X. Wang et al.
Brain and Cognition 146 (2020) 105631
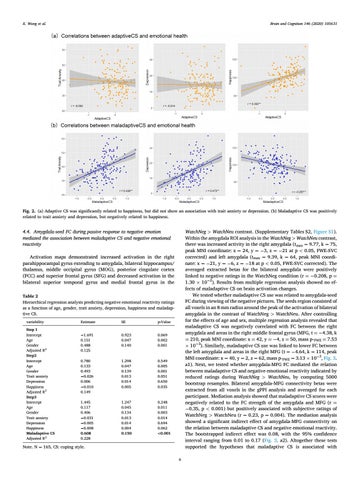
Fig. 2. (a) Adaptive CS was significantly related to happiness, but did not show an association with trait anxiety or depression. (b) Maladaptive CS was positively related to trait anxiety and depression, but negatively related to happiness.
4.4. Amygdala-seed FC during passive response to negative emotion mediated the association between maladaptive CS and negative emotional reactivity
WatchNeg > WatchNeu contrast. (Supplementary Tables S2, Figure S1). Within the amygdala ROI analysis in the WatchNeg > WatchNeu contrast, there was increased activity in the right amygdala (tmax = 9.77, k = 75, peak MNI coordinate: x = 24, y = − 3, z = − 21 at p < 0.05, FWE-SVC corrected) and left amygdala (tmax = 9.39, k = 64, peak MNI coordi nate: x = − 21, y = − 6, z = − 18 at p < 0.05, FWE-SVC corrected). The averaged extracted betas for the bilateral amygdala were positively linked to negative ratings in the WatchNeg condition (r = − 0.208, p = 1.30 × 10− 2). Results from multiple regression analysis showed no ef fects of maladaptive CS on brain activation changes. We tested whether maladaptive CS use was related to amygdala-seed FC during viewing of the negative pictures. The seeds region consisted of all voxels in an 8 mm radius around the peak of the activation of bilateral amygdala in the contrast of WatchNeg > WatchNeu. After controlling for the effects of age and sex, multiple regression analysis revealed that maladaptive CS was negatively correlated with FC between the right amygdala and areas in the right middle frontal gyrus (MFG, t = − 4.38, k = 210, peak MNI coordinate: x = 42, y = − 4, z = 50, mass p-FWE = 7.53 × 10− 3). Similarly, maladaptive CS use was linked to lower FC between the left amygdala and areas in the right MFG (t = − 4.64, k = 114, peak MNI coordinate: x = 40, y = 2, z = 62, mass p-FWE = 3.13 × 10− 3, Fig. 3. a1). Next, we tested whether amygdala-MFG FC mediated the relation between maladaptive