THESIS PHASE

HOUSING IN TOD ZONES : CASE OF BHOPAL





INTRODUCTION
• Cities are dynamic in nature. Current level of urbanisation in cities necessitates the development of physical, institutional, social, and economic factors in a coordinated and planned manner. TOD helps in redirecting the growth.

• Housing is a critical component. The aim of building large and diverse real estate projects near transit stations is to create a critical mass of destinations, that can be accessed by transit.
• Aim- The major aim of this study is to propose appropriate housing typology for residential land uses within the influence zone of Transit Oriented Development in preferred area of Bhopal city.
Scope and Limitations


1. The study will concentrate on housing as an important component of TOD, with an emphasis on the infrastructure that goes along with it
2. While there are many factors that influence housing, this study will focus on social criteria rather than economic ones.
Understanding concepts of TOD and how Housing is incorporated in it.
OBJECTIVES

To understand land use pattern of Bhopal and TOD zone and its potential Proposal for developing Housing typology on land as per demand.
Need of Study
Transportation has long been regarded as a vital link connecting all elements of life around the world because it links social, economic and environmental parameters.
Cities expand outwards. When housing density is increased within transit zones, this expansion is contracted.TOD areas are preferred locations for housing
Housing TOD
Obj1
Understanding concepts of Smart city and TOD as a trend to influence the cities for better growth.
Smart cities concept evolution from literature studies
Literature study about TOD Policies and guidelines
Smart city and TOD need and significance in national and global scenario.
1 REVIEW
To understand how Housing is related and is incorporated as an important component in both of these concepts.
Housing inTOD zone of a City
Literature studies related to Housing and Smart cities
Components in TOD catchment
Obj 2 Integration of Smart city, TOD and Housing
Case studies of Global and Indian cities Obj 3
Understanding Parameters required for Housing in a TOD catchment
Inferences from case study
Identification of case Area
Housing and associated infrastructure as component of TOD. Built environment and its characteristics in TOD zones
Commercia
Affordable residential,
Residential Commercial Community
Comme
Affordab
Objective 1
Studying the Case Area in context of TOD.
METHODOLOGY
Objective 2
Identifying Housing Typology with respect to Housing demand
Study of Case City and its features Identification of TOD zone and its Potential
Land inventory
To know the needs and requirement , Issues and challenges in study area
The study will be based on both Primary and Secondary data sources and case studies.
A literature study is done for understanding the factors required for housing within TOD zones
A million plus city Bhopal is selected and its potential in terms of TOD will be understood.
Housing demand study for TOD zone
Suitable land for housing demand near work center
Perception of Stakeholders and Users
Housing typologies feasible for TOD zone as per housing demand.
Corridors with development opportunities will be identified by looking at transportation routes.
Vacant land will be identified, and land inventory will be prepared.
Demand in terms of preferred Housing typologies will be known by doing primary survey.
Objective 3
Proposal of suitable Housing within TOD Zone. .
By identifying land and proposing suitable typologies for land.
Proposal for Housing and amenities by knowing people's preferences. .
Proposal for suitable housing typology will be given with other attributes like Density, FAR, Height etc.
BACKGROUND
Calthorpe (1993) lists the key components of TOD as follows:
• Growth organized on a regional level to be compact and transit-supportive
• Commercial, housing, jobs parks, and civic uses within walking distance.
• Pedestrian-friendly street networks connects local destinations
A mix of housing types, densities, and costs
Preservation of sensitive habitat, riparian zones, and high-quality open space
Public spaces become the focus of building orientation and neighbourhood activity
Additionally,Transit Oriented Development Institute adds the following to that list
Walk-able design with pedestrian as the highest priority
Transit station as prominent feature of town centre
UNDERSTANDING
Nodes with mixture of activities around them.
Pedestrian-friendly street networks that directly connect local destinations
High density walk-able neighbourhoods (10 min walking distance)
Design to include easy use for bicycles as daily transport
Reduced and managed parking within 10 min circle
AREA OF INFLUENCE
As per National TOD Policy -500-800 Meters
MP TOD Policy draft which has been approved for Bhopal the influence zone is up to 1000m
In BDP 2031 draft the TOD zone is defines taking the radius of 500m

