Sustainability Strategy & ESG Framework
Environmental & Social Governance
June 2025


June 2025

Dear Reader,
Welcome to the ADNEC Group Sustainability Strategy and ESG Framework. Since its inception, this strategy has been revitalised to capture the significant progress we have made in advancing our ESG maturity and embedding sustainability at the heart of our business, growth and operations. Over the past decade, we have implemented transformative initiatives across the Environmental, Social, and Governance pillars, building on and feeding into the foundation of our initial strategy and framework. Throughout this journey, we have continuously refined our policies and frameworks to ensure they remain robust, forward-looking, and reflective of the organisation's evolving aspirations and achievements.
Our environmental journey has been pivotal. We have not only calculated our carbon footprint across Scopes 1, 2, and 3, but have also delved into extended Scope 3 emissions to comprehensively understand and address our environmental impact. These efforts have resulted in the development of our Net Zero Transition Plan, outlining key projects and initiatives to achieve our 50% carbon reduction by 2030 and net zero by 2045 commitment. These include deploying renewable energy solutions, enhancing energy and resource efficiency, and reducing emissions across our value chain.
Meanwhile, our social impact initiatives has been equally transformative to our social sustainability pillar and goals. We have prioritised initiatives that enhance employee well-being, foster gender balance and diversity while strengthen community engagement and stakeholder value creation. Notable achievements include launching programmes that support Emiratisation, employee talent development, establishing partnerships to promote community resilience, and implementing initiatives that improve workplace equality and culture. Through these efforts, we have reinforced our commitment to social responsibility, ensuring that our growth is inclusive and aligned with global best practices.
Governance remains at the heart of our ESG and sustainability strategy. Our governance frameworks have evolved to reflect our ESG maturity, embedding transparency, accountability, and ethical decision-making across all levels of the organisation. In alignment with our commitment to responsible business practices, we have introduced an ethical and responsible procurement process that incorporates ESG criteria, engaged actively with our stakeholders and specifically our suppliers through strengthened due diligence across our supply chain.
This updated strategy builds upon the foundation of our original strategy and framework, incorporating learnings from our journey while addressing emerging challenges and opportunities. It reaffirms our commitment to Abu Dhabi’s and the UAE’s ESG. sustainability and social responsibility ambitions, aligning with national strategies and global frameworks to deliver meaningful impact.
As we move forward, we recognise that sustainability is an evolving journey. By continuously refining our approach, engaging with stakeholders, and monitoring our progress, we remain committed in our mission to create a sustainable, inclusive, equitable and low-carbon future. This document offers some insight into our accomplishments and the road ahead, and we invite you to join us in driving this vision forward.
ESG and Sustainability Team




























Joined the Abu Dhabi Sustainability Group and introduced structured waste management and recycling initiatives
Published our first Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) report and achieved ISO 14001 Environmental Management certification
Integrated into ADQ
Won the EFQM Challenge for circular economy
Secured ISO 20121 certification for sustainable events
Issued 1st ESG report from this year onwards

ADNEC Group is ranked 3rd among 32 ADQ entities in reference to ESG practices
ADNEC Group joins the global initiative Net Zero Carbon Events
Summary of Key Achievements
1. ESG strategy and sustainability framework
2. Issued annual ESG reports – Year 2021 onwards
3. Alignment with Modon Holding ESG Policy & Strategy
4. Developed Group-wide Net Zero Transition Plan with targeted projects
5. Commissioned key projects at ADNEC Centre Abu Dhabi: EWEC Trade Agreement, Solar PV, AI Energy Optimisation Project






Developed and launched our first Sustainability Strategy and ESG Framework, along with a carbon emissions strategy and plan.
Integrated into Modon Holding & alignment with ESG Strategy
Developed Group-wide Net Zero Transition Plan & Commissioned key projects such as EWEC, Solar PV, AI Energy Optimisation, and more
Launched second Sustainability and ESG strategy & framework Integrated ESG criteria into procurement Ethical Procurement & Supply Chain Engagements
1. Implement Targeted Efficiency and Carbon Reduction Projects
2. Transition scope 3 emissions from supplier spend to activity based
3. Further develop procurement ESG criteria – formalise process
4. Engage with suppliers – ESG Training and Awareness
5. Reduce 50% of Scope 1 & 2 emissions by year 2030 – as per NZTP ...and more



In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.
SECTOR SCOPE TITLE
General International United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
United Nations Global Compact
Global Reporting Index (GRI)
National UAE Principles of the 50
Green Agenda 2030
UAE Net Zero 2050
Abu Dhabi Climate Change Strategy
UAE Energy Strategy 2050
We the UAE 2031
Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030
Abu Dhabi Environment Vision 2030
In-Country Value (ICV) Program
Modon Holding ESG Policy & Strategy



A universal framework comprising 17 goals adopted by all UN member states to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030.
A voluntary initiative based on ten principles covering human rights, labour standards, environmental protection, and anti-corruption practices.
An internationally recognised framework that provides a standardised approach to sustainability reporting, enhancing transparency, comparability, and stakeholder engagement.
Ten strategic principles guiding the UAE’s long-term economic, political, and social development, emphasising sustainability, human capital, and global partnerships.
A UAE-wide action plan aimed at accelerating the transition to a green economy through sustainable economic growth, environmental stewardship, and increased competitiveness.
A national commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, promoting sustainable development, clean energy, and low-carbon economic diversification.
A strategic framework aimed at reducing Abu Dhabi’s greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to climate change through comprehensive mitigation and adaptation initiatives.
A national strategic roadmap focused on diversifying the UAE’s energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and increasing the share of renewable and clean energy to ensure sustainable economic growth.
A comprehensive national vision outlining strategic objectives and initiatives to position the UAE as a global leader in innovation, sustainable development, economic prosperity, and societal well-being by 2031.
A long-term strategic plan designed to diversify Abu Dhabi’s economy, reducing reliance on oil by developing high-value, knowledge-driven sectors and promoting sustainable economic growth and competitiveness.
A long-term strategic plan integrating economic growth with environmental sustainability, focusing on resource efficiency, biodiversity conservation, and quality of life improvements in Abu Dhabi.
A UAE national initiative designed to stimulate local economic development, enhance competitiveness, and promote local content, employment, and investments within supply chains.
Modon Holding’s ESG governance framework, guiding and embedding environmental, social, and governance principles across all subsidiaries, including ADNEC Group.





In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.
SECTOR SCOPE TITLE
Sector Related International Net Zero Carbon Events (NZCE)
Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)
National ADNEC Group Corporate Strategy
ADNEC Group ESG and Sustainability Framework and Strategy
OVERVIEW
An events industry-led initiative committed to halving greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and achieving net zero emissions by 2050, aligned with the Paris Agreement targets.
An initiative that guides companies in setting scientifically aligned, measurable greenhouse gas emission reduction targets to effectively address climate change.
ADNEC Group’s corporate strategy, defining ambitions and targets for sustainable growth, stakeholder value creation, and integrated ESG management across its investments and operations.
ADNEC Group’s ESG-specific strategy outlining clear sustainability objectives, targets, and governance processes that guide responsible operations across all business clusters.








In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.














A benchmark was conducted with the aim of understanding of what other organisations are doing with regards to their Sustainability strategy and ESG framework and to use this information as part of ADNEC Group’s own ESG journey
Overarching Criteria for Selection:
Type of organisation




Availability of information
ESG maturity
Disclaimer: This benchmark is not intended to provide a one-to-one comparison, nor intended to rank ADNEC Group against the selected organisations.



















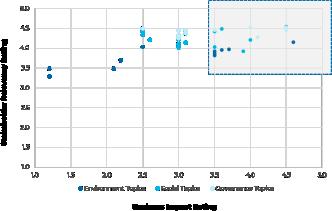
The Material Topics outline what issues mater most to the Group’s stakeholders and to the business itself – in surveying and engaging internal and external stakeholders; the Group was able to identify 20 material topics
Business Impact Rating
Environment Governance Social








The resulting material ESG topics for the ADNEC Group are:
Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas emissions
Energy Efficiency
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Sustainable Materials
Renewable Energy
Water Conservation and Management
Workforce Well-Being
Work-Life Balance
Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity
Nationalisation
Customer Experience & Satisfaction
Community Initiatives and Engagement
Health & Safety
Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Oversight
Data Security and Integrity
Business Ethics and Values
Corporate Governance
Business Continuity and Resilience
Transparency and ESG Disclosures
Operational Excellence and Innovation
and Habitat Protection
(if relevant for ADNEC operations)
(if relevant)
*Biodiversity: Currently, biodiversity is explicitly mentioned in Modon Holding’s ESG policy but is not explicitly listed in ADNEC Group’s updated material topics. Confirm whether biodiversity applies significantly to ADNEC Group’s operations when assessing initiatives and projects. *Talent Development: Included under Workforce Well-Being for simplicity, as ADNEC Group does not explicitly mention it separately.








Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
- Absolute Carbon Emissions (tCO₂e)
- Carbon Intensity per Employee
- Carbon Intensity per Event
- Carbon Intensity per Visitor
- NOx/SOx Emissions
Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Environment
- Water Consumption (m³)
- Water Intensity per event
- Electricity Consumption (kWh)
- Electricity Intensity (kWh/m²)
- Total Waste (kg)
- Recycled Waste (kg)
- Diversion Rate (%)
- Hazardous Waste (kg)
- Number of Major Spills
Potential loss of business opportunities due to increased stakeholder and regulatory demand for net-zero carbon operations. Financial and reputational impacts.
Medium
Increased regulatory scrutiny leading to potential fines or restrictions on operations if emission standards are exceeded. Medium
Water Conservation and Management Risk of water scarcity impacting operations and regulatory penalties for exceeding consumption limits. Increased operational costs.
Energy Efficiency
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Inefficient energy use increases operational costs and contradicts ESG commitments, impacting reputation and regulatory compliance.
Medium
Implementation of a robust Net Zero Transition Plan, energy efficiency improvements, renewable energy projects, and active supply chain engagement.
Ineffective waste management leading to increased operational costs, regulatory fines, environmental pollution incidents, and reputational damage.
Medium
emissions monitoring, compliance checks, and implementation of pollution-control technologies.
Regular water audits, installation of water-efficient fixtures, recycling and reuse initiatives, and employee awareness programmes.
Energy efficiency upgrades, LED lighting, HVAC optimization aligned with ASHRAE standards, solar PV installations, energy monitoring systems, and audits.
- Number of Environmental Violations Compliance and Environmental Management
Environmental violations causing financial penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational harm.








Medium
Enhanced waste management strategy, WasteMaster technology implementation, increased recycling programmes, hazardous waste protocols, and employee training.
Regular environmental audits, enhanced compliance training, proactive management reviews, and robust monitoring and reporting procedures. All
Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
- Employee WellBeing and Work-Life Balance Workforce Well-Being
- Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity, Nationalisation Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity
- Customer Satisfaction Score Customer Experience & Satisfaction
- Community Engagement Activities
Community Initiatives and Engagement
- Health & Safety Incidents Health & Safety
- Ethical Sourcing Compliance Rate
Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Oversight
- Data Breaches Incidents Data Security and Integrity
- Number of Ethics Violations Reported Business Ethics and Values
- Governance and Compliance Audits Corporate Governance
- Business Continuity Plan Activation Business Continuity and Resilience
- ESG Disclosure Completeness (%)
- Operational Excellence and Innovation Index

Transparency and ESG Disclosures
Operational Excellence and Innovation

Reduced productivity and high staff turnover due to inadequate support for employee well-being and worklife balance.
Reputational risk and limited innovation due to lack of diversity and non-compliance with nationalisation objectives.
Loss of revenue and reduced market competitiveness due to poor customer experiences and reduced satisfaction ratings.
Reduced community support and loss of social license to operate if local engagement is insufficient.
Operational disruptions, regulatory fines, and reputational damage due to workplace accidents or inadequate safety practices.
Operational and reputational risks arising from unethical supply chain practices and supplier noncompliance.
Financial, regulatory, and reputational impacts from data security breaches.
Financial, legal, and reputational risks from unethical business practices.
Regulatory penalties and reputational damage due to governance failures.
Financial losses and operational disruptions due to inadequate preparedness for crises.
Loss of stakeholder trust due to insufficient transparency in ESG reporting.
Reduced competitive advantage due to lack of innovation and operational inefficiencies.



