The Guide to Sixth Form

C I

Welcome to The City School International Dubai
The City School International stems from the renowned ‘City School’s’ establishments which was initially founded in 1978 originating from Pakistan and now based in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Philippines, and Bangladesh. We are even more proud to state that The City School International is home to multiple nationalities and over 700 students and counting as well as a well-proven track record of success in both academic and extra-curricular activities.

Our ‘Sixth Form’ , (Years 12 – 13) offers a wide range of courses that prepare students for further education, training, and employment. The students will be expected to select at least 3 to a maximum of 4 AS subjects which will be carried forward to their second year. However, the students can opt for 3 and keep 3 or opt for 4 and keep a total of 4 in year 13. Moreover, the ability to keep 4 subjects in both years will give them an opportunity to choose from a wide range of universities within different disciplines enabling them to make the right career choice for them.
The Sixth Form Curriculum is enriched by a robust Future Leader Enrichment Programme, academic and careers education and a programme of learning that develops 21st century skills. The school is an approved center for international examination board CAIE (Cambridge Assessment International Education) and also gained a Fellowship status, a prestigious award for continuing excellence in examination results, with CAIE.
It has been an honour for us to be able to provide the A-Level’s programme at The City School International for the first time in 2021 We understand that a large percentage of our students in the past have carried on to higher education through other various avenues at a time where we had not been able to. Now, we are not only preparing them but helping them choose from the most common university pathways which are the UK, Canadian, American, Australian and UAE based universities. Our detailed student enrichment programme designed by TCSI will prepare students for various application procedures inhouse. Information sessions provided by the TCSI school council and the head of sixth form will be conducted throughout the year as well as visiting guest speakers from various local and international institutions. An annual Careers Fair will be organised at the school campus, which will give students a further opportunity to meet and discuss future options/plans with representatives from local and international universities.
The City School International will endeavor to offer a unique international learning experience for students to help them become independent citizens and help them cope for higher studies whether they will stay local or travel abroad. Its education programme maintains a holistic perspective and is based on the principles of Integrity, Compassion, Innovation, Leadership and Global Citizenship.

The City School International Education

The TCSI Systems proudly manages a growing network of quality international schools, providing high standards of education to children around the world. We maintain a high emphasis on the services that we provide as well as ensuring the quality assurance is impeccable that are hallmarks of the TCSI system. With decades of experience TCSI has the expertise to provide a variety of curriculums including the National Curriculum of England.
TCSI has the desire, passion and capability to unlock the potential of our students. Below are the Five Core Principles that form the foundation of TCSI, each designed to help our students reach their full 360 degree potential.
TCSI Core Values
Integrity
We are honest in all our interactions
We demonstrate fairness in our judgment and actions
We gain our reputation by adhering to the highest ethical standards and conduct
Innovation
We embrace change as an opportunity
We question existing ideas and bring forth our own
We have a passion for continuous improvement and creativity
Global Citizenship
Compassion
We fulfil our commitments and promises
We aim to understand the circumstances and viewpoints of others
We strive to find positive ways to contribute to the broader community
Leadership
We strive for excellence in all that we do individually and as a team
We communicate actively and openly
We demonstrate problem solving and decision making skills and help others do the same
We believe in the inherent dignity of all people
We honour the uniqueness of each individual and embrace diverse cultural backgrounds
We value and appreciate diversity
Get ahead with Sixth Form at TCSI
There are many reasons for extending your education beyond IGCSE’s:
• The desire to continue into Higher Education
• Improving qualifications already obtained
• To gain a wider range of experiences prior to committing yourself to a job or full time course of
vocational study.
Whatever your reasons, think things through, establish what has motivated you and set yourself a clear, realistic target you can aim for. You may wish to speak to your Learning Manager (Form Tutor / Class Teacher) or other professionals at school about your plans so that they may get involved in helping you to make the most appropriate choices that will set you on the right path.
What’s on offer at TCSI Dubai?
The Sixth Form community is an integral part of the school, and you will have many opportunities to play a full part in your school life. As an older member of a community, you have a lot to offer the younger members of the school; your experience, your abilities, and your time. How you decide to get involved and to what extent will depend upon you, but simply by establishing a mature presence in the school you will influence the attitudes and expectations of younger students.

There is a very distinctive ethos of respect for the maturity of Sixth Form students We aim to respect the choice which has been made to continue studying and to forge a new relationship between students and teachers based on a partnership in learning. We give considerable responsibility to our students and in return expect an adult approach to their work and looking after their working environment.
There are also considerable opportunities for broadening your experience and developing important skills and qualities through the wide range of extra-curricular opportunities which you will find described in this booklet
Here are some important features of our Sixth Form provision:
• Quality teaching and results
• Build excellent links with Higher Education establishments around the World The school will look to organize ‘Annual Careers Fair’ that gives students and universities the opportunity to meet and speak about future academic and career plans.
• A refreshed, robust and extremely successful Student Leadership Programme
• A Community Service programme that is certificated (space)

• One-to-One university research programme highlighting various avenues to upskill yourself in order to meet the requirements of universities of your choice
• Helping out students to become independent thinkers, and create the best versions of themselves.
Expectations of Sixth Form students at TCSI, Dubai
TCSI, Dubai gives you an opportunity to choose the subjects that you want to study; whether as a preparation for further education or to gain the qualifications that you need in order to embark on the employment of your choice. It also gives you time to investigate more individual methods of study both in school and out of school, as you will be studying fewer subjects in Sixth Form. Your timetable will include HSS time (Health and Social Studies) and Community Service time. You will be trained to study independently in line with the requirements of higher studies and help you feel more in control by creating your own personal, work and study timetable.
You will find that there is a big gap between IG’s and AS Level in terms of class delivery methods, and your learning techniques We at TCSI will be right behind you to help you plan your time out better and to be more focused The challenges it brings to you are equally as satisfying as it provides an opportunity to explore your own interests within subject areas as well as meeting the requirements of public examinations. It is expected for each hour of instruction in class time you devote another hour out of class time to reviewing the subject matter. You are required to show a mature attitude to your studies and the extra opportunities open to you. Getting involved will ensure that you leave the school with the skills you need to be successful in your future
To support you, each student will be allocated a Learning Manager who will help in guiding you through your time with us. Their work is coordinated by the Head of Year 12. Learning Managers work with you in a variety of ways and act as a pivotal contact for you in school, such as registration, community-based activities and a guiding hand in applications and other formal processes. Ultimately, the motivation and drive to excel and succeed must come from within.
You, as future Sixth form students will play an integral role in the life of the school and through your presence and, by participating in positions of leadership; organizing clubs and societies for younger members of the school, you will be expected to lead by example.
All students must adhere to the Sixth form dress code and respect the TCSI rules set to keep the school in an orderly manner and for everyone’s wellbeing. Doing so, will ensure that the TSCI community maintains a responsible outlook and represents the school with Integrity within the school and the wider community outside of the school.

Our Sixth Form community has a high focus on achieving personal and social development in addition to academic success. We believe that teaching creates a strong bong between the staff and students, who look up to their mentors within any sphere for guidance We have also ensured that Community Service has been made a compulsory part of the programme to help students grow as human beings, to help them become more thoughtful of others, stronger, develop leaderships skills, more compassionate and responsible.
We must emphasis that Attendance and punctuality are taken very seriously at TCSI which will have a direct impact on the additional benefits; such as excursions, references and leadership opportunities. Whilst being at TCSI your teachers and the Sixth Form team will be working with you and judging you based on your holistic approach to your studies, your outlook, and how you conduct yourselves at school. Remember, your teachers at TCSI will be the one writing academic references for you for your university applications along with your Head of year, and school counselor. Universities place high regards to those who are punctual, studious and students who look to better themselves through extracurricular activities and certifications. They look for reliability and leadership qualities, and therefore we will not accept tardiness, attendance, or punctuality to be any less than perfect.
The Sixth Form Curriculum
Students are required to select four AS levels of their choice with the full guidance of the TCSI team given to the students in Year 12. As mentioned before, students will have the option to drop one AS-level in year 13, should the feel it is difficult to manage. Please note that, external examinations in most subjects will take place during May/June for Year 12. It is important to remember that all courses offered are from CAIE, UK

Furthermore, In compliance with the Ministry of Education requirements, it is mandatory for all students to complete Arabic studies in Year 12, this applies to both Arab and Non-Arab students.
Selecting the right course of study
• Before you consider which subjects you would like to select, research a range of universities and career options so that the subjects you select satisfy the entry requirements and your future goals.
• You are advised to use our new online Career product called: UNIFROG to assist you with subject selection as well as university and career options. This tool is a product of a UK based organization that helps students explore many different career opportunities. Students will have the latest academic and career information available especially when choosing IGCSE and AS Level subjects.
• Ensure that you have the correct number and combination of AS, A level to satisfy any university or career requirements prior to application
• Think about which subjects you enjoy now but also consider new subjects you haven’t experienced before but which sound interesting
• Prioritize your subjects in order of interest and value to you
• Decide how you are going to organize your subjects across the two years.
• Speak to your mentors, and those within your chosen industry to get an idea of what it is like to be in that particular field.
By getting the best grades possible at IGCSE level you will ensure you have a wide range of options available at Sixth Form
Arabic A for Arabs (Ministry Mandatory)
All students in Year 12 who are either Emirati or whose UAE residency visa is on an Arab passport is required to take Arabic lessons, as per the UAE law and the Ministry of Education Guidelines.
The students will study the Y12_MOE Books.
Arab students will be provided with 4 lessons per week, and the students later can get the will be to use the attested certificate to apply to UAE based universities. Ongoing assessments will take place to monitor the progress and provide support where needed and parents will be made fully aware of the learning journey to ensure success.
Assessment Summary: The exam will consist of one paper divided into two parts:
Reading
Percentage
Marks
Type of the questions
50%
50 Marks
Structured and extended writing questions
50%
50 Marks
Writing
Course Outline:
Two composition tasks Questions will be based on Arabic passages
Arabic B for non-Arabs
(Ministry Optional)
The syllabus content is based on five broad Topic areas which provide contexts for the acquisition of vocabulary and the study of grammar and structures. Through the study of these Topic areas, candidates gain insight into target language countries and communities. The Topic areas are:
• Family and home
• Out and about
• Future plans, education, and work
• Media and culture

• Customer services and transactions
• Everyday activities
• Personal and social life
• The world around us
• The world of work
• The international world.
Course Aims:
The specific aim of the course is to enable students to:

• Communicate accurately, appropriately and effectively in writing.
• Understand and respond appropriately to what they read.
• Enjoy and appreciate the variety of language.
The course duration is one lesson per week, and it will be conducted during the school hours. At the end of the course, the students will have a ministry exam and a certificate of completion will be issued to them.
Assessment Summary
The exam will consist of one paper divided into two parts:
Percentage 50% 50%
Marks
50 Marks
50 Marks
Type of the questions
Structured and extended writing questions
Two composition tasks Questions will be based on Arabic passages
Important notes regarding the Sixth Form Curriculum
Additionally, it is imperative to note that the subjects chosen by the students must also be in line with the Ministry of Education criteria:

• Arabic is compulsory for all Arab students. For Non-Arab it is optional.
• Islamic studies are compulsory for Muslims (Arab and Non-Arab).
• Moral Education is compulsory for all students.
• Equivalency requirements: To be able to gain the Ministry of Education High School Equivalency Certificate (needed if intending to study in the UAE or if attested certificates are required for further education) students must complete a minimum of either 1 full A level subject or 2 AS level subjects with grades A, B, C or D attested by school (Excluding Arabic)
For the High School Equivalency Certificate, it is also compulsory that students complete Year 13, therefore, we do advise all students to complete full A-Level programme (Year 12 & 13). Please note that if you are intending to leave after Year 12, we would require a waiver certificate to state that you are fully understand and are aware that you will not qualify for the MOE certificate
TCSI Sixth Form Future Leaders Enrichment Programme (FLEP)
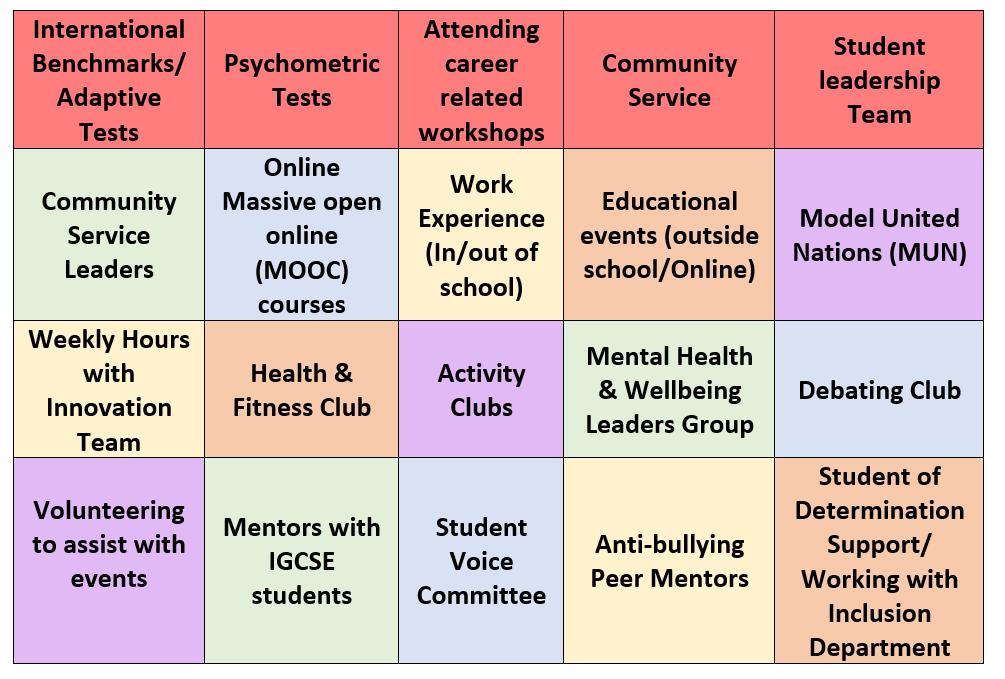
The TCSI Sixth Form Future Leaders Enrichment Programme is a dynamic pastoral programme that is an integral part of the A-Level curriculum. Every Sixth Form student develops personal skills and attributes through the completion of a variety of Community Service activities across the Lower, Middle and Senior schools as well as outside of school. This valuable addition to the Sixth Form curriculum is monitored and certificated by the school. Your selection will help you further your passion and act as an additional skill in support of your AS level choices, personal interests and what lends itself best to a particular career pathway. Students are left to make their own decisions about their area of focus.
Working Plan:
• Students can pick up any 2 (or more) optional enrichment options from above, while mandatory options (in red) will remain the compulsory for all.
• Student will have to record the number of hours training took place in ‘Evidence Sheet’ later signed by Class Teacher, Training Instructor and Head of Sixth Form
• Teacher Training program will take place to ensure all programs take place according to the requirement of enrichment program
The Community Service Programme has developed greatly since its inception, particularly in the area of activities offered and the way it is successfully led with the assistance of the students. As the program is run for students by students it offers many opportunities for all those wanting to take an active leadership role within the school. Its success is also due to the cooperation and feedback from the students and staff who are regularly surveyed for their feedback and ideas on how it can be improved.

Induction/Orientation: Making a successful start to Sixth Form
Sixth Form students will take part in an induction programme at the start of the term, which will require full attendance and is extremely important for new students joining TCSI.
This interactive programme will focus on developing the necessary skills required for a successful transition into the Sixth Form community, especially if you are a student joining us from a different school. Concepts such as team building, target setting, research techniques, critical thinking and self-management will be explored. The induction is also an excellent way for students to interact with one another, get to know their learning manager and become familiar with the expectations of student life in the Sixth Form community.
Careers and Higher Education Guidance
Higher Education choices are discussed from an early point in Year 11 and 12, to assist in establishing the importance of AS level subject choices.
We would also like to highlight that TCSI has strong links with universities, both nationally and internationally, and guests from visiting universities are often invited to the school to give presentations on university life, subjects offered, costs and other deciding factors that can help students make their decisions. The destination of all students is important and so our programme of support for students is strong and targeted at preparation for both University and the work-place. The school continues to develop students’ ability to be prepared for Higher Education in many different ways, including;
✓ Experts from both the industry and Higher Education are invited to brief the students on the range of opportunities that will be made available to them and the process of application for both
✓ All students will have a One-to-One an interview with a member Sixth form team that will help identify the students strengths and weaknesses, help them understand their passion, and assist in learning methods to increase their chances for their desired choice.
✓ Representatives of various industry workers and companies in the local community will be invited in to deliver seminars outlining the demands and requirements of their area of work.
✓ Visits to local Higher Education fairs will be arranged to stimulate ideas and identify key options.
✓ Students will be trained in writing CVs, application forms and in interview skills.

✓ Mock interviews will be carried out for work and university applicants.
✓ An experienced and dedicated team oversees the applications of all students and writes positive, detailed references.
Higher Education Application Support
The Careers Counsellor provides support to all senior students collaboratively with Head of Year and Learning Managers, irrespective of which country they are applying to study in.
The Universities and Colleges Admissions Service (UCAS) is a central organization that processes applications for most courses in the UK, you can also go to their website www.ucas.com which provides detailed information about courses and institutions in the UK. There is also a parent section www.ucas.com/parents where parents can familiarize themselves with the application process and sign up for bulletins from the UCAS portal, which provide news and information, as well as important deadlines.
Students are supported by a dedicated Careers Counsellor with all applications processes and are encouraged to begin the application process early, by choosing a subject area/specific related course for further education. The ‘course search’ section of the UCAS website will help you narrow the options and help you make the decision right for you
All UCAS applications are completed online and candidates are required to pay the standard UCAS application fee (mentioned on the portal). Students are supported and guided through the application procedure in school but are encouraged to carry out their own personal research with their parents to make an informed decision.
Learning Manager Support and Guidance
The Learning Manager will be your main focal point for supporting you through any anxiety or concerns that you as a student, parents or teachers may have. Learning Managers spend 15 minutes in the morning with the year 12 and 13’s during Form time where students can voice their concerns and for teachers to maintain a strict registration process. During this time, we are able to closely monitor our students and build a strong supportive relationship. Learning Managers also meet with all students regularly throughout the year for personal progress reviews in which the focus is on academic performance and determining helpful targets and strategies for improvement.

Further Opportunities at TCSI
Sports
Students who wish to continue their sport activities can participate in both on-site and off-site activities, in competitive teams, for fitness and recreation. Our school teams compete successfully at the highest level and individual students have represented us in regional events. You will have the option of continuing core PE lessons in your Complementary Studies time.
The Sixth form students will have a timetabled sports session during the week and will be expected to actively participate. Studies have shown that exercise helps students feel less stressed and help them focus, perform better in class and during the exam period. The sports session will be flexible to suit a range of different requirements.
Debate, Public Speaking, Model United Nations and Journalism
TCSI has a very strong successful tradition in these arenas and is something the school wants to build upon further. Students with a talent for writing or speaking have no shortage of opportunities for the development and practice of their skills. In line with the rest of the school Sixth form students will play a pivotal role in assisting the production of the school newsletter and yearbook, as well as the organization of major school events.
Sixth form Student Council and Leadership Body opportunities

Involvement in the student council committee gives students an opportunity to discuss issues that are of concern and play a role in helping a positive change take place. The committee meets regularly, planning upcoming social events and other extra-curricular activities. The Sixth form Student Council work as a team; helping shape the future of their growing community.
There are significant opportunities for students to build and develop their leadership skills and capabilities. At TCSI, there are several leadership roles that students can engage with and are encouraged, as a senior student in the school, to lead by example by role modeling excellent behaviour and attitudes.
Gaining Entry to TCSI Sixth Form
To make the right decisions about subjects of study, you need to work in a team who will be able to help you reach your target such as subject leaders, the Year 11 and Sixth form team, as well as your family and friends. You will need to research thoroughly, looking into university access requirements prior to selecting courses of study.
All application forms are provided in this document. All you need to do is print them out, complete and submit them to the Sith Form team / Ms. Zahra, no sooner the results are published, gaining support along the way.
You will find that most of the Science, Business, Humanities and BTEC subject combinations are available in our option blocks. There are four option blocks, the student will have to choose one from the available four blocks Equally, it is possible that certain courses may not run if numbers are insufficient. A minimum of five (5) students are required for running the subjects
The Sixth form team will be drawn from our current pool of Learning Managers and leaders, including the student body. Those chosen will have prior experience of the needs of Sixth form students and how best to support them.

