DISTRICT SKILL DEVELOPMENT







The District Administration, Koraput has initiated a “Skill Gap Assessment” to establish “District level Skill Development Action Plans for Odisha”. The study aims to identify sources of wage employment and self employment (including entrepreneurship) in the district of Koraput, estimate the sector-wise current and future workforce demand assess the overall labour supply, and estimate the existing and emerging skill gaps. This study was designed for the district of Koraput in a manner to offer insights into:
Which skills are required to support the State’s economic growth, while also responding to the career aspirations of the youth?
How to design appropriate interventions that will enable active collaboration between various stakeholders for the common good
Training Service Providers: A total of 4 training institutions were interviewed (Training Providers, ITI and RSETI) to understand the training needs and demand for the trades offered in these institutions.
Employer survey: A quantitative survey covering 30 employers with adequate representation from Large, Medium, Small and Micro Industries across the key sectors defining the district economy.
Focus- Group Discussions & stakeholder consultations across a wide group of stakeholders including, representatives from Industrial units (with additional focus on Micro entrepreneurs including the Nano Unicorns), Self Help Groups, District level Industry Associations across priority sectors, officials from various Government departments, representatives from various higher education institutions, & training service providers.
This DSDP will give an insight in the skilling ecosystem in Koraput with the future estimation of requirements. Maximum data has beentaken through primary sources and the fieldwork carried out by the DSC team. All the sources of information that are collected from secondary sources are cited in the Bibliography section of this report. Koraput District has used the principle of Decentralization to prepare this plan. By going through the report one may come across the following:
District has an amalgamation of Rural Urban population which gives the diversity in population & demographic dividend to achieve the vision of our Hon. Prime Minister of “Atmanirbhar Bharat”.
District is equipped with all necessary infrastructure for potential growth and it has the capacity as well as the capability to become the growth engine of Odisha State.
As Agriculture is the backbone of our country, the District also considers Agriculture as an important factor which needs to be focused on to increase the GDP of our Country. Youth in this district is not ready to migrate allows for our district to channelize the youths in advanced agricultural activities.
When we talk about skilling, Koraput has repeatedly made efforts for the inclusion of tribal. This can be viewed from the information provided in the report.
Sector wise power requirement has been estimated in this plan which is the result of various stakeholders’ interactions
This report gives a rough figure of our targeted people for skilling activities and this population will help the district to bridge up the gap between the demand and supply. Reverse migration that has took place due to Covid 19 Pandemic has raised a challenge for the district to meet up the demand.
SWOT analysis of each Taluka is shown in the report following with that of the District.
Supply
5 Trades
5 Trades
low in supply
5 Trades which are high in supply
5 Trades which are low
4 Action Plan
5 initiatives for district skilling
Projects
Counselling
Project
high
high
low
High School Students
Figure
Figure
Figure
Figure
Figure
Figure
Figure
of
Population Growth
Population
Age
Literacy Rate of
Contribution to
Figure 8 per Capita Income
Figure
Participation of the Workforce
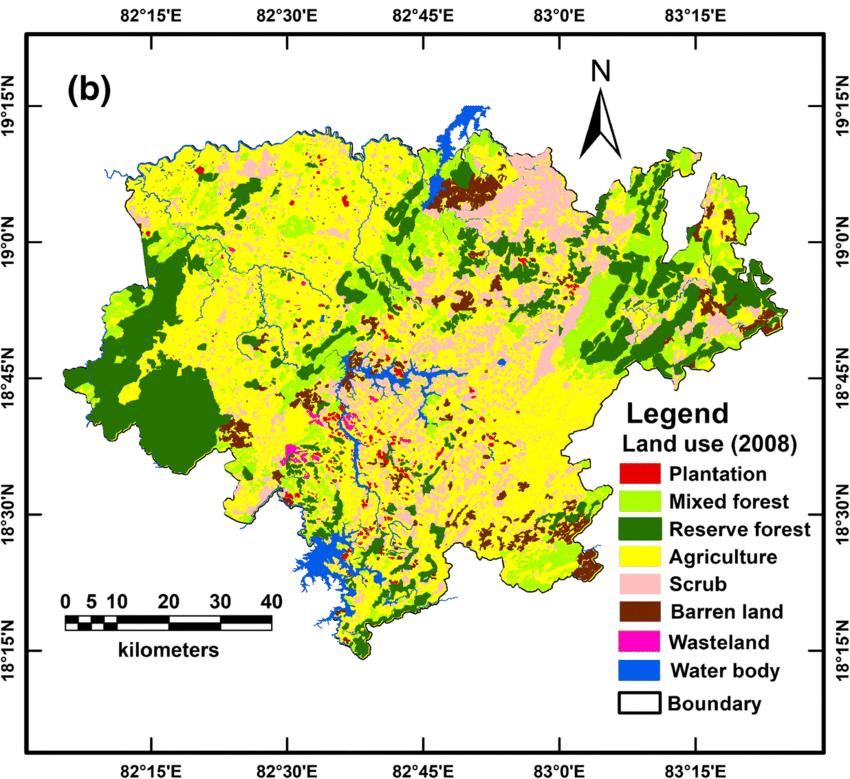
Figure 10 Land use Distribution Map of
Figure
Segregations of Land use in
Figure 12 Irrigation Status of Koraput
Figure 13 Design Concepts for Kotpad
Figure 14 Growth Rate of Wages/ Day and LABOUR
Figure 15 Koraput Coffee Brand
Figure 16 Productivity Rate vs Retail Price
Figure 17 Market Linkages for Coffee Beans
Figure 18 Industry Presence vs Hiring Rate
Figure 19 Sectors in Self employment
Figure 20 Dropout Analysis for Schools
Table 1 District At a Glance
Table 2 Block Information of Koraput
in the Coffee Industry
Table 3 Demography Data of Koraput........................................................................................
Table 4 Literacy data of Koraput
Table 6 Irrigation and rainfall
Table 7 Agriculture & Horticulture Production
Table 8 Horticulture
Table 9 Fishery Production
Table 10 Skill Development Training under
Table
Table
Table
Table
Animal Husbandry
Agro-allied
In-demand
MSMEs
Table 15 Job roles required for
Table
Job Roles required
Table 17 Industry Associations in Koraput
Table 18 Servicing Enterprises
Table 19 Target Population Profile of Koraput
Table
Mapping Current Infrastructure
Table 21 Education Infrastructure of Koraput
Table 22 Enrollment Data for Schools
Table 23 Block wise list of Govt. & Pvt.
Table
Table
Table
Table
Table
I.T.I.s Institutes present in Koraput
Trade wise of I.T.I.s
Graduation and Post Graduation
List Skill Hubs of Koraput
Social Category Analysis
Table 29 Sector wise Analysis
Year 2020 23) 29
Table 30 Details of Training Center 30
Table 31 Niti Aayog Skill Parameters 31
Table 32 Inclusion of SC, ST and Women candidates in Trades 31
Table 33 District SWOT Analysis 32
Table 34 Skill Training SWOT 33
Table 35 Potential Employment Scenario 35
Table 36 Training done on Entrepreneurship 35
Table 37 Emerging sectors for the year 2021 25 36
Table 39 Migration Analysis of District 36
Table 40 Skilling Analysis for Migrants 37
Table 41 Analysis of Current Skill Development in District 39
Table 42 Top 5 Trades which are high in supply but low in demand 39
Table 43 Top 5 Trades which are low in supply but high in demand 39
Table 44 Top 5 Trades which are high in supply and high in demand 39
Table 45 Top 5 Trades which are low in supply and low in demand 40
Table 46 RPL Plan 40
Table 47 Top 5 Initiatives for Skilling.........................................................................................41
Table 48 Estimated cost for the above action
Koraput district is located in the southern part of Odisha. In 1936 Koraput district came into formation. It is surrounded by forests and hilly ranges and is located in Eastern Ghats Highland and South Eastern Ghats Agro climatic zones. In the territorial aspect, on the eastern side, Andhra Pradesh is located and on its western side Chhattisgarh, similarly in the northern side Nabarangpur and Rayagada districts and on the southern side Malkangiri districts are located respectively. The district headquarters are situated in Koraput Town. The geographical area of Koraput is 8807 sqkm. As per the 2011 census the district has a population of 13, 79,647. The population density is 160 people per sq. km.
Figure 1 Location of Koraput district in Odisha Map
Source: Comprehensive District Annual Plan, Koraput 2020 21
Koraput is rich in terms of minerals. Bauxite is a major mineral we can find here. Other minerals like Black Granite, Red Ocher, Granite, Quartz, Limestone, Dolomite, Clay and Mica are also found in Koraput. Therefore Large scale Industries like NALCO, Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd, Ballarpur Industries Ltd and Toshali Cement Pvt, etc. here boosting the economy. These industries export items such as Alumina, Aero Engines, Portland cement and Packing Paper etc. But despite this, people depend on agriculture as their main source of livelihood.
Paddy, Vegetables, Ragi, Pulses, Maize and Sugarcane are the major crops that are grown here. Koraput is famous for its Coffee, Lemon Grass essential oil and other spices. These items are not only famous in Odisha but also have a worldwide demand. The climate in Koraput is warm & humid during April and May and cold from October to February. The monsoon breaks during June. The average annual rainfall of the district is 1794.0 m.m. Koraput is a well known tourist place for people as it is full of natural beauty. It is surrounded by miles of greenery, mountains and valleys. Some of the famous tourist places are Kolab, Sabar Srikhetra, Gupteshwar, Deomali, Machhkunda, Kechela, Jolaput, Dumuriput, Nandapur, Balda caves, Onukadelli, etc.
Population Headquarters Area
Koraput Town 8807 sq. km.
District
Tahsils
Municipality
Villages
Assembly Constituencies
Gram Panchayat
Panchayat Samiti
NAC
Tourist places
Industrial area
Major crops
Rivers / Dams
Ratio Literacy
49.21%
Gupteswar Temple, Sabara Srikhetra, Duduma Waterfall, Kolab Dam, Deomali
- MSME Major: NALCO, HAL, SEWA (BILT) & Toshali Cement
Tobacco, Potato, Banana, Chili, Coffee, Ginger Paddy, Vegetables, Ragi, Pulses, Maize And Sugarcane
Kolab Dam
ODOP Product(s)
the district/ GITag Products for the district
Glance
Spices, Coffee, Kotpad Handloom
District Annual Plan, Koraput
Population of Koraput has grown significantly at a rate of 17%. In the year 2001 02, the population was 11.8lk whereas according to the 2011-12 census it is 13.8lk, numbers have gone significantly higher in recent numbers due to growing urbanization and migration. Of the total population of 13, 79,647 around 2, 26,169 people lives in urban area which is 16.39% which
close to state statistics i.e. 16.69%. Koraput is the 7th urbanized district in the state. Whereas around 11.53lk people still live in rural areas. An Increase in population results in the available potential workforce which will lead to the district economy in near future.
Figure 2 Population Growth Rate
Code
Name
Female
3 Population Distribution