Medium High
Employee wellness programmes, flexible working policies, regular employee surveys, and continuous improvement in workplace conditions.
Human Resources


Medium Medium
Inclusive hiring practices, diversity and inclusion training, nationalisation targets with strategic workforce planning.
Medium High
Medium Medium
Enhanced customer feedback mechanisms, service excellence training, continuous quality improvement programmes.
Human Resources
Business Clusters Quality / Customer Experience
Active community investment programmes, regular stakeholder dialogues, CSR initiatives aligned to local community needs. All
Strategy, Sustainability & ESG Champions
Medium High
Comprehensive health and safety management system, regular safety training, incident reporting and analysis, continuous safety audits.
All Business Clusters Health, Safety and Environment
Medium High
Medium High
Medium High
Medium High
Medium High
Medium Medium
ESG-integrated procurement policies, rigorous supplier due diligence, and periodic supplier audits.
Robust cybersecurity framework, employee training, regular penetration testing, and IT security audits.
Clear ethics policies, robust whistleblowing channels, regular ethics training.
Strong governance frameworks, regular compliance audits, board oversight.
Regularly updated business continuity plans, scenario testing, employee preparedness drills.
Comprehensive ESG reporting aligned with global standards, external assurance.
Risk & Compliance
All Business Clusters
Risk & Compliance IT & Digital Transformation
All Business Clusters
Risk & Compliance
All Business Clusters Risk & Compliance
All Business Clusters
Business Continuity
Strategy & Sustainability
All Business Clusters
All Business Clusters
Medium High

Continuous innovation programmes, operational efficiency initiatives, technology integration.
Business Excellence Team
Innovation Committee
Develop and implement a group-wide decarbonisation roadmap to achieve Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2045, accelerating the existing 2050 pledge. This initiative focuses on cutting greenhouse gas emissions through energy efficiency measures, adoption of renewable energy, and carbon offset programs in event operations. It involves working closely with event organizers and suppliers to minimize the carbon footprint of venues and exhibitions.
Invest in energy-efficient infrastructure and practices at all venues. This includes retrofitting lighting systems with LED technology, optimizing HVAC and cooling systems, installing smart building controls, and engaging staff in energy conservation training and awareness. These upgrades reduce electricity use and align with national energy efficiency targets for 2050.
Expand the use of clean energy by installing on-site renewable power systems (e.g. solar panels on exhibition hall rooftops and parking structures) and procuring clean electricity from the grid. Generating renewable energy on-site will directly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and cut Scope 2 emissions from venue operations. Any surplus energy could be fed back or stored to further improve efficiency.
Implement a comprehensive waste management initiative aiming for zero waste to landfill in events and operations. Measures include expanding recycling and composting facilities onsite, phasing out single-use plastics in venues, reusing or donating exhibition materials, and working with contractors to design booths and stages for disassembly and reuse. The program also entails educating exhibitors and attendees on waste sorting and reduction.
Adopt water-saving technologies and practices across venues and hotels to minimize water usage. This includes installing low-flow fixtures and sensor faucets, optimizing irrigation systems for landscaping, implementing greywater recycling for plant irrigation or toilet flushing, and improving chillers/cooling towers for efficient water use. Regular monitoring of water consumption will identify and fix leaks promptly.
Operational cost savings from energy reduction and resource efficiency, enhanced brand reputation as a sustainability leader in the events industry (leading to increased stakeholder trust and preference), and proactive compliance with global climate initiatives (positioning ADNEC ahead of emerging carbon regulations).
Significantly lower operating costs due to reduced energy consumption, decreased carbon emissions contributing to climate goals, and improved compliance with energy regulations and green building standards (reducing the risk of future energy price or carbon cost increases).
Long-term energy cost savings and insulation from utility price volatility, a demonstration of innovation and climate leadership that provides competitive advantage as stakeholders increasingly prefer low-carbon partners, and tangible progress toward ADNEC’s emission-reduction targets (mitigating transition risks associated with carbon).
Lower waste disposal and material procurement costs due to reduced waste generation and increased recycling, improved operational efficiency in resource use, and enhanced corporate reputation for environmental responsibility – visibly aligning ADNEC with circular economy principles and client sustainability expectations.
Reduced water utility costs and improved efficiency (important as businesses in water-scarce regions should implement strategies to cut usage), increased resilience against future water scarcity or stricter water regulations, and support of UAE sustainability goals on water conservation (strengthening ADNEC’s license to operate in the community).








Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
Occupational Health & Safety Excellence
Employee Wellbeing & Engagement Program
Employee Health & Safety
Employee Engagement & Well-being
Strengthen health and safety practices to ensure safe venues for employees, contractors, and visitors. This includes regular HSE training and drills, rigorous risk assessments for events, certification to international safety standards (e.g. ISO 45001), and a “safety-first” culture campaign. By investing in advanced safety equipment and clear emergency response plans, ADNEC can minimize workplace incidents and ensure all events meet high safety standards.
Implement programs to support employees’ physical and mental well-being and to foster engagement. Initiatives could include wellness workshops, access to mental health resources, fitness activities, flexible working arrangements, and regular employee feedback surveys (with action plans based on results). Emphasizing work-life balance and well-being benefits will improve overall job satisfaction.
Fewer accidents and incidents, leading to lower costs related to injuries or disruptions (companies that prioritize employee health and safety can reduce costs associated with accidents and illnesses). Additionally, a robust safety record boosts ADNEC’s reputation as a reliable, world-class venue operator and ensures compliance with labor and event safety regulations (reducing legal risk).
Higher employee morale and productivity, and improved talent retention –employees are more likely to stay with and be attracted to a company that invests in their well-being and shares their values. A positive workplace culture also enhances innovation and service quality (as engaged employees are more motivated), and strengthens ADNEC’s brand as an employer of choice.
Diversity & Inclusion Strategy Diversity & Inclusion
Roll out a comprehensive diversity and inclusion strategy to ensure equal opportunity and a workforce that reflects the community. This strategy would set targets (e.g. increasing female representation in leadership and hiring more UAE nationals), enforce unbiased recruitment and promotion practices, provide mentorship and leadership programs for underrepresented groups, and conduct regular staff training on unconscious bias and inclusive culture.
Invest in developing employee skills and leadership pipeline. This encompasses graduate recruitment schemes and internships, continuous training and upskilling workshops, clear career progression paths, and partnerships with educational institutions (e.g. sponsoring industry-related courses or hosting job fairs). By mapping career development plans for employees and recognizing high performers, ADNEC can build a strong internal talent pipeline.
A more diverse and inclusive workforce drives greater innovation and problem-solving by bringing varied perspectives. It also strengthens the company’s appeal to a broader talent pool and improves employee engagement and loyalty. Moreover, demonstrating commitment to D&I enhances ADNEC’s compliance with local employment goals and its reputation among global partners and clients as an equitable, modern organization.
Improves workforce capabilities and innovation capacity, ensuring the company has the skills needed for future growth. These programs also increase employee loyalty (reducing turnover costs) and help attract top talent externally – as employees are drawn to organizations with strong development opportunities and values alignment. In the long term, succession planning through talent development secures leadership continuity for the Group.
Customer Experience Enhancement
Higher client satisfaction and loyalty, leading to repeat business and positive word-ofmouth. Strengthening customer-centricity also enhances ADNEC’s brand reputation and competitive position – companies known for responsible practices and superior service tend to enjoy better stakeholder loyalty. Additionally, actively engaging with customer feedback drives continuous improvement in operations and can spark service innovations. Community
Customer Satisfaction & Service Quality
Leverage technology and staff training to elevate the experience for customers, clients, and event attendees. This opportunity involves deploying advanced CRM systems and data analytics to personalize services, implementing real-time feedback tools (surveys/apps) during events, and training frontline staff in service excellence. By using customer insights and focusing on client care, ADNEC can set itself apart in service quality.
Engagement & Social Impact Initiatives Community Engagement & Impact



Establish robust community outreach and investment programs to ensure ADNEC’s growth benefits the local society. For example, partner with local schools and universities on education and internship initiatives, support community events and charitable programs, encourage employee volunteering days, and collaborate with local businesses (such as SMEs and social enterprises) for event services. Regularly measuring and communicating the Group’s economic and social contributions to Abu Dhabi demonstrates transparency in impact.





Strengthens relationships with local stakeholders and ADNEC’s “social license to operate.” A proactive community engagement approach enhances the company’s reputation among residents and regulators and contributes to the local economy and social development. Such goodwill can translate into easier project approvals, government support, and a preference from clients who value working with a socially responsible venue partner.
Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
Integrated Risk Management & Business Continuity
Risk Management & Business Continuity
Strengthen the Group’s ethics and compliance framework to uphold the highest standards of corporate governance. Key actions include periodic training for all employees on the Code of Conduct and anti-corruption policies, establishing an anonymous whistleblower hotline, performing regular compliance audits, and enforcing zero tolerance for violations. Leadership oversight (e.g. an ethics committee) will monitor compliance and address any misconduct swiftly.
Implement robust data protection measures to safeguard customer, employee, and partner data across all business units. This opportunity involves upgrading cybersecurity infrastructure (firewalls, intrusion detection, encryption), conducting regular vulnerability assessments and penetration tests, and enforcing strict data governance policies (in line with GDPR and UAE data laws). Employees will also receive training on cybersecurity awareness and data privacy best practices.
Integrate environmental and social criteria into procurement and supply chain management. ADNEC will update procurement policies to favor suppliers with strong ESG credentials, use more local and eco-friendly products (e.g. sustainable event materials, green catering options), and require key suppliers to abide by ADNEC’s supplier code of conduct. Supplier ESG performance will be monitored and ADNEC can collaborate with vendors on initiatives to reduce waste and improve labor practices in the supply chain.
Adopt best practices in ESG reporting and disclosure to improve transparency. This includes publishing an annual ESG/Sustainability report aligned with international frameworks (GRI, SASB, etc.), clearly communicating performance on each material topic and progress toward targets. ADNEC should also report climate-related risks in line with TCFD recommendations and ensure data in reports is externally assured. Regularly updating stakeholders on ESG progress (via the company website or newsletters) is part of this initiative.
Embed ESG considerations into enterprise risk management and strengthen business continuity plans. This involves regularly updating the corporate risk register to include ESG risks (e.g. climate change impacts, supply chain disruptions, health pandemics), and developing robust contingency and continuity plans for critical operations. ADNEC will conduct scenario planning and simulation drills (for events of various crisis situations) to ensure preparedness. Business continuity policies (aligned with ISO 22301 or similar) will be maintained and communicated to all relevant teams.





Company A
Reduces the risk of legal breaches or reputational scandals by proactively preventing misconduct (effective ESG risk management lowers the likelihood of financial, legal, or reputational damage). It also builds stakeholder trust – investors, partners and regulators gain confidence that ADNEC operates ethically and transparently – and ensures adherence to all applicable laws and regulations, avoiding penalties.
Prevents data breaches and the associated financial and reputational harm that can result from such incidents. Maintains customer and stakeholder trust by demonstrating that ADNEC takes data privacy seriously and ensures compliance with data protection regulations (avoiding regulatory fines). A strong cybersecurity posture also protects business continuity by reducing the risk of IT disruptions.
Mitigates supply chain risks and can lead to cost savings – for example, sourcing materials more sustainably and efficiently, and reducing waste in the supply chain can lower costs over time. It also enhances ADNEC’s brand credibility and consistency, as the company’s ESG values are extended to its partners (which is increasingly important to clients and investors). Additionally, this program ensures compliance with emerging regulations or client requirements regarding responsible sourcing.
Increases accountability and builds stakeholder confidence in the company’s commitments. High-quality ESG disclosure meets investor expectations and regulatory requirements, potentially improving access to capital as investors and lenders favor companies with strong ESG transparency. It also helps internal decision-making by tracking progress and enhances ADNEC’s reputation for governance excellence and openness.
Enhances organizational resilience against crises and unexpected disruptions, thereby protecting employees, customers, and financial performance. Proactive risk management of ESG issues helps avoid or mitigate potential losses (identifying and managing ESG-related risks lowers the likelihood of costly incidents). A strong continuity capability also assures stakeholders – from clients to regulators – that ADNEC can sustain operations under challenging conditions, which builds trust and reliability.



Pledge
“Create long-term value for all our stakeholders through consciously ethical and sustainable practices across our group activities”







emissions by improving energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy, and managing emissions from logistics and travel.
2. Minimise waste generation by enhancing recycling, promoting reuse, and prioritising sustainable and recyclable materials through circular economy practices.
3. Strengthen infrastructure and operational resilience by proactively addressing climate-related risks, implementing green building practices, and managing environmental impacts across events.
4. Responsibly manage natural resources by optimising water use, reducing pollution and protecting soil and land quality









1. Foster a supportive workplace by prioritising employee well-being, work-life balance, and occupational health and safety, creating a resilient and productive workforce.
2. Promote diversity, gender balance, and equal opportunity through inclusive hiring practices, development opportunities, and equitable career advancement.
3. Accelerate nationalisation and talent retention by investing in continuous training and development, preserving Emirati culture and identity, and positioning the organisation as an employer of choice.
4. Uphold fundamental human rights and proactively prevent discrimination, while encouraging employees to actively engage in meaningful volunteerism and community initiatives.



“Create long-term value for all our stakeholders through consciously ethical and sustainable practices across our group activities”









1. Promote ethical conduct, responsible communication, and transparent governance practices that uphold stakeholder trust and regulatory compliance.
3. Ensure strong governance, senior management diversity, and responsible sourcing through robust oversight and alignment with ESG principles. Our Pledge
3. Drive sustainable growth by embedding human rights, innovation, and ethical practices across our value chain and partnerships.






2. Strengthen cyber security, business continuity, and risk governance frameworks to ensure secure, adaptive, and future-ready operations



ADNEC Group’s ESG framework strategically aligns environmental, social, and governance priorities with business performance. By applying a unified set of metrics across all clusters, we enhance our capability to:
Manage Risk Create Impact & Value Build Trust & Governance Achieve Operational Excellence
Identify emerging regulations, climate risks, and stakeholder expectations to enable proactive decision-making.
Drive stronger revenue growth, improve cost efficiency, enhance staff productivity, and secure access to favourable financing.
Uphold transparent governance, ethical conduct, and responsible supply chains to mitigate legal, regulatory, and reputational risks.
Improve energy, waste, and resource efficiency, while fostering innovation and sustainable service delivery.








