18 NEWS
AW MAY 2021
Industrial Cybersecurity Concerns Heat Up in The Era of COVID-19 By David Miller
Senior Technical Writer, Automation World
A
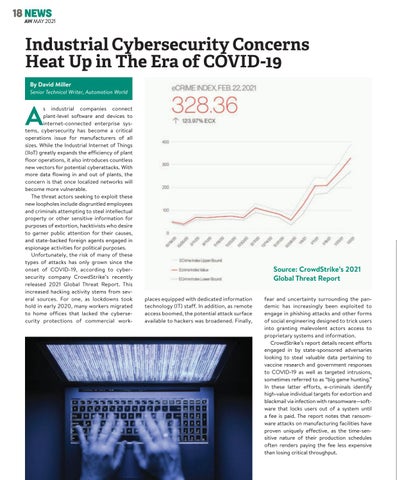
s industrial companies connect plant-level software and devices to internet-connected enterprise systems, cybersecurity has become a critical operations issue for manufacturers of all sizes. While the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) greatly expands the efficiency of plant floor operations, it also introduces countless new vectors for potential cyberattacks. With more data flowing in and out of plants, the concern is that once localized networks will become more vulnerable. The threat actors seeking to exploit these new loopholes include disgruntled employees and criminals attempting to steal intellectual property or other sensitive information for purposes of extortion, hacktivists who desire to garner public attention for their causes, and state-backed foreign agents engaged in espionage activities for political purposes. Unfortunately, the risk of many of these types of attacks has only grown since the onset of COVID-19, according to cybersecurity company CrowdStrike’s recently released 2021 Global Threat Report. This increased hacking activity stems from several sources. For one, as lockdowns took hold in early 2020, many workers migrated to home offices that lacked the cybersecurity protections of commercial work-
2105_News.indd 18
Source: CrowdStrike’s 2021 Global Threat Report places equipped with dedicated information technology (IT) staff. In addition, as remote access boomed, the potential attack surface available to hackers was broadened. Finally,
fear and uncertainty surrounding the pandemic has increasingly been exploited to engage in phishing attacks and other forms of social engineering designed to trick users into granting malevolent actors access to proprietary systems and information. CrowdStrike’s report details recent efforts engaged in by state-sponsored adversaries looking to steal valuable data pertaining to vaccine research and government responses to COVID-19 as well as targeted intrusions, sometimes referred to as “big game hunting.” In these latter efforts, e-criminals identify high-value individual targets for extortion and blackmail via infection with ransomware—software that locks users out of a system until a fee is paid. The report notes that ransomware attacks on manufacturing facilities have proven uniquely effective, as the time-sensitive nature of their production schedules often renders paying the fee less expensive than losing critical throughput.
4/28/21 9:22 AM