – Weld metal which is deposited for the purpose of corrosion protection only. Weld Distortion Warping of the base material due to welding and the associated heating and cooling.
Welded Fabrication or Weldment Any assembly where component parts are joined by welding.
Weld Layer A single stratum (layer) of weld metal consisting of one or more adjacent weld passes. The thickness of a layer shall not be greater than the thickness of a pass. Weld Pass A weld bead extending the entire length or block of a longitudinal weld or a maximum of 360° of a circumferential or spiral weld. A weld pass may include several starts and stops. Weld Reinforcement Weld metal in excess of the quantity required to fill a joint. Weld Root The points, shown in a cross section, at which the root surface intersects the base metal surfaces. Weld Spatter Material particles which deposit on the surface of the weld or adjacent base metal during welding and which do not form a part of the weld. Weld Toe The junction of the weld face and the base metal. Workmanship Samples Samples (actual or replications), photos, or other visual aids used to evaluate conditions. Wrap Weld applied to seal-off a fillet weld at the end of a member (flat bar, angle, channel, or tee). Wrought Material Pipes, bars, plates, forgings and extrusions.
Page 85 of 115 Revision 4/7/2021