WHY TOD?
• Rising fuel prices, pollution, congestion, urbanization etc contributed to its development.
• Transport and Housing are large expenditures. If housing is present near transit, the money saved by people can be used for other purposes.
• Housing is truly affordable if (Housing +services) is affordable (ITDP)
• Housing near TOD increases accessibility to essential services including employment.
• Use of NMT and walk-ability helps in reducing pollution and creates a healthy environment.
• TOD aims to discourage private vehicles users leaving more space on roads.
• Concentrating development by providing high density helps in making compact cities leaving space for green and agricultural areas.
TOD PRACTICES IN INDIA


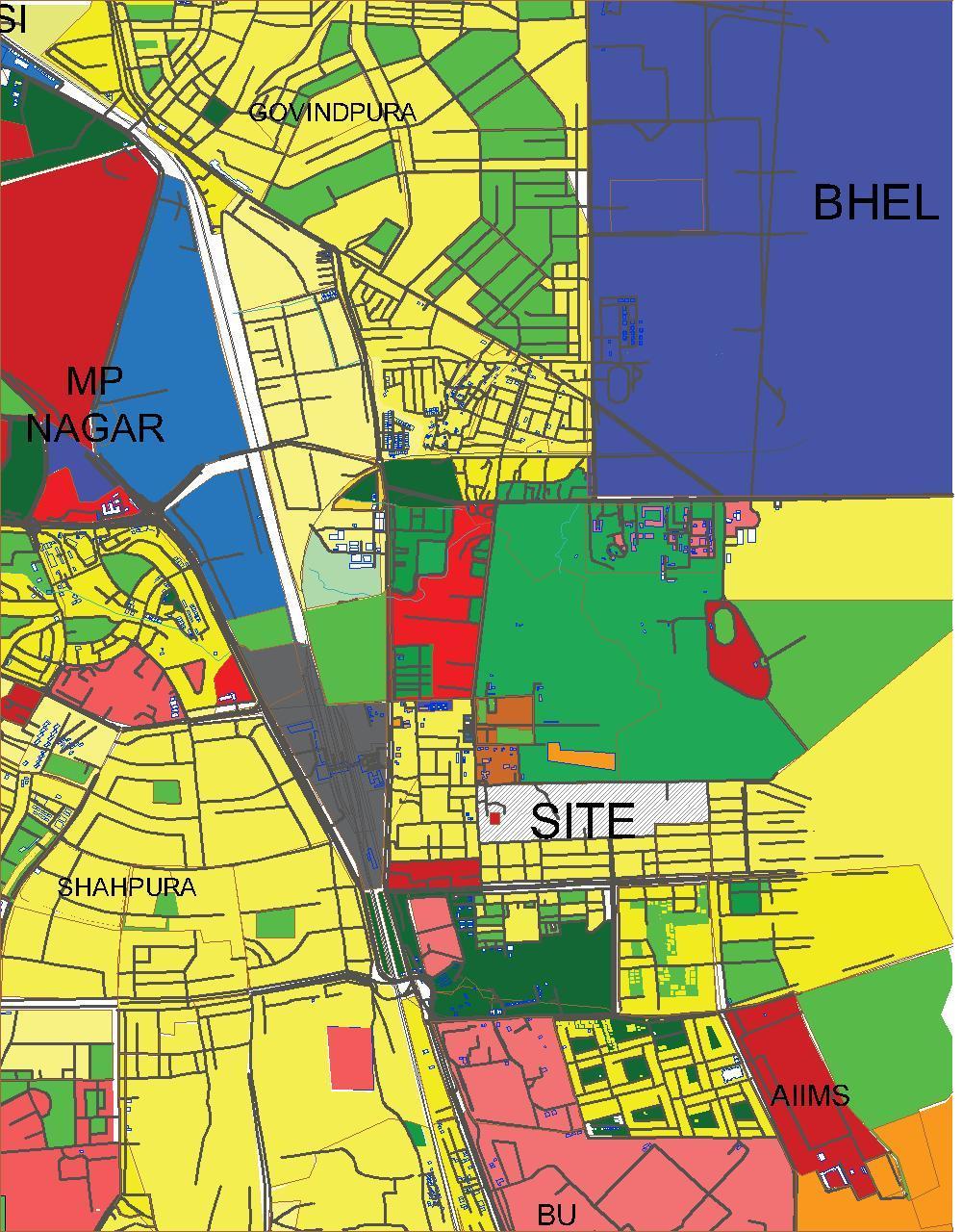
CASE AREA
BHOPAL- A MILLION PLUS CITY
ABOUT BHOPAL
• These are major urban centers of the country and are contributing to fast population growth which necessitates TOD