Detailed on the next few pages are the admissions criteria that all applicants need to meet to secure a place on their choice of study. It is also important to understand that subjects cannot be moved from one option block to another. When selecting options, you need to ask yourself the following three questions.
1. Have I achieved / Am I on target to achieve the required IGCSE grade to access the courses I want to study?
2. Are the subjects I want to study in separate blocks?
3. Will I be dedicated enough to see these four subjects through to the next two years?
If the answer to these questions is ‘yes’, you are well on the path towards making a successful application to the TCSI Sixth form. If the answer is no, you may need to seek further advice.
Interview and receiving a ‘TCSI Conditional Offer’
All TCSI applications as well as external applications will receive a conditional offer after they will be interviewed, immediately after the IGCSE results in August 2020.
All applicants will be interviewed by a member of the Sixth Form team, made up of Learning Managers and the leadership body. If successful at interview, you may receive a ‘TCSI Conditional Offer’.
Students will only be interviewed if they have paid the registration fees.
Sample taken from a Conditional Offer letter
If you attain the grades you require to be able to accept this offer, you must contact and inform the school within five days of the results being released, in order to avail the conditional offer. You will need to supply proof of achievement to the school but you will not need to attend school for an interview and your place will be secured for the courses that you have selected. You will need to pay the relevant fees within three days of contacting the school about your results or your application will be rejected If you have not contacted the school by the allotted date your conditional offer will expire and you will need to begin the application process again.
All students who do not attain the grades required by the school to access courses will unfortunately be declined a seat.
Criteria for admissions to Sixth Form are as follows:
• A minimum of 5 A*-B grades (a minimum of a B in the subjects the student intends to study at AS level must be achieved: also see Subject Admission Requirements page)
• IGCSE passes at A*-D with a C-grade in English.
• Fully completed Sixth Form Application Form, including a reference letter from the school /

Learning Manger
• A thorough interview with the Principal/ Sixth Form team
• A Sixth Form contract signed by the student and parents committing to positive behaviour and
regular attendance.
What to do when you receive your IGCSE results
Places in Sixth Form at TCSI are limited so it is important to secure your place within 5 days of receiving your results or you may miss the opportunity to study at TCSI
1. If you achieved the entry requirements for the subjects you selected at interview; contact the school admissions department by e-mail to confirm your place (subject to receiving a conditional offer letter from the school).
2. If you did not achieve the grades required, you must contact the school and attend an interview straight away to discuss what options are available to you.
For further information please contact or visit the School and speak to:
TCSI Section Head for Sixth Form

Year 12 Option Groupings 2022-2023
Business Studies (CAIE 9609)
Economics (CAIE 9708)
Accounting (CAIE 9706)
ICT (CAIE 9626)
Biology (CAIE 9700)
Chemistry (CAIE 9701)
Physics (CAIE 9702)
Mathematics (Core, Mechanics & Statistics) (CAIE 9709)
Computer Science (CAIE 9618)
Psychology (CAIE 9990)
English Language (CAIE 9093)
Business Studies (BTEC)
Sociology (CAIE 9699)
Design and Tech (CAIE 9705)
Important notes:
English Literature (CAIE 9695)
Geography (CAIE 9696)
Sports (BTEC)
Law (CAIE 9084)
1. Students are required to select one subject from each block.

Applied Science (BTEC)
Digital Media and design (CAIE 9481)
2. CAIE does not allow the combination of Computer Science & IT or Design and Technology with Digital Media and Design.
3. Students choosing science subjects are recommended to choose Business Studies BTEC, while students with commerce or humanities are recommended for Science BTEC.
4. Arabic is compulsory for all Arab students. They will do Arabic A (special Arabic), whereas for non-Arab’s Arabic is optional. They will do Arabic B, if required.
5. Islamic is compulsory for all Muslim students. Arab students will do Islamic-A, where as non-Arabs will do Islamic-B
6. Moral Education is a compulsory for Year 12 students.
7. Students choosing Science subjects are recommended to choose Business Studies Btec, while student with commerce or Humanities are recommended for science Btec
8. BTEC courses are offered by Pearson Education. It is well recognized in UK and US as well.
UAE Ministry of Education is now attesting its certificate, with no additional cost. Nb
Subject Specific Admission Requirements

To gain access to a course, you should be attaining/predicted the following grades:
Minimum B in ICT. If IGCSE ICT, or equivalent has not been completed, applicant requires a B grade in English first language and
Minimum B grade in Psychology or B in Biology/ English Language if Psychology has not been studied at IGCSE.
Minimum B grade in Sociology or B in English Language if Sociology has not been studied at IGCSE. Design

Business (BTEC) B or C
Minimum B grade in ICT at IGCSE
Minimum B grade in ICT at IGCSE
Minimum B grade in Geography at IGCSE
Minimum B grade in Sociology or B in English Language if Sociology has not been studied at IGCSE
Minimum B grade in English as a 2nd Language at IGCSE.
Minimum A in English as a 1st Language or Minimum A* grade in English as a 2nd Language at IGCSE if English as 1st Language has not been studied at IGCSE
Minimum C grade in Business Studies or C in English Language or Mathematics if Business Studies has not been studied at IGCSE
Applied Science (BTEC)
Minimum C grade in any Science subject or C in English Language or Environmental Management if Science has not been studied at IGCSE. B or C
Minimum A in internal grade (to be signed by teacher in reference form) for Physical Education if Sports has not been studied at IGCSE

Biology (CAIE 9700)
Course Outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Biology develops a set of transferable skills including handling data, practical problem-solving, and applying the scientific method. Learners develop relevant attitudes, such as concern for accuracy and precision, objectivity, integrity, enquiry, initiative, and inventiveness. They acquire the essential scientific skills required for progression to further studies or employment.
Key Concepts
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Biology are:
9. Cells as the units of life
A cell is the basic unit of life and all organisms are composed of one or more cells. There are two fundamental types of cell: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Understanding how cells work provides an insight into the fundamental processes of all living organisms.
10.Biochemical processes
Cells are dynamic structures within which the chemistry of life takes place. Biochemistry and molecular biology help to explain how and why cells function as they do.
11.DNA, the molecule of heredity
Cells contain the molecule of heredity, DNA. DNA is essential for the continuity and evolution of life by allowing genetic information to be stored accurately, to be copied to daughter cells, to be passed from one generation to the next and for the controlled production of proteins. Rare errors in the accurate copying of DNA known as mutations result in genetic variation and are essential for evolution.
12.Natural selection
Natural selection acts on genetic variation and is the major mechanism in evolution, including speciation. Natural selection results in the accumulation of beneficial genetic mutations within populations and explains how populations can adapt to meet the demands of changing environments.
13.Organisms in their environment
All organisms interact with their biotic and abiotic environment. Studying these interactions allows biologists to understand better the effect of human activities on ecosystems, to develop more effective strategies to conserve biodiversity and to predict more accurately the future implications for humans of changes in the natural world.
14.Observation and experiment
The different fields of biology are intertwined and cannot be studied in isolation. Observation, enquiry, experimentation, and fieldwork are fundamental to biology, allowing relevant evidence to be collected and considered as a basis on which to build new models and theories. Such models and theories are further tested by experimentation and observation in a cyclical process of feedback and refinement, allowing the development of robust and evidence-based conceptual understandings.
Assessment Summary
For The City School International AS and A Level Biology, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1, 2 and 3 (for The City School International AS Level qualification) in one series, then Paper 4 & 5 (for The City School International A Level qualification) in a later series.

40 marks
40 multiple-choice questions
Questions are based on the AS Level syllabus content
60 marks
Structured questions
Questions are based on the AS Level syllabus content.
Paper 3 (Advanced Practical Skills)
40 marks
Practical work and structured questions
2 hours 23% 11.5%
Questions are based on the experimental skills in the Practical assessment section of the syllabus. The context of the questions may be outside the syllabus content.
Paper 4 (Advanced)
100 marks Structured questions
2 hours ------
Questions are based on the A Level syllabus content; knowledge of material from the AS Level syllabus content will be required.
Paper
30 marks Candidates answer two compulsory questions.
Questions are based on the experimental skills in the Practical assessment section of the syllabus. The context of the questions may be outside the syllabus content.
Career and University Pathways

38.5%
11.5%
A-Level biology help students to enter in University undergraduate course to learn anatomy, biophysics, cell and molecular biology, computational biology, ecology and evolution, environmental biology, forensic biology, genetics, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biosciences, natural science, neurobiology, physiology, zoology and many others.
Chemistry (CAIE 9701)
Course Outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Chemistry develops a set of transferable skills including handling data, practical problem-solving and applying the scientific method. Learners develop relevant attitudes, such as concern for accuracy and precision, objectivity, integrity, enquiry, initiative and inventiveness. They acquire the essential scientific skills required for progression to further studies or employment.
Key Concepts
The key concepts identified below, carefully introduced and developed, will help to underpin the course you will teach. You may identify additional key concepts which will also enrich teaching and learning. The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Chemistry are:
✓ Atoms and forces
Matter is built from atoms interacting and bonding through electrostatic forces. The structure of matter affects its physical and chemical properties and influences how substances react chemically.
✓ Experiments and evidence
Chemists use evidence gained from observations and experiments to build models and theories of the structure and reactivity of materials. Theories are tested by further experiments and an appreciation of accuracy and reliability is gained.
✓ Patterns in chemical behaviour and reactions
Patterns in chemical behaviour can be identified and used to predict the properties of substances. By applying these patterns, useful new substances can be designed, and synthetic routes created.
✓ Chemical bonds
The understanding of how chemical bonds are made and broken by the movement of electrons allows us to predict patterns of reactivity. Appreciation of the strength of chemical bonds leads to the understanding of a material’s properties and its uses.
✓ Energy changes
The energy changes that take place during chemical reactions can be used to predict the extent, feasibility and rate of such reactions. An understanding is gained of why and how chemical reactions happen.
Assessment Summary
For The City School International AS and A Level Chemistry, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1, 2 and 3 (for The City School International AS Level qualification) in one series, then Paper 4 & 5 (for The City School International A Level qualification) in a later series.