Code Block Version Block Name
English) (In English)
3205
3211
Bandhugaon
Boipariguda
3200 Boriguma
3202 Dasmantpur
3209
KORAPUT
Jeypore
3207 Koraput
3199 Kotpad
3210 Kundra
3213
3203
3214
3204
3218
3215
2 Block Information of Koraput
Lamtaput
Laxmipur
Nandapur
Narayanpatna
Pottangi
Semiliguda
median age of the Koraput population is 24 years which is relatively young. The workforce will increase productivity resulting in high growth in district potential output. The administration and industries must invest in the skill development of the youth by providing appropriate & demanding skill training. The economic potential output of a district depends on 3 major factors i.e. Human Capital, Physical Capital and Technology. Urbanization of the district is below the state average. By providing proper skill training we can invest in Human capital, but Physical Capital and Technology grow with the increasing urbanization.
Attributes
2011 Expected Growth Rate
Total No. of Blocks 14
Total No. of Gram Panchayats 240
Total No. Villages 2042
Total HH 3,36,200
Total Deprived HH1 250
Expected Population (2020-21)
Total Population 13, 79,647 16.86% 16,12,255
Total Male Population 6,78,809 14.91% 7,80,019
Total Female Population 7,00,838 18.81% 8,32,665
Total Population 0 6 2,25,126
Total Male 0 6 1,13,742
Total Female 0 – 6 1,11,384
Total Population - Scheduled Castes 1,96,540
Male - Scheduled Castes 96,789
Female Scheduled Castes 99,751
Total Scheduled Tribe 697,583
Male - Scheduled Tribe 3,37,373
Female Scheduled Tribe 3,60,210
Decadal Population Growth 16.86%
Population Density 157
3 Demography Data of Koraput
Source: District Census Book, Koraput 2011
4 Caste wise distribution
Age Distribution
is majorly a tribal district with Bondas and Gadabas who still lives here and follows their rituals to this day. The Government of Odisha has launched many schemes targeting the tribal population such as the Integrated Tribal Development Agency (ITDA).
Koraput is ranked among the bottom 5 districts in Odisha in terms of education. The average literacy rate of the district is approximately 49% Gender-wise male and female literacies are 61.30% & 35.72% respectively. Due to the lack of urbanization and many inhabitant villages we observed a low literacy rate. Hence tribal majority blocks are Bandhugaon, Pottangi and Dasamantapur have a literacy rate is in between 19.25% to 22%. Compared to semi-urban areas like Jeypore, Koraput & Damanjodi where the literacy rate is 35% to 96%.
No. Attributes Total Male Female
01 Literate Population All 5,68,090 3,40,843 2,27,247
02 Literacy Rate All 49.21% 60.32% 38.55%
03 Literate people SC 86,321 51,969 34,352
04 Literacy rate SC 35.43% 48.52% 22.45%
05 Literacy people – ST 2,02,341 1,26,799 75,542
06 Literacy rate ST 18.68% 29.25% 8.38%
Table 4 Literacy data of Koraput
70.00%
60.00%
50.00%
40.00%
30.00%
20.00%
10.00%
Source: Comprehensive District Annual Plan, Koraput 2020 21
60.32% 48.52% 29.25%
Male Female
38.55% 22.45% 8.38% 0.00%
Total SC ST
Figure 6 Literacy Rate of Koraput





Source: Comprehensive District Annual Plan, Koraput 2020 21
Koraput features among the most poverty struck districts, in terms of economic progress and contribution to State GDP. The total Gross Value Added by all sectors of the economy, in 2015 16, was INR 8.9 Thousand Crores, estimated at 2011 12 prices. In terms of sectorial allocations, the industries and services to the chart with 39% each in 2007. There is a growth in the contribution of industries and a steady decline in the contribution of agriculture. If one looks at the
sectoral distribution of the district’s economy and that of the state, one can find two notable differences – the contribution of the agriculture & allied sectors and the mining sector to their respective economies.
Agriculture & allied, 23.5
Utility, 4.3
87,600
Manufacturing, 17.7
Service sector, 34.5
Mining sector, 4.3 Construction, 15.6
87,400
87,200
87,000
86,800
86,600
86,745
87,367 86,400
Koraput State
Figure 7 Contribution to GDP Figure 8 per Capita Income






Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in the district in 2018 19 was 60%. The unemployment rate is under 2%. 2/3rd of the entire district’s labour force is engaged in the agriculture and construction sector. The workforce gets their employment on a seasonal basis. Around 20% of the total workforce is employed in the service sector which is now booming due to urbanization. Even the State and Central government schemes also focus on providing service oriented skill training rather than traditional ones. The service industry contributed 35% of the total Gross Value Added, which is indicating the higher productivity rate in this sector.
Mining and Manufacturing sectors. Industries like NALCO, HAL, and Toshali Cement.
Organized Form of Service and Tourism Sectors.
Primary Sector
Secondary Sector
Tertiary Sector
Agriculture and Construction Sectors.
Figure 9 Participation of the Workforce
Koraput’s majority workforce is self employed. Due to the lack of urbanization, peoples are less leaning toward salaried jobs. Mostly the self-employed workers are considered to be farmers. But it has been observed that today’s generation is preferring regular jobs. Around 18% of the workforce is having regular salaried jobs. Approximately, 1/5th of the total workforce was engaged as casual labour in the construction sector. The unemployment rate is very negligible as in the 2018 19 year the district workforce was 6.1lk from which 6lk is employed.
Figure
Cultivable Area,




Cultivable wasteland, 17000
Land under miscellaneous tree crops etc., 23000

Permanent pastures and other grazing lands, 19000
The area under Non agricultural uses, 40000
Forests land, 93000
Source: Comprehensive District Annual Plan, Koraput 2020
Cultivates
Barren
Figure






Land use

Geographically, except for the north western and west west central parts, almost the entire district is occupied by dense forests and highly rugged mountains, interspersed with narrow intermountain valleys. The average altitude of the hilly terrain ranges from 900 to 1400 m AMSL. North Western and West west central parts are characterized by gently undulating plains dotted with isolated hillocks. The Kola and Indrāvati Rivers and their tributaries constitute the main drainage system of the district. The main slope of the district is towards the west and northwest. The drainage pattern in the district is controlled by Indrāvati, Sabari (Kolab), and Sileru, Vegavati, Subarnamukhi, Jaryhavati and their tributaries. The river Indrāvati and Kolab drains the major parts of the Koraput district. Most of the tributaries of Kolab River and Indrāvati River are perennial.
No. Status of Irrigation
Area (‘000 Ha) % of net sown area