• Bhopal, the capital city of MP is an emerging metropolis of central India. Population of Bhopal is nearly 1.79 million in 2011 and is poised to 3.1 million in 2030 (Census of India Madhya Pradesh 2011).
Source- (Tiwari & Mishra, 2019)
• 2nd most populated city of MP. Urbanization is increasing since 3 decades.
• Activities coming up in cities have impacted the development pattern. Built up has increased drastically in last few decades which have consumed the land of city
NEED FOR TOD IN BHOPAL
• Developed Industrial infrastructure. It has major industrial areas in connection like Mandideep and Govindpura.
• The city has many small and medium scale companies. HEG, various Laboratories, Eicher Tractor, Action Group of Company, BHEL etc
• The city house many educational institutes of national importance.
• Growing mostly in South East direction.
- (Tiwari & Mishra, 2019)
• Work-participation rate was 34.2 percent which is 4.6 percent higher than previous decade i.e. 29.6% (2011 census)
Bhopal has a well-established BRT system, 44% of the work trips are made by public transport (Khare, 2021)
Presently around 40,000-45,000 passengers per day travel in MyBus on BRT corridors (Srivastava, 2017)
Housing – Shortage of 1.02lakhs Dus
• Residential Real estate market is significant. Market grew around 1.80% in Q1FY2015
Potential TOD Users
•NHB Index, Bhopal has shown the 2nd best growth, driven partly by the RE development. (TOI)
It is necessary to take advantage of the land value potential near BRT & Metro stations.
CASE OF BHOPAL

Bhopal Master Plan 2005

The BDP 2005, implemented on 9th June 1995 it included the area of BMC and contiguous 146 villages, with an area of 601.06 Sq. Km. as the planning area.
Differential densities were specified for city with higher density areas proposed around the existing and the proposed work centres


The plan had also proposed Mass Rapid Transit System connecting major work centres, and traffic generating zones of the city
It also recommends variable FSIs based on site context.
IN MASTER PLANS
Bhopal Master Plan 2031 (Draft)
Proposed planning area for the BDP 2031 is 1,016.9 sq kms,.
Revenue generation through premium FAR and saving through TDR generation.
It would enhance mixed use development, specifically in MP Nagar, New Market, Karond and Misrod.
The CDP is also based on TOD whereby areas along BRTS and Metro rail development would benefit from additional Floor Area Ratio (FAR)
mptownplan.gov.in
REVIEW
TRANSIT REVIEW




Transit Review
MRTS (Under Construction)
Bhopal Metro or Bhoj Metro project with 2 lines & 28 stations is an under construction mass rapid transit system (MRTS)
6 metro lines criss-crossing the city out of which 2 lines (line 2 & 6) have been selected for implementation in Phase 1


-MPMRCLB
the phase 1 metro corridor
selected as suitable
CORRIDOR WITH DEVELOPMENT POTENTIALS

MACRO LEVEL SURVEY RESULTS






MACRO LEVEL
QUESTION OUTCOME



People want to live in high rise while it is not a trend
INFERENCES FROM MACRO SURVEY
• Hoshangabad road is most preferred & frequently accessed corridor.
• Most people access it two to five times a week: For work.
• Trend is changing in Bhopal; People want to live in high rise buildings in Apartments.
• While independent bungalow is preferred by most of the people yet people can live in apartments if the amenities are in proximity i.e. Proximity to services is important.
• Open spaces and greenery are liked by the people near their homes.
• Connectivity, infrastructure, budget, presence of employment centre near to the residences and budget are four major things that people look for while buying the house; Connectivity adds value
DATE-
POTENTIAL CORRIDOR










 Pul
Pul
CORRIDOR LEVEL SURVEY ANALYSIS






CORRIDOR LEVEL SURVEY ANALYSIS
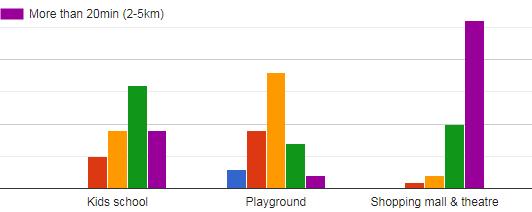
graph shows the preferred distance of the amenities present near to their houses..