Structured questions Questions are based on the AS Level syllabus content.
Practical work and structured questions
Questions are based on the experimental skills in the Practical assessment section of the syllabus. The context of the questions may be outside the syllabus content.
Paper 4 (Advanced) 2 hours
100 marks Structured questions
Questions are based on the A Level syllabus content; knowledge of material from the AS Level syllabus content will be required.
Paper 5 (Planning, Analysis and Evaluation) 1 hour 15 minutes
30 marks Candidates answer two compulsory questions.
Questions are based on the experimental skills in the Practical assessment section of the syllabus. The context of the questions may be outside the syllabus content.
Career and University Pathways

38.5%
11 5%
A level chemistry is a great background for employment in research, environmental regulation,
teaching, commerce and industry. The growing prospects are in excellent demand for chemist, Industrial research chemists, Research & development scientists, environmental scientists, synthetic chemists, medicinal chemists, analytical chemists, climate scientists, hazardous waste consultants, laboratory managers, quality assurance manager and University or secondary school lecturer.
Physics (CAIE 9702)
Course Outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Physics develops a set of transferable skills including handling data, practical problem-solving, and applying the scientific method. Learners develop relevant attitudes, such as concern for accuracy and precision, objectivity, integrity, enquiry, initiative, and inventiveness. They acquire the essential scientific skills required for progression to further studies or employment.
Key Concepts
The key concepts identified below, carefully introduced and developed, will help to underpin the course you will teach. You may identify additional key concepts which will also enrich teaching and learning.
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Physics are:
✓ Models of physical systems
Physics is the science that seeks to understand the behaviour of the Universe. The development of models of physical systems is central to physics. Models simplify, explain, and predict how physical systems behave.
✓ Testing predictions against evidence
Physical models are usually based on prior observations, and their predictions are tested to check that they are consistent with the behaviour of the real world. This testing requires evidence, often obtained from experiments.
✓ Mathematics as a language, and problem-solving tool
Mathematics is integral to physics, as it is the language that is used to express physical principles and models. It is also a tool to analyse theoretical models, solve quantitative problems and produce predictions.
✓ Matter, energy and waves
Everything in the Universe comprises matter and/or energy. Waves are a key mechanism for the transfer of energy and are essential to many modern applications of physics.
✓ Forces and fields
The way that matter and energy interact is through forces and fields. The behaviour of the Universe is governed by fundamental forces with different magnitudes that interact over different distances. Physics involves study of these interactions across distances ranging from the very small (quantum and particle physics) to the very large (astronomy and cosmology).
Assessment Summary
For The City School International AS and A Level Physics, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1, 2 and 3 (for The City School International AS Level qualification) in one series, then Paper 4 & 5 (for The City School International A Level qualification) in a later series.

40 multiple-choice questions
Questions are based on the AS Level syllabus content
Structured questions
Questions are based on the AS Level syllabus content.
40 marks
Practical work and structured questions
Questions are based on the experimental skills in the Practical assessment section of the syllabus. The context of the questions may be outside the syllabus content.
Paper 4 (Advanced) 2 hours
100 marks Structured questions
Questions are based on the A Level syllabus content; knowledge of material from the AS Level syllabus content will be required.
- 38.5%
Paper 5 (Planning, Analysis and Evaluation) 1 hour 15 minutes
30 marks Candidates answer two compulsory questions. Questions are based on the experimental skills in the Practical assessment section of the syllabus. The context of the questions may be outside the syllabus content.
Career and University Pathways

A level Physics student can choose their further studies at Universities as astrophysics,
11 5%
mathematical physics, thermodynamics, nanotechnology and become future engineers, physicists and much more With a Bachelor of Science degree in Physics or Engineering physics, students can pursue careers in research and development, science, engineering, education, medicine, law, business, and the military.
Course Outline

Accounting (CAIE 9706)
The specific aim of the course is to develop a critical and analytical approach to examining and evaluating accounting policies and practices and develop skills of communication, analysis, interpretation and presentation of both qualitative and quantitative accounting information.
Key concepts
The key concepts on which this syllabus is built are set out below. These key concepts can help teachers think about how to approach each syllabus topic in order to encourage learners to make links between topics and develop a deep overall understanding of the subject.
✓ A true and fair view
Financial statements are designed to give a true and fair view of the business to internal and external stakeholders.
✓ Duality (double entry)
Duality (double entry) in accounting recognises that every financial transaction has a double (or dual) effect on the position of a business as recorded in the accounts.
✓ Consistency
Consistency in the treatment of financial transactions enables the performance of a business to be compared meaningfully over different time periods.
✓ Business entity
A business is a separate legal entity from the owner of a business. The accounting records must relate only to the business and not to the personal assets and spending of the owner.
✓ Money measurement
Financial accounts only include transactions that can be expressed in terms of money. For example, the purchase of raw material is recorded in the accounts whereas staff creativity is not.
Assessment Summary
For The City School International AS and A Level Accounting, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 (for The City School International AS Level qualification) in one series, then Paper 3 (for The City School International A Level qualification) in a later series.

Paper 1 (Multiple Choice)
30 multiple choice questions based on the AS Level syllabus content 30 marks
Paper 2 (Structured Questions)
Four structured questions on the AS Level syllabus content
Question 1 on financial accounting (30 marks)
Questions 2 and 3 on financial accounting (2 × 15 marks)
Question 4 on cost and management accounting (30 marks)
Total 90 marks
Paper 3 (Structured Questions)
Paper 3 tests the additional content for the A Level, but also requires a knowledge and understanding of the AS Level content.
Section A: Four structured questions on financial accounting (4 × 25 marks)
Section B: Two structured questions on cost and management accounting (2 × 25 marks)
Total 150 marks
Career and University Pathways
A level Accounting provides a sound base for students who seek careers in Accounting such as BBA, MBA Success in this subject can also lead to further studies in Accounting such as Management Accounting, Financial Accounting, Chartered Accountancy, Financial Analyst, Cost Accountant and other Business-related Projects. Many students also choose careers in banking, management, insurance or industry. Other accounting careers for you include internal auditing, tax preparation and planning or management accounting.
Business Studies (CAIE 9609)
Course Outline
Students develop an understanding and appreciation of the nature and scope of business and its role in society whilst examining the various types of business organization. As well as investigating the process of decision-making in business, the course aims to develop the student’s own skills in terms of analysis of problems, interpretation of data and communication. A keen interest in the business world and an enthusiasm and willingness to read around the subject are essential
Key concepts
The key concepts on which this syllabus is built are set out below.

✓ Change is the only constant. Exciting new enterprises are often created in response to economic, cultural or technological changes. Existing businesses must adapt to change if they are to survive and grow.
✓ Management is relevant to every person in a business. Good leadership, strong motivation in workers, effective systems and clear communication are hallmarks of successful businesses.
✓ Customer focus means a business will design and produce goods and services that people want to buy. Customers provide the revenue which sustains a business. Successful businesses really understand their customers and strive to provide products that their customers love.
✓ Innovation enables a business to re-invent itself and stay ahead of the competition. The business world is dynamic, and companies must seek to innovate through product development, more efficient processes and finding better ways ‘to do business’.
✓ Creating value is the core reason why any organisation exists. Effective organisations aim to maximise stakeholder value. For most businesses this will be about maximising shareholder value, but social enterprises will also have other, non-financial, aims. Stakeholders also need to measure the value that is created.
✓ Strategy is about knowing where you are, where you want to get to and how you are going to get there. Managers need to think about, decide on and put into action major long term plans –such as buying another business, entering a new market or developing a new technology.
Assessment Summary
For The City School International AS and A Level candidate follow a staged route taking Papers 1 and 2 (for The City School International AS Level qualification) in one series, then Paper 3 (for The City School International A Level qualification) in a later series.

Section A: Four short answer questions (20 marks)
Section B: One essay from a choice of three questions (20 marks)
Based on the AS Level syllabus
Two data response questions based on AS Level syllabus content 60 marks
Five questions and one essay (from a choice of two) based on a case study.
Based on the additional A Level syllabus content and assumes knowledge and understanding of the
AS Level syllabus content
100 marks
Career and University Pathways
Students with A Level Business Studies have access to a wide range of possible career and higher education opportunities. You learn and use a variety of transferable skills throughout the course These include the important business skills of decision making and planning. You can start a career in business armed with an excellent knowledge of how businesses operate. You may choose a range of professional and business careers including leisure management, financial service, retailing, marketing, public service management and human resource management. The course would also be of interest to those that have ambitions to start their own business at some stage in their lives.

Course Outline
Economics (CAIE 9708)
Students learn to understand and interpret economic information and explain contemporary events and familiar phenomena with relevant economic principles and apply them in real-life situations. Students who choose to study Economics are expected to be interested in world affairs and should remain abreast of world and local news. Levels of learning range from learning basic definitions of concepts to fully applying theoretical concepts to real-life situations and events.
Key concepts
The key concepts on which this syllabus is built are set out below.

✓ Scarcity and choice
The fundamental problem in economics is that resources are scarce and wants are unlimited, so there is always a choice required between competing uses for the resources.
✓ The margin and change
Decision-making by individuals, firms and governments is based on choices at the margin; that is, once behaviour has been optimised, any change will be detrimental as long as conditions remain the same.
✓ Equilibrium and efficiency
Prices are set by markets, are always moving in to and out of equilibrium, and can be both efficient and inefficient in different ways and over different time periods.
✓ Regulation and equity
There is a trade-off between, on the one hand, freedom for firms and individuals in unregulated markets and, on the other hand, greater social equality and equity through the government regulation of individuals and markets.
✓ Progress and development
Economics studies how societies can progress in measurable money terms and develop in a wider more normative sense.
Assessment Summary
Students sit an external examination. For TCSI AS and A Level Economics, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 in one series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the A Level qualification) in a later series.
Paper 1 Multiple Choice 1 hour 30 multiple choice questions based on the AS Level syllabus content 30 marks
Paper 2 Data Response and Essay 1 hour 30 minutes
Section A: one data response question (20 marks)
Section B: one structured essay from a choice of three (20 marks) Based on the AS Level syllabus content 40 marks
Paper 3 Multiple Choice 1 hour 15 minutes
30 multiple choice questions based on the A Level syllabus content 30 marks 15%
Paper 4 Data Response and Essays 2 hours 15 minutes
Section A: one data response question (20 marks)
Section B: two essays from a choice of six (50 marks) Based on the A Level syllabus content 70 marks
Career and University Pathways

-10% 25%
An Economics degree develops a very useful contribution of attributes: mathematical ability and literacy. The course will promote the important skills of decision-making and problem solving. Careers paths may include a professional economist, a banker, an administrative manager, an entrepreneur, a public relations officer and a financial journalist.
Information Technology (CAIE 9626)

Course Outline
Information Technology (IT) is the application of technology to process information. In a world where IT is constantly changing, individuals increasingly need technological and information literacy skills that include the ability to gather, process and manipulate data.
Key concepts
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Information Technology are:
✓ Impact of IT
The application of technology to process information impacts all aspects of our lives. The enormity of the impact can be seen in industry and commerce, transport, leisure, medicine, in the workplace and the home. Communications using technologies have made the world seem smaller.
✓ Hardware and software
Hardware and software interact with each other in an IT system. It is important to understand how these work, and how they work together with each other and with us in our environment.
✓ Networks
Computer systems can be connected together to form networks allowing them to share data and resources. The central role networks play in the internet, mobile and wireless applications and cloud computing has rapidly increased the demand for network capacity and performance.
✓ The internet
The internet is a global communications network that uses standardised communications protocols to allow computers worldwide to connect and share information in many different forms. The impact of the internet on our lives is profound. While the services the internet supports can provide huge benefits to society, they have also introduced issues, for example security of data.
✓ System life cycle
Information systems are developed within a planned cycle of stages that cover the initial development of the system and continue through to its scheduled updating or redevelopment.
✓ New technologies
As the information industry changes so rapidly, it is important to keep track of new and emerging technologies and consider how they might affect everyday life.
Assessment Summary
Students sit an external examination for ICT. For TCSI AS and A Level ICT, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 in one series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the A Level qualification) in a later series.
Paper 1 Theory 1hour 45 minutes
70 marks
Questions are based on sections 1–11 of the subject content. Candidates answer all questions on the paper.