Our governance framework includes continuous evaluation and measurement of ESG performance, independent oversight to reinforce accountability, and regular refinement of governance structures to effectively address evolving sustainability risks and opportunities.
Modon Holding - Board of Directors
Establishes the overarching sustainability and ESG strategy for Modon Holding and its subsidiaries, including ADNEC Group. Sets strategic objectives, highlevel targets, and priorities aligned with applicable mandates and regulations. Provides oversight through regular reviews of ESG performance against established targets as reported by the Group CEO, ensuring accountability and transparency.
Modon Holding - Group CEO
Holding - Executive Management Committee
ADNEC Group - Managing Director & Group CEO
Leads the operational integration and execution of Modon Holding’s sustainability and ESG strategy across all subsidiaries. Ensures subsidiaries adhere to the established ESG framework and achieve set targets. Reports regularly to the Board of Directors on ESG performance, highlighting key achievements, challenges, and recommended actions.
Supports the Group CEO by reviewing and advising on ESG strategic direction, business planning processes, and priorities. Provides guidance on ESG policy development, strategic targets, procedures, risk management, annual goals, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Provides executive leadership and strategic direction for ADNEC Group’s sustainability strategy and ESG agenda. Ensures full alignment with Modon Holding’s ESG policies, targets, and standards. Oversees the management of ESG performance, risk management frameworks, and sustainability initiatives and projects across the organisation.
Leads the development, implementation, and monitoring of ADNEC Group’s ESG strategy and initiatives. Manages the ESG performance framework, coordinates sustainability activities across all business clusters, ensures alignment with recognised global ESG standards, and facilitates transparent ESG reporting. Advises senior leadership on sustainability best practices, monitors performance against defined ESG objectives, and recommends areas for continuous improvement. Provides regular reporting to the Managing Director and Group CEO, detailing ESG achievements, challenges, and strategic recommendations.









• Sustainability leadership enhances competitiveness in international bids and events
• Clean energy, waste innovation, and ESG-aligned services open new commercial opportunities (e g sustainable event packages, green certifications, carbon-neutral partnerships).
• Strategic ESG positioning supports access to sustainability-linked financing and impact-focused investments.

• Energy-efficient operations (AI-driven BMS, HVAC optimisation, solar PV) lower utility costs and carbon intensity.
• Waste diversion and food valorisation reduce disposal costs and improve operational sustainability across F&B and events
• Water-saving fixtures and greywater reuse reduce consumption and avoid excess utility charges
• ESG performance strengthens brand equity and stakeholder trust
• Enhances talent attraction and retention through well-being, inclusion, and upskilling initiatives
• Enables stronger regulatory compliance and futureproofs operations against climate, data, and ethical risks.
• Drives innovation in event delivery and builds thought leadership in net-zero and sustainable MICE practices







Protecting
1. Scope 1, 2 & 3 GHG emissions (absolute & intensity)
2. Renewable energy consumption (% of total use)
3. Energy, water & waste intensity per event/visitor
4. Waste diversion & food waste valorisation rates
5. % of sustainable materials used in operations & events
6. Climate risk assessments & mitigation actions
7. Green building certifications (LEED/Estidama)
8. Water reuse & quality management projects
1. Employee satisfaction & engagement scores
2. Occupational health & safety indicators ( LTI, incident rate)
3. Gender diversity & leadership representation
4. Emiratisation rate & retention of UAE talent
5. Participation in training, development & upskilling programmes
6. Volunteer hours and employee social impact participation
1. Supplier ESG compliance rate & ethical sourcing audits
2. % of local and sustainable procurement spend
3. Community investment (amount, beneficiaries, partnerships)
4. Customer satisfaction (NPS, complaints resolved)
5. Engagement in cultural inclusion and accessibility programmes
1. ESG reporting alignment (GRI, TCFD, SDGs)
2. ESG assurance & verification status
3. Data breaches & cybersecurity incident frequency
4. Whistleblowing reports & resolution rate
5. Business continuity test coverage & scenario simulation frequency
6. Compliance with internal controls & ethics training participation




In this phase, the Group conducts its materiality assessment, stakeholder engagement, and other research activities to identify material topics, risks and opportunities that will shape its ESG strategy. This also includes articulating the Group’s aspirations in ESG, and defines its goals, targets, and plans – and linking these to the Group’s policies and procedures.
In this phase, the Group collects insights and data regarding its ESG performance in order to collate this information and disseminate it as part of its annual report and as required to its stakeholders, including shareholders, regulators and ratings agencies.
In this phase, the Group carries out periodic maturity and performance analysis to identify areas of improvement and track progress against the strategy, across the Group. Moreover, this phase includes the on-going research and coordination conducted by the ESG team(s) to identify ESG best practices, guidelines and improvements that can benefit the Group.












1 This is based on ADNEC Group’s responsibility to align with its shareholder‘s (Modon Holding) aspirations and strategy for adopting ESG practices. ADNEC Group on an annual basis must submit its updated ESG performance against the topics and criteria that are material to the business. The information provided is based on: the strategy/targets the Group has defined, the measures (activities) deployed, and the results achived for each of the criteria identified by Modon Holding.
2 This consists of the reporting that ADNEC Group (or its specific business clusters / subsidiaries) submits to external stakeholders, in order to comply with the standards, guidelines, and mandates it has agreed to. Each external stakeholder represents its own specific reporting expectations.
3 This report is prepared and published annually, as part of the Group’s Annual Report. In it, ADNEC Group shares its ESG and sustainability goals, strategy, programmes and results.
4 This consists of ADNEC Group’s internal performance reporting that tracks the progress against its ESG strategy, updates on any ESG activities and the programmes defined, and the maturity of the organisation’s ESG capabilities. These reports are submitted to the ESG Committee and Executive Management / Board on a regular basis.
5 Annual targets are prepared and shared by each business cluster / subsidiary within the Group, in line with the Group’s reporting to its shareholders, the public, and any other external stakeholders as required. Additionally, on a regular basis, each business cluster prepares and shares its performance updates against the Group’s ESG strategy.




ADNEC Group develops an ESG Index outlining annual targets for each business cluster, aligned with the Group’s ESG Strategy and Modon Holding’s overarching strategy and policy; the index is updated bi-weekly and reported to senior management on a quarterly basis.
















ADNEC Group has accelerated its decarbonisation journey by launching a comprehensive Net Zero commitment. Guided by the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol and aligned with the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi), the Group established 2022 as its baseline year and committed to a robust, scientifically validated emissions-reduction pathway.
Year 2030
Reduce absolute Scope 1 and 2 emissions by at least 50% & ensure that suppliers representing 67% of Scope 3 Purchased Goods and Services have adopted science-based targets aligned with the 1.5°C pathway.








Reach full net zero across Scopes 1, 2, and 3, with any residual emissions (no more than 10%) neutralised through accredited carbon removal solutions only, such as direct air capture or longterm bio-based sequestration.
Our updated and re-baselined year 2022 carbon footprint of 146,279 tCO₂e covers all relevant GHG Protocol categories including extended scope 3 emissions. Our carbon footprint scope 3 emissions are broken down as follows
















ADNEC Group’s journey to achieving net zero by 2045 follows a structured, phased approach combining technology, operational excellence, and stakeholder collaboration.
Near-Term Targets for 2030
- Reduce absolute Scope 1 and 2 emissions by at least 50%
- Suppliers covering 67% of emissions from Purchased Goods and Services to set net zero targets








Medium-Term
2035 Reduce absolute Scope 1 and 2 emissions by at least 90%
Long-Term Target for 2045
Absolute Emissions by 90%
tCO2e
Our Net Zero Transition Plan outlines a clear roadmap structured around three distinct phases:.
• Carbon Baselining and Net-Zero Transition Plans
• Waste Management Initiatives
• ADNEC Centre Abu Dhabi - Clean Energy Agreement & AI Energy Optimisation Projects
• ExCeL London - Electricity Submetering, Voltage Optimisation & Lighting Controls
• Ethical Procurement Framework Development
• Data Collection / Reporting / ESG IT Solution
• ADNEC Centre Al Ain Clean Energy Agreement, On-site PV & Energy Audit
• ADNEC Centre Abu Dhabi Onsite PV & Energy Audit
• ExCeL London - Onsite PV (Phases 1 & 2), HVAC Controls & Voltage Optimisation
• ADNEC F&B – Voltage Optimisation
• ADNEC Media – Energy Audit & Clean Energy Trade Agreement
• Fleet Decarbonisation Phase 1
• Group-wide Lighting Redesign, Controls








• Group wide Energy Audits / ESCO Shared Savings Agreements
• Building Envelope Upgrades
• Travel Fleet Decarbonisation - Phase 2
• Environmentally Friendly Refrigerants
• Boilers & Heat Pump Upgrades
• Material lifecycle Analysis
• Transition Scope 3 emissions spend to activity based.
• Supplier awareness & training








Sustainability and ESG certifications, labels and frameworks have gained in popularity as transparency and stakeholder expectations become more important. A comprehensive approach in ESG driven organisation and strategy, should consider all 3 of these pillars.
For a company to establish and delivery its sustainability journey, several key activities need to be conducted first as they present prerequisites for a clear and coherent strategy.
All players should know their environmental footprint to assess their impact on climate and the society A scope 3 analysis will present emission heavy aspects and will thus provide reduction indicators Many tools and providers on the market offer GHG accounting services


The materiality assessment helps stakeholders to find out how important specific environmental, social or governance issues are to them. The assessment combines this view with an understanding of the impact of these issues to the organisation’s financial and strategic success. A double materiality assessment can also be conducted to further consider the impact of these issues to the society
To develop an ESG strategy a company needs to determine its main priority areas and goals in line with its values and its materiality. Here, the UN Sustainable Development Goals present an internationally recognized framework, with specific targets, that the organisation can work towards – including other key mandates that the organisation specifically contributes to.







Sustainability reporting becomes mandatory To take the sustainability accreditation even for organisations in all sectors and sizes. The further some companies, mainly stock public and private sector demand for exchange companies also aim for ESG transparency and some organizations offer recognition. This gives investors additional third party accreditation services to avoid confidence of the organisation’s management greenwashing and promote collaborative capabilities and commitments in line with the action. Some of these organizations are SBTi, rating agencies ESG guidelines and standards. CDP, Ecovadis, ACT, GRI, etc.


ESG ratings are based on environmental, social and governance pillars which are all covered and step 1 and 2 of the recommendations. The most popular ESG rating companies are MSCI, Sustainalytics, etc.






1. Strategic Alignment:
ADNEC Group’s ESG Framework and Strategy are aligned with the Group’s overall Corporate Strategy and guided by shareholder directions.
2. Vision and Aspirations:
The Group’s ESG vision and aspirations are shaped by shareholder priorities and relevant external frameworks, including the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Science-Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), and UAE national priorities.
3. Implementation and Action Plans:
Guided by the overarching ESG Strategy, targeted substrategies and detailed action plans are developed and implemented across ADNEC Group to effectively deliver ESG objectives.
4. Subsidiary and Cluster Contributions:
Each subsidiary or business cluster actively contributes to the Group’s ESG Strategy by defining tailored goals and action plans. These are aligned with Group-level strategic direction, while addressing specific material topics, operational requirements, constraints, and stakeholder expectations unique to their context.








The ADNEC Group ESG Model is aligned with international guidelines for ESG integration and reporting, leveraging the Group’s existing corporate strategy and management frameworks. The model comprises three interconnected activities:
Covers internal oversight, alignment, and continuous improvement of the Group’s ESG initiatives, ensuring robust governance and accountability.

Covers defining material ESG topics, setting strategic ESG goals, and formulating actionable plans aligned with the Group’s vision.
Covers the management, execution, and monitoring of ESG action plans, including regular performance reporting to key stakeholders.








The development of ADNEC Group’s ESG Strategy followed a structured 4-step process outlined below:
Identify and align ADNEC Group’s ESG strategy with key national and international sustainability mandates and priorities.
Perform comparative analysis of ESG practices among leading organisations to identify relevant strategic elements and industry best practices.
Define critical ESG topics most relevant to ADNEC Group’s operations and stakeholders, informing strategic direction.
Utilise detailed descriptions ("baseline cards") of each material ESG topic, capturing relevance, context within ADNEC Group, and associated risks and opportunities.
Establish ADNEC Group’s overarching sustainability ambition and commitment.
Identify major ESG themes and areas of strategic focus, derived directly from the ESG pledge.
Set measurable targets and specific outcomes to guide ESG strategy implementation and performance assessment.
Define critical enabling factors required for the successful achievement of ESG goals and effective strategy execution..








Outline comprehensive programmes, projects, initiatives, and timelines necessary to operationalise and deliver the ADNEC Group ESG Strategy effectively.








In developing a robust ESG framework and strategy for the ADNEC Group, a clear understanding of the organisation’s current state and maturity needs to be established in addition to determining the key ‘issues’ it needs to tackle through its strategy – represented by the ‘material’ ESG topics.
Snapshot analysis of the organisational capabilities, tools and practices adopted by the organisation in implementing and managing an ESG framework, and which looks at the following elements:
1. Objectives and Strategy Definition
2. Implementation and Reporting
3. Governance and Control
This is used to help determine the key areas that can be addressed that would add value to the organisation’s ESG journey.
This assessment looks at the different topics that will directly inform the organisation's ESG strategy. The topics stem from global and local trends, including the organisation's own priorities based on its business activities and strategy, some of these sources include:
1. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG)
2. United Nations Global Compact (UNGC)
3. Net Zero Carbon Events (NZCE)
4. UAE Net Zero 2050
5. Modon Holding ESG Policy and Strategy
Risk management is an integral part of ESG and the aim here is to look at the key related risks and potential opportunities facing the organisation –based on its overarching business activities.
These risks and opportunities are taken from the perspective of each issue and are subsequently prioritized based on the material topics identified⁶
List of key gaps in the organisation’s ESG management practices.



Material topics relevant to ADNEC Group and its ESG Strategy.