INFERENCES FROM MICRO SURVEY
• Most of the working population along the corridor is in age range of 20-40 years.
• People are ready to live in a mixed-use neighborhood. Mixed use should be promoted, and it should have activities that are liked by the people.
• People want to live in high rise buildings which is not a trend in Bhopal city hence High rise should be promoted.
• Flats are preferable option if amenities are provided nearby. Moreover, flats are affordable than detached or semidetached houses. 2 and 3bhk is most demanded type of accommodation.
• Most of the people can change their mode of transport to public transport. Metro and bus stop should be easily accessible from the houses
DATE-
ANALYSIS FOR PREFERRED DISTANCE OF AMENITIES
SITE IDENTIFICATION
POTENTIAL SITES ALONG THE CORRIDOR

Factors
CRITERIA FOR SITE SELECTION
Score
Connectivity (Distance) Transit stops 200-500m 500-1000m 1000-1500m 1500-2000m 2000-2500m Activity zone 500-1500m 1500-2500m 2500-3500m 3500-4500m 4500-5500m
Accessibility (Ease of access)
Density (Potent1al of
To quality public spaces Extremely accessible Very accessible Moderately accessible Slightly accessible Least accessible School 500-1000m 1000-1500m 1500-2000m 2000-2500m 2500-3000m College 500-1000m 1000-1500m 1500-2000m 2000-2500m 2500-3000m Hospital 500-1000m 1000-1500m 1500-2000m 2000-2500m 2500-3000m Public areas 500-1000m 1000-1500m 1500-2000m 2000-2500m 2500-3000m
for
Likert scale
SITE

