3 minute read
Trimble's Tales
HOME • TRIMBLE’S TALES
Lt. J.C. Ives had a Grand Canyon adventure






By Marshall Trimble

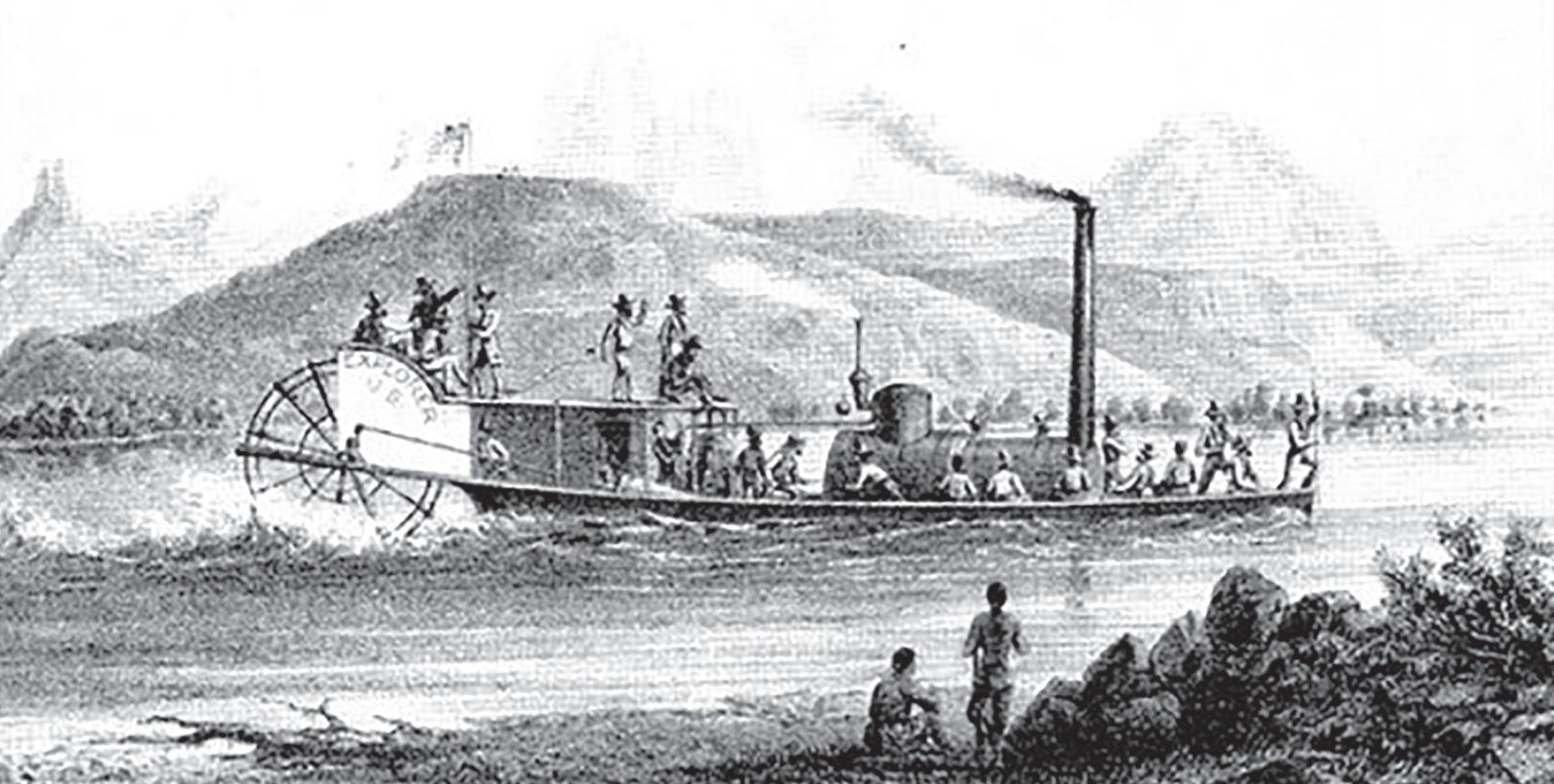
Little was known about the navigability of the Colorado River above Fort Yuma until 1858, when Capt. George Johnson took his steamboat, a side-wheeler dubbed the General Jessup upstream from Fort Yuma. On his heels was, Lt. Joseph Christmas of the Army Corps of Topographical Engineers and his iron-hulled, 54-foot-long military stern-wheeler, aptly named the Explorer. Th ey both set out to see how far up the river a ship could travel. Th e little Explorer certainly wasn’t the most graceful-looking steamer to navigate the river. Th e expedition artist, Baldwin Mollhausen called her a “water-borne wheelbarrow.” She had an oversized boiler and an undersized engine. Th e paddle wheel was at the stern and the boiler and smokestack shared the front with a fourpound deck-mounted gun. In between was a small cabin and observation deck. Atop the cabin, a U.S. fl ag fl apped in the breeze. Earlier, Johnson had off ered to do the job for the Army for $3,000 a month, a fraction of the $75,000 the Army appropriated to do the same survey. His generous off er was refused, and the Army went on a spending binge. It was assembled in Philadelphia, tested on the Delaware River, where it received poor grades, disassembled and shipped to San Francisco via Panama. Th en it was transported by schooner to the mouth of the Colorado where it was reassembled in chilly, galeforce winds and christened, the Explorer. Th e journey up the river to Fort Yuma took 10 days and the little steamer managed to hit most of the snags and sandbars on that stretch of the river. Earlier, Capt. Johnson had decided to explore with his own steamboat, the General Jessup. Accompanying him on the journey was a curious assortment of fellows including the great scout, Paulino Weaver, Pasqual, the 6-foot-7 chief of the Yuma (“Quechan”) Indians, an Army offi cer and 15 enlisted men.
He took his side-wheeler up the siltladen river to Pyramid Canyon, over 300 miles above Fort Yuma and determined the river was navigable all the way to the Virgin River. Th en, he turned around and headed downstream. Th e next day, near today’s Needles, they met Lt. Ned Beale and his Camel Corps surveying the 35th parallel, the future Route 66. Th e meeting of a steamboat and a pack of hump-backed camels in the Mohave Desert had to be one of the most unlikely events in the history of the American West. Meanwhile, Ives and his little Explorer, clawed their way up the Colorado and came to the same conclusion as Capt. Johnson. On his way back Ives, decided to leave his boat, head east and explore the mighty Grand Canyon. With the help of some local native guides, he snaked his way into the canyon, thus becoming the fi rst white man to accomplish the feat. His comments afterward were most interesting. “It can be approached, only from the south and after entering it there is nothing to do but leave. Ours has been the fi rst and will doubtless be the last party of whites to visit this profi tless locality.” It’s all in the eyes of the beholder.




In 1858 the USS Explorer was the fi rst military ship on the Colorado River. (Marshall Trimble/Submitted) Maj. John Wesley Powell and his small crew became the fi rst to navigate the Colorado in 1869. At the time it was the last of the United States major rivers to be traveled by boat. (Marshall Trimble/Submitted)