Risks and Opportunities Associated with Each Material Topic
This maturity assessment provides a snapshot of the organisation’s current strengths and weaknesses in relation to its ESG management capabilities. The assessment is based on a review of the available information shared by the ADNEC Group strategy team and is informed by the interviews conducted with key members across the organisation as well as a review of the documentation made available.
1. Does the organisation have an overarching vision for ESG?
2. Is ESG incorporated as part of the organisation’s broader strategy?
3. Is ESG incorporated as part of the organisation’s broader risk management framework?
4. Has the organisation defined objectives and targets?
5. Are the targets in accordance with any established standards (e.g. SASB, CPD, SBTi)?
6. Has the organisation engaged with its stakeholders to determine its material issues?
7. Does the organisation have a set of programmes / initiatives that directly contribute to the ESG strategy?
1. Does the organisation report or communicate internally and externally on its ESG performance?
2. Does the organisation provide any publicly accessible information about its ESG strategy and performance?
3. Does the organisation track the impact of its activities on its ESG strategy and targets?
4. Does the organisation enable the achievement and implementation of its ESG strategy through a dedicated budget allocation?
5. Does the organisation have the tools and technology to track and monitor ESG performance?
1. Are there clearly defined roles for ESG management embedded within the organisation?
2. Is the ESG strategy and performance reviewed by the executive leadership and Board of the organisation.
3. Does the organisation have a dedicated manager / team to oversee ESG?
4. Are ESG principles and policies integrated into the operations and management systems of the organisation?
5. Is ESG supported by a clear approach and mechanism for change management?
6. Is the organisations ESG report reviewed and assured by a third party?
The aim of this assessment is not to give ADNEC Group a specific score or rating that it can use to benchmark itself to its peers – but to highlight to the reader and the team the current state of the organisation’s ESG management capabilities and the key gaps that it can address through its on-going ESG efforts








1. Sustainability is a core component in the Group (and cluster) strategies.
2. Key elements from the social and governance perspectives are represented in the Group strategy
3. The Group has several initiatives and projects that directly contribute towards ESG and sustainability.
4. A materiality assessment was previously conducted and will be expanded to include further stakeholders to provide further insights and alignment with stakeholder needs
5. The Group has individual targets related to ESG performance metrics, that support the Group in delivering a comprehensive ESG strategy.
1. The Group has GRI reports on ESG and has publicly published annual ESG reports from 2021 to present date, and has been publishing sustainability reports since 2014.
2. ADNEC Group has positioned itself as a market leader in ESG and Sustainability through the various ESG and sustainability initiatives it has implemented over the years
3. The prioritisation and budgeting process for the Group is being expanded to factor in ESG programmes and ESG driven investments.
4. The Group has implemented several practices, programmes, and standards that contribute towards key topics within ESG (e g ISO 14001, 21021 and 22000)
5. The Group is tackled specific ESG topics (e.g. sustainability) and is planning broader awareness and training campaigns across ESG issues.
1. The Group has an established ESG Committee consisting of members from across the organisation and who meet bi-weekly.
2. ESG is an item on the agenda of every Board of Directors meeting, and is reported to Modon Holding monthly
3. The Group has implemented many programmes and policies that support ESG, such as; Anti-Bribery & Corruption Policy, Conflict of Interest and Related Party Policy and a Whistle-blowing Policy.
4. The mechanism to manage ESG within the clusters and to track overall ESG performance across the Group has been developed
5. The Group has developed a framework for ESG definition and management.
1. Key ESG performance metrics need to be re-baselined considering the growth of the Group’s activities.
2. The Group’s enterprise risk management (ERM) approach is being factors in ESG risks but this could be further improved / enforced through more adequate risk and compliance resources
1. The Group is taking steps to align with international reporting standards including those from SASB, TCFD, CDP.
2. ESG data is managed on an ad-hoc basis and the Group’s systems are being expanded to support in collecting, managing and utilising ESG related data








1. ESG principles and goals are being integrated across the organisation’s policies and procedures – while some policies are being reviewed against ESG to ensure alignment.
2. The Group’s ESG / sustainability disclosures have not yet been assured or validated by a third party –however, this is considered for future discolosures.
1 Air pollution
2 Climate Risk and Resilience
3 Desertification
4 Ecosystem biodiversity
5 Waste Management and Circular Economy
6 Carbon Footprint & Greenhouse Gas emissions
Contamination of the atmosphere by harmful substances including gases, chemicals, and particulates.
Physical and transition risks posed by climate change, and an organisation’s capacity to adapt effectively.
Degradation of land in dry regions caused by climate variability and unsustainable practices.
The diversity of living organisms and ecosystems, including genetic, species, and habitat variations.
Minimising waste and extending the lifecycle of materials through reuse, recycling, and closed-loop systems.
Total greenhouse gases emitted directly and indirectly by an organisation’s operations and value chain.
7 Green Building and Infrastructure Design and operation that minimises inefficiency and negative impacts throughout lifecycles.
8 Sustainable Materials Materials sourced and utilised to minimise negative environmental and social impacts.
9 Emissions from Travel and Logistics Greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions from the transportation of people and goods.
10 Energy Efficiency
11 Event-Based Environmental Footprint
12 Noise Pollution
Reducing energy consumption and losses while delivering the same level of output or service.
Total environmental impact of energy, water, waste, and emissions, generated by an event or project.
Excessive or disturbing noise levels that negatively impact people or wildlife.
13 Renewable Energy Energy derived from naturally replenished sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower.
14 Soil & Land Use Impact Impact on soil health, erosion, and land conversion caused by operational activities.
15 Water Conservation and Management Efficient use and sustainable stewardship of potable or freshwater resources.
16 Water Quality Management Actions to preserve or enhance the chemical, physical, and biological conditions of potable or freshwater.
1 Community Initiatives and Engagement
2 Cultural Accessibility & Inclusive Tourism
3 Health and Safety
4 Customer Experience & Satisfaction
5 Equitable Access
6 Non-Discrimination
Programmes to support and involve local communities in social or environmental improvements.
Tourism experiences that are accessible, inclusive, and respectful of diverse cultures and abilities.
Protecting employees, contractors, visitors and occupants from injuries, illnesses, and health hazards.
Ensuring products and services consistently meet or exceed customer expectations, fostering loyalty.
Providing fair and unbiased access to products, services, or opportunities for all individuals.
Preventing unfair treatment based on characteristics such as gender, race, religion, or other attributes.
7 Emirati Culture and Identity Preserving and promoting the UAE’s national cultural heritage and values.
8 Employee Training and Development Improving employee capabilities and career prospects through ongoing learning and skills enhancement.
9 Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity Ensuring equitable representation, opportunities, and progression for all genders across the organisation.
Human Rights Respecting and protecting fundamental human rights and freedoms across operations and supply chains.
Prioritising the hiring and development of local citizens to enhance national workforce participation.
Creating or enhancing products and service to deliver value and address societal or environmental challenges.
1 Accurate and Timely Communication Providing clear, consistent, and timely information to stakeholders.
2 Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Oversight Ensuring suppliers adhere to responsible labour, environmental, and ethical practices.
3 Business Ethics and Values Operating with integrity, fairness, transparency, and adherence to ethical principles.
4 Operational Excellence and Innovation Continuously improving organisational efficiency, performance, and outcomes through innovation.
5 Board Composition and Diversity Having a diverse and qualified board of directors for balanced decision-making.
6 Fair Competition Engaging in open market practices and preventing anticompetitive behaviour.
7 Data Security and Integrity Protecting data from breaches, ensuring its confidentiality, accuracy, and availability.
8 Greenwashing Risk & Integrity Preventing false or misleading claims about environmental or social impacts.
9 Project Management Effectively planning, executing, and delivering projects within scope, time, and budget.
10 Regulatory Compliance Ensuring organisational adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
11 Corporate Governance Structures and processes that ensure accountability, oversight, and strategic guidance.
12 Transparency and ESG Disclosures Openly communicating accurate environmental, social, and governance performance and risks.
13 Risk Management and Internal Controls Identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks through robust internal oversight systems.
14 Sustainability-Linked Finance Readiness Capability to secure finance linked to achieving specific sustainability targets.
15 Whistleblowing Providing secure channels to report unethical or illegal activities without fear of retaliation.
16 Business Continuity & Resilience Maintaining organisational operations effectively during and after disruptions.








147 people responded to our survey that consisted of internal and external stakeholders, asking them to rate the relevance of key ESG topics. 36% of the respondents were internal stakeholders and 64% were external stakeholders.
OVERALL (n = 147)
1. Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas emissions
2. Energy Efficiency
3. Waste Management and Circular Economy
4. Sustainable Materials
5. Renewable Energy
6. Water Conservation and Management
1. Workforce Well-Being
2. Work-Life Balance
3. Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity
4. Nationalisation
5. Customer Experience & Satisfaction
6. Community Initiatives and Engagement
7. Health & Safety
EMPLOYEES (n= 53)
1. Waste Management and Circular Economy
2. Energy Efficiency
3. Renewable Energy
4. Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas emissions
5. Sustainable Materials
6. Noise Pollution
1. Workforce Wellbeing
2. Work-life Balance
3. Employee Training and Development
4. Nationalisation
5. Non-Discrimination
6. Emirati Culture and Identity
7. Talent Attraction and Retention
(n =48)
1. Energy Efficiency
2. Ecosystem Diversity
3. Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas emissions
4. Air Pollution
5. Sustainable Materials
6. Water Conservation and Management
OTHERS* (n = 46)
1. Energy Efficiency
2. Sustainable materials
3. Waste Management and Inventory Planning
4. Water Conservation and Management
5. Green Building and Infrastructure
6. Renewable Energy
1. Customer Relations
2. Customer Experience & Satisfaction
3. Health & Safety
4. Equal Opportunities
5. Human Rights
6. Gender Balance and Diversity
7. Equitable Access
1. Health & Safety
2. Workforce Wellbeing
3. Customer Relations
4. Training and Development
5. Work-life Balance
6. Community Initiatives and Engagement
7. Workforce Wellbeing
Survey Methodology Observations & Recommendations
• At least 3 stakeholder groups were consolidated as “others” in order to provide more meaningful interpretation to their responses. Encouraging stronger participation and responses from stakeholders will help to ensure better response rates.
• Some responses were all “1” or “5” indicating that there is perhaps a lack of maturity in understanding the impact of the topics to the stakeholder. With time, maturity will naturally develop, however, ADNEC Group play a role in creating awareness about these (and other) ESG topics, and can also invite a more targeted audience to participate in the survey in the future.








* This includes those that identified as “suppliers”, “operating partners” and “others”.
The impact to the business was assessed based on an understanding of ADNEC Group’s overarching strategy and operational activities, supported by discussions with key internal stakeholders. The resulting analysis reflects the perspective of ADNEC Group as the parent company overseeing its various business clusters.
Each topic was scored on a scale from 1 to 5 (with 1 being very low and 5 being very high) across three distinct categories These scores were then weighted and aggregated to produce a total score reflecting performance across all categories This total was subsequently combined with stakeholder relevance ratings to generate a graphical plot, enabling the identification of the most material ESG topics








The ESG topics are plotted on a matrix, with the top-right quadrant—where scores in both categories exceed 3.5— highlighting the topics that are most material to ADNEC Group
Business Impact Rating
Environment Governance Social








The resulting material ESG topics for the ADNEC Group are:
Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas emissions
Energy Efficiency
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Sustainable Materials
Renewable Energy
Water Conservation and Management
Workforce Well-Being
Work-Life Balance
Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity
Nationalisation
Customer Experience & Satisfaction
Community Initiatives and Engagement
Health & Safety
Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Oversight
Data Security and Integrity
Business Ethics and Values
Corporate Governance
Business Continuity and Resilience
Transparency and ESG Disclosures Operational
and
Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
- Absolute Carbon Emissions (tCO₂e)
- Carbon Intensity per Employee
- Carbon Intensity per Event
- Carbon Intensity per Visitor
- NOx/SOx Emissions
Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Environment
- Water Consumption (m³)
- Water Intensity per event
- Electricity Consumption (kWh)
- Electricity Intensity (kWh/m²)
- Total Waste (kg)
- Recycled Waste (kg)
- Diversion Rate (%)
- Hazardous Waste (kg)
- Number of Major Spills
Potential loss of business opportunities due to increased stakeholder and regulatory demand for net-zero carbon operations. Financial and reputational impacts.
Medium
Increased regulatory scrutiny leading to potential fines or restrictions on operations if emission standards are exceeded. Medium
Water Conservation and Management Risk of water scarcity impacting operations and regulatory penalties for exceeding consumption limits. Increased operational costs.
Energy Efficiency
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Inefficient energy use increases operational costs and contradicts ESG commitments, impacting reputation and regulatory compliance.
Medium
Implementation of a robust Net Zero Transition Plan, energy efficiency improvements, renewable energy projects, and active supply chain engagement.
Ineffective waste management leading to increased operational costs, regulatory fines, environmental pollution incidents, and reputational damage.
Medium
emissions monitoring, compliance checks, and implementation of pollution-control technologies.
Regular water audits, installation of water-efficient fixtures, recycling and reuse initiatives, and employee awareness programmes.
Energy efficiency upgrades, LED lighting, HVAC optimization aligned with ASHRAE standards, solar PV installations, energy monitoring systems, and audits.
- Number of Environmental Violations Compliance and Environmental Management
Environmental violations causing financial penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational harm.