01 Total irrigation land area 57,355 100
02 Total un irrigation land area 0 0
03 Source of irrigation: Canals 47,687 83.14
04 Source of irrigation: Wells / Tube wells 4,264 7.43
05 Source of irrigation: Tanks / Lakes 5,404 9.42
06 Annual Rainfall 190cm
Table 5 Irrigation and rainfall data
Source: Brief Industrial Profile of Koraput District, 2019 20
Source of irrigation: Tanks / Lakes, 9.42
Source of irrigation: Wells / Tube wells, 7.43
Source of irrigation: Canals, 83.14
Figure 12 Irrigation Status of Koraput
The majority of the workforce of Koraput depends on the agriculture sector for their daily livelihood, which is sustainable. Cereals, millets, oilseeds, pulses, vegetables etc. are various groups of crops grown in the district. Paddy, Ragi, Maize, Niger and other oil seeds are the main
crops and Cotton, Tobacco, Potato, Banana, Chili, coffee, ginger and vegetables are the principal cash crops cultivated in the district. Due to the cold atmosphere, it’s suitable for beekeeping, so the Department of Agriculture should provide training for nourishing the production of honey along with Sericulture, which is a primary economic advantage for the tribal community as they grow exquisite silk and tassar fabrics. It is suggested that farmers adapt to the use of modern machinery in to grow their production.
No Name Of The Crop Area In Hact
Production Data 202122 In Qtl
Production Data 202021 In Qtl
Annual Growth Rate
Average Price Of Crops Rs/Qtl
Market Value In Rs/Qtl
1 Paddy 500 1489 1414 5% 1940 2350
2 Ragi 30 540 513 5% 3377 3800
3 Hy. Maize 50 300 285 5% 1870 2350
4 Bengal Gram 200 1260 1209 4% 6300 7000
5 Biri 20 104 1008 3% 6300 7000
6 Kulthi 304 1854 1761 5% 5500 6500
7 Field pea 1290 4644 4411 5% 6930 8000
8 Cowpea 235 2820 2707 4% 6930 8000
9 Other Pulses 10 70 69 2% 3950 7900
10 Ground nut 10 80 76 5% 5550 3300
11 Sunflower 10 220 190 5% 6015 7200
12 Mustard 120 2160 2095 3% 6930 8310
13 Potato 510 7140 6854 4% 2150 2500
14 Onion 172 3440 3371 2% 3200 4000
15 Chilly 95 6650 6240 4% 8000 8500
16 Garlic 127 1270 1219 4% 3000 3250
17 Coriander 125 1250 1212 3% 9500 10500
Table 6 Agriculture & Horticulture Production Data
Source: District Agriculture Department, Koraput
Due to the cold atmosphere, it’s suitable for beekeeping, so the Department of Horticulture should provide training for nourishing the production of honey along with ginger and mushroom cultivation which is a primary economic advantage for the tribal community as they grow exquisite silk and tassar fabrics. It is suggested that farmers adapt to the use of modern machinery in to grow their production.
Indicators
2020-21
2019-2020
Target in 2022
Vegetables (Avg Yield) 13000 kg/Hact 13000 kg/Hact 13000 kg/Hact
Fruits (Area) 15358 Ha. 16893 Ha 20000 Ha Spices (Area) 13000 Ha. 13300 Ha 14000 Ha
Table 7 Horticulture Production
Source: Comprehensive District Annual Plan, Koraput 2020 21
Koraput as a district is far from any coastal region so the population depends on inland production and export from neighboring states Andhra Pradesh. Now, the Departments have extended their support to promote fish farming in blocks. In the blocks of Similiguda, Koraput, Jeypore and Kotpad Aquarium accessories have gained popularity. The Fishery department has now far trained multiple SHGs and farmers to start their fish ponds and production.
No. Fishery Production In Metric Tones
01 Fish Production (Freshwater) 7279.73
02 Fresh Water Prawn Production 2.215
Table 8 Fishery Production
No. Name of the Scheme
Source: District Fisheries Office, Koraput 2020 21
Total Trained Farmers
01 Input Assistance to WSHGs on GP tank 108 WSHGs
02 Bio Flock Technologies 35 Farmers 03 Pisciculture Activity 30 Framers
Table 9 Skill Development Training under Fishery Department
Source: District Fisheries Office, Koraput 2020 21
There is a growing demand for Goat Farming and Poultry farming. Not only can it be sustainable for the youth but also be economically beneficial for them. On today’s date, a 3 days of training is being provided in Similiguda, Pottangi, Nandapur, Narayanpatna and Bandhugaon blocks. There is a scope of dairy production in the district if we can convert cattle farming into more commercialize rather than being limed to households. In Borigumma, Kotpad, Jeypore, Koraput and Similiguda blocks Poultry farming training is being provided. Industries like dairy, poultry and goat farming will engage a good portion of our youth towards self employment. No. Animals & Poultry Numbers
01 Cattle 425091
Buffalo 59320
Sheep 127810
Goats 142590
Poultry 583548
Pig 5542
Table 10 Animal Husbandry Production
Source: District Veterinary Office, Koraput 2021 22
Koraput as a district is far from any coastal region so the population depends on inland production and export from neighboring states Andhra Pradesh. Now, the Departments have extended their support to promote fish farming in blocks. In the blocks of Similiguda, Koraput,
Jeypore and Kotpad Aquarium accessories have gained popularity. The Fishery Department has now far trained multiple SHGs and farmers to start their fish ponds and production.
No. Sector Production Data 2020-21 in Qtl Production Data 2019-20 in Qtl
01 Dairy 71.01 mt 68 mt
Poultry 153026 174852
03 Fishery 3659.40 4218.54
05 Livestock 1919983 1845267
Table 11 Agro allied Production data
No.
01 Similiguda, Pottangi, Bandhugaon
Tissue Culture Banana Farming
02 Tribal communities in Koraput Organic coffee farming
03 Similiguda and Koraput Rooftop gardening
Table 12 In demand Allied Farming sectors
3.8 Traditional Occupations
3.8.1 Kotpad Handloom
Migrant Tribal Community of Kotpad village of Koraput weave Kotpad handloom hence got the nomenclature from the place of origin. The handloom fabric is woven by vegetable dyed fabric obtained from Aul trees. Products like Sarees, stoles and other dress materials were dyed with organic dye. Around 30 families have been involved and artisans are being supported not only by the Government such as DIC, OLM, and ORMAS but also by various NGOs and donations.
Source: Department of Textile, Koraput 2021 22
3.8.2 Lemongrass
Lemongrass usually grows in the hilly areas of the tropical region of this district. Narayanpatna and Bandhugaon districts have almost 80% of the lemongrass. More than 150 families of this region are being involved in this work, additionally getting support from ORMAS. It has a strong citrus flavor. The grass is distilled to extract oil from them and it has great use. Eventually, the essential oil of the grass has a very high demand in the state along with the neighboring states.
Market Linkage:
• Online Stores: Adisha, Koraput Coffee Website
• Tribal Development Co operative Corporation (TDCC), Bhubaneswar
• Odisha Livelihood Mission & ORMAS
• DoTERRA (Utah, U.S.)
• Swaraj Aromatics Ltd, Hyderabad
• Patanjali India

Seller FPO
• Koraput District Aromatic Farmers Association
• Koraput and Basmati Farmers Multipurpose Co operative society Ltd, Balda, Nandapur
• Bandhugaon Lemon grass Farmers Association
Koraput district is also very well known for its quality of coffee cultivation. The geographical location of the district i.e. surrounded by the Eastern Ghats makes it suitable for coffee cultivation. The cool weather is a bonus point for this work. In the district of Nandapur and Lamtaput blocks, about 40 50 families have found employment through this product. Coffee production is supported by Government departments like TDCC, ITDA, ORMAS and KAPPCO. The supply of coffee is not only limited to Odisha but also outside of the state.





is rich in terms of minerals. Bauxite is a major mineral we can find here. Other minerals like Black Granite, Red Ocher, Granite, Quartz, Limestone, Dolomite, Clay and Mica are also found in Koraput. Therefore Large scale Industries like NALCO, Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd, Ballarpur Industries Ltd and Toshali Cement Pvt Ltd are situated here which boosts the economy. These industries export items such as Alumina, Aero Engines, Portland cement and Packing Paper etc. In the year 2021 25, we can estimate that around 70,000 jobs will be introduced. The majority of employees will be provided from the construction sector
service sector with 45% and 40% respectively. The manufacturing sector will have a 13% and the utility sector will have a 2% increase in human resource demand. Hence we will witness a huge increase in the employment sector in near future.
investments made in the State till March 2010. Based on the Employers who have been communicated mainly belong to the manufacturing and services sectors. The manufacturing sector included Automotive, Construction, Mining, Aerospace and Aviation, and Power covering almost 60% of the industry presence while the service sector included Healthcare, Tourism & Hospitality, BFSI and Apparel which covers 40% of the industry presence in the district. The manufacturing sector hires 57% of youth through placement and job drives conducted at their colleges and off campus drives while the service sector hires 27% through direct advertisement or recommendations. In recent times Food Processing is emerging as a profitable industry to work in. The district administration is focusing on exporting processed goods rather than raw products This industry hires 20% of the youth. Most job role prefers skilled workers but manufacturing sectors hires institutes and trained them on their job.
No Type of Industry Units Investment (lk) Employment
1 Food and Allied 1696 8151.1 14044
2 Chemical & Allied 125 428.3 761
3 Electrical & Electronics 60 165.96 248
4 Engineering & Metal based 402 1093.92 2566
5 Forest and Wood based 272 159.22 1887
6 Glass and Ceramics 277 1885.54 5269
7 Livestock & Leather 23 27.14 84
8 Paper & Paper Product 84 280.34 445
9 Rubber 7 Plastics 126 435.86 499
10 Textiles 247 143.06 1203
11 Misc. Manufacturing 337 676.31 1175
12 Repairing & Servicing 2513 8216.76 8001
Table 13 MSMEs industrial Data
Source: Brief Industrial Profile of Koraput District, 2019 20




