ENVIRONMENT AND SECURITY
Andkhoi
Sher Khan Bandar Kunduz
ab
Sheberghan
Balkh
Pol-e Khumri
Maimana
F
R arah
ud
A
N
I
S
T
Farah
Sistan Lakes
Zabol
I R A N
K
He
as
A
N
Ghazni
Tarin Kowt
A
a rgh
a
Quetta
Helmand
Zahedan nL Pishi
Dalbandin
Khost
Sibi
ora
Lahore
u
Okara Marshland Sahiwal Railways
Rangeland
Chaman
Chahar Borjak
Sialkot
Zhob environment, land-use and infrastructure vi Afghanistan’s Leiah Ra
(projected)
Zaranj
Gujrat
Minawali
Kandahar
Lashkar Gah
Ind
Jhelum
Qalat
Delaram
Taftan
nd
Bannu
b
hR
ud
Swa
Thal
Khost
Srinagar
Islamabad
Peshawar Kohat
Gardez
lm
Torkham
nab
H
ul
Mongora Malakand Mardan Havelian
Jhelum
G
Jalalabad
s
Che
H ari Rud
Kab
d
F
Kabul
Band-e Amir
Rainfed cropland Dera Gahzi Khan and gardens Irrigated cropland
Protected areas
PAKISTAN
Su
tley
Main forest areas
Sand dunes
s
Herat
A
Asadabad
Bamiyan Charikar
an
Mashad - Herat (under construction)
Gilgit
Chitral t
Gushgy
Torbat-e Jam
Wakhan l
Mazar-e Sharif
Khorug
tra
Herat - Sher Khan Bandar (projected)
Qurghonteppa Feyzabad
b
Termiz
b
Tejen
Mashad
l
Kokcha
Murga
Sarahs
Cana
Alichur
Kulob
Atamyrat
rga
Karakum
TAJIKISTAN
UZBEKISTAN
ya
CHINA
Mu
Mary
ar
uD
TURKMENISTAN
Kyrgyzstan - China (projected)
Dushanbe
Chi
Am
Map produced by Zoï Environment Network, December 2010
Tejen
Qarshi
Turkmenabat
Panj
200 km
du
150
In
100
h
50
Vak hs
0
Bahawalpur
Projected railways Ganganagar Iron deposits Copper deposits Lithium deposits
Sources: Afghanistan Information Management Service; Afghan Geological Survey; Geology and mineral resources of Afghanistan (2008); Railway Gazette
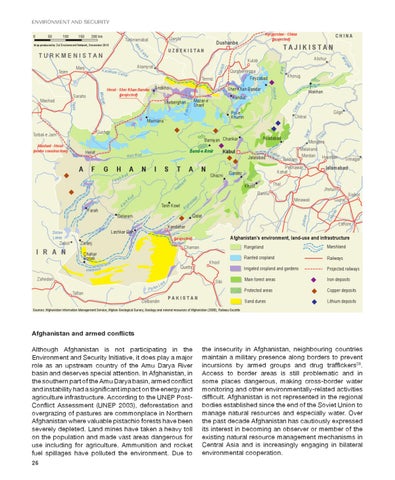
Afghanistan and armed conflicts Although Afghanistan is not participating in the Environment and Security Initiative, it does play a major role as an upstream country of the Amu Darya River basin and deserves special attention. In Afghanistan, in the southern part of the Amu Darya basin, armed confl ict and instability had a signifi cant impact on the energy and agriculture infrastructure. According to the UNEP PostConfl ict Assessment (UNEP 2003), deforestation and overgrazing of pastures are commonplace in Northern Afghanistan where valuable pistachio forests have been severely depleted. Land mines have taken a heavy toll on the population and made vast areas dangerous for use including for agriculture. Ammunition and rocket fuel spillages have polluted the environment. Due to 26
the insecurity in Afghanistan, neighbouring countries maintain a military presence along borders to prevent incursions by armed groups and drug traffi ckers38. Access to border areas is still problematic and in some places dangerous, making cross-border water monitoring and other environmentally-related activities diffi cult. Afghanistan is not represented in the regional bodies established since the end of the Soviet Union to manage natural resources and especially water. Over the past decade Afghanistan has cautiously expressed its interest in becoming an observer or member of the existing natural resource management mechanisms in Central Asia and is increasingly engaging in bilateral environmental cooperation.