CS and negative emotional reactivity indicated by reduced ratings during WatchNeg > WatchNeu, by computing 5000 bootstrap resamples. Bilateral amygdala-MFG connectivity betas were extracted from all voxels in the gPPI analysis and averaged for each participant. Mediation analysis showed that maladaptive CS scores were negatively related to the FC strength of the amygdala and MFG (r = − 0.35, p < 0.001) but positively associated with subjective ratings of WatchNeg > WatchNeu (r = 0.23, p = 0.004). The mediation analysis showed a significant indirect effect of amygdala-MFG connectivity on the relation between maladaptive CS and negative emotional reactivity. The bootstrapped indirect effect was 0.08, with the 95% confidence interval ranging from 0.01 to 0.17 (Fig. 3. a2). Altogether these tests supported the hypotheses that maladaptive CS is associated with
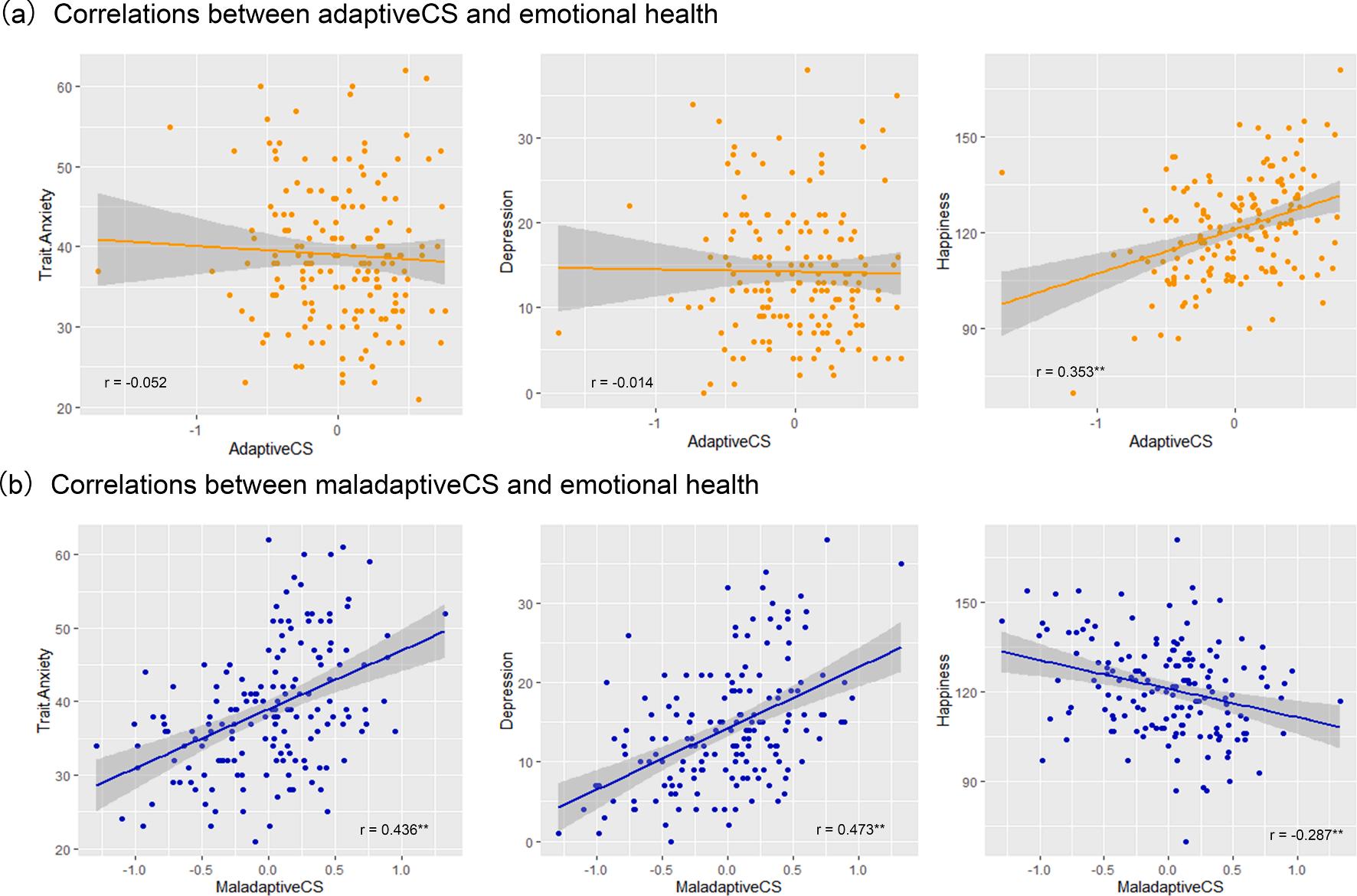
Activation maps demonstrated increased activation in the right parahippocampal gyrus extending to amygdala, bilateral hippocampus/ thalamus, middle occipital gyrus (MOG), posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) and superior frontal gyrus (SFG) and decreased activation in the bilateral superior temporal gyrus and medial frontal gyrus in the Table 2 Hierarchical regression analysis predicting negative emotional reactivity ratings as a function of age, gender, trait anxiety, depression, happiness and maladap tive CS. variability Step 1 Intercept Age Gender Adjusted R2 Step2 Intercept Age Gender Trait anxiety Depression Happiness Adjusted R2 Step3 Intercept Age Gender Trait anxiety Depression Happiness Maladaptive CS Adjusted R2
Estimate
SE
p-Value
− 1.691 0.151 0.488 0.125
0.923 0.047 0.140
0.069 0.002 0.001
0.780 0.133 0.493 − 0.026 0.006 − 0.010 0.149
1.298 0.047 0.139 0.013 0.014 0.005
0.549 0.005 0.001 0.051 0.650 0.035
1.445 0.117 0.406 − 0.031 − 0.005 − 0.008 0.608 0.228
1.247 0.045 0.134 0.013 0.014 0.004 0.150
0.248 0.011 0.003 0.014 0.694 0.062 <0.001
Note. N = 165, CS: coping style. 6