ANALYSISL



Connectivity Accessibility Density Ecology Total Score Distance to Distance to Development Density in nearby neighbourhood
Surrounding features (Lake, barren land, agricultural land, etc)Bus stop Metro Railway Stn Major activity center (MP Ngr)
Education School<2km College<5km
Nearest Hospital (2-5km)
Public areas (500-2km Quality public spaces
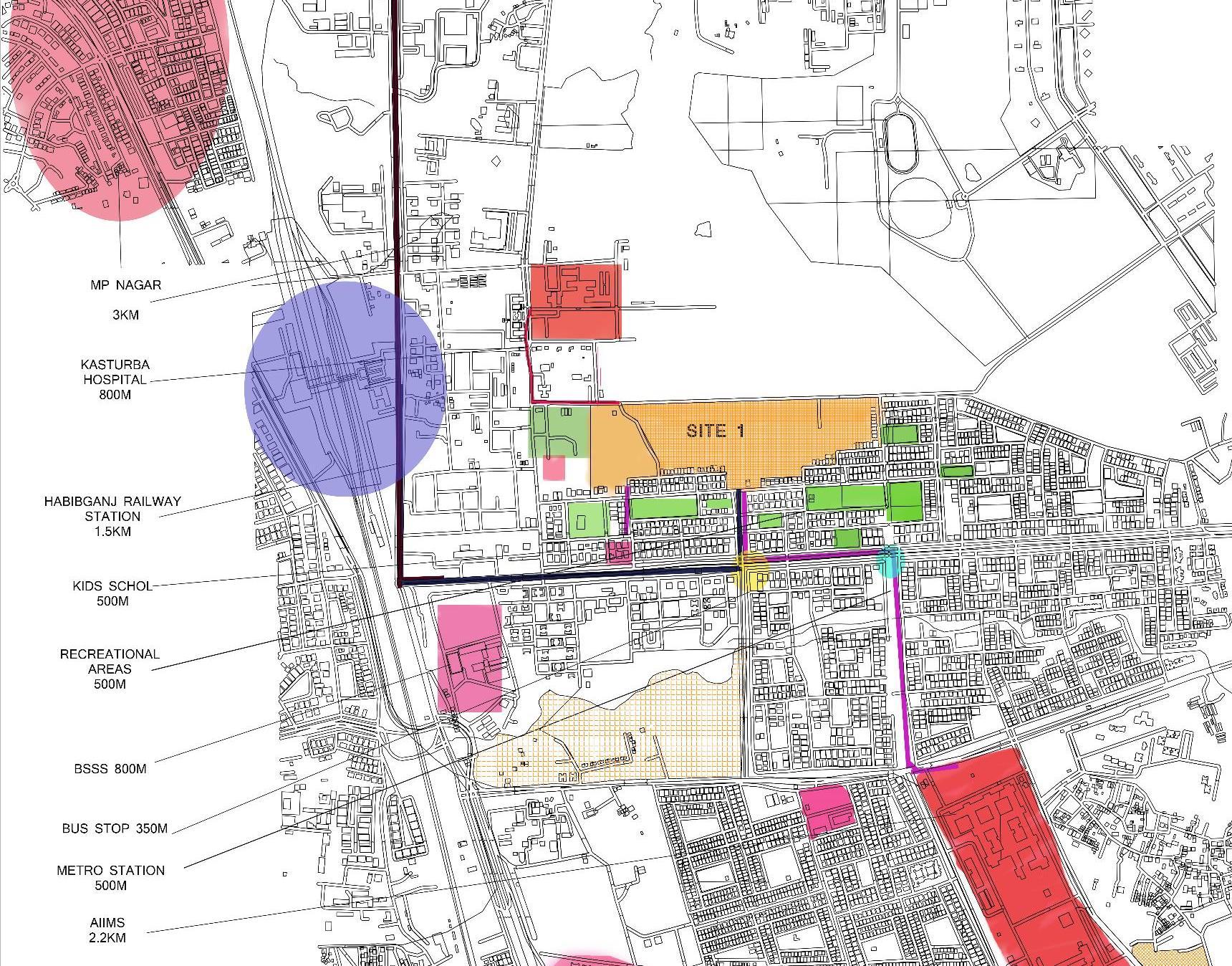
SITE 1 (35 ac) 350m 500m 1.5km 3km 500m (Kids scls) 800m (Hbgnj) Aiims (2.2km)
2 (40 ac)
(8.5 ac)
500m Shakti nagar public areas
Extremely accessible 17 DU/ac Site is adjacent to shakti nagar on one side while greenery on the other. 800m (BSSS)
2.5km 3km 1.1 km (SPS) 1.5km (AIIMS) 2km (MD sports complex)
Moderately accessible 7DU/ac None, Site is in Railway colony with settled areas nearby1.2Km (BSSS)
1 29
3.5km 5km 1.4km (SPS) 500m (AIIMS) 600m NRI complex
Very Accessible 14DU/acre Agricultural land, slums are surrounding the site. 4km (BU)
PROPOSAL
Details of Apartments
Details of Plots
DETAILS
Service
Cost of
Sq.ft
Sq.ft
Cost of
Cost of
Cost of
Park
Lumpsum
space Lumpsum
of
Nursery school -3 @1/2500p, Primary school-2 @ 1/5000p Lumpsum
@1/15000
Sq.ft
Sq.ft 4.30sqft/p as per URDPFI
Sq.ft Area 8611sqft/ nursery, 4305sqft/primary 800sqm, 400sqm
Sq.ft 0.8Ha