Engineering
ICWA/
(HR)
Technical
Aluminum
Infrastructure Project Ltd.
Machinery)
Area Manager (Auto Components)
Executive
Operator
Vehicle Driver Level 4
Data entry Operator
(Plant & Machinery)
Maintenance Assistant/ Helper
Labour
Fitter Fabrication
Graduation & Above 35,000
Graduation & Above 20,000
Graduation & Above 18,000
Higher Secondary and Above 20,000
Graduation & Above 15,000
Higher Secondary and Above 15000
Attained School 7,500
Attained School 300/DAY
Pass 6,000
TATA Motors
MRF Tires
HCL Technology
Engine Repair Technician Level 4
Accessory Fitter
and Quality Checker
Developer
Service Desk Operator
Security & Intelligent Service Security Guard
Edujobs Academy Private Limited Faculty
Welspun India Private Limited and GRG Group
Pass 10,000
Pass 15,000
th Pass & 1yr I.T.I.s 10,000
1st Division 20,000
1st Division 17,000
th pass 14,000
Graduation 25,000
Customer Care Service 12th Pass 12,000
Worker
Quality Checker
Production Worker
Job roles required for Large Employers
Company Job Roles
M/S Maruti Enterprises
Preservation
Storage
th Pass 8,000
th Pass 12,000
th Pass 10,000
Job Fair 2021, District Employment Exchange, Koraput
Qualification Salary
Executive Graduation & Above 10,000
(Plant & Machinery)
Vehicle Driver Level 4
Operator
Assistant/ Helper
Labour
Maintenance
Technician Air Conditioner
Security Guard
Technician
Higher Secondary and Above 10,000
Class & Above 12,000 15,000
Higher Secondary and Above 10,000 15,000
and Above 5,000
6,000
th Pass 20,000
Secondary 27,000
th 10th Pass 7,500
th Fail 9,000
Dibyajyoti
Construction, Stone Crusher
Accounts Executive
Commercial Vehicle Driver Level 4
Supervisor (Plant & Machinery)
Graduation 20,000
10th Class & Above 11,000
Higher Secondary and Above 11,000 and 8,000
Crusher Operator Graduation 22,000
Maintenance Assistant/ Helper
Class & Above 3,500
Mountaineering Camp Cook 4th & Above 10,000
Labour
Operator
Excavator Operator
Gayatri Stone Crusher Unit 1 & 2
Illiterate 320/Day
Graduation 10,000
Higher Secondary and Above 11,000
Supervisor (Plant & Machinery) Graduation 20,000
Mountaineering Camp Cook 5th Class & Above 7,000
Commercial Vehicle Driver Level 4 5th Class & Above 10,000
15 Job Roles required for MSMEs
Unskilled Labour
Illiterate 250/Day
Source: Job Fair 2021, District Employment Exchange, Koraput
Koraput has many industries related to agriculture, mining, automobile, gold etc. sectors. Among all the industry associations these 3 industries are prominent in their sectors. These associations hire candidates who are unskilled or semi skilled but due to the increasing urbanization and demand of their respective sectors, they require candidates with prior skill training either short term or long term. With the required assistance from the DIC candidates are taking training from skill hubs and applying for subsidized loan through various schemes.
No. Industry Association
Roles recruited by Association
mill Machine Operator
Service Person
Chamber of Commerce
Industries
Cashew
District Rice-mill
Industry Associations
Attendant
Operators
Labour
labour
Operator
labour
Operator
Brief Industrial Profile of Koraput District, 2019 20
Plan,
Based on these figures, there is an eminent requirement of setting up incubation centers for these youth to understand the nature of this business and how to run it successfully. This states that the need of the hour is to invest heavily on career counselling and awareness generation activities/interventions. The District Skill Committee (DSC) with support from District Administration and District Employment Office shall plan to organize counselling cum awareness generation advocacy camps on Entrepreneurship Development, inviting successful entrepreneurs for sharing their success mantra and other guest lectures.
Koraput majorly depends on the agriculture sector for employment but in recent years’ the service sector has grown significantly comparatively to all the other sectors. The service sector contributes around 20% contribution to district GDP and youth is more opportunities in service sector the than rest others. The district collector is also focusing on expanding and empowering service and food processing sector more than rest of other traditional ways of occupation. Following list shows services that are in high demand in Koraput currently:
Service Enterprises
Servicing
Cleaning
Medium




Low
High
High
High
9 Packaging Industry Unskilled 7,00,000 6,000 10 Medium
10 Well furnished Restaurant Unskilled 20,00,000 40,000 20 High
11 Nursing Home Skilled 20,00,000 35,000 25 High
12 Industrial Consultancy centre Skilled 7,00,000 15,000 30 High
13 Pathological Testing Skilled 10,00,000 15,000 10 Medium
14 Lodging & Boarding Unskilled 60,00,000 50,000 20 High
16 Xerox/FAX/ Lamination Skilled 2,00,000 6,000 25 High
17 Gift Shop Unskilled 4,00,000 12,000 20 High
Table 17 Servicing Enterprises
5 Skilling Infrastructure
5.1 Target Population
Source Census 2011
Source: Brief Industrial Profile of Koraput District, 2019 20
Total Population
Total Rural Urban Odisha 4,19,74,218 3,49,70,562 70,03,656 Koraput 13,79,647 11,53,478 2,26,169
Age wise Population
16 20 Years 117147 95524 21623
21 - 25 113428 92102 21326
26 30 108118 87393 20725
30 34 93375 74843 18532
Male
16 20 Years 56680 45770 10910
21 25 Years 53033 42559 10474
26 30 Years 53841 43381 10460
30 34 Years 46063 36605 9458
Female
16 20 Years 60467 49754 10713
21 25 Years 60395 49543 10852
26 30 Years 54277 44012 10265
30 34 Years 47312 38238 9074
Table 18 Target Population Profile of Koraput
Source: District Statistical Hand Book 2020 Koraput
DDU GKY
Enrolled Trained Placed
80 80 66 Handicrafts & Carpets [Bamboo Basket Maker] 80 80 34
Agriculture [Mushroom Grower
Handicrafts & Carpets [Handmade Bamboo Agarbatti Stick Making
240 240 188
Handicrafts & Carpets [Lacquerer (Paper Mache)] 180 180 28
Handicrafts & Carpets [Traditional Hand Embroiderer 260 260 180 Handicrafts & Carpets [Jute Product Maker] 80 80 75
Healthcare [Front Line Health Worker 20 20 0
IT ITES [Domestic Data entry Operator] 40 40 16
Agriculture [Small poultry farmer] 100 100 67 Apparel, Made Ups & Home Furnishing [Self Employed Tailor] 100 100 67
Beauty & Wellness [Assistant Beauty Therapist] 60 60 43
Domestic Worker [General Housekeeper] 20 20 0 Electronics & Hardware [Electrical Technician] 60 60 35
Electronics & Hardware [Service Technician Home Appliances] 240 240 50
Food Processing [Traditional Snack and Savory Maker] 140 140 79 Handicrafts & Carpets [Stringing/Beading Artisan (Fashion Jeweler)] 100 100 33
Nursery worker 60 60 50
Mushroom Grower (small entrepreneur 100 100 85 Small poultry frame 60 60 52
Self Employed Tailor 140 140 130
Assistant Hair Stylist 120 120 59
Helper Mason 80 80 11 Electrical Technician 60 60 50
Traditional Snack and Savory Maker 120 120 100
Bamboo Basket Maker 140 140 87
Engraving artisan (Metal Handicrafts) 100 100 78
Traditional Hand Embroiderer 100 100 58
Applique Artisan 140 140 50
Jute Product Maker 160 160 34
Domestic Data entry Operator 40 40 13
Plumber (General) Helper 100 100 66
Field Technician Other Home Appliances
160 160 133
Furniture Making 40 40 0
Hand Rolled Agarbatti Maker 80 80 60
Self employed Tailor 66 66 66
Assistant Beauty Therapist
55 55 55
Hand Rolled Agarbatti Maker 60 60 51
HE/HSPT
Lineman
AGICULTURE
SBI RSETI
EDP
Basic Weaving Training
Textile Dept.
120 97
60 46
90 78
504 326
281 186
97 12
82 32
20 0
Basic Weaving Training 20 20 0
Skill Upgradation Training Dyeing Aul 20 20 0 Skill Upgradation Training Dyeing Aul 40 40 0
19 Mapping Current Infrastructure
6.1 Primary, Upper Primary, Secondary and Intermediate Schools
For higher education, there are 27 junior colleges and higher secondary schools (10+2) offering courses in Arts, Sciences and Commerce streams. As per the Department of Higher Education (DHE), the total sanctioned strengths in each of these streams were 2848, 1666 and 768 respectively.
No. Attributes
Government Private 2022-23 2022-23
01 Total No. of Primary Schools 1410 36
Total No. of Primary Schools with toilets 1410 36
Total No. of Upper Primary Schools 705 49
Total No. of Upper Primary Schools with toilets 705 49
Total No. of Secondary Schools 287 33
Total No. of Secondary Schools with toilets 287 33
Total No. of Intermediate Colleges 23 15
Total No. of Colleges for Graduation and Post Graduation 10 2
Total Number of Polytechnics / I.T.I.s Colleges
Schools with seating facilities
Schools with Internet Connection 47
20 Education Infrastructure of Koraput
11
115
District Education Department, Koraput
Education level Male Female Total Male Female Total Dropouts
Primary (I V) 66977 64188 131165 73134 70275 143409 917