Paper 2 Practical 2 hours 30 minutes
90 marks
The tasks in this practical paper test sections 8–11 of the subject content. Candidates apply knowledge and understanding from sections 1–7 of the subject content. All tasks are compulsory. Candidates select the most appropriate software and must use the most efficient methods to solve each task.
Paper 3 Advanced Theory 1hour 45 minutes
70 marks
Questions are based on sections 12–20 of the subject content. Sections 1–11 are assumed knowledge and understanding. Candidates answer all questions on the paper.
Paper 4 Advanced Practical 2hours 30 minutes
90 marks
The tasks in this practical paper test sections 17–20 of the subject content. The paper includes tasks from sections 8–10 within a problem-solving context. Candidates apply knowledge and understanding of all subject content. All tasks are compulsory. Candidates select the most appropriate software and must use the most efficient methods to solve each task.
Career and University Pathways

25%
25%
ICT programs may prepare scholars for careers in the business world by teaching them to effectively solve problems related to information and communication technologies. ICT professionals commonly have knowledge of computer networks, software, telecommunications, databases, programming and much more. A course in ICT prepares graduates for many potential jobs with corporations, small businesses, schools and other organizations.
Computer Science (CAIE 9618)
Course Outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science encourages learners to meet the needs of Higher Education courses in computer science as well as twenty-first century digital employers. It encourages learners to think creatively, through applying practical programming solutions, demonstrating that they are effective users of technology
Key concepts
The key concepts identified below, carefully introduced and developed, will help to underpin the course you will teach. You may identify additional key concepts which will also enrich teaching and learning.
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Computer Science are:
✓ Computational thinking
Computational thinking is a set of fundamental skills that help produce a solution to a problem. Skills such as abstraction, decomposition and algorithmic thinking are used to study a problem and design a solution that can be implemented. This may involve using a range of technologies and programming languages.
✓ Programming paradigms
A programming paradigm is a way of thinking about or approaching problems. There are many different programming styles that can be used, which are suited to unique functions, tools and specific situations. An understanding of programming paradigms is essential to ensure they are used appropriately, when designing and building programs.
✓ Communication
Communication is a core requirement of computer systems. It includes the ability to transfer data from one device or component to another and an understanding of the rules and methods that are used in this data transfer. Communication could range from the internal transfer of data within a computer system, to the transfer of a video across the internet.
✓ Computer architecture and hardware
Computer architecture is the design of the internal operation of a computer system. It includes the rules that dictate how components and data are organised, how data are communicated
between components, to allow hardware to function. There is a range of architectures, with different components and rules, that are appropriate for different scenarios. All computers comprise of a combination of hardware components, ranging from internal components, such as the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and main memory, to peripherals. To produce effective and efficient programs to run on hardware, it is important to understand how the components work independently and together to produce a system that can be used. Hardware needs software to be able to perform a task. Software allows hardware to become functional. This enables the user to communicate with the hardware to perform tasks.
✓ Data representation and structures
Computers use binary and understanding how a binary number can be interpreted in many different ways is important. Programming requires an understanding of how data can be organised for efficient access and/or transfer.
Assessment Summary
The two assessment objectives in Computer Science are knowledge and understand and problem solving skills. Students sit an external examination for Computer Science. For TCSI AS and A Level Computer Science, candidates follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 in one series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the A Level qualification) in a later series.
75 marks
Paper 1 will assess sections 1 to 8 of the syllabus content. Written paper. Externally assessed. Candidates answer all questions.

75 marks
Paper 2 will assess sections 9 to 12 of the syllabus content. Candidates will need to write answers in pseudocode. Written paper. Externally assessed. Candidates answer all questions.
Paper 3 Advanced Theory 1hour 30 minutes
75 marks
Paper 3 will assess sections 13 to 20 of the syllabus content. Written paper. Externally assessed. Candidates answer all questions. 25%
Paper 4 Advanced Practical 2hours 30 minutes
75 marks
Paper 4 will assess sections 19 to 20 of the syllabus content. Candidates will submit complete program code and evidence of testing. Candidates will be required to use either Java, VB.NET or Python programming languages. Externally assessed. Candidates answer all questions on a computer without internet or email facility
Career and University Pathways

-- 25%
A levels can further apply for admissions in Digital Management, Engineering in Computer Science, Computer Science with Business application, Software Development and Entrepreneurship and Software Engineering
Students with Computer Science
Course Outline

Mathematics (CAIE 9709)
Mathematics develops a set of transferable skills. These include the skill of working with mathematical information, as well as the ability to think logically and independently, consider accuracy, model situations mathematically, analyze results and reflect on findings. Learners can apply these skills across a wide range of subjects and the skills equip them well for progression to higher education or directly into employment.
Key Concepts
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics are:
✓ Problem solving
Mathematics is fundamentally problem solving and representing systems and models in different ways. These include:
o Algebra: this is an essential tool which supports and expresses mathematical reasoning and provides a means to generalise across a number of contexts. –Geometrical techniques: algebraic representations also describe a spatial relationship, which gives us a new way to understand a situation
o Calculus: this is a fundamental element which describes change in dynamic situations and underlines the links between functions and graphs.
o Mechanical models: these explain and predict how particles and objects move or remain stable under the influence of forces.
o Statistical methods: these are used to quantify and model aspects of the world around us. Probability theory predicts how chance events might proceed, and whether assumptions about chance are justified by evidence.
✓ Communication
Mathematical proof and reasoning is expressed using algebra and notation so that others can follow each line of reasoning and confirm its completeness and accuracy. Mathematical notation is universal. Each solution is structured, but proof and problem solving also invite creative and original thinking.
✓ Mathematical modelling
Mathematical modelling can be applied to many different situations and problems, leading to predictions and solutions. A variety of mathematical content areas and techniques may be required to create the model. Once the model has been created and applied, the results can be interpreted to give predictions and information about the real world.
Assessment Summary

The Cambridge International A Level Mathematics qualification offers two different options:
• Route 1: Pure Mathematics, Mechanics and Probability & Statistics (Papers 1, 3, 4 and 5) or
• Route 2: Pure Mathematics and Probability & Statistics (Papers 1, 3, 5 and 6).
Important Note: At TCSI, we recommend science stream students who are planning to take admission in Engineering courses in future to take route 1. While students with combination of business stream subjects are recommended to take route 2.
Route 1 (Science Stream): Students follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 5 in one series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the A Level qualification) in a later series.
Route 2 (Business Stream): Students follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 5 in one series, then Papers 3 and 6 (for the A Level qualification) in a later series.
Career and University Pathways
Every year thousands of students with Cambridge International AS & A Levels gain places at leading universities worldwide. Cambridge International AS & A Levels are accepted across 195 countries. They are valued by top universities around the world including those in the UK, US (including Ivy League universities), Europe, Australia, Canada and New Zealand. Students with mathematical skills learnt at AS & A level can choose courses relevant to engineering, research analyst, education and work in Government sector, Firms and Banks.

Psychology (CAIE 9990)
Course Outline
This syllabus aims to encourage an interest in and appreciation of psychology through an exploration of the ways in which psychology is conducted. This exploration includes:
• a review of a number of important research studies
• an opportunity to look at the ways in which psychology has been applied
Key concepts
The key concepts on which this syllabus is built are set out below.

✓ Nature versus nurture
The nature–nurture debate is a crucial discussion running through all aspects of psychology in order to explain behaviour. Behaviours could be seen as resulting from innate, genetic factors (nature) or behaviours could be explained in terms of the environmental influences that begin to shape us from the moment of conception (nurture). The focus of contemporary psychology is to consider the relative contributions of each influence.
✓ Ethics in psychological research
The need for ethical research constrains the investigation of some topics, or the use of some research techniques. Our approach to ethics has changed over time, so some of the earlier studies that were the basis of the discipline are now no longer acceptable. Ethics must be considered when designing a psychological investigation to ensure that data is gathered without compromising the wellbeing of the participant(s).
✓ Choice of psychological research methods
Psychologists have to carefully choose the research method they use in terms of the information they wish to gather. Every research method, whether quantitative or qualitative, has strengths and weaknesses, and the psychologist must evaluate how the method they have chosen supports the validity and reliability of their specific investigation and contributes to the wider body of psychological research.
✓ No one view in psychology is definitive
Psychological theories are developed by posing hypotheses which are then tested through research. The research will be influenced by the psychological approach of the researcher and
the time and context they are working in. A single topic is likely to be studied in more than one psychological approach, and each approach has its own assumptions, strengths and weaknesses. These different explanations can work together or be in opposition, so psychologists have to balance the evidence for each explanation.
✓ Relevance of psychology in contemporary society
Psychology is now used to underpin many aspects of our lives – it is used in organising businesses, in planning our shops and homes, in treating medical conditions and to improve how we learn. Every study is undertaken with a specific purpose in mind which can then be applied in everyday life – whether it is improving our lives in general, understanding how groups of people behave or treating a disorder. By understanding psychology we can improve how we live our lives and society in general.
Assessment Summary
For Cambridge International AS and A Level Psychology, students take a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 (for Cambridge International AS Level qualification) in one examination series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the Cambridge International A Level qualification) in a later examination series
Paper 1 Approaches, issues and debates
1 hour 30 minutes
Candidates answer all questions. Short answer questions and an essay question, based on core studies. Candidates answer each question in the spaces provided on the question paper.

60 marks
Paper 2 Research methods
Candidates answer all questions.
1 hour 30 minutes
Section A: Short answer questions, some based on the core studies (22 marks).
Section B: Scenario-based questions (24 marks).
Section C: A design-based question divided into two parts (14 marks).
Candidates answer each question in the spaces provided on the question paper.
60 marks
50% 25%
Paper 3 Specialist options: theory
1 hour 30 minutes
Candidates answer two questions from two specialist options. Each specialist option is out of 30 marks.
Question 1: The question is divided into three parts (12 marks).
Question 2: Structured essay-based question divided into two parts (18 marks).
60 marks
Paper 4 Specialist options: application 1 hour 30 minutes
Candidates answer questions from two specialist options.
Section A: Candidates answer two questions from a choice of four (30 marks). Each of these questions is based on stimulus material and is divided into four parts.
Section B: Candidates answer one design-based question from a choice of four (18 marks). Each question is divided into two parts.
Section C: Candidates answer one essay question from a choice of four (12 marks).