PATHWAYS AND OTHER AMENITIES

COSTING OF UNITS
Apartmen
t details
Area of land sellable land total on GF
Area of land unsellable land (Land area*70%)/30 %
Land area for calculating unit cost
Cost of land 3750/sqft
A ) Cost of land shared by I unit (Cost/No of units type)
B) Cost of services, contingencies, amenities etc, excluding cost of construction (3%)
C) Cost of construction (1600/sqft) Buili up of one unit*Cost
Total cost of 1 unit A+B+C Profit %AGE Profit amount Selling price of a unit
2BHK 1,03,414.27 241299.9575 3,44,714.23 1230629783 1337641.069 198911.02 1619850.9 3156403 30 946920.8966 4103323.89
1BHK 62,048.56 144779.9745 206828.535 738377870 1122154.818 198911.02 1206877.959 2527943.8 40 1011177.518 3539121.31
3BHK 41365.707 96519.983 137885.69 492251913 1953380.608 198911.02 2086639.41 4238931 40 1695572.415 5934503.45
Plots Area of sellable land Land area for calculation plot cost
A- Cost of the land (3750/sqft)
B- Cost of services, contingencies, amenities etc, excluding cost of const (3%)
C- Cost of construction (1800/sqft) Total cost per unit (A+B+C) Profit %AGE Profit amount Selling price of a unit
2425500 51,23,411 25 1280852.76 64,04,264
2728687.5 57,38,974 25 1434743.38 71,73,717
7207200 1,48,31,711 20 2966342.2 1,77,98,053
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Contents Area Units Selling price Built up area in Sq.ft
Land area
Cost of development(Transformer (2), Palar water)
Contigency cost
Total cost of development of other services
Total cost of Amenities
Sq.ft
Hect Cost of land
Sq.ft
Lumpsum
Lumpsum Total Builtup area
Sq.ft Cost of construction for plots
Sq.ft
Sq.ft Cost of construction for Apartment
Total number of dwelling units in plots
Total number of dwelling units in apartments
Total number of dwelling units
units Cost of 2BHK Apartment
Cost of 1BHK Apartment
Cost of 3BHK Apartment
Cost of plot (Least)
Cost of plot (Middle value)
Cost of plot (highest)
Permissible FAR
profit from all
percentage
Sq.ft
Sq.ft
Sq.ft
Sq.ft
Sq.ft
Sq.ft
41,03,323.89
35,39,121.31
59,34,503.45
64,04,263.78
1,77,98,053.22
CONCLUSIONS
• Bhopal is a rapidly growing city . There are many opportunities of development as metro is under construction and real estate market has been revived.
• TOD is not just development around transit. It’s a development with opportunities. Rich mix of activities is essential.
• TOD is successful where transit users are in plenty. and established transport system is available. Case study
• Housing is critical, Housing near transit saves money. People use transit more (Study)
• TOD areas can be made socially equitable and inclusive through certain steps. Provisions of LIG housing and spaces for informal sectors.
• Successful Housing is one that fulfill the needs of every kind of residents.
CONCLUSIONS
Housing should give equal opportunities for everyone.
Proposed Housing development is within 800m from transit stops
• The layout has been proposed following the DCRs,TOD principles and keeping in view the preferences of people
As people wanted ample green spaces It is designed with larger ratio to open areas to club the residences with sprawling green open areas and enticing Parks.
Principles of TOD consisted in project are-
Density- Should be planned for maximum density.
Diversity- Diverse sizes of units and diverse range of amenities.
Distance – Proximity to services. Primary survey should be done to know the preference of people.
CONCLUSIONS
• Accessibility- Fast and reliable transport is critical. Accessible by people.
• Walk-ability and Pedestrian friendliness- Knowing the walking preferences of people. Green areas are liked by people, both small and big to be provided. Street network should be safe and pedestrian friendly. 90* turns without obstructions.
• TOD housing is different in terms of infrastructure, transport availability, density, walkability and pedestrian friendliness.
• Some Recommendations-
• Socio economic study should be done prior to planning at city and locality level.To know its potential
• Corridor should be marked =, High density and high rise should be promoted.
• Strict norms like large scale mixed use or commercial should be along corridor only.
• Non residential activities should be permitted effectively on Residential premises considering needs , Environmental impacts and safety of people.
CONCLUSIONS
• Mixed land uses and their quantum of distribution within planning area should be clearly enmarked
• FAR in non-TOD zones should be reduced and increased in TOD areas. Development fees relaxation for TOD zones.
• Street network is important in any development around transit. Enhancement of public spaces should be done.
• FAR may vary depending on available infrastructure land use zoning, transit efficiency etc. But it should be higher in areas where all mentioned things are available.
Building much of activities around transit corridor like commercial, institutional, residential, public areas will concentrate the development within influence zone of transit. TOD is vast development. Future study can touch other aspects which relates to housing and infrastructure.
REFERENCES
• UTTIPEC. "Transit Oriented Development,TOD." UTTIPEC website. December 2012. http://uttipec.nic.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/5925889094.pdf (accessed October 9, 2021).
• The Next American Metropolis: Ecology, Community, and the American Dream. Los Anegeles: Princeton: Princeton Architectural Press, 1993
• Bhopal development plan 2005 retrieved from mptncp.gov.in
• Bhopal development plan 2031 draft retrieved from mptncp.gov.in
• Chatman, D. G. (2013). Does TOD Need the T? On the Importance of Factors Other Than Rail Access. Journal of the American Planning Association , 17-31, DOI: 10.1080/01944363.2013.791008.
• CMP. (2012). City Mobility Plan . Bhopal.
DATE- 12/05/2022