Upper Primary (VI VIII) 34901 32367 67268 40166 36603 76769 2041
Secondary (IX X) 20566 17367 37933 20498 17901 38399 4294
Higher Secondary (XI XII) 8769 7173 15942 7616 6231 13847 658
500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 4500
917
2041
4294 169 172 87
Primary Upper Primary Secondary 2020-21 917 2041 4294 2019-20 169 172 87
The district has a total of 5 Polytechnic institutes among them only 1 institute is Government aided while the rest 4 are privately operated. These colleges provide training for branches like Mechanical, Electrical, AE & IE, Civil, EC, Computer Sc. Engineering etc. Out all the branches Mechanical and Civil branches are popular among Koraput students. Students got placement and internships at companies like OPTCL, TATA Power Odisha, Mando India, Ultratech Cement, Gujarat Bolt metric Bengaluru, Mahindra & Mahindra etc. The major human resource challenges that the industry experiences are the following:
Lack of skilled manpower
Graduates are not industry ready
Lack of formal short term training
More emphasis is to be put on Apprenticeship and internship programs.
No. Block Govt./Pvt.
Name of the Institutions Seats Available
01 Koraput Govt. Govt. Polytechnic College 180
02 Koraput Pvt. Hi Tech. Institute Of Information & Technology 175
03 Jeypore Pvt. Institute of Engineering & Management 356
04 Koraput Pvt. Siddhartha Institute Of Eng. & Technology 130
05 Similiguda Pvt. Samantha Chandra Sekhar Institute of Technology & Mgt 206
Table 22 Block wise list of Govt. & Pvt. Polytechnic Colleges
Source: District Skill Development Plan, Koraput. 2020 21
The district has 11 Industrial Training Institutes. Among the 11 Institutes, 4 are Government and 7 are Private. The ITIs offered courses in 15 different trades, namely Fitter, Electrician, Draughtsman (Civil), Electronic Mechanic, Machinist, Mechanic (Motor Vehicle), Mechanic (Refrigeration and Air Conditioning), Surveyor, Turner, Welder, Wireman, Plumber, Sewing Technology, Computer Operator and Programming Assistant, Horticulture etc. Fitter and Electrician trade is popular and in high demand for Koraput. Students do their apprenticeship at companies like NALCO Damanjodi, HAL Sunabeda, Vizag Steel plant, TATA Motors, Maruti Suzuki etc. These institutes provide mainly 2-year I.T.I. courses. The following data included all the institutes which provide industrial training.
No. Block Govt./P vt
Name of the Institutions Seats Available
01 Ambaguda Govt. G.I.T.I Ambaguda 668
Kotpad Govt. Govt. I.T.I KOTPAD 120
Pottangi Govt. Govt. I.T.I. POTTANGI 128
Laxmipur Govt. Govt. I.T.I LAXMIPUR 184
Nandapur Govt. Govt. I.T.I. NANDAPUR 128
Jeypore Pvt. Panchabati Industrial Training Centre 216
Jeypore Pvt. Padmanav Industrial Training Centre 128
Koraput Pvt. Koraput Industrial Training Centre, Koraput 140
Koraput Pvt. Damanjodi Industrial Training Centre 164
Borigumma Pvt. Aryan Industrial Training Centre 104
Koraput Pvt. Institute of Engineering and Management I.T.C 80
Semiliguda Pvt. Samanta Chandra Sekhar Institute of Technology and Management I.T.C 68 Table 23 I.T.I.s Institutes present in Koraput
Source: https://skill.samsodisha.gov.in/
227 Fitter
G.I.T.I Ambaguda
231 Electrician 24 Months 100 100 554 Sewing Technology 12 Months 40 40 949 Solar Technician (Electrical) 24 Months 40 40 222 Machinist 24 Months 60 60 215 Mechanic (Motor Vehicle) 24 Months 48 48 218 Mechanic (Refrigeration and Air Conditioning) 24 Months 24 24 207 Surveyor 24 Months 24 24 221 Turner 24 Months 40 40 212 Welder 24 Months 60 60 232 Wireman 24 Months 40 40 242 Computer Operator and Programming Assistant 12 Months 48 48
24 Months 120 120 35
I.T.I KOTPAD
Govt. I.T.I LAXMIPUR
231 Electrician 24 Months 40 40 7227 Fitter 24 Months 40 40 554 Sewing Technology 12 Months 40 40
231 Electrician 24 Months 40 40 13 227 Fitter 24 Months 40 40 215 Mechanic (Motor Vehicle) 24 Months 24 24 212 Welder 24 Months 40 40
I.T.I. POTTANGI
Govt. I.T.I. NANDAPUR
231 Electrician 24 Months 40 40 14227 Fitter 24 Months 40 40 242 Computer Operator and Programming Assistant 12 Months 48 48
212 Welder 24 Months 40 40 9 231 Electrician 24 Months 20 20 227 Fitter 24 Months 20 20 242 Computer Operator and Programming Assistant 12 Months 48 48
Panchabati
Industrial Training Centre
Padmanav Industrial Training Centre
Aryan Industrial Training Centre
231 Electrician 24 Months 20 20 6
227 Fitter 24 Months 100 92 215 Mechanic (Motor Vehicle) 24 Months 24 24 209 Plumber 24 Months 24 24 242 Computer Operator and Programming Assistant 12 Months 48 48
231 Electrician 24 Months 20 20 9209 Plumber 24 Months 48 48 227 Fitter 24 Months 60 60
227 Fitter 24 Months 40 40 11231 Electrician 24 Months 20 20 113 Horticulture 24 Months 24 10
554 Sewing Technology
12 Months 20 15
Damanjodi Industrial Training Centre
Electrician 24 Months 20 20 14227 Fitter 24 Months 120 120 215 Mechanic (Motor Vehicle) 24 Months 24 24 Institute of Engineering and Management I.T.C
Electrician
Electrician
24 Months 20 20 25
24 Months 40 36 6 227 Fitter 24 Months 40 34 Koraput Industrial Training Centre, Koraput
Fitter 24 Months 120 120 Samanta Chandra Sekhar Institute of Technology and Management I.T.C
Table 24 Trade wise of I.T.I.s
Fitter 24 Months 20 20 9
Computer Operator and Programming Assistant 12 Months 48 48
There are 15 colleges which offer various courses. There is a private engineering college in Koraput along with two diploma polytechnic institutes offering courses in telecom engineering, computer science & engineering, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering and instrumental engineering. The total combined capacity of these institutes taken together is approximately 1448 seats per year.
01 Kotpad Govt. Kotpad College, Kotpad, Koraput
Jeypore Govt. Vikram Dev Auto. College, Jeypore
Sunabeda Govt. Sunabeda Women’s College, Sunabeda
Similiguda Govt. Similiguda College
Kundra Govt. Biju Patnaik College, Kundra
Koraput Govt. S L N Medical College & Hospital, Koraput
Laxmipur Govt. Laxmipur College, Laxmipur, Koraput
Jeypore Govt. Govt. Women’s College Jeypore
Koraput Govt. Central University of Odisha, Koraput
Koraput Govt. Govt. College, Koraput
Nandapur Pvt. Sindhadebi Mahavidyalaya, Nandapur
Sunabeda Pvt. Aeronautics College Sunabeda, Koraput
Table 25 Graduation and Post Graduation Colleges
Training programs have been implemented in the RSETI and other TSPS on job roles like Pickle making, Mushroom cultivation, Fitter etc. The Welfare Officer of the district is providing Short Term skill training through OSFDC & OSTFDC to SC/ST candidates on Data Entry Operator, Tourism & Hospitality, etc. The Social Welfare Office of the district has arranged
awareness training in convergence with the various Agriculture, Health & Nutrition departments for SHG members and Anganwadi workers at the block level under the supervision of the CDPO. Through DDU GKY, the ORMAS has implemented short term training on Fitter Fabrication, Helper Bar Bender & Steel Fixer, in the district. With the aim of economic transformation through capacity building of the vulnerable society, the ORMAS has implemented NRLM/NRETP for the producer group of Siali Leaf plate, Spices, Turmeric, Ginger Black Paper, Millet, Pulses etc. The Industry Centre of the district has implemented PMEGP to facilitate the EDP trained Youth.
01 Skill Development Training Centre
02 Sarvodaya Samiti
03 SBI Rural Self Employment Training Centre
04 Gram Tarang Employment Training Centre, Semiliguda
05 Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Sunabeda
O.S.D.A. Suryakanta Behera
KVIC Pradip Ku. Mahanty
RSETIs Pramod Kumar Dash
P.M.K.V.Y. Himanshu Kumar Khora
K.V.K. Dr. Biswanath Sahoo
06 Government Industrial Training Institute, Pottangi I T I Dharmaprakash Samal
07 Government Industrial Training Institute, Laxmipur I T I Subhen Ku. Behera
Government Industrial Training Institute, Kotpad I.T.I. Balaram Sethy
Gopabandhu Industrial Training Institute, Jeypore I.T.I. Sisir Kumar Dalai
Government Industrial Training Institute, Nandapur I T I
Government Polytechnic College Polytechnic
Van Dhan Vikash Kendras (VDVK) VDVK Jogeswar Nayak
Quess Corporation Jeypore
Asmacs System Solution Private Limited
BVG India Private Limited
Redtech Private Limited
DDU GKY Sasmita Raula
DDU-GKY Rajendra Moharana
DDU GKY Batakrushna Behera
DDU GKY Rishikesh Singh
Skill Extension Center, Ambaguda OSDA Training Partner
Skill Training Center, Laxmipur OSDA Training Partner
Skill Training Center, Koraput
List Skill Hubs of Koraput
OSDA Training Partner
Source: District Administration, Koraput
Sikhsan
KORAPUT
Grower
Basket Maker
Handmade Bamboo Agarbatti Stick Making
(Paper Mache)]
Hand Embroiderer
Product Maker
Line Health Worker
Domestic Data entry Operator]
poultry farmer
Self Employed Tailor
Beauty Therapist
Snack and Savory
16
214 58
63 14
156
1474
5000/ 6000/
15 5000/ 6000/
181 5000/ 6000/
28 5000/ 6000/
180 5000/ 6000/
75 5000/ 6000/
6000/ 7000/
8 6000/7000/
56 5000/ 6000/
5000/ 6000/
5000/6000/
5000/ 6000/
7000/ 8000/
7000/ 8000/
5000/ 6000/-
(Fashion
Jan Sikhsan Sansthan
Nursery worker
Mushroom Grower