60 marks
Career and University Pathways
25%
25%
Cambridge International A Level Psychology provides a suitable foundation for the study of Psychology or related courses in higher education. Equally it is suitable for learners intending to pursue careers or further study in social sciences, or as part of a course of general education With a psychology degree, you're well placed to pursue careers in both arts and scientific fields, depending on your personal interests. There are many options within public and private healthcare, education, mental health support, social work, therapy and counseling
Sociology (CAIE 9699)

Course Outline
Cambridge International AS & A Level Sociology encourages learners to think sociologically about contemporary social, cultural and political issues. The syllabus provides opportunities to explore key concepts and debates that underpin the discipline of sociology and to develop the skills of interpretation, application, analysis and evaluation while studying a range of stimulating topics and realworld issues
Key concepts
The key concepts identified below, carefully introduced and developed, will help to underpin the course you will teach. You may identify additional key concepts which will also enrich teaching and learning.
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Sociology are:
✓ Inequality and opportunity
Inequality has a major influence on people’s opportunities and life choices. Sociologists study the different forms of inequality (age, ethnicity, gender, class), seeking to understand why inequality exists and how it affects different sections of society.
✓ Power, control and resistance
Power is important in understanding how order and control are achieved in society. There are many different theories about who holds power and how power is used to shape human behaviour. Sociologists are also interested in the ways people oppose and resist the exercise of power.
✓ Social change and development
Understanding how societies have changed and developed helps sociologists to make sense of the way people live today. The change from traditional society to modern industrial society is particularly important. The terms ‘modernity’ and ‘post-modernity’ are used to reflect on this transition and on contemporary issues, such as how societies are affected by globalisation and the digital revolution in technology.
✓ Socialisation, culture and identity
Sociologists believe that people learn how they are expected to behave through socialisation. The norms and values learned through socialisation may vary between cultures, impacting on social identity. The study of different social identities is central to contemporary sociology.
✓ Structure and human agency
A central debate in sociology concerns the relationship between the individual and society: is behaviour shaped by wider social forces or is the social world shaped by the actions of individuals? Structural theories focus on how people’s behaviour is constrained by social systems and institutions. Action theories emphasise how individuals establish meaning through social interaction and how this impacts on the behaviour of social groups and institutions.
Assessment Summary
For Cambridge International AS and A Level Sociology, students take a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 (for Cambridge International AS Level qualification) in one examination series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the Cambridge International A Level qualification) in a later examination series
Candidates answer four questions.
Section A: three compulsory questions
Section B: one essay (26 marks) from a choice of two
60 marks
Candidates answer four questions.
Section A: three compulsory questions
Section B: one essay (26 marks) from a choice of two

Paper 3 Education
50 marks
Candidates answer four compulsory questions.
Question 4 is an essay (26 marks)
Paper 4 Globalisation, Media and Religion
70 marks
1 hour 15 minutes
20%
1 hour 45 minutes
Candidates answer two essay questions (35 marks each).
Section A: Globalisation
Section B: Media
Section C: Religion Each section has two essay questions. Candidates select one question from two different sections
Career and University Pathways

30%
Cambridge International A Level Sociology provides a foundation for the study of sociology or related courses in higher education. Equally it is suitable as part of a course of general education. Most popular careers include Advice worker, Community development worker, further education teacher, Higher education lecturer, International aid/development worker, Policy officer, Secondary school teacher and Social researcher
English Language (CAIE 9093)
Course Outline
Cambridge International AS & A Level English Language develops a set of transferable skills. These include critical analysis; constructing arguments; presenting knowledge and understanding; and writing English in a balanced, articulate and fluent manner. Learners can apply these skills across a wide range of subjects and real-world situations. These skills will also equip them well for progression to higher education or directly into employment.
Key concepts
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level English Language are:
✓ Text and context
A text can be defined as a single, coherent unit of language, from the briefest spoken utterance to a book published across several volumes. However, no text exists without context; students of English language must always consider how a text’s meaning is informed by the circumstances not only of its production, but also of its communication and reception
✓ Meaning and style
The study of English language involves developing a range of strategies for exploring the complex ways in which different linguistic elements come together to create meaning. Whether producing their own texts or analysing texts produced by others, students of English language must consider how choices regarding form, structure and language also interact to create a distinctive style

✓ Audience
Students of English language must learn to identify and analyse the strategies writers and speakers use to communicate with their intended audience(s) Likewise, they must be able to predict, recognise and analyse the various responses these strategies might elicit.
✓ Creativity
Whether writing artfully for a specified purpose and audience, reading deeply between the lines of a challenging text, or developing strategies for acquiring the language in the first place, users of the English language must demonstrate creativity in a range of forms and contexts.
✓ Diversity
Constantly subject to a range of influences – whether personal, social, geographical or otherwise – the English language exists in a range of competing and overlapping forms at any given moment. This extraordinary diversity offers a rich opportunity for analysis, comparison and exploration.
✓ Change
The phonological, morphological, semantic, syntactic and other aspects of the English language are liable to change over time. Students of English language must analyse these changes and explore in detail the factors that drive them.
Assessment Summary
For Cambridge International AS and A Level English Language, students take a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 (for Cambridge International AS Level qualification) in one examination series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the Cambridge International A Level qualification) in a later examination series
50 marks Candidates answer two compulsory questions: Question 1 in Section A, and Question 2 in Section B.
50 marks Candidates answer two questions: one compulsory question from Section A, and one question from a choice of three in Section B.

Paper 3 Language Analysis
50 marks Candidates answer two compulsory questions: Question 1 in Section A, and Question 2 in Section B.
Paper 4 Language Topics
2 hours 15 minutes
25%
2 hours 15 minutes
50 marks Candidates answer two compulsory questions each on a separate topic area: Question 1 in Section A, and Question 2 in Section B. --- 25%
Career and University Pathways
English language at A level can help students to enter Universities at undergraduate level to become Social Media Manager, Technical Writer, Public Relations Specialist, Lawyer, Grant Writer, Librarian, Editor, Content Manager and Human Resources Specialist.

English Literature (CAIE 9695)
Course Outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Literature in English develops a set of transferable skills. These include critical analysis, constructing arguments and presenting knowledge and understanding in a balanced, articulate and fluent manner. Learners of Literature in English will be well-equipped for progression to higher education or directly into employment; finding that the skills needed will support them in a wide range of subjects and real-world situations.
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Literature in English are:
✓ Language
Exploring the variety and use of language in literary texts. Identifying literary techniques and explaining how their use contributes to a reader’s analysis and understanding of the text.
✓ Form
Considering the ways in which writers use – or depart from – conventions of literary forms of prose, poetry and drama and how those inform meaning and effects.
✓ Structure
When analysed in reading: the organisation of a text or passage, its shape and development and how this contributes to the readers’ understanding of its meaning and effects. When used in writing: the construction of a relevant and supported argument appropriate to the question.
✓ Genre
Exploring the characteristics of different text types: for example, tragedy, comedy and satire.
✓ Context
Exploring the relationship between a text and its historical, social and cultural backgrounds and the ways in which this can illuminate the reading of a text. In response to unseen texts, considering the ways in which a text’s meaning is shaped by conventions of form alongside those of language and style.
Analysing the ways in which choices regarding form, structure and language interact to create a distinctive style, for different forms and genres.
Interpretation At AS and A - Level:
Evaluating and explaining different ideas within a text. At A Level: Evaluating and explaining different ideas within a text and using different critical readings to explore an understanding of texts and to help support literary arguments
Assessment Summary
For Cambridge International AS and A Level English Literature, students take a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 (for Cambridge International AS Level qualification) in one examination series, then Papers 3 and 4 (for the Cambridge International A Level qualification) in a later examination series
50 marks Candidates answer two questions: one question from Section A: Drama and one question from Section B: Poetry.

50 marks Candidates answer two questions: one question from Section A: Prose and one question from Section B: Unseen.
50 marks Candidates answer two questions: one question from Section A: Shakespeare and one question from Section B: Drama.
50 marks Candidates answer two questions: one question from Section A: Pre-1900 Poetry and Prose, and one question from Section B: Post-1900
Poetry and Prose. Candidates respond to both a poetry and a prose text.
Career and University Pathways

25%
English degree graduates learn very strong communication and written skills through the A levels course. This help them to set their career paths at university level to become editor, journalist, proof reader and majority of them work in Media related fields.
Design and Technology (CAIE 9705)
Course outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Design & Technology syllabus are to enable candidates to develop the ability to be innovative and creative, recognize constraints and produce high quality products with the awareness of design technology in society. You will develop an understanding of the processes of technological activities and industrial practices through the use of ICT to further enhance your design using critical evaluation skills in technical, aesthetic, economic, environmental, social and cultural contexts
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Design and Technology are:
✓ Awareness
Develop an awareness of the significance of design and technology to society
✓ Processes and Practices
learn more about production processes and industrial practices
✓ Evaluation Skills
develop critical evaluation skills which they can employ in a variety of technical, aesthetic, economic, environmental, social and cultural contexts.
Interpretation at AS and A- Level
Evaluation and testing of the knowledge, understanding, product analysis and design. At A-Level this stage involves a coursework project concerning individual design problem and production of a design model.
Assessment Summary
For Cambridge International AS and A Level Design Technology, students take a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and coursework (for Cambridge International AS Level qualification) in one examination series, and then Papers 2 and 3 (for the Cambridge International A Level qualification) and coursework 4 and 5 in later examination series
Component 1 for AS Level This is a written paper which tests knowledge, understanding, product analysis and design. There are three sections; in each section candidates answer one question from a choice of three.
Coursework 1 This is a coursework project which involves an individual design problem and production of a design model
Component 1 for Cambridge International A Level is the same as Component 1 for Cambridge International AS Level.
Coursework 2 for Cambridge International A Level is the same as Component 1 for Cambridge International AS Level.
Paper 2 This is a written paper which tests design, knowledge and understanding in three focus areas; candidates specialise in one of these areas. There are two sections in this paper. In Section A candidates answer two structured knowledge application questions from a choice of three on their chosen focus area. In Section B candidates answer the one design question on their chosen focus area.
Coursework 3, and it can either be developed from the Component 2 project or be a completely new project covering Components 2 and 4 in an holistic way
Career and University Pathways
Students who study Design and Technology at and A-Level are well equipped for the creative industry Some of which are: Sound engineer, Graphic designer, Interior designer, Industrial designer, Video Game design, Art director, Web developer, Civil engineer, Mechanical engineer, Robotics engineer, Systems engineer, UX designer, Aeronautical engineer, Architect and Software developer.