Medium
Enhanced waste management strategy, WasteMaster technology implementation, increased recycling programmes, hazardous waste protocols, and employee training.
Regular environmental audits, enhanced compliance training, proactive management reviews, and robust monitoring and reporting procedures.
Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
- Employee WellBeing and Work-Life Balance Workforce Well-Being
- Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity, Nationalisation
Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity
- Customer Satisfaction Score
- Community Engagement Activities
Customer Experience & Satisfaction
Community Initiatives and Engagement
- Health & Safety Incidents Health & Safety
- Ethical Sourcing Compliance Rate
- Data Breaches Incidents
- Number of Ethics Violations Reported
Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Oversight
Data Security and Integrity
Business Ethics and Values
Governance
- Governance and Compliance Audits
- Business Continuity Plan Activation
- ESG Disclosure Completeness (%)
- Operational Excellence and Innovation Index

Corporate Governance
Business Continuity and Resilience
Transparency and ESG Disclosures
Operational Excellence and Innovation


Reduced productivity and high staff turnover due to inadequate support for employee well-being and worklife balance.
Medium High
Reputational risk and limited innovation due to lack of diversity and non-compliance with nationalisation objectives.
Loss of revenue and reduced market competitiveness due to poor customer experiences and reduced satisfaction ratings.
Reduced community support and loss of social license to operate if local engagement is insufficient.
Operational disruptions, regulatory fines, and reputational damage due to workplace accidents or inadequate safety practices.
Operational and reputational risks arising from unethical supply chain practices and supplier noncompliance.
Financial, regulatory, and reputational impacts from data security breaches.
Financial, legal, and reputational risks from unethical business practices.
Regulatory penalties and reputational damage due to governance failures.
Financial losses and operational disruptions due to inadequate preparedness for crises.
Loss of stakeholder trust due to insufficient transparency in ESG reporting.
Reduced competitive advantage due to lack of innovation and operational inefficiencies.


Medium Medium
Employee wellness programmes, flexible working policies, regular employee surveys, and continuous improvement in workplace conditions.
Inclusive hiring practices, diversity and inclusion training, nationalisation targets with strategic workforce planning.
Medium High


Medium Medium
Enhanced customer feedback mechanisms, service excellence training, continuous quality improvement programmes.
Clusters Quality / Customer Experience
Active community investment programmes, regular stakeholder dialogues, CSR initiatives aligned to local community needs. All
Clusters Strategy, Sustainability & ESG Champions
Medium High
Comprehensive health and safety management system, regular safety training, incident reporting and analysis, continuous safety audits.
All Business Clusters Health, Safety and Environment
Medium High
Medium High
Medium High
Medium High
Medium High
Medium Medium
ESG-integrated procurement policies, rigorous supplier due diligence, and periodic supplier audits.
Robust cybersecurity framework, employee training, regular penetration testing, and IT security audits.
Clear ethics policies, robust whistleblowing channels, regular ethics training.
Strong governance frameworks, regular compliance audits, board oversight.
All Business Clusters
Risk & Compliance
All Business Clusters Risk & Compliance IT & Digital Transformation
All Business Clusters
Risk & Compliance
All Business Clusters Risk & Compliance
Regularly updated business continuity plans, scenario testing, employee preparedness drills. All Business Clusters Business Continuity
Comprehensive ESG reporting aligned with global standards, external assurance.
Medium High

Continuous innovation programmes, operational efficiency initiatives, technology integration.
Strategy & Sustainability
All Business Clusters
All Business Clusters
Business Excellence Team Innovation Committee
Net Zero Transition Plan Climate Change & GHG Emissions
Develop and implement a group-wide decarbonisation roadmap to achieve Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2045, accelerating the existing 2050 pledge. This initiative focuses on cutting greenhouse gas emissions through energy efficiency measures, adoption of renewable energy, and carbon offset programs in event operations. It involves working closely with event organizers and suppliers to minimize the carbon footprint of venues and exhibitions.
Operational cost savings from energy reduction and resource efficiency, enhanced brand reputation as a sustainability leader in the events industry (leading to increased stakeholder trust and preference), and proactive compliance with global climate initiatives (positioning ADNEC ahead of emerging carbon regulations).
Venue Energy Efficiency Upgrades Energy Efficiency & Management
On-Site Renewable Energy Generation Climate Change & GHG Emissions
Invest in energy-efficient infrastructure and practices at all venues. This includes retrofitting lighting systems with LED technology, optimizing HVAC and cooling systems, installing smart building controls, and engaging staff in energy conservation training and awareness. These upgrades reduce electricity use and align with national energy efficiency targets for 2050.
Significantly lower operating costs due to reduced energy consumption, decreased carbon emissions contributing to climate goals, and improved compliance with energy regulations and green building standards (reducing the risk of future energy price or carbon cost increases).
Waste Reduction & Circular Economy Program
Waste Management & Circular Economy
Expand the use of clean energy by installing on-site renewable power systems (e.g. solar panels on exhibition hall rooftops and parking structures) and procuring clean electricity from the grid. Generating renewable energy on-site will directly reduce reliance on fossil fuels and cut Scope 2 emissions from venue operations. Any surplus energy could be fed back or stored to further improve efficiency.
Implement a comprehensive waste management initiative aiming for zero waste to landfill in events and operations. Measures include expanding recycling and composting facilities onsite, phasing out single-use plastics in venues, reusing or donating exhibition materials, and working with contractors to design booths and stages for disassembly and reuse. The program also entails educating exhibitors and attendees on waste sorting and reduction.
Long-term energy cost savings and insulation from utility price volatility, a demonstration of innovation and climate leadership that provides competitive advantage as stakeholders increasingly prefer low-carbon partners, and tangible progress toward ADNEC’s emission-reduction targets (mitigating transition risks associated with carbon).
Lower waste disposal and material procurement costs due to reduced waste generation and increased recycling, improved operational efficiency in resource use, and enhanced corporate reputation for environmental responsibility – visibly aligning ADNEC with circular economy principles and client sustainability expectations. Water Conservation Initiatives Water Management
Adopt water-saving technologies and practices across venues and hotels to minimize water usage. This includes installing low-flow fixtures and sensor faucets, optimizing irrigation systems for landscaping, implementing greywater recycling for plant irrigation or toilet flushing, and improving chillers/cooling towers for efficient water use. Regular monitoring of water consumption will identify and fix leaks promptly.
Reduced water utility costs and improved efficiency (important as businesses in water-scarce regions should implement strategies to cut usage), increased resilience against future water scarcity or stricter water regulations, and support of UAE sustainability goals on water conservation (strengthening ADNEC’s license to operate in the community).








Occupational Health & Safety Excellence
Employee Wellbeing & Engagement Program
Employee Health & Safety
Employee Engagement & Well-being
Strengthen health and safety practices to ensure safe venues for employees, contractors, and visitors. This includes regular HSE training and drills, rigorous risk assessments for events, certification to international safety standards (e.g. ISO 45001), and a “safety-first” culture campaign. By investing in advanced safety equipment and clear emergency response plans, ADNEC can minimize workplace incidents and ensure all events meet high safety standards.
Implement programs to support employees’ physical and mental well-being and to foster engagement. Initiatives could include wellness workshops, access to mental health resources, fitness activities, flexible working arrangements, and regular employee feedback surveys (with action plans based on results). Emphasizing work-life balance and well-being benefits will improve overall job satisfaction.
Diversity & Inclusion Strategy
Diversity & Inclusion
Roll out a comprehensive diversity and inclusion strategy to ensure equal opportunity and a workforce that reflects the community. This strategy would set targets (e.g. increasing female representation in leadership and hiring more UAE nationals), enforce unbiased recruitment and promotion practices, provide mentorship and leadership programs for underrepresented groups, and conduct regular staff training on unconscious bias and inclusive culture.
Talent Development & Retention Programs
Customer
Talent Attraction & Development
Invest in developing employee skills and leadership pipeline. This encompasses graduate recruitment schemes and internships, continuous training and upskilling workshops, clear career progression paths, and partnerships with educational institutions (e.g. sponsoring industry-related courses or hosting job fairs). By mapping career development plans for employees and recognizing high performers, ADNEC can build a strong internal talent pipeline.
Leverage technology and staff training to elevate the experience for customers, clients, and event attendees. This opportunity involves deploying advanced CRM systems and data analytics to personalize services, implementing real-time feedback tools (surveys/apps) during events, and training frontline staff in service excellence. By using customer insights and focusing on client care, ADNEC can set itself apart in service quality.
Community
Engagement & Social Impact
Initiatives
Community Engagement & Impact
Strengthens relationships with local stakeholders and ADNEC’s “social license to operate.” A proactive community engagement approach enhances the company’s reputation among residents and regulators and contributes to the local economy and social development. Such goodwill can translate into easier project approvals, government support, and a preference from clients who value working with a socially responsible venue partner. Selected due to their


Establish robust community outreach and investment programs to ensure ADNEC’s growth benefits the local society. For example, partner with local schools and universities on education and internship initiatives, support community events and charitable programs, encourage employee volunteering days, and collaborate with local businesses (such as SMEs and social enterprises) for event services. Regularly measuring and communicating the Group’s economic and social contributions to Abu Dhabi demonstrates transparency in impact.






Fewer accidents and incidents, leading to lower costs related to injuries or disruptions (companies that prioritize employee health and safety can reduce costs associated with accidents and illnesses). Additionally, a robust safety record boosts ADNEC’s reputation as a reliable, world-class venue operator and ensures compliance with labor and event safety regulations (reducing legal risk).
Higher employee morale and productivity, and improved talent retention – employees are more likely to stay with and be attracted to a company that invests in their wellbeing and shares their values. A positive workplace culture also enhances innovation and service quality (as engaged employees are more motivated), and strengthens ADNEC’s brand as an employer of choice.
A more diverse and inclusive workforce drives greater innovation and problem-solving by bringing varied perspectives. It also strengthens the company’s appeal to a broader talent pool and improves employee engagement and loyalty. Moreover, demonstrating commitment to D&I enhances ADNEC’s compliance with local employment goals and its reputation among global partners and clients as an equitable, modern organization.
Improves workforce capabilities and innovation capacity, ensuring the company has the skills needed for future growth. These programs also increase employee loyalty (reducing turnover costs) and help attract top talent externally – as employees are drawn to organizations with strong development opportunities and values alignment. In the long term, succession planning through talent development secures leadership continuity for the Group.
Higher client satisfaction and loyalty, leading to repeat business and positive word-ofmouth. Strengthening customer-centricity also enhances ADNEC’s brand reputation and competitive position – companies known for responsible practices and superior service tend to enjoy better stakeholder loyalty. Additionally, actively engaging with customer feedback drives continuous improvement in operations and can spark service innovations.
Selected due to their link with the KPIs of our ESG Index
Sustainable Procurement Program
Enhanced
Sustainable Procurement
Strengthen the Group’s ethics and compliance framework to uphold the highest standards of corporate governance. Key actions include periodic training for all employees on the Code of Conduct and anti-corruption policies, establishing an anonymous whistleblower hotline, performing regular compliance audits, and enforcing zero tolerance for violations. Leadership oversight (e.g. an ethics committee) will monitor compliance and address any misconduct swiftly.
Implement robust data protection measures to safeguard customer, employee, and partner data across all business units. This opportunity involves upgrading cybersecurity infrastructure (firewalls, intrusion detection, encryption), conducting regular vulnerability assessments and penetration tests, and enforcing strict data governance policies (in line with GDPR and UAE data laws). Employees will also receive training on cybersecurity awareness and data privacy best practices.
Integrate environmental and social criteria into procurement and supply chain management. ADNEC will update procurement policies to favor suppliers with strong ESG credentials, use more local and eco-friendly products (e.g. sustainable event materials, green catering options), and require key suppliers to abide by ADNEC’s supplier code of conduct. Supplier ESG performance will be monitored and ADNEC can collaborate with vendors on initiatives to reduce waste and improve labor practices in the supply chain.
Adopt best practices in ESG reporting and disclosure to improve transparency. This includes publishing an annual ESG/Sustainability report aligned with international frameworks (GRI, SASB, etc.), clearly communicating performance on each material topic and progress toward targets. ADNEC should also report climate-related risks in line with TCFD recommendations and ensure data in reports is externally assured. Regularly updating stakeholders on ESG progress (via the company website or newsletters) is part of this initiative.
Reduces the risk of legal breaches or reputational scandals by proactively preventing misconduct (effective ESG risk management lowers the likelihood of financial, legal, or reputational damage). It also builds stakeholder trust – investors, partners and regulators gain confidence that ADNEC operates ethically and transparently – and ensures adherence to all applicable laws and regulations, avoiding penalties.
Prevents data breaches and the associated financial and reputational harm that can result from such incidents. Maintains customer and stakeholder trust by demonstrating that ADNEC takes data privacy seriously and ensures compliance with data protection regulations (avoiding regulatory fines). A strong cybersecurity posture also protects business continuity by reducing the risk of IT disruptions.
Mitigates supply chain risks and can lead to cost savings – for example, sourcing materials more sustainably and efficiently, and reducing waste in the supply chain can lower costs over time. It also enhances ADNEC’s brand credibility and consistency, as the company’s ESG values are extended to its partners (which is increasingly important to clients and investors). Additionally, this program ensures compliance with emerging regulations or client requirements regarding responsible sourcing.
Increases accountability and builds stakeholder confidence in the company’s commitments. High-quality ESG disclosure meets investor expectations and regulatory requirements, potentially improving access to capital as investors and lenders favor companies with strong ESG transparency. It also helps internal decision-making by tracking progress and enhances ADNEC’s reputation for governance excellence and openness. Integrated
Embed ESG considerations into enterprise risk management and strengthen business continuity plans. This involves regularly updating the corporate risk register to include ESG risks (e.g. climate change impacts, supply chain disruptions, health pandemics), and developing robust contingency and continuity plans for critical operations. ADNEC will conduct scenario planning and simulation drills (for events of various crisis situations) to ensure preparedness. Business continuity policies (aligned with ISO 22301 or similar) will be maintained and communicated to all relevant teams.
Enhances organizational resilience against crises and unexpected disruptions, thereby protecting employees, customers, and financial performance. Proactive risk management of ESG issues helps avoid or mitigate potential losses (identifying and managing ESG-related risks lowers the likelihood of costly incidents). A strong continuity capability also assures stakeholders – from clients to regulators – that ADNEC can sustain operations under challenging conditions, which builds trust and reliability.
