Small poultry frame
Self Employed Tailor
Hair Stylist
Mason
Electrical Technician
Traditional Snack and Savory Maker
Bamboo Basket Maker
Engraving artisan (Metal Handicrafts)
Traditional Hand Embroiderer
Applique Artisan
Jute Product Maker
Domestic Data entry Operator
Plumber (General) Helper
Field Technician
Home Appliances
Furniture Making
Hand Rolled Agarbatti Maker
employed
Beauty
5000/ 6000/
10000/
8000/
140
41 6000/ 7000/
75 6000/7000/
37 6000/ 7000/
120 6000/ 7000/
59 7000/8000/
0
140
0
100 6000/ 7000/
87 6000/ 7000/
78 6000/ 7000/
58 6000/ 7000/
50 6000/ 7000/
160 0 34 5000/6000/
8000/ 25
7000/ 8000/ 20
0 7000/ 8000/
0 7000/ 8000/
13 7000/ 8000/
6000/ 7000/
8000/
8000/
RSETI (NRLM)
21
GENERAL EDP
Employed
Employed
Employed
SBI RSETI (NRLM)
22
PRODUCT
EDP
SBI RSETI (NRLM) 2022-23
Textile Dept.
PROCESS
General EDPs
Skill Upgradation Training Dyeing Aul
Basic Weaving Training
Basic Weaving Training
Skill Upgradation Training Dyeing Aul
PMKVY Short Term Training 220 158
Covid Crash Course 20 20
28 Sector wise Analysis (Financial Year 2020 23)
Employed
Employed
164 146 Self Employed 5000/
20 20 0 8000/
211 82 Self Employed 6000/
117 43 Self Employed 5000/
65 12 Self Employed 10000 /
0 Self Employed 8000/
65 0 Self Employed 8000/
Employed 8000/ 32 0 Self Employed 8000/
Self Employed 8000/ 23 0 Wage Employed 8000/
10000/ 20 0 Self Employed 8000/
Employed 10000/ 9 0 Self Employed 8000/
20 0 Self Employed 8000/
0 40 0 Self Employed 8000/
0 363 0 Wage Employed 8000/
8000/ 96 96 Wage Employed 8000/
Jeypore
employed
Technician
Snack and Savory Maker
Basket Maker
artisan (Metal Handicrafts)
Hand Embroiderer
Applique Artisan
Kotpad
Product Maker
Data entry Operator
(General) Helper 100
Technician Other Home Appliances 140
Making
Hand Rolled Agarbatti Maker
SBIRSETI KORAPUT
N
N
35 NO
Vegetable 35 NO
Papad, Pickle 35 NO
Pisciculture 35 NO
PMKK Semiliguda Short Term Training 60 NO
Covid Crash Course 60 NO
Details of Training Center
Part A No of youth, certified and Employed in FY
Name No of youth in District
Jan Sikhsan Sansthan
Placed
2198
DDU GKY 2,01,273 3057 2261
SBI RSETI (NRLM) 2,01,273
547
2,01,273 698 139
2,01,273
Part B Number of Vulnerable
youth certified
00
Name Women Certified SC Certified ST Certified OBC Certified PWD Certified
Jan Sikhsan Sansthan
DDU GKY
SBI RSETI (NRLM)
2969 0
2146 179 0
267 435 0
135 413 123 0
0
Scheme Name
PMNAM 1.0
Apprenticeship Mela
Part C - Number of apprentices completing
No of the youth in District Apprentice Attended Trainees got selected
120
177
Part D No. of people certified under Recognition of Prior Learning
Recognition of Prior Learning
Field Technician Computing and Peripherals
Field Technician Computing and Peripherals
Mobile phone Hardware Repair Technician
phone Hardware Repair Technician
of the youth in District Trained Certified
19
20
27
28
Inclusion Gaps Gaps in a training capacity
Trades for SC Inclusion
Trades for ST Inclusion Trades for Women Inclusion Training capacity needed Training capacity is excess
Distribution of Line man Distribution of Line man Sewing Machine Operator Green Jobs Beauty and Wellness
Sewing Machine Operator Sewing Machine Operator Input Assistance to WSHG on GP tank Food Processing Automobile
Solar Panel Installer Solar Panel Installer Health Care & Multipurpose worker IT $ ITES Infrastructure Equipment
Entrepreneurship Skill Development ProgramPanchayat Specific
Entrepreneurship Skill Development ProgramPanchayat Specific
Beauty Therapy & Hair Styling Banking and Finances Appeal Industry
Helper Electrician Helper Electrician Women’s Tailor Mining and Manufacturing Management and Entrepreneurship and Professional
Helper Bar bender Helper Bar bender Coffee Plantation Animal Husbandry Construction
Coffee Plantation Coffee Plantation
Fitter Fabrication
Fitter Electrical Assembly
Fabrication
and Hardware Aerospace and Aviation Agriculture
Worker
Sales
and Carpets Capital Goods
Healthcare Front Office Associate
Inclusion of SC, ST and Women
Trades
There are limited trades such as self employed tailors, electricians, carpenters, plumbers, fitters, etc., in the district. There are duplicates of these trades under different schemes due to low infrastructure investment and the easy availability of trainers for Training Partners.
Infrastructure and Trainers: These programs lack certified trainers, proper labs, and proper infrastructure, as well as little or no monitoring.
Retention and Placement: All skilling programs have low retention and placement rates, which are not adequately documented.
1. Varieties of mineral deposits like Bauxite, Iron Ore, Limestone and China Clay are abundantly present in the district.
2. Perennial streams and rivulets are available in almost all parts of the district.
3. The vegetable mineral dyed fabric of Kotpad has earned Odisha’s first GI tag.
4. Semi organic production of fruits and vegetables.
5. Presence of Model Career Center with dedicated staff working towards Job Drives/Fairs, Counselling and Vocational Guidance of Youths.
1. Favourable soil and climatic conditions for the cultivation of coffee, cashew, cotton, tobacco, vegetable, Ginger, Turmeric and fruits.
2. Implementation of integrated watershed development technologies.
3. Ample scope for regeneration / extension of private and public land.
4. Unexplored mineral deposits.
1. Immense potential for promotion of eco ethnic tourism and adventurous sports supported by rich natural beauty and tribal culture.
2. Youths are getting more educated and literate in Vocational Courses.
3. High scope for regeneration of forests and marketing of Non Timber forest produce for enhancement of income of the tribal.
4. Tribal Jewelry prepared by the local artisans
1. The majority of the land is not covered under irrigation facilities and is dependent on rainwater for cultivation.
2. Low level of nutrition among children and women.
3. Low level of awareness among rural people.
4. High degree of unemployment and underemployment.
1. Gradual degradation of forest areas due to shifting cultivation practice.
2. Out migration of skilled weavers causing threats to the handloom & weaving industry.
3. Irregular and insufficient patterns of rainfall cause drought in many parts of the district.
4. Outdated machinery and syllabus of I.T.I and Polytechnic lead to a mismatch of skills and industry expectations
1. Low level of literacy, particularly in female literacy.
2. Limited livelihood option.
3. Poor marketing, storage and processing facilities are affecting the agro & allied sector.
4. Lack of backward and forward linkage in Agro & Handloom industries.
5. The district has a poor rail and road
has a demand by the tourists.
5. Skill based activities such as bamboo crafts, terracotta products, paddy crafts, handloom weaving have demand.
1. Favourable agro climate conditions for taking up horticulture, sericulture including coffee and cashew.
2. Large potential for development of Pisciculture.
3. Production of Ginger and other spices can be utilized in food processing industry.
4. Presence of industries i.e. NALCO and HAL absorbing local candidates through Apprenticeship Mela
Table 33 Skill Training SWOT
network.
6. Youths want to get employment in the district preferably.
1. Wide economic disparity.
2. Huge out migration
3. Natural calamities.
4. Local artisans are sometimes exploited by the middlemen as their products are sold at distressed prices.
Food Processing
Additional no next 3 years
Industrial Production Worker Food Processing 395 Milling Technician 20
Packing Machine Worker Food Processing 14 Grain Mill Operator 30 Assistant Lab Technician Food and Agricultural Commodities 15
Agriculture Allied Activities Beekeeper 30
Agriculture Crop Production
Seri culturist 30
Agriculture Machinery Operator 30 Machinery Repair and Service Provider 30 Farm Workshop Foreman/Supervisor 30 Harvesting Machine Operator 30 Maize Cultivator 30 Operator Reaper, Thresher and Crop Residue Machinery 30
Pesticide & Fertilizer Applicator 30 Rooftop Gardener 30 Tractor Operator 30
Vermicomposting Producer 30 Tractor Mechanic 30
Agriculture Industries Supply Chain Field Assistant 30 Agro Service Input Dealer 30
Fishery Aquaculture Technician 30
Fish Seed Grower 30
Fishing Boat Maintenance Worker 30 Inland Capture Fisherman cum Primary Processor 30
Fishing Boat Maintenance Worker 30
Animal Health Worker 30
Veterinary Field Assistant 30 Goat Farmer 30
Dairying Dairy Farmer/Entrepreneur 30
Broiler Farm Supervisor 30
Broiler Farm Worker 30
Layer Farm Worker 30
Small Poultry Farmer 30
Coffee Plantation Worker 300
Coffee Plantation Supervisor 60
Coffee
Coffee Plantation Manager 60 Coffee Tester 15
Drying Range Machine Operator 45 Hand Operated Knitting Machine Operator (Circular & Flat) 45
Handloom Entrepreneur 30 Knitting Machine Fitter 30
Iron & Steel
Additional no next3 years
Laboratory Technician Physical 65 Shift in Charge Furnace Ferro Alloys 42
Mine Machinist 158 Assistant Support Underground Mines 126 Mechanic / Fitter 93 Reclamation Supervisor 50 Surface Miner Operator 40 Power Technician Distribution Transformer Repair 816