Digital Media and Design (CAIE
9481)
Course outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Digital Media & Design encourages independent creative expression and the development of a critical, reflective practice. The syllabus provides opportunities for learners to enrich their understanding of innovative uses of technology and to improve their skills in a wide range of contemporary techniques. The syllabus is designed to accommodate a range of interests, materials and resources, and the skills and interests of the teaching staff.
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Digital Media & Design are:
✓ Communication
The essential purpose of any piece of digital design is to communicate. Designers need to understand that the relationship their work builds with the audience is influenced by many things, including their chosen media and methods. Effective communication is also essential for operating in today’s design world, which demands collaboration and engagement with wider cultures and emerging technologies.
✓ Creativity
Creativity is at the heart of a designer’s processes. It pushes designers to question, investigate, experiment and take risks to create solutions that are original and effective. Creative practitioners use curiosity, imagination and innovation to solve design problems in new ways.
✓ Innovation
Innovation means experimenting with processes, approaches and technologies. A willingness to innovate builds confidence, and helps develop awareness of new ways of looking at things, which is fundamental to digital media and design. A skilled designer selects the techniques and processes that communicate their message in the most effective way.
✓ Intention
An intention is the starting point of any project, from which a designer starts to develop ideas. An intention or purpose can come from a brief, proposal or research, while at other times it might begin as an idea or feeling. Though an intention is the reason to start a project, it is important to understand that the intention can evolve as work develops.
✓ Critical reflection
Critical reflection and user feedback is the ongoing process that helps designers to learn what works and what doesn’t. Designers need to evaluate how the media, techniques and processes they choose affect how their work communicates meaning. This process can help work become more relevant and coherent.
✓ Research
Research and context First-hand research helps designers to develop their ideas and refine their practice. Actively researching and responding to other practitioners, cultures and creative movements gives the designer a broader view. A designer can use this to improve their practice and understand how their work connects with its intended audience.
Interpretation at AS and A- Level
Cambridge International AS & A Level Digital Media & Design is for candidates who want to explore a range of processes and techniques in digital media. The subject content allows space for teaching and learning to be creative. It is grouped into three broad areas of study: Digital photography, Moving image, Mobile and multimedia applications
Assessment Summary
AS Level only (Candidates take both AS components in the same series) A Level (staged over two years) Year 1 AS Level Year 2 Complete the A Level: A Level (Candidates take all components in the same examination series)

Portfolio There are two elements to the portfolio:
• supporting studies and a proposal
Paper 1 There are two elements to the assignment:
• supporting studies and an outcome
Personal Investigation This is a practical component supported by written work. Candidates research a topic or theme of their choice. There are two elements to the investigation: A final practical outcome and written analysis
(1000–1500 words)
Career and University Pathways

50% 25%
50% 25%
--- 50%
Students have the ability to use this as a platform to go into career pathways such as a digital media photographer, video editor, animator, social media specialist, graphic designer, video game designer, web analyst specialist, and web developer.
Course outline

Cambridge International AS & A Level Law is accepted by universities and employers as proof of an understanding of the main principles of the law in England and Wales. Successful Cambridge International AS & A Level Law students gain lifelong skills, including: Knowledge and understanding of the English Legal System and, at A Level, Contract Law and Tort Law; Ability to analyse realistic scenarios by applying legal concepts, rules and precedents; Greater command of language to express interpretation, reasoning, comment and judgement
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Law:
✓ Knowledge
Knowledge and understanding An ability to recall, select, use and develop knowledge and understanding of legal principles and rules by means of example and citation.
✓ Analysis
Analysis, evaluation and application An ability to analyse and evaluate legal materials, situations and issues and accurately apply appropriate principles and rules.
✓ Communication
Communication and presentation Use appropriate legal terminology to present logical and coherent argument and to communicate relevant material in a clear and concise manner
Interpretation at AS and A- Level
Cambridge International AS & A Level Law syllabus are to: Provide an introduction to legal concepts and rules and the machinery involved in their introduction, application and enforcement; Encourage candidates to explore and understand the substantive rules of law; Explore and critically assess the value of legal rules, processes and institutions; Develop skills of communication, interpretation, and reasoning and analysis.
Assessment Summary
Take all A and AS components at one exam series, leading to the full Advanced Level qualification (Papers 1, 2, 3 and 4) or Take the AS components (Papers 1 and 2) at one exam series and, having received the AS qualification, take the additional A2 components (Papers 3 and 4) at a later series, leading to the full Advanced Level qualification or Take the AS components only (Papers 1 and 2) at one exam series, leading to the Advanced Subsidiary qualification.
Paper 1 (Structure and operation of the English 1 hour 30 mins Legal System) Candidates answer three essay questions from a choice of six 60% 30%
Paper 2 (Data response: the English Legal 1 hour 30 mins System)
Candidates answer one question from a choice of two. The paper tests the candidate’s ability to apply their knowledge to examine critically and analyse a given case. The data may be drawn from any area of English law.
Paper 3 (Law of Contract) 1 hour 30 mins
Section A: 3 essay questions
Section B: 3 scenario-based problem questions Candidates answer three questions: one from Section A, one from Section B and one other.
Paper 4 (Law of Tort) 1 hour 30 mins
Section A: 3 essay questions
Section B: 3 scenario-based problem questions Candidates answer three questions: one from Section A, one from Section B and one other.
Career and University Pathways
A law student will successfully transition to a career of their choice whether they choose to be a barrister, solicitor, chartered legal executive, company secretary, judge, lecturer, lawyer, legal secretary, licensed conveyancer, mediator, paralegal, patent attorney, trademark attorney, and an usher. They have umpteen opportunities to go into Investment banking, civil service, legal publishing, management consultancy, pension, and politics

Course outline
Geography (CAIE 9696)
Cambridge learners will develop: an understanding of the principal processes operating within physical geography and human geography, an understanding of the causes and effects of change on natural and human environments , an awareness of the usefulness of geographical analysis to understand and solve contemporary human and environmental problems ,the ability to handle and evaluate different types and sources of information, the skills to think logically, and to present an ordered and coherent argument in a variety of ways ,an excellent foundation for studies beyond Cambridge International A Level in Geography, in further or higher education, and for professional courses
The key concepts for Cambridge International AS & A Level Geography: Space:
the implications of spatial distributions and patterns of a range of physical and human geographical phenomena.
✓ Scale
The significance of spatial scale in interpreting environments, features and places from local to global, and time scale in interpreting change from the geological past to future scenarios.
✓ Place
The importance of physical and human characteristics which create distinctive places with different opportunities and challenges.

✓ Environment
How the interactions between people and their environment create the need for environmental management and sustainability.
✓ Interdependence
How the complex nature of interacting physical systems, human systems and processes create links and interdependencies.
✓ Diversity
The significance of the similarities and differences between places, environments and people.
✓ Change
The importance of change and the dynamic nature of places, environments and systems.
Interpretation at AS and A- Level
Cambridge International AS and A Level Geography, candidates: take Papers 1 and 2 only (for the Cambridge International AS Level qualification) or follow a staged assessment route by taking Papers 1 and 2 (for the Cambridge International AS Level qualification) in one series, then Paper 3 and 4 (for the Cambridge International A Level qualification) in a later series or take Papers 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the same examination series, leading to the full Cambridge International A Level.
Paper 1 Core Physical Geography 1 hour 30 minutes
Section A: Three data response questions (30 marks)
Section B: One structured question from a choice of three (30 marks)
60 marks 50% 25%
Paper 2 Core Human Geography 1 hour 30 minutes
Section A: Three data response questions (30 marks)
Section B: One structured question from a choice of three (30 marks)
60 marks 50% 25%
Paper 3 Advanced Physical Geography Options 1 hour 30 minutes
Candidates answer questions on two of the optional topics. Each topic consists of one structured question (10 marks) and a choice of essay questions (20 marks).

60 marks
Paper 4 Advanced Human Geography Options 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates answer questions on two of the optional topics. Each topic consists of one structured question (10 marks) and a choice of essay questions (20 marks).
25%
60 marks --- 25%
Career and University Pathways
As you climate change and general geographical change is the one of the most leading industries right now. If the student decides to pursue this career, they have the ability to go into numerable career opportunities such as: cartographer, climate change analyst, climatologist, emergency management specialist, geomorphologist, geospatial analyst, GIS specialist, hydrologist, location analyst, meteorologist, pollution analyst, remote sensing analyst, soil conservationist, surveyor, town planner and water conservation officer

Pearson BTEC International Level 3 Subsidiary Diploma in Business
Course Outline
Assessment
Assessment is designed to fit the purpose and objective of the qualification. It includes a range of assessment types and styles suited to vocational qualifications in the sector.
All assessment is internal but some mandatory units have extra controls on assessment and are assessed using Pearson Set Assignments. Additionally, some units are synoptic. Set assignment units Some mandatory units in the qualifications are assessed using a set assignment.

Each assessment is set by Pearson and may need to be taken under controlled conditions before it is marked by teachers. Set assignment units are subject to external standards verification processes common to all BTEC units.
By setting an assignment for some units, we can ensure that all learners take the same assessment for a specific unit. Learners are permitted to re sit set assignment units during their programme.
Note: Set assignments are available from September each year and are valid for one year only.
Qualification Structure
Mandatory units
There are two mandatory units, one internal and one set assignment unit. Learners must complete and achieve a Pass or above in these mandatory units.

Optional units
Learners must complete additional units totaling at least 180 GLH. Some combinations of optional units may result in an additional 30 GLH being taken.
Grading for units and qualifications
Units are assessed using a grading scale of Distinction (D), Merit (M), Pass (P) and Unclassified (U). All mandatory and optional units contribute proportionately to the overall qualification grade, for example a unit of 120 GLH will contribute double that of a 60 GLH unit.
Certification and results
Once a learner has completed all the required components for a qualification, the centre can claim certification for the learner, provided that quality assurance has been successfully completed.
Career and University Pathways
The qualifications are recognised by higher education providers as contributing to meeting admission requirements to many relevant courses, for example:
• BSc (Hons) in Business and Management
• BA (Hons) in Business and Finance
• BA (Hons) in Business with Human Resource Management
• BA (Hons) and BSc (Hons) in Business Studies
• BSc (Hons) in International Management
• BSc (Hons) or BA (Hons) in Marketing
• BSc (Hons) in Retail Management.
After this qualification, learners can also progress directly into employment, however it is likely that many will do so via higher study. Areas of employment include junior business roles in marketing, administration, finance, financial services, procurement, events management, human resources, and other related areas in the business sector.
Pearson BTEC International Level 3 Subsidiary Diploma in Sport
Course Outline
Assessment
Assessment is designed to fit the purpose and objective of the qualification. It includes a range of assessment types and styles suited to vocational qualifications in the sector.
All assessment is internal but some mandatory units have extra controls on assessment and are assessed using Pearson Set Assignments. Additionally, some units are synoptic. Set assignment units Some mandatory units in the qualifications are assessed using a set assignment.