In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.
SECTOR SCOPE TITLE
General International United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
United Nations Global Compact
Global Reporting Index (GRI)
National UAE Principles of the 50
Green Agenda 2030
UAE Net Zero 2050
Abu Dhabi Climate Change Strategy
UAE Energy Strategy 2050
We the UAE 2031
Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030
Abu Dhabi Environment Vision 2030
In-Country Value (ICV) Program
Modon Holding ESG Policy & Strategy



A universal framework comprising 17 goals adopted by all UN member states to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030.
A voluntary initiative based on ten principles covering human rights, labour standards, environmental protection, and anti-corruption practices.
An internationally recognised framework that provides a standardised approach to sustainability reporting, enhancing transparency, comparability, and stakeholder engagement.
Ten strategic principles guiding the UAE’s long-term economic, political, and social development, emphasising sustainability, human capital, and global partnerships.
A UAE-wide action plan aimed at accelerating the transition to a green economy through sustainable economic growth, environmental stewardship, and increased competitiveness.
A national commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050, promoting sustainable development, clean energy, and low-carbon economic diversification.
A strategic framework aimed at reducing Abu Dhabi’s greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to climate change through comprehensive mitigation and adaptation initiatives.
A national strategic roadmap focused on diversifying the UAE’s energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and increasing the share of renewable and clean energy to ensure sustainable economic growth.
A comprehensive national vision outlining strategic objectives and initiatives to position the UAE as a global leader in innovation, sustainable development, economic prosperity, and societal well-being by 2031.
A long-term strategic plan designed to diversify Abu Dhabi’s economy, reducing reliance on oil by developing high-value, knowledge-driven sectors and promoting sustainable economic growth and competitiveness.
A long-term strategic plan integrating economic growth with environmental sustainability, focusing on resource efficiency, biodiversity conservation, and quality of life improvements in Abu Dhabi.
A UAE national initiative designed to stimulate local economic development, enhance competitiveness, and promote local content, employment, and investments within supply chains.
Modon Holding’s ESG governance framework, guiding and embedding environmental, social, and governance principles across all subsidiaries, including ADNEC Group.





In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.
Sector Related International Net Zero Carbon Events (NZCE)
Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)
National
ADNEC Group Corporate Strategy
ADNEC Group ESG and Sustainability Framework and Strategy
An events industry-led initiative committed to halving greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and achieving net zero emissions by 2050, aligned with the Paris Agreement targets.
An initiative that guides companies in setting scientifically aligned, measurable greenhouse gas emission reduction targets to effectively address climate change.
ADNEC Group’s corporate strategy, defining ambitions and targets for sustainable growth, stakeholder value creation, and integrated ESG management across its investments and operations.
ADNEC Group’s ESG-specific strategy outlining clear sustainability objectives, targets, and governance processes that guide responsible operations across all business clusters.








In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.
UAE Principles of the 50
Green Agenda 2030
UAE Net Zero 2050
Abu Dhabi Climate Change Strategy
UAE Energy Strategy 2050
We the UAE 2031
In-Country Value (ICV) Program
Modon Holding ESG Policy & Strategy

ADNEC Group aligns through strategic contributions to economic diversification, Emiratisation, and sustainable growth, fostering innovation, and enhancing community engagement.
ADNEC Group supports the Green Agenda through initiatives promoting resource efficiency, renewable energy, waste reduction, and sustainable infrastructure across its operations.
ADNEC Group has a Net Zero Transition Plan aiming for a 50% carbon reduction by 2030 and net zero by 2045, leveraging renewable energy and energy efficiency.
ADNEC Group integrates climate resilience and emissions reduction across its value chain, supported by climate risk assessments and mitigation actions.
ADNEC Group advances energy efficiency, renewable energy projects, and innovative energy solutions such as AI-driven energy optimisation and solar PV installations.
ADNEC Group contributes by enhancing community well-being, promoting sustainable practices, and supporting inclusive economic growth through responsible business operations.
ADNEC Group supports this vision by investing in sustainable infrastructure, economic diversification, Emiratisation, talent development, and fostering innovation across business clusters.
ADNEC Group maintains certifications like ISO 14001 and Estidama, focusing on waste management, resource efficiency, and environmental conservation practices.
ADNEC Group aligns by prioritising local sourcing, supplier development, and ensuring significant local economic impact through ethical and responsible procurement practices.
ADNEC Group adheres closely to Modon Holding’s ESG policy, embedding ESG principles into its procurement, governance, and operational activities, ensuring comprehensive sustainability alignment.







In formulating its ESG Strategy, ADNEC Group undertook an extensive analysis of local and global trends, strategies, and methodologies, while gaining a deeper understanding of stakeholder expectations, to effectively define its ESG priorities and strategic direction.
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
United Nations Global Compact
ADNEC Group aligns its sustainability and ESG strategy with relevant SDGs, addressing global challenges through targeted actions in environmental, social, and governance dimensions. |
ADNEC Group adheres to UN Global Compact principles through responsible business practices, ethical sourcing, and comprehensive governance frameworks.
Global Reporting Index (GRI)
Net Zero Carbon Events (NZCE)
ADNEC Group ensures transparency and accountability by reporting its ESG performance annually in line with GRI standards, reflecting comprehensive disclosure of its sustainability impacts.
ADNEC venues actively participate in the NZCE initiative, adopting net-zero carbon standards in events management to minimise carbon emissions and enhance event sustainability.
Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi)
ADNEC Group’s emissions reduction strategy is aligned with SBTi, ensuring scientifically validated and robust pathways towards achieving its ambitious carbon reduction targets.
















1. Protecting Our Land, Air, and Seas
1. Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas emissions
2. Energy Efficiency
3. Waste Management and Circular Economy
4. Sustainable Materials
5. Renewable Energy
6. Water Conservation and Management
1. Minimize (and offset where necessary) Scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions, and align to Net Zero Goals (50% reduction by 2030 and Net Zero by 2050)
2. Optimize energy and water consumption to reduce negative consequences while creating immediate cost savings
3. Switch to as much renewable energy as possible for on-site needs
5. Reduce food waste generation and achieve 0% food waste disposal to landfill
6. Reduce non-food waste generation and achieve 0% non-food waste disposal to landfill
7. Decrease waste generation through reduction, reuse and recycling strategies. Increase use of reusable and recycled materials as much as possible.
1. Invest into green technology to reduce Scope 1 emissions
2. Become more energy efficient and invest into renewable energy to reduce Scope 2 emissions
3. Engage external entities to collect accurate data on Scope 3 emissions and invest into carbon offsetting initiatives to achieve net zero
4. Actively work with facilities management to optimize energy consumption
5. Invest into technology and expedite implementation of BMS
6. Engage employees to raise awareness and change behaviours to achieve energy savings
7. Leverage physical space and facilities for solar panels
8. Conduct feasibility studies on emerging technologies such as solar windows and invest into viable opportunities
9. Adopt advanced demand analytics and raise customer awareness
10. Develop better segregating and composting/conversion capabilities
11. Partner with entities on food donation initiatives
12. Maximize reliance on re-usable and recyclable materials and reduce single use of plastic
13. Raise awareness and incentivize employees, customers and suppliers to take advantage of existing capabilities and to seek out new ideas and methodologies for removing waste
14. Engage with the industry to redesign events to utilise sustainable materials and be waste free
15. Offer solutions for sale that leverage sustainable materials to support stakeholder efforts and decisions








Growing and Investing in Our People
Workforce Well-Being
Work-Life Balance
Gender Balance and Equal Opportunity
Nationalisation 5. Health & Safety
1. Promote a comprehensive approach to employee wellbeing to improve engagement, retention, and overall job satisfaction
2. Instill balanced working hours, and separation between personal and professional time; and achieve 0% resignations due to burnout
3. Grow the representation of women in senior leadership positions across ADNEC Group
4. Rank amongst the top local semigovernment organisations for Nationalisation in key positions
5. Provide a consistently safe and healthy environment for employees, visitors, and partners.
1. Regularly engage employees in multiple ways to collect insights and ideas, and to determine their wellbeing
2. Expand the wellbeing program to introduce new initiatives and offers to employees, including part-time and temporary employees
3. Understand the underlying reasons for burnout / work-life imbalance
4. Review and realign manpower planning across all business lines.
5. Develop policies and raise awareness towards respecting employee’s personal time
6. Identify and enrol high potential women in ADNEC Group into tailored leadership development programmes
7. Develop and implement a clear strategy to attract, develop and retain women across all levels within ADNEC Group
8. Identify and enrol high potential Emiratis in ADNEC Group into tailored leadership development programmes
9. Develop and implement a clear strategy to attract, develop and retain Emiratis across all levels within ADNEC Group
10. Engage with educational institutions and social programmes to promote relevant ADNEC Group careers to Emiratis
11. Implement rigorous health and safety management systems and ensure compliance at all operational levels.








3. Collaborating with Our Communities, Partners, and Suppliers
1. Customer Experience & Satisfaction
2. Community Initiatives and Engagement
3. Health & Safety
1. Procure 100% of materials and services from suppliers that are complying with ESG standards (and based on a minimum ESG score)
2. Deliver exceptional experiences that consistently exceed customer expectations.
3. Foster meaningful community partnerships that enhance local wellbeing and prosperity.
4. Provide a consistently safe and healthy environment for employees, visitors, and partners.
1. Incorporate ESG as a key requirement and decision factor for all procurement and investment activities
2. Raise awareness and work with suppliers to adopt standards related to sustainability/ESG
3. Raise awareness within ADNEC Group on ESG compliance
4. Conduct regular ESG audits of suppliers
5. Map end-to-end customer journeys across each business and streamline processes to remove pain points and enhance customer experience
6. Develop a culture of transparency and responsiveness amongst customer facing and back-office employees, at all levels
7. Invest in competencies, technologies, and communication that fosters engagement with customers
8. Continuously gather and act on customer feedback to improve services and satisfaction levels.
9. Actively engage with the community to understand their needs and create targeted initiatives.
10. Implement rigorous health and safety management systems and ensure compliance at all operational levels.








6. Transparency and ESG Disclosures
7. Operational Excellence and Innovation
1. Establish a responsible and sustainable supply chain aligned with global ethical standards.
2. Ensure robust protection of data integrity, confidentiality, and availability at all levels.
3. Embed integrity and ethical conduct throughout every aspect of business operations.
4. Demonstrate exemplary governance with transparency, accountability, and strong oversight.
5. Ensure resilience and uninterrupted delivery of critical business services under any circumstances.
6. Achieve best-in-class transparency through comprehensive and clear ESG disclosures.
1. Implement rigorous supplier assessments and enforce compliance with ethical sourcing guidelines.
2. Maintain advanced cybersecurity measures and continuously monitor and mitigate risks.
3. Foster a culture of ethical awareness and transparency, supported by strong compliance frameworks.
4. Maintain effective governance structures and continuously improve board-level decision-making processes.
5. Regularly review, test, and enhance business continuity plans and risk management procedures.
6. Regularly publish accurate, timely, and relevant ESG performance reports aligned with international standards.


















ADNEC Group rigorously adheres to Modon Holding’s Investment Governance Framework, ensuring all investment decisions are strategically aligned, comprehensively risk-managed, and drive sustained value creation.









*Note: ESG Benchmarking study was completed in year 2021 upon issuance of the first ESG and Sustainability strategy and framework.







The benchmark aims to provide the ADNEC Group team with an understanding of what other organisations are communicating and doing with regards to their ESG strategy and to use this information as part of its own ESG journey. This benchmark is not intended to provide a one-to-one comparison, nor intended to rank ADNEC Group against the selected organisations.
1. Type of organisation: the aim here was to select from a broad range of organisations that include those from within ADNEC Group’s shareholder portfolio (i.e. peer companies), local peers that operate across the UAE landscape and within a similar sector, and finally international organisations that operate in different markets albeit with a similar focus to ADNEC Group’s business activities.
2. Availability of information: ESG requires significant public disclosure in order to convey to investors and other stakeholders what the organisation’s ESG aspirations and performance entails. Hence, organisations that brought the most visibility were selected for benchmarking.
3. ESG maturity: finally, the quality and perception of the target organisation’s ESG capabilities and information was factored into the selection process – in order to ensure that ADNEC Group identifies lessons learned from some of the most mature organisations around.
Based on criteria for selection outlined, a list of companies were identified and eventually this was shortlisted into the companies chosen to include in this report.

































TAQA has incorporated ESG as an underlying model within its overall strategy and has defined ESG priorities and contributions to the UN SDGs. Its approach to ESG is informed by its emphasis towards supply chain management and stakeholder engagement
TAQA’s 2030 strategy focuses on three themes: optimization, growth and capability building, with the ESG framework underpinning all initiatives under these themes

To achieve its decarbonization and ESG agenda, highlighted in the 2030 corporate strategy, the Group has embarked on a Group-wide ESG strategy and net zero strategy that will define the pathways and practical steps to achieve its ESG ambitions.
This will include an ESG operating model, with ESG governance across the entire portfolio, as well as embedding ESG metrics into the Group’s capital allocation framework.