Mining
Construction
Helper Mason 273 Assistant Mason 125 Assistant Construction Fitter 45 Store Assistant Construction 43 Helper Fabrication 31
Service Sector
Sector Job Role
Green Jobs
Additional no next 3 years
Solar PV Designer 120 Solar PV Engineer 120 Solar PV Installer (Suryamitra) 120
Customer Care Executive 120 Draftsman 60 Electrical Technician 240
Electronic Hardware Design Engineer 150 Electronic Sub assembly Technician 60
Design for Test Engineer 17
Front Office Associate 15 Kitchen Helper 10 Captain 45
Aerospace & Aviation Aerospace Design Assistant
Structural Fitter
Apparel, Made-Ups & Home Furnishing Sewing Machine Operator
Commercial Vehicle Driver Level 4
Maintenance Technician Service Workshop
Automotive Engine Repair Technician Level 4
Automotive
Washer
Sales Consultant (Retail) Level 4
Service Supervisor
Sales Manager
Banking, Financial Services and Insurance Microfinance Executive
Loan Processing Officer
Accounts Executive
Electronics & Hardware Field Technician Air Conditioner
Field Technician
ITES Domestic Data entry Operator
Potential Employment Scenario
Name Trained Certified
RSETI
NIESBUD center
EDI
NSTI/ITI
Krishi Vigyan Kendra
Table 35 Training done on Entrepreneurship
240
1932
The district level consultations, and ongoing/conducted training projects suggests the potential areas for skill development interventions and job opportunities in the future. It identifies the potential job roles mapped with NSQF linked QPs and the potential employment opportunities over the next 5 years with a focus on youth. The job roles have been shortlisted based on the analysis of findings from the skill gap analysis, secondary research, youth aspiration survey, enterprise survey, district level consultations and discussions with industry associations.
In the year 2021-25, we can estimate that around 70,000 jobs will be introduced. The majority of employment will be provided from the construction sector and service sector with 45% and 40% respectively. The manufacturing sector will have a 13% and the utility sector will have a 2% increase in human resource demand. Hence we will witness a huge increase in the employment sector in near future.
Sectors
Utilities
Service
Koraput
39.8%
100.0%
Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Mela has held on July 11th 2022. This Apprenticeship Mela is to be held every 2nd Monday in every 3 Months.
The purpose of PMNAM Mela is to.
1. Create a platform between candidates and Establishments.
Facilitate candidates to avail opportunities in Apprenticeship training.
3. Facilitate Establishment to identify potential candidates and selection of Apprentices.
MSME drive for participation.
A total of 178 candidates have participated in the 1st PMNAM Apprenticeship Mela which was conducted at Govt. I.T.I., Ambaguda where 7 companies came for selection. Companies that are absorbing candidates in this Apprenticeship Mela are:
1. TPSODL Jeypore
OHPC
3. TOYOTA BOSUOKU Automotive India Pvt. Ltd.
OPTCL
NALCO
OMFED
Within District Within State
Within India International
Inward: Coming into district/ tehsil
Education and economic prospects lead to migration from rural areas to urban areas.
The movement of people from Tribal areas to urban is majorly due to
Prestigious Educational technical, non technical, and medical institutions
Need for a skilled / unskilled workforce.
•Most of the individuals come as industrial workers or officers at HAL and NALCO.
•For the job in various PSUs.
Many individuals come to the district as per their project requirements or tourism.
Going out from District
From urban to rural migration occurs to set up cottage industries and do organic farming.
Migration
For better prospects, the people rarely migrate from Koraput to other parts of the state.
Individuals migrate from Koraput to other states for diversity and the betterment of employment prospects.
a) Semi skilled and potential skilled labour be given authentic skill certificate.
b) Needs awareness about schemes like RPL and other short term training programs?
c) Demand based training instead of supply based training.
d) According to the skill mapping needs of migrant workers for better trades.
Table 38 Skilling Analysis for Migrants
a) Most of the inward migrants are semi skilled so short term training program based skill validation should be done.
b) Industry ready skills for local industries.
c) Potential skill recognition using local level career counselling.
d) Trainee’s data sharing with different department.
Lack of Counselling Infrastructure
Lack of Expert Counsellors.
Most of the training centres concentrated in urban areas
Koraput & Jeypore
Lack of training providers in Service Sector
Lack of Entrepreneurial spirit in youth
Set Up Well Equipped Career Guidance and Counselling Centre.
Identify Location (3000 sq. feet Space)
Submit Proposal Make a Pool of Expert Counsellors
Appeal to institutes to empanel Infrastructure unavailability in rural area
TCs prefer urban areas due to regular flow of candidates Empanel more TCs in rural
Empanel interested institutesMore employment opportunities in urban area
Lack of infrastructure
Lack of awareness about skilling programme among candidates
Government institutes not interested in participation
No assured income
Lack of awareness of local opportunities
Empanel more training providers in agriculture sector Government institutions
Identifying and approach Institutes / colleges
Awareness drive among institutes about skilling programme
Inclination towards job security Guide interested candidates
Lack of awareness about schemes and guidance facilities
Motivate and guide youth for entrepreneurship
Connect with banks/ Mahamandals for financing
Unavailability of training centres for PwD and transgender community
Skill development training programs are running based on targets allotted by the Central or State Government
Lack of Vocational Courses which are suitable for PwD candidates
Scholarship Opportunities for PwD and Transgender candidates
Mobilization of PwD and Transgender
Awareness drive among institutes about skilling programme Regular Counselling
Difficulty in mobilization of transgender candidates Develop universally accessible Training Centres Guide interested candidates
No fixed schedule for skill training Pre planned skill training Calendar Monthly review meeting with TPs
No Centralized Monitoring System of various Training Centers
Less female candidates admitting to Vocational Institutes
No system to gather micro level Demand in District Devise a proper mechanism for gathering micro level demands
Lack of coordination between different line departments
Very few schemes targeted at women skilling are active in the District.
Lack of Residential accommodation facility
Lack of awareness about schemes and guidance facilities
Unwillingness towards Technical Jobs
Awareness drive among institutes about skilling programme
Career Counselling of Students along with their guardians
Scholarship Opportunities for female candidates
Creation of Centralized Monitoring System
Awareness drive among institutes about skilling programme
Career Counselling of Students along with their guardians
Scholarship Opportunities for female candidates
Lack of Mechanist for Maintenance and servicing of Agricultural Equipment
Unavailability of Short / Long Term Training facility in this specified trade
No Placement Assurance after completion of Training
Introduction of appropriate vocational training in district
Make a proposal
Identifying and approach Institutes / colleges
Placement Assurance Awareness drive among institutes about skilling programme
Minimal Utilization of Solar energy in district through Solar Water Pump and Solar Panels
Lack of Awareness of local opportunities
Introduction of vocational training courses in Solar Energy Domain
Make a proposal on Solar Energy Domain Unavailability of Short / Long Term Vocational Training Courses in Green Jobs Sector
Lack of awareness about skilling programme among I.T.I. and Polytechnic pass outs
Placement Assurance
Support and coordination from Sector Skill Council for Green Jobs
Identifying and approach Institutes / colleges
Table
Uncertainty of job prospect after completion of Training
Analysis of Current Skill Development in District
Awareness drive among institutes about skilling programme
12.2 Demand & Supply Gap Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sector
12.2.1 Top 5 Trades which are high in supply but low in demand
No Sector Trade Demand Supply
01 Beauty and Wellness SSC
Assistant Beauty Therapist
Agriculture SSC Paddy Farmer
Construction SSC Draughtsman
Management and Entrepreneurship and Professional SSC Unarmed Security Guard
Infrastructure Equipment SSC Mechanic (Electrical/Electronics/Instrumentation)
Table
Top 5 Trades which are high in supply but low in demand
12.2.2 Top 5 Trades which are low in supply but high in demand
240
120
150
48
01 Green Jobs SSC Solar PV Installer (Suryamitra)
Automotive SSC Commercial Vehicle Driver Level 4
Food Processing SSC Grain Mill Operator
240
30
15