Each assessment is set by Pearson and may need to be taken under controlled conditions before it is marked by teachers. Set assignment units are subject to external standards verification processes common to all BTEC units.

By setting an assignment for some units, we can ensure that all learners take the same assessment for a specific unit. Learners are permitted to re sit set assignment units during their programme.
Note: Set assignments are available from September each year and are valid for one year only.
Qualification Structure
Mandatory units
There is one mandatory unit. Learners must complete and achieve a Pass or above in the mandatory unit.
Optional units
Learners must complete optional units totalling at least 270 GLH.

Grading for units and qualifications
Units are assessed using a grading scale of Distinction (D), Merit (M), Pass (P) and Unclassified (U). All mandatory and optional units contribute proportionately to the overall qualification grade, for example a unit of 120 GLH will contribute double that of a 60 GLH unit.
Certification and results
Once a learner has completed all the required components for a qualification, the centre can claim certification for the learner, provided that quality assurance has been successfully completed.
Career and University Pathways
These qualifications support progression to job opportunities in the sports industries at a variety of levels. Examples of job roles available in sports areas include: • physical education instructor • assistant coach. Jobs available in fitness and personal training areas include: • gym instructor • personal trainer.
Jobs available in sports coaching and development areas include community coach, sport-specific school coach, club sports coach. Jobs available in sports business and management areas include sports administrative assistant and sports agent.
Jobs available in sports facilities operations and management areas include leisure assistant, leisure duty manager, sport facilities manager.
After achieving these qualifications, while learners can progress directly to entry-level assistant coaching roles, it is likely that many will do so via higher study. These qualifications are recognised by higher-education providers as contributing to meeting admission requirements to many relevant courses in a variety of areas of the sport sector, for example: BA (Hons) in Sports Coaching and Development, BA (Hons) in Sports Management, BA (Hons) in Sport and Physical Education, BA (Hons) in Health and Fitness, BA (Hons) in Diet, Fitness and Wellbeing, BA (Hons) Sports Business Management, BA (Hons) Stadium and Sports Facility Management, BSc in Community Sports Coaching and BSc in Sports, Physical Education and Teaching Science.
Pearson BTEC International Level 3 Subsidiary Diploma in Applied Science
Course Outline
Assessment
Assessment is designed to fit the purpose and objective of the qualification. It includes a range of assessment types and styles suited to vocational qualifications in the sector.
All assessment is internal but some mandatory units have extra controls on assessment and are assessed using Pearson Set Assignments. Additionally, some units are synoptic. Set assignment units Some mandatory units in the qualifications are assessed using a set assignment.

Each assessment is set by Pearson and may need to be taken under controlled conditions before it is marked by teachers. Set assignment units are subject to external standards verification processes common to all BTEC units.

By setting an assignment for some units, we can ensure that all learners take the same assessment for a specific unit. Learners are permitted to re sit set assignment units during their programme.
Note: Set assignments are available from September each year and are valid for one year only.
Qualification Structure
Mandatory units
There are three mandatory units, which are all set assignment units. Learners must complete and achieve a Pass or above in all mandatory units.

Optional units
Learners must complete optional units to a minimum value of 180 GLH.
Grading for units and qualifications
Units are assessed using a grading scale of Distinction (D), Merit (M), Pass (P) and Unclassified (U). All mandatory and optional units contribute proportionately to the overall qualification grade, for example a unit of 120 GLH will contribute double that of a 60 GLH unit.
Certification and results
Once a learner has completed all the required components for a qualification, the centre can claim certification for the learner, provided that quality assurance has been successfully completed.
Career and University Pathways
This qualification supports progression to job opportunities in the science industry at a variety of levels. Jobs available in these areas include Chemical Technician, Biomedical Scientist, Clinical Scientist and Environmental Scientist
After achieving this qualification, while learners can progress directly to entry-level science roles, it is likely that many will do so via higher study. This qualification is recognised by higher-education institutions as fully meeting admission requirements to many relevant courses in a variety of areas of the science sector, for example: BSc (Hons) in Chemistry with Analytical Science, BSc (Hons) in Bioscience, BSc (Hons) in Environmental Science and Higher National Diploma (HND) in Applied Science.

Application Forms
In order to make your application to Sixth Form you will need to print-out the application form and complete them using black or blue pen. Please keep all of these pages together and in the correct order. Applications will not be accepted if they contain errors and corrections. Should you make a mistake, please start again with a fresh form.

Personal Details:
NAME (as in passport):
Date of Birth:
Name of Present School:


Parents Details:
NAME (as in passport):
Email Address:
NAME (as in passport):
Sixth Form 2022-23 Application form
Gender:
Contact Number:
Photo
Email Address: Contact Number:
Subjects being taken at IGCSE:
Year 12 Options Selection:
Note: - All students must complete 4 subjects. Please be aware that some subjects may not run if there are insufficient numbers of students to make the course viable.
Please fill out the following sections in as much detail as possible:
Interests in and out of school (e.g. involvement with clubs, teams, groups/drama, music, sports, as well as individual interests)
Any positions or responsibility in your previous school (e.g. prefect, sports captain, student council)

Any awards received / qualifications gained (e.g. school prizes, music exams)
What career plans do you have?
Any other information you wish the school to be aware of:

Please Note:
• All students need to complete the application form accurately.
• All students need to have a completed confidential reference form.
• TCSI / External candidates must send this reference form and option choices to the school along with the application form.
• TCSI students can seek their references from their current class teachers.
• You will see that there are also letters within the Sixth Form for Arabic/Islamic studies. Please ensure that you have read these carefully and they are signed and returned as part of your application.
• Letters and the signed Sixth Form contract MUST be completed and signed before an interview can take place.
Reference Form
Internal Candidates (TCSI Candidates)
Dear Learning Manager, please comment on the student’s attitude towards his/her IGCSE studies, contribution to school life and their ability to cope with an A-Level programme as well as punctuality and attendance. Your accurate view of the student will be highly appreciated in a way for us to come to a decision.
External Candidates
Please attach a reference to your application form, this must be on school headed paper with your school stamp.

Signature of Teacher:
Name:
Position:
Sixth Form Community Contract 2022-2023
We understand that my son/daughter____________________ has accepted a place at The City School International Sixth Form Community subject to the following requirements being met at all times.

• Attend all school lessons and other activities within their Sixth Form timetable regularly and punctually
• Be present for every registration session and shall attend assemblies as required
• Use any non-timetabled time for individual private study in allocated areas (Common Room/Library)
• Not leave the school site during lesson time unless previously agreed and discussed with the Head of Secondary respectively and in consultation with parents
• Wherever possible make routine appointments with the doctor, dentist etc. outside of school hours.
• Adhere to the Sixth Form Dress Code by being smart and presentable at all times
• Meet all deadlines set for homework and coursework for all subjects
• At all times set a good example to the younger students in the school
• Behave in an exemplary manner in accordance with the school’s Code of Behaviour
• Respect his/her surroundings and recognize the right of other students to study in peace
• Notify the Learning Managers / Head of Sixth Form respectively in case of absence
• Will use any study lessons effectively and be at the correct designated place
• Will complete the required community service hours during the designated days and complete the log
I/We agree that________ ___ shall meet the above requirements at all times and understand that failure to do so will result in a meeting to discuss her/his continuing education at The City School International Sixth Form Community.
We have also read and understand the requirements and expectations of the courses being opted for.
Signed_________________ (Parent)
Signed_______________________(Student)
In this section please complete the form which is appropriate to you and return it along with the application form.
Dear Principal,
Re: Year 12 Arabic
I am writing to request the withdrawal of my son / daughter (Name), from his / her Arabic lessons in Year 12. My son / daughter will not study in the UAE or an Arabic University in the region after completion of his/her Year 12, therefore, I believe these lessons will not be required to complete his/her studies or affect his/her future work or career prospects. I understand that should my son/daughter wish to study or work in the UAE in the future or my home country requires the MOE attestation, in such cases to obtain a High School Completion Equivalency Certificate, the Ministry may require an attested certificate proving the study of Arabic in Year 12.
I understand that The City School International, Dubai cannot issue such a certificate if a student has not undertaken this study. I, the parent, take full responsibility and accountability in such circumstance.

Please withdraw my son/daughter from the Arabic lesson lists as of now.
Yours sincerely,
Full Name of Parents/Guardian: _____________________________________
Parents Signature: ___________
Parent’s Mobile number: ____________
Students Mobile Number: _______
Parents Email Address: ___________________________
Dear Principal,
Re: Year 12 Arabic
Please read and sign the letter below and return it along with the application form.
I am writing to confirm I understand that Arabic is a compulsory subject for all Arab & Non- Arab students in Year 12.
I agree that my son / daughter ______ ___ will be regularly attending all Arabic classes at The City School International, Dubai. Failure to attend 95% of all Arabic lessons and sit the required examinations means the school cannot issue a school leaving certificate that includes Arabic. Therefore, the various ministries may not attest their school leaving certificate which means my son / daughter may not be able to continue further studies in the UAE, or at a number of Arabic universities in the Middle East region. It may also mean they are not eligible to work in the UAE or obtain an MOE High School Completion Equivalency.

Name of Parents/Guardian: _________________
Parents Signature: ____________________Parent’s Mobile number: __________
Students Mobile Number: __________
Parents Email Address: _____
Dear Parents, Re Year 12 Islamic Studies
Please read and sign the letter below and return it along with the application form.
I am writing to confirm I understand that Islamic Studies is a compulsory subject for all Muslim students in Year 12.
I agree that my son / daughter _______________________ __ will be regularly attending all Islamic Studies classes at The City School International, Dubai. Failure to attend 95% of all Islamic Studies lessons and sit the required examinations means the school cannot issue a school leaving certificate that includes Islamic Studies. Therefore, the various ministries may not attest their school leaving certificate which means your son / daughter may not be able to continue further studies in the UAE, or at a number of Arabic universities in the Middle East region. It may also mean they are not eligible to work in the UAE or obtain an MOE High School Completion Equivalency.

Name of Parents/Guardian: _________________
Parents Signature: ____________
Parent’s Mobile number: _______________
Students Mobile Number:
Parents Email Address: __
For further details on course content please speak to the relevant Faculty Leader or simply go online and research your courses for yourself. Each course specification number is given on the subject page. The examination board website is:www.cie.org.
The City School International, Dubai

Plot # 416-1297, Nadd-Al-Hamar, 1212 Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Email: info@tcsidxb.ae
Contact: 04 2899722