In developing its ESG framework and strategy, TAQA has considered strategic contributions to several relevant mandates that include:
1. Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030;
2. Abu Dhabi Environment Vision 2030;
3. ADX Disclosure Guidelines and SCA Corporate Governance Guidelines;
4. Abu Dhabi Demand Side Management (DSM) and Energy Rationalisation Strategy 2030;
5. Global Reporting Initiative (GRI); and
6. United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs)
In lieu of a published group ESG strategy, it can be assumed that the guidelines, goals and plans set forth by the aforementioned mandates will help to inform TAQA and its subsidiaries’ ESG strategy.
As part of its materiality assessment, TAQA has engaged stakeholders to determine important topics to them and analyse the importance of these topics to the business. From which, TAQA was able to identify 28 material ESG issues that directly feed into its sustainability strategy and against which it reports its ESG performance
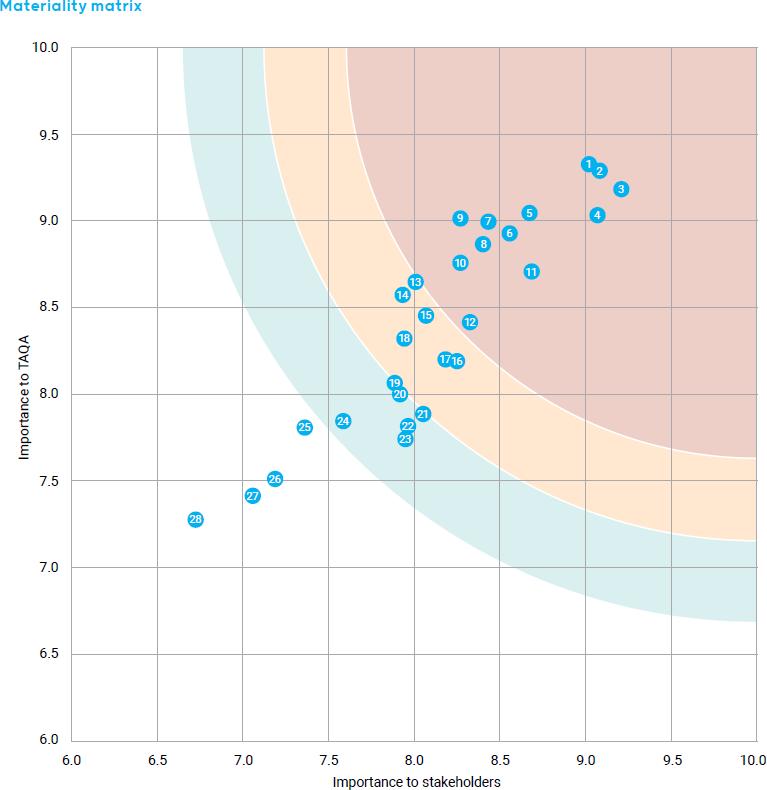


















“Dare Today, Change Tomorrow” is Majid Al Futtaim’s (MAF) roadmap to address material ESG topics. Its ESG framework is build around three pillars and 11 Sustainable Business Commitments (SBCs)
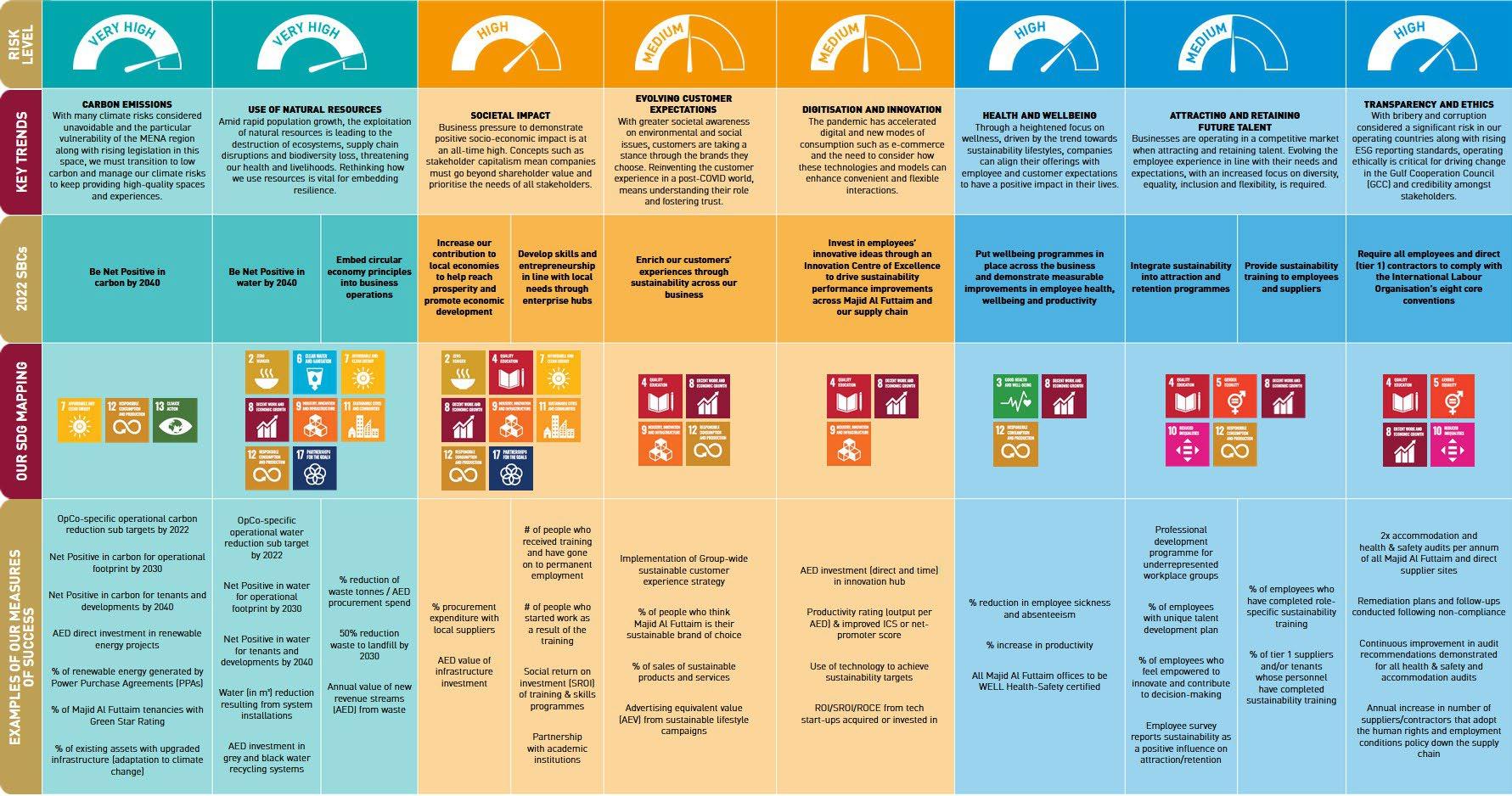
1. Be Net Positive in Carbon by 2040
2. Be Net Positive in Water by 2040
3. Embed Circular Economy Principles into Business Operations
4. Increase Our Contribution to Local Economies to Heal Reach Prosperity and Promote Economic Development
5. Develop Skills and Entrepreneurship Inline with Local Needs Through Enterprise Hubs
6. Enrich Our Customers’ Experience Through Sustainability Across Our Business
7. Invest in Employees’ Innovation Centre of Excellence to Drive Sustainability Performance Improvements Across Majid Al Futtaim and Our Supply Chain
8. Put Wellbeing Programmes in Place Across the Business and Demonstrate Measurable Improvements in Employee Health Wellbeing and Productivity
9. Integrate Sustainability into Attraction and Retention Programmes
10. Provide Sustainability Training to Employees and Suppliers
11. Require All Employees and Direct (tier 1) Contracts to Comply with International Labour Organisation’s Eight Core Conventions








The aforementioned SBCs are informed through the 21 material issues that MAF has identified as part of its ESG strategy, based on the importance to stakeholders and to the business itself
1. Climate Change Adaptation
2. Changing Role of Women in
3. Ecosystem Services
4. Crime & Security
5. Transport & Logistics
6. Product Quality & Safety
7. Responsible Procurement
8. Promoting Sustainable Lifestyles
9. Healthy Products & Services



















Emaar has developed a value creation model building on a deep understanding for its stakeholders, and in which it has linked 5 ‘capital’ pillars to this model and its subsequent outcomes and contributions towards sustainability









Emaar has identified 5 stakeholders groups that it engages closely in order to establish a deeper appreciation for their needs. These include: investors, customers, (their) people, partners and suppliers, and communities.
Through interviews, surveys, and other direct and indirect interactions – Emaar determine the topics and issues that are material to them which it combines with its own analysis of trends/megatrends, and those identified through established ESG guidelines (e.g. SASB and GRI).
Based on identifying these issues, it clusters them into 6 categories and prioritises them based on stakeholder feedback and importance.
These are subsequently validated and integrated into Emaar’s strategy and risk management process.
Through this approach, Emaar creates a model in which it creates value for its stakeholder groups that captures direct financial return and addresses risks on the material issues.
Emaar’s materiality map that demonstrates the overlap in importance of issues between internal vs external stakeholders

These material topics, and Emaar’s contribution and priorities towards other strategic drivers, have been translated into three overarching goals as part of its ESG Strategy:
1. Greenprint for the Future
2. The Wind Beneath our Wings
3. Leading with Integrity
Together, these guide and inform Emaar and its stakeholders on the organisation's ESG priorities, actions and performance.


















Marriott has translated its ESG Strategy into 4 but interconnected pillars, each with its own set of goals and plans, and which are linked to the UN SDGs

1. 15 million cumulative volunteer hours
2. 50% of volunteer hours will serve children and youth
3. 50% of volunteer activities will be skillsbased
Empower Through Opportunity
1. $35 million invested to develop hospitality skills and opportunity among diverse, atrisk, and underserved communities
2. Achieve global gender parity in executive positions by 2023
3. Increase the representation of people of color in U.S. executive positions to 25%
Sustain Responsible Operations
1. 15% water intensity reduction
2. 30% carbon intensity reduction
3. 45% waste-to-landfill (and 50% food waste) reduction
4. 30% renewable electricity
5. Locally source 50% of all produce, in aggregate
6. … (+5 other goals)
Welcome All and Advance Human Rights
1. 100% of on-property associates completed human rights training
2. Enhance or embed human rights criteria in our recruitment and sourcing policies
3. $500,000 toward partnerships that drive, evaluate, and elevate travel and tourism’s role in cultural understanding
Rewards and Recognitions
















Marriott’s Material ESG topics were informed by its sustainability and social impact assessment, which included interviews representing owners, customers, industry associations, and nongovernmental organizations



Child Labor, Forced or Compulsory Labor (Human Rights)
Customer Health and Safety (Guest Engagement, Wellbeing, & Satisfaction)
Indirect Economic Impacts
Procurement Practices








7.2 | Link between ESG Goals and Mandate Contributions









Understanding the alignment between the national and international mandates and ADNEC’s ESG Priority Areas will help to determine the relevant goals that will inform ADNEC’s own ESG Goals and Key Success Factors
Relevant to ADNEC’s ESG Priority Area?
Key National and International Mandates Protecting Our Land, Air, and Seas Growing and Investing in Our People Collaborating with Our Communities, Partners, and Suppliers
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG)
United
Global Compact (UNGC)








Safeguarding Our Assets and Values
Protecting Our Land, Air, and Seas
Key National and International Mandates Mandate Goals Applicable to the Priority Area and the ADNEC ESG Material Issues
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG)
1. Switch to renewable energy and contribute to increasing the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix by investing in clean energy infrastructure, research and technology. (SDG 7.2, 7.a)
2. Double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency. (SDG 7.3)
3. Reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse. (SDG 12.5)
4. Reduce food waste at retail and consumer level and reduce food losses along production and supply chains. (SDG 12.4)
5. Reducing the Group’s GHG emissions and work towards a Net Zero trajectory to align with the Paris Agreement. (SDG 13)
United Nations Global Compact (UNGC)
1. Businesses should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges. (7th Principle)
2. Undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility (8th Principle)
3. Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies. (9th Principle)
UAE Net Zero 2050 1. In alignment with the Paris Agreement, which calls on countries to prepare long-term strategies to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and limit the rise in global temperature to 1.5 C compared to pre-industrial levels.
2. The deployment and use of clean energy solutions
Abu Dhabi Environment Vision 2030
1. Minimising the impact of climate change. (Priority Area 1)
2. Clean air and noise pollution, contributing to safe and healthy living conditions. (Priority Area 2)
3. Enhanced value creation through optimised material flows and waste management. (Priority Area 5)
Net Zero Carbon Events (NZCE)
1. Power events efficiently, with clean, renewable energy.
2. Redesign events to utilise sustainable materials and be waste free.
3. Source food sustainably, and eliminate food waste.
4. Move goods and equipment efficiently and transition to zero emissions logistics.








