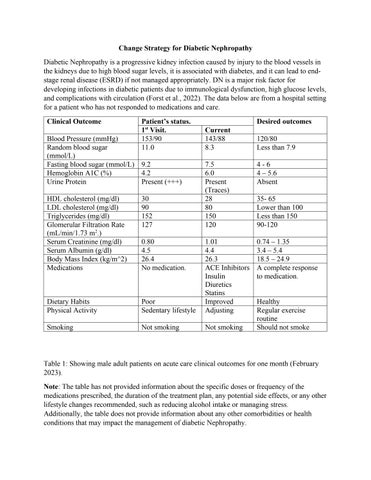
Change Strategy for Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic Nephropathy is a progressive kidney infection caused by injury to the blood vessels in the kidneys due to high blood sugar levels, it is associated with diabetes, and it can lead to endstage renal disease (ESRD) if not managed appropriately. DN is a major risk factor for developing infections in diabetic patients due to immunological dysfunction, high glucose levels, and complications with circulation (Forst et al., 2022). The data below are from a hospital setting for a patient who has not responded to medications and care. Clinical Outcome
Patient’s status. 1st Visit. 153/90 11.0
Current 143/88 8.3
4-6 4 – 5.6 Absent
HDL cholesterol (mg/dl) LDL cholesterol (mg/dl) Triglycerides (mg/dl) Glomerular Filtration Rate (mL/min/1.73 m2.) Serum Creatinine (mg/dl) Serum Albumin (g/dl) Body Mass Index (kg/m^2) Medications
30 90 152 127
7.5 6.0 Present (Traces) 28 80 150 120
0.74 – 1.35 3.4 – 5.4 18.5 – 24.9 A complete response to medication.
Dietary Habits Physical Activity
Poor Sedentary lifestyle
1.01 4.4 26.3 ACE Inhibitors Insulin Diuretics Statins Improved Adjusting
Smoking
Not smoking
Not smoking
Blood Pressure (mmHg) Random blood sugar (mmol/L) Fasting blood sugar (mmol/L) 9.2 Hemoglobin A1C (%) 4.2 Urine Protein Present (+++)
0.80 4.5 26.4 No medication.
Desired outcomes 120/80 Less than 7.9
35- 65 Lower than 100 Less than 150 90-120
Healthy Regular exercise routine Should not smoke
Table 1: Showing male adult patients on acute care clinical outcomes for one month (February 2023). Note: The table has not provided information about the specific doses or frequency of the medications prescribed, the duration of the treatment plan, any potential side effects, or any other lifestyle changes recommended, such as reducing alcohol intake or managing stress. Additionally, the table does not provide information about any other comorbidities or health conditions that may impact the management of diabetic Nephropathy.