COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO CAR ENGINE PARTS







Understanding the various components of an engine, including inlet manifold, is crucial for anyone interested in automotive mechanics or performance tuning.
This guide provides an overview of key car engine parts, their functions, and how they contribute to the overall performance of a vehicle.
The engine block is the foundation of an engine. It houses the cylinders and other components, and it's typically made of cast iron or aluminum. The design and material of the engine block play a crucial role in the engine’s durability and performance.


The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. It is connected to the pistons via connecting rods and is a critical component in determining the engine’s smoothness and power output.
Pistons move up and down within the cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture and transferring force to the crankshaft.
High-performance pistons are often made from lightweight materials to reduce engine weight and increase efficiency.


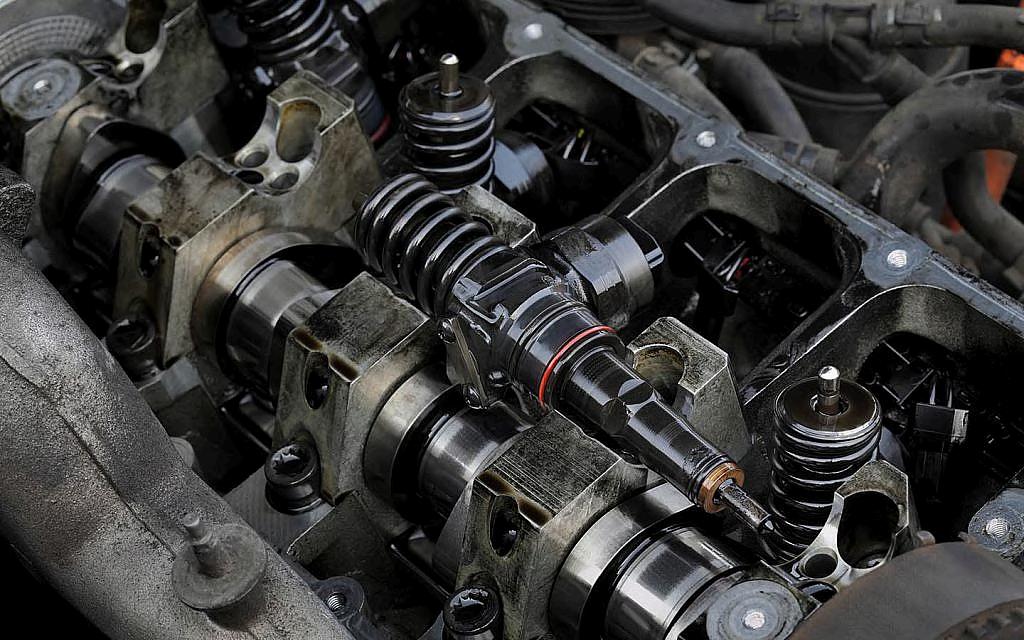
The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. It plays a vital role in the engine’s breathing process, affecting power and fuel efficiency.
The camshaft can be located in the block or in the cylinder head (overhead cam).

The cylinder head sits atop the engine block and contains the combustion chambers, valves, and spark plugs. It is crucial for the engine’s airflow and combustion process. Advanced cylinder heads are designed to improve airflow and combustion efficiency.
Valves control the intake of air and fuel and the expulsion of exhaust gases. There are typically two types of valves in an engine: intake valves and exhaust valves. Proper valve timing and sealing are essential for engine performance and efficiency.


The timing chain or belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring the valves open and close at the correct times during the engine’s cycle. A broken or slipped timing belt can cause severe engine damage.
The oil pump circulates engine oil under pressure to the rotating bearings, sliding pistons, and the camshaft. Proper lubrication is essential to minimize friction and wear on engine components.
Fuel injectors deliver fuel into the engine’s combustion chambers. They are critical for precise fuel delivery, which affects the engine’s performance, efficiency, and emissions. Modern fuel injectors are highly efficient and contribute to better fuel economy.

Turbochargers and superchargers are forced induction systems that increase the engine’s power output by compressing the intake air.
This allows the engine to burn more fuel and produce more power. Turbochargers use exhaust gases to spin a turbine, while superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine.
Inlet manifolds, also known as intake manifolds, distribute the air-fuel mixture to the engine’s cylinders. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the mixture is evenly distributed, which is essential for optimal combustion.
The design of the inlet manifold can significantly affect engine performance, as it influences airflow and the engine's ability to mix air and fuel efficiently.