IT ITES SSC Domestic Data entry Operator 150 60
Banking Financial Services and Insurance SSC Accounts Executive
Table 41 Top 5 Trades which are low in supply but high in demand
12.2.3 Top 5 Trades which are high in supply and high in demand
20
No Sector Trade Demand Supply
01 Banking Financial Services and Insurance SSC Microfinance Executive
Apparel Made Ups and Home Furnishing SSC Sewing Machine Operator
Electronics and Hardware SSC Field Technician - Air Conditioner
300
2570
48
Automotive SSC Maintenance Assistant/ Helper 75 84
Construction SSC Helper Mason
Table 42 Top 5 Trades which are high in supply and high in demand
300
5 Trades
Aerospace and Aviation SSC
Construction SSC
Handicrafts and Carpets SSC
Infrastructure Equipment SSC
Food Processing
13.1 Goals
Structural Fitter
Fabrication
Artwork Maker
Maintenance
Equipment)
Lab Technician Food and
90
25
25
8
3
Trades
Street Vendors and Cooks
Bamboo Handicraft Artisans
Book Keepers
Domestic Data entry Operator
Poultry Farm Manager
Plan
Approx. Number Sector Possible QP No Time line
Tourism and Hospitality THC/Q3004 December 2022
Handicrafts and Carpet HCS/Q8702 January 2023
BFSI BSC/Q0901 January 2023
IT ITES SSC/Q2212 December 2022
Agriculture AGR/Q4303 February 2023
13.3 Top 5 initiatives for district skilling
No Initiative Goal Key Actions
Skill Development Training on Cloth Bag / Folder Making
Skill Development Training to 30 WSHG Members in Apparel Sector
Identifying, Empanelment, Counselling, Training, Post training support
2022 December 2023
DIC Koraput
Odisha Livelihood Mission
ORMAS
TC, Funding, Trainers, Post training support Smooth Processing for availing of Bank Loans
2
E-Mobility Driving Lessons to Tribal Women
Promote selfemployment activities among 30 Tribal Women
Market Linkage to Outlets and E Commerce Sites
Mobilization of Urban Tribal Women
Providing Subsidy in purchasing E Vehicles
Providing assistance in availing bank loans
October 2022
December 2023
d. Green Jobs SSC
a. DIC Koraput b. Odisha Livelihood Mission c. Dist. Welfare Dept.
TC, Funding, Trainers, Post training support
3
Skill Training in Solar Pump Technician and Solar PV Designer Trade
Employment Generation of 240 candidates in Green Energy
Mobilization of I.T.I. and Diploma Pass outs
Training and assessed by Green Job SSC Post Training Placement Assistance
Mobilization of I.T.I. and Diploma Pass outs
October 2022 February 2023
a. DIC Koraput b. Green Jobs SSC c. I.T.I.s and Polytechnic Colleges
TC, Funding, Trainers, Post training support
4
Skill Training in servicing Agriculture Machineries
Promote self employment activities among 60 unemployed youth
Training and assessed by Agriculture SSC Post Training assistance Providing assistance in availing bank loans
October 2022 January 2023
a. DIC Koraput b. Krishi Vigyan Kendra
c. I.T.I.s and Polytechnic Colleges
NGOs, DIC, Industries, SHGs, etc. Well equipped Govt./ private training centres
5
Strengthening Coffee Eco system through Coffee Plantation Supervisor and Manager
Table
Engagement of 60 Educated Coffee Growers as Coffee Plantation Supervisor and Manager
Mobilization of potential Coffee Growers
Training at Central Coffee Board Exposure Visit to Chikmagalur Additional Certification in Coffee Testing
October 2022 January 2023
a. Coffee Board Koraput b. Coffee Development Trust c. Dist. Employment Exchange
TC, Funding, Trainers, Post training support
Agriculture
Agriculture Machinery Repair
Maintenance
Tractor Mechanic
Coffee Planation Manager
6,23,280
2,50,000
6,60,000
Coffee Planation Supervisor -- 60 3,00,000
Solar Pump Technician SGJ/AGR/Q6701 120 11,76,000
Solar PV Designer SGJ/Q0111 120 17,64,000
Paper Bag Entrepreneur SGJ/Q8701 60 5,73,750
Automotive Auto Rickshaw Driver ASDC/04506 30 4,46,880
Exposure Visit to Vocational Institutes 14 2,40,000
Livelihood Project Manager 60 7,00,000
Table 46 Estimated cost for above action plan
Career talks by the Principals / Faculties of ITIs and Polytechnic; and District Employment Officers along with Young Professional and counsellors of Model Career Center, Koraput in selected High schools of each block covering all the blocks in the district.
One day exposure visit of selected 9th and 10th class students (of which 50% should be girls) of the High Schools to Government ITIs and Polytechnics or Short term Skill Development Training Centres accompanied by the HMs/Senior Teachers for learning about vocations, machines, applications of science/math, principles of designs, technology, dexterity, the world of work, etc.
1 High School from each block will be selected for career talk based on the student strength (Class 8th 10th), HSC result, and preferably co educational institutions. Career talks on ‘career options after 10th ‘ will be conducted in the selected High School of the block. The Principals of TVETs or the District Employment Officers of the district shall join as the key speaker. Powerpoint presentations, motivational videos, leaflets, etc will be used for educating students on career options. Role model the district's role models will be invited to interact with the participating high school students.
Interested and willing 9th and 10th class students (50% boys + 50% girls) from these high schools shall be taken on a one day exposure visit to the Government ITIs and Polytechnics or Short term Skill Development Training Centres accompanied by the Headmaster or a Senior Teacher.
Students of the high schools are informed about the career options, after passing 10th class, with knowledge of the vocational education and skill training landscape.
Students are exposed to the vocations and application of theoretical knowledge in the world of work.
Bi monthly review of progress by the District Skill Committee of the district
Quarterly review by the Director of Employment and Director, Technical Education and Training
Young Professional and Counsellors of Model Career Center, Koraput along with Principals of 4 Govt I.T.I.s and 1 Polytechnic will implement and monitor the project.
DSC proposed to involve the following in the implementation process:
Young Professional and counsellors of Model Career Center, Koraput will monitor the implementation process.
During exposure visit Principals of 4 Govt I.T.I.s and 1 Polytechnic will provide guidance.
This project is based on the problems faced in execution of NRLM projects at the grassroots due to low literacy, banking and financial awareness among the beneficiaries etc. He suggested including a new job role in which skill trained professionals can monitor & supervise the NRLM activities from its inception to project completion. His role will be to generate awareness among the beneficiaries, prepare a DPR for financing the project, provide a linkage between banks and the beneficiaries and supervise the execution of the project as per the guidelines etc.
Educated unemployed Youth
Local Employment
SC/ST Youth
Graduate Candidates
Expected Outcome:
Selected candidates will assist in the following areas:
Making of Detailed Project Report for aspiring Entrepreneurs
Assist beneficiaries of various Govt. Schemes in bank proceedings
Monitoring and supervising NRLM/NRUM Projects in the field
Create a smooth linkage of beneficiaries and bank
Monitoring Mechanisms
Bi-monthly review of progress by the District Skill Committee of the district
Quarterly review by the Director of Employment and Director, Technical Education and Training
DSC proposed to involve the following in the implementation process:
Line Departments of Koraput will monitor the implementation process.
To ensure that the administration delivers its commitments both in terms of qualitative and quantitative targets, it is necessary that there is a robust monitoring and evaluation framework in place. The following are the ways and techniques to ensure the same:
• Comprehensive, & robust evaluation mechanism for existing training infrastructure

• Rating and Grading of all agencies & centres across the state on pre decided KPIs
• Quantifiable parameters ensuring accurate grades
• Allotment of future Short Term Trainings targets based on Grades
• Structural alignment of roles and responsibilities & KPIs for all district staffs
• Monitoring based on defined roles and responsibilities
• Regular collection and evaluation of feedback covering multiple stakeholder groups
• All feedbacks shall be kept confidential and only be used to evaluate & improve the ongoing training infrastructure
Round the Calendar Capacity Building Initiatives at the grassroots levels
Regular capacity building and training initiatives at the village/block level across multiple domains to upgrade/ up skill the existing workforce: Technical, Behavioral and Functional
Aspirational District . (2020). Koraput: Skills Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood (SANKALP) .
Authority, O. S. (2021). District Skill Development Plan.
Brief Industrial Profile of Koraput District. (2019 20). MSME Development Institute , Cuttack. Retrieved from http://www.msmedicuttack.gov.in/
DISTRICT CENSUS HANDBOOK Koraput. (2011). DIRECTORATE OF CENSUS OPERATIONS.