5 minute read
Blockchain Technology in the Oil and Gas Industry
APPLICATION STATUS
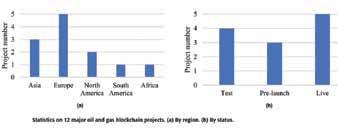
In the past two years, blockchain technology has begunto emerge in the oil and gas industry. Many energygiants have begun to invest in the development of thistechnology. Among them, BP and Shell are pioneersin blockchain application technology in the oil and gasindustry.At the end of 2017, Sinochem Group successfully completedChina›s first blockchain crude oil import trading pilotproject from the Middle East to China. There are twomajor applications in the project - digital bill of ladingand smart contracts, which can significantly improve the efficiency of crude oil trading execution and optimize thetransaction financing cost by 20% to 30%. In addition,the blockchain platform jointly developed by Abu DhabiNational Oil Company (ADNOC) and IBM will be the firstapplication of blockchain technology in global oil and gasproduction accounting. Unlike other projects, it willapply to the entire oil and gas life cycle, not just a criticalpart of the commodity supply chain. ADNOC expects toautomate the transaction process through the platform, andby deploying advanced technology resources, it will reduceits drilling time by 30% in 2019 and achieve savings ofup to $1 billion.The Table lists 12 major oil and gas industry blockchainprojects worldwide, and the Fig. summarizes the statusof these projects from the region and status. It can be seenthat as of mid-2018, most of the blockchain projects in theoil and gas industry are in operation and commissioning, andsome are in the testing stage. Europe has the largest number ofprojects, and Asia and Europe have the fastest developmentin the application of blockchain in the oil and gas industry.But overall, there are few blockchain projects in the oil andgas industry relative to other industries.
Advertisement
UNDERSTANDING LEVEL
From the perspective of understanding blockchain in theoil and gas industry, this report summarizes the followinginformation from the statistical records of 1053 respondentsin ‹›Deloitte›s 2018 global blockchain survey››: (1) 72% of respondents in the oil and gas industry believethat blockchain technology will have a big impact on theindustry; (2) 61% of respondents in the oil and gas industry believethat the blockchain is only a currency database and can onlybe used in the financial services sector;
(3) Regarding the level of understanding, 87% of respondentsin the oil and gas industry believe that their understandingof the blockchain is ‹›Excellent›› rather than ‹›Expert››(only two levels in this survey); (4) In terms of investment in blockchain technology, 72%of respondents in the oil and gas industry invested between$1 million and $10 million, while only 9% invested morethan $10 million. In contrast, 38% of respondents in theautomation field invested more than $10 million in theirorganization; (5) Only 15% of the organizations in the oil and gas industryhave applied the blockchain to production, while 84% areonly in the consciousness or experimental phase. For another report, the World Energy Council interviewed39 people in the energy field in 2018 and releaseda report called ‹›Is blockchain in energy driving an evolutionor a revolution?››. They have a maturity modelbased on the interviewees› responses. It can be concludedfrom the two survey reports that the understanding of theblockchain by the oil and gas industry is not comprehensive enough, and the application of the blockchain isstill in the experimental stage. In addition, the oil and gasindustry›s investment in the blockchain is not strong enough.
OPPORTUNITY AND CHALLENGE OPPORTUNITY AND CHALLENGE
Due to the decentralization and transparency of Due to the decentralization and transparency of theblockchain, it can bring many opportunities to the oil theblockchain, it can bring many opportunities to the oil and gas industry. However, a new technology will inevitably and gas industry. However, a new technology will inevitably encounter many challenges when it is first applied, as shown encounter many challenges when it is first applied, as shown in Table.in Table.
RISKRISK
Although the blockchaintechnology has many advantages, the Although the blockchaintechnology has many advantages, the current operating system is still not perfect, and there are many current operating system is still not perfect, and there are many risks. Risks can be divided into operational risks, cyber risks, risks. Risks can be divided into operational risks, cyber risks, and legal risks. Operational risk means that if the blockchain is and legal risks. Operational risk means that if the blockchain is applied to the oil and gas industry, technical or social problems applied to the oil and gas industry, technical or social problems may produce bad results. It may be reflected in: may produce bad results. It may be reflected in:
management.management. Ó Ó Initial applications may have technical problems. Initial applications may have technical problems. Ó Ó Lack of a standardized mode of operation, function and Lack of a standardized mode of operation, function and security deficiencies.security deficiencies. Cyber risk refers to bad behavior such as fraud due to Cyber risk refers to bad behavior such as fraud due to insufficient security or design flaws, it is reflected in: insufficient security or design flaws, it is reflected in: Ó Ó There may be fraud in the interface between the real world There may be fraud in the interface between the real world and the blockchain world.and the blockchain world. Ó Ó The exchange may be attacked by hackers, and the user›s The exchange may be attacked by hackers, and the user›s password may be hacked and funds transferred. password may be hacked and funds transferred. Ó Ó The hard fork of the block will cause the trust of the entire The hard fork of the block will cause the trust of the entire network system to be questioned. network system to be questioned. Legal risk refers to some illegal acts that may occurinthe Legal risk refers to some illegal acts that may occurinthe Ó Ó Loss of data and identity.Loss of data and identity. operation of block chains, it is re_ected in: operation of block chains, it is re_ected in: Ó Ó The transaction costs of the public blockchain are high. The transaction costs of the public blockchain are high. Ó Ó Tax evasion may be triggered. Tax evasion may be triggered. Ó Ó Lack of recipients and users. Lack of recipients and users. Ó Ó Illegal use of information.Illegal use of information. Ó Ó Lack of long-term experience leads to imperfect Lack of long-term experience leads to imperfect Ó Ó Blockchains are used for illegal transactions. Blockchains are used for illegal transactions.