Growing and Investing in Our People
Key National and International Mandates Mandate Goals Applicable to the Priority Area and the ADNEC ESG Material Issues
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG)
1. End all forms of discrimination against women and girls everywhere. (SDG 5.1)
2. Ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision making. (SDG 5.5)
3. Adopt and strengthen sound policies and enforceable legislation for the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls at all levels. (SDG 5.c)
4. Ensure full productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value. (SDG 8.5)
5. Protect labour rights and promote safe and secure working environments for all workers, including migrant workers, in particular women migrants, and those in precarious employment. (SDG 8.8)
6. Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome, including by eliminating discriminatory laws, policies and practices and promoting appropriate legislation, policies and action in this regard (SDG 10.3)
7. Adopt policies, especially fiscal, wage and social protection policies, and progressively achieve greater equality (SDG 10.4)
United Nations Global Compact (UNGC)
1. Businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights. (1st Principle)
2. Make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses. (2nd Principle)
3. Businesses should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining. (3rd Principle)
4. The elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labour. (4th Principle)
5. The effective abolition of child labour. (5th Principle)
6. The elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation. (6th Principle)
UAE’s Principles of the 50
1. The main future driver for growth is human capital. Developing the educational system, recruiting talent, retaining specialists and continuously building skills will be key to ensuring the Emirates remains the most competitive national economy. (4th Principle)
2. The core value system in the Emirates shall remain based on openness and tolerance, the preservation of rights, the rule of justice and the law. We believe in the preservation of human dignity, the respect for cultural diversity, the strengthening of human fraternity, together with enduring respect for our national identity. The country will remain supportive, through its foreign policy, of all initiatives, pledges and international organisations that promote peace, openness and humanity. (8th Principle)
Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030 1. Developing a highly skilled, highly productive work force








Key National and International Mandates Mandate Goals Applicable to the Priority Area and the ADNEC ESG Material Issues
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG)
1. Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors. (SDG 8.2)
2. By 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products. (SDG 8.9)
3. Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all. (SDG 9.1)
4. By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, with all countries taking action in accordance with their respective capabilities (SDG 9.4)
5. Adopt public procurement practices that are sustainable, in accordance with national policies and priorities. (SDG 12.4)
6. Enhance international support for implementing effective and targeted capacity-building in developing countries to support national plans to implement all the Sustainable Development Goals, including through North-South, South-South and triangular cooperation. (SDG 17.9)
7. Enhance the global Partnership for Sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources to support the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals in all countries. (SDG 17.16)
8. Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships, building on the experience and resourcing strategies of partnerships. (SDG 17.17)
UAE’s Principles of the 50
Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030
Net Zero Carbon Events (NZCE)
1. Consolidating the reputation of the Emirates globally is a national mission for all institutions. The Emirates is one destination for business, tourism, industry, investment and cultural excellence. Our national institutions must unify their efforts, benefiting mutually from their shared capabilities, and work to build global enterprises under the umbrella of the Emirates. (6th Principle)
1. Building an open, efficient, effective and globally integrated business environment
1. Work with and influence partners in the travel sector to reduce and mitigate the emissions of travel to events.








Safeguarding Our Assets and Values
Key National and International Mandates Mandate Goals Applicable to the Priority Area and the ADNEC ESG Material Issues
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDG)
United Nations Global Compact (UNGC)
Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030
1. Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms (SDG 16.5)
2. Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels. (SDG 16.6)
3. Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making at all levels. (SDG 16.7)
4. Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development (SDG 16.b)
1. Businesses should work against corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery. (10th Principle)
1. Developing a sufficient and resilient infrastructure capable of supporting anticipated economic growth

















ESG related initiatives have a lot in common with traditional – strategic – initiatives and should be considered as part of ADNEC Group’s standard process for identifying, prioritizing, evaluating and managing initiatives. There are some notable differences however, in determining what constitutes a ‘good’ ESG initiative compared with the norm.



• Aligned with the ESG Strategy of ADNEC.
• Solutions target multiple aspects that contribute to the risks and opportunities in parallel.
• Long-term mindset, but where solutions tend to be shorter in time-frames and sustained over a longer period.
• More centralized management and oversight by the ESG team and committee.
• Adheres to the company’s Project Management Guidelines








• Aligned with the Group Strategy of ADNEC (or its individual business cluster / subsidiary strategies).
• Target specific sources of the issues or opportunities – based on a more linear understanding of the cause-and-effect relationship.
• Mid-to-long term mindset, while solutions can range from quick wins to long-term initiatives that start and end around specific timeframes.
• Centralised oversight by the strategy and PMO teams – but with decentralized management by the respective owner.
• Adheres to the company’s Project Management Guidelines










1. Identify ideas and solutions to address ESG goals (linked to the transformation agenda and baseline analysis).
2. Connect solutions to form interconnected initiatives that tackle multiple aspects of an ESG goal, and which addresses the underlying issues identified in the baseline.
3. Prioritise and align initiatives to the ESG goals to ensure sufficient coverage of risks and opportunities.
4. Define the detailed milestones and plans to implement each initiatives, and where required; conduct further studies to assess the viability of a solution to meet the required goals
5. Determine the resourcing required and establish a sustainable model for financing as required
6. Develop a comprehensive ESG plan and implementation roadmap, and launch initiatives accordingly








ESG fit reflects how well the proposed initiative contributes to the material topics / ESG goals of the Group or cluster.
Does not contribute significantly to one or more topic or goal.
Contributes moderately or only to one or two topics and goals.
Contributes significantly or to several topics and goals.
The impact reflects how significant the contribution and ‘return’ of the initiative will be in helping the Group achieve their stated goals and targets.
Only has an incremental impact to achieving the ESG targets. Has a moderate impact to achieving ESG targets. Has a significant impact to achieving ESG targets.
Complexity represents the Group’s ability to readily implement the proposed initiative based on existing enablers (e.g. capabilities, technology, and management systems).
Requires significant amounts of enablers that are not currently available in ADNEC.
Some enablers exist, but more are required to implement the solution
Most, or all, of the required enablers are readily available within the Group.
The resource intensity represents the level of investment (human and financial) required in order to implement the proposed initiative.
Requires significant amounts of resources in order to implement the solution.
Requires moderate amounts of resources in order to implement the solution.
Requires low amounts of resources in order to implement the solution.
By applying the prioritisation criteria to the list of initiatives identified across the Group, a score for each proposed initiative can be determined, and the resulting initiatives plotted on a matrix that allows the ESG team, committee, and responsible stakeholders to identify the priority initiatives that will help to deliver ESG results.
The matrix is based on plotting the “relevance” and “delivery capacity” scores for each initiative (as illustrated below), and those scoring above the pre-determined threshold would be considered for final approval and implementation.
The recommended prioritisation thresholds for each criteria are per the below:
2








| Governance Structure Design Options









1. Ease of standardising level of service and quality of output across the Group.
2. Ease of oversight and control over the ESG strategy and plans.
3. Consolidate ESG knowledge and resources.
1. Promotes ESG efforts and implementation through the subsidiaries / business clusters
2. More control and autonomy within each subsidiary / business cluster over their ESG plans.
3. Reduces burden on ADNEC HQ to invest in internal resources to manage and oversee the Group’s ESG efforts.
1. Maintains control over certain key ESG governance activities at the ADNEC HQ level – while promoting accountability and efforts at the subsidiary / business cluster level.
2. Shared resourcing and investment model between ADNEC HQ and the subsidiaries / business clusters.
1. Requires a significant organisational (re)design for the associated function.
2. Requires significant resourcing and investment.
3. Potentially reduced visibility and connection with ESG efforts at the subsidiary/business cluster level.
1. ADNEC HQ adopts a reduced role in ESG governance for the Group – therefore, less control and direction.
2. Potential lack of consistent standards and practices applied across the Group.
3. Duplicating efforts, resources, and competencies across the subsidiaries / business clusters.
1. Requires seamless coordination and collaboration across the Group.
2. Potential overlap of responsibilities for resources involved in ESG governance across the Group.
Organisational Design Principles Promote operational accountability and responsibility











GRI Context Index









EC2
EC6
























Total workforce by employment type, employment contract, and region, broken down by gender.
LA7 Rates of injury, occupational diseases, lost days, and absenteeism, and number of workrelated fatalities by region and by gender.
Education, training, counseling, prevention, and risk-control programs in place to assist workforce members, their families, or community members regarding serious diseases.
Health and safety topics covered in formal agreements with trade unions.
LA10 Average hours of training per year per employee or volunteer by gender, and by employee category.
Programs for skills management and lifelong learning that support the continued employability of employees and assist them in managing career endings.
of employees and volunteers receiving regular performance and career development reviews, by gender and by employee category
Composition of governance bodies and breakdown of employees per employee category according to gender, age group, minority group membership, and other indicators of diversity.Q
Ratio of basic salary and renumeration of women to men by employee category, by significant locations of operation.
HR1 Percentage and total number of significant investment agreements and contracts that include clauses incorporating human rights concerns, or that have undergone human rights screening.
HR2 Percentage of significant suppliers, contractors and other business partners that have undergone human rights screening, and actions taken.
HR3 Total hours of employee and volunteer training on policies and procedures concerning aspects of human rights that are relevant to operations, including the percentage of employees and volunteers trained.
HR4 Total number of incidents of discrimination and corrective actions taken.
































Reference of ESG Ratings









Disclosure Project)









A CDP score provides a snapshot of a company’s disclosure and environmental performance. The CDP scores show organizations and their stakeholders where they are on the road towards operating in line with a 1.5-degree, deforestation-free and water-secure future.
Disclosure drives action and by scoring companies from D- to A, organisations are taken on a journey from disclosure through awareness and management, and finally to leadership.
It is important to note that companies that achieve an A score are not at the end of their environmental journey - they are among the most transparent when it comes to disclosure and performance on climate change, deforestation or water security.
The CDP’s scoring methodology is aligned with the Taskforce for Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and with major environmental standards, and therefore provides a comparable dataset across the market
CDP’s scoring methodology assesses the level of detail and comprehensiveness in a response, as well as the company's awareness of environmental issues, its management methods and progress towards environmental stewardship.
Questionnaire scoring is conducted by accredited scoring partners trained by CDP. The internal scoring team then collates all scores, running data quality checks to ensure that scoring standards are accurate and consistent.
(A score)
To earn an “A” score from CDP, organizations must show environmental leadership, disclosing action on climate change, deforestation or water security. They must demonstrate best practice in strategy and action as recognized by frameworks such as the TCFD, Accountability Framework and others. As well as having high scores in all other levels these companies will have undertaken actions such as setting science-based targets, creating a climate transition plan, developing waterrelated risk assessment strategies, or reporting on deforestation impact for all relevant operations, supply chains and commodities.
A “B” score indicates environmental management. Companies that score a B have addressed the environmental impacts of their business and ensure good environmental management. A “B-” score indicates that a company is showing some evidence of managing its environmental impact but is not undertaking actions that mark it out as a leader in its field.
A “C-” or ”C” score indicates awareness-level engagement, with the differentiator being the level of awareness a company has shown in their response.
Every question in the questionnaires is scored for disclosure. At disclosure level, companies are awarded roughly one point per data point provided. This level features both “D” and “D-” score. To score a “D” over a “D-” organizations need to have disclosed a more extensive set of information.
An “F” score is given when a requested company fails to disclose through CDP.









ESG risks and opportunities can vary by industry and company. The MSCI ESG Ratings model identifies the ESG risks, that are most material to a sub-industry or sector.
Overview
MSCI ESG Ratings uses a rules-based methodology designed to measure a company’s resilience to long-term, industry material environmental, social and governance (ESG) risks.
MSCI conducts research and rates companies on a ‘AAA‘ to ‘CCC’ scale according to their exposure to industry-material ESG risks and their ability to manage those risks relative to peers.
The approach consists of 4 steps:
1. Data; MSCI collects and standardizes public data including alternative data including government, regulatory and NGO datasets, company disclosure documents, and 3,400 media sources. It does not conduct questionnaires.
2. Metrics; MSCI applies a standardized methodology to assess company Risk Exposure and Risk Management relative to industry peers. MSCI’s ESG issuer communications team engages with companies for data verification.
3. Evaluation; Industry-specific key issues are scored (0-10) using a rules-based methodology, and the team monitors daily and weekly updates of controversies and events to align their scoring methodology.
4. Rating; finally, key ESG issue scores and weights are combined to create an overall ESG rating (AAA – CCC) relative to industry peers. These ratings are subject to industry and market-led checks and formal committee review










The ESG Risk Ratings measure the degree to which a company’s economic value is at risk driven by ESG factors or, i.e. the magnitude of a company’s unmanaged ESG risks
The quantitative score represents units of unmanaged ESG risk with lower scores representing less unmanaged risk. Unmanaged Risk is measured on an open-ended scale starting at zero (no risk) and, for 95% of cases, a maximum score below 50. Based on their quantitative scores, companies are grouped into one of five risk categories (negligible, low, medium, high, severe).
The ESG Risk Ratings are composed of three building blocks that contribute to a company’s overall rating.
These building blocks include Corporate Governance, material ESG issues (MEIs), and idiosyncratic ESG issues.
Building Block #1: Corporate Governance. Only Category 4 or 5 events result in an adjustment of a company’s exposure score. On average, unmanaged Corporate Governance risk contributes round about 20% to the overall unmanaged risk score of a company.
Building Block #2: Material ESG Issues. The assessment of material ESG issues occurs at the subindustry level and is reviewed annually through a comprehensive and structured process. At a company level, material ESG issues can be removed from the rating if they are not relevant to the company’s business model.
Building Block #3: Idiosyncratic Issues. These Issues are ‘unpredictable’ or unexpected in the sense that they are unrelated to the specific subindustry and the business model(s) that can be found in that subindustry. Idiosyncratic issues become material issues only for the specific company in question, not for the entire subindustry that company is part of.





The final ESG Risk Ratings scores are a measure of unmanaged risk, which is defined as material ESG risk that has not been managed by a company. It includes two types of risk:
• Unmanageable risk, which cannot be addressed by company initiatives.
• Management gap, which represents risks that could potentially be managed by a company but aren’t sufficiently managed according to Sustainalytics assessment.
The final ESG Risk Ratings score is calculated as the sum of the individual material ESG issues’ unmanaged risk scores. It




