
5 minute read
Health Canada's recent approvals in 2025
by Brigitte Leonard, Ph.D.
In 2025, Health Canada approved three highly targeted innovative treatments for rare diseases and cancers. One is for a rare disease called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). (1) Another is for a cancer called metastatic or recurrent locally advanced Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC)(2). The third targets advanced or metastatic breast cancer (3). For more information about these disorders and innovative treatments, follow me in this publication.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive, neurodegenerative, muscle-wasting condition affecting the body in several challenging ways. Several motor functions are impacted, such as mobility, breathing, communication, and mental health. These symptoms worsen over time. Life expectancy is 3 to 5 years after the appearance of symptoms. Approximately 2% of ALS cases are linked with mutations in a gene encoding superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1). (4) The toxic mutant SOD1 protein causes neuron degeneration in this disorder. (4)
In February 2025, Biogen received approval for QALSODY (Tofersen) for treating adults with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) associated with a mutation in the SOD1 gene (Figure 1). The complete indication can be found in Health Canada or on the Biogen website.
QALSODY is a molecule that can bind to the RNA messenger that produces the mutated protein. By binding to this mutated RNA, QALSODY stimulates the cellular defence mechanism, which destroys the mutated RNA. So, the toxic product cessed (Figure 2). (5)
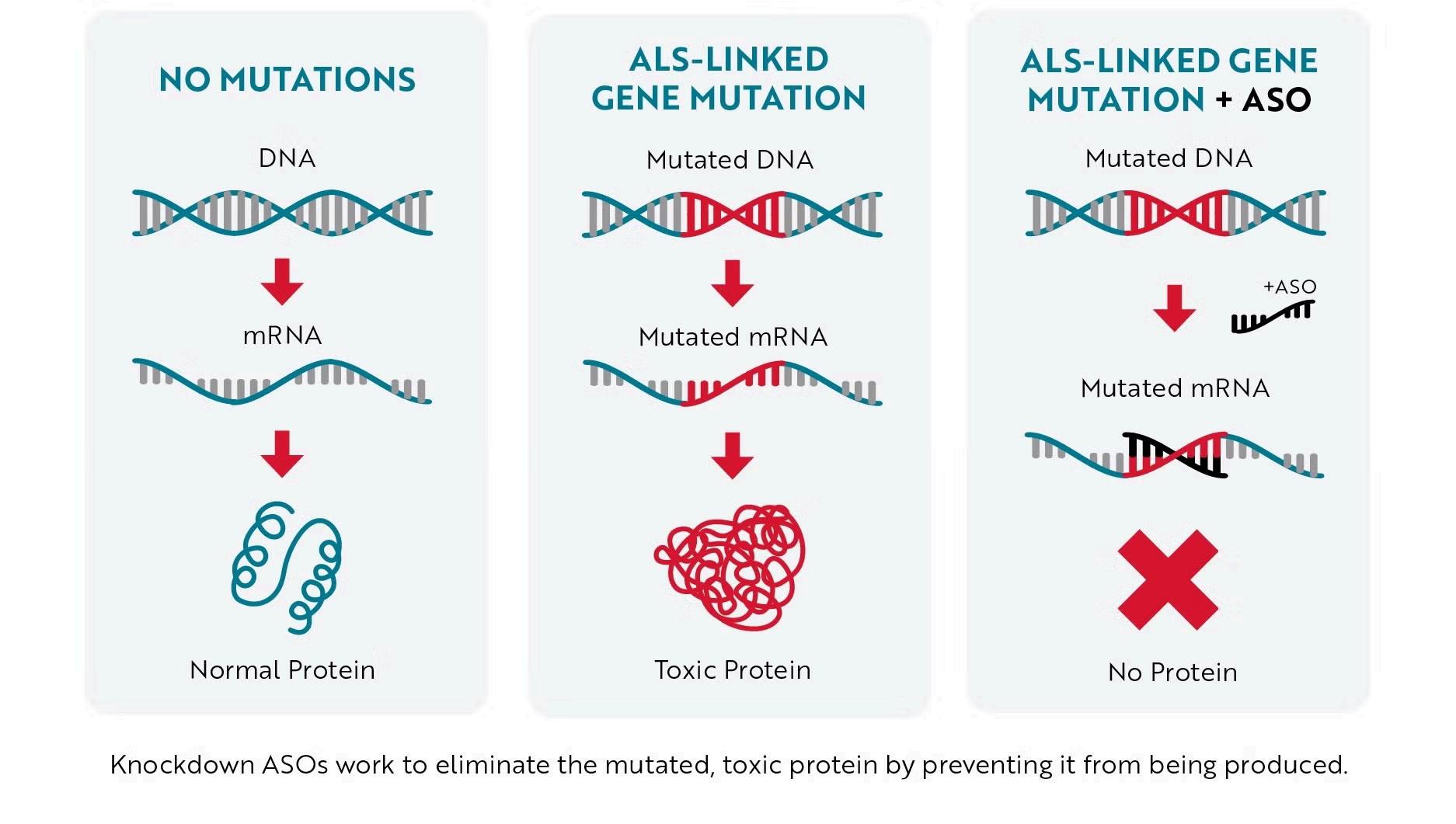
Tofersen is an injection that needs to be delivered directly close to the spine in the back (Figure 3).

Health Canada's recent approvals in 2025 cont'd
Health Canada approved QALSODY with conditions based on the VALOR phase III clinical trial results and its extension (VALOR OLE). See the design of the study in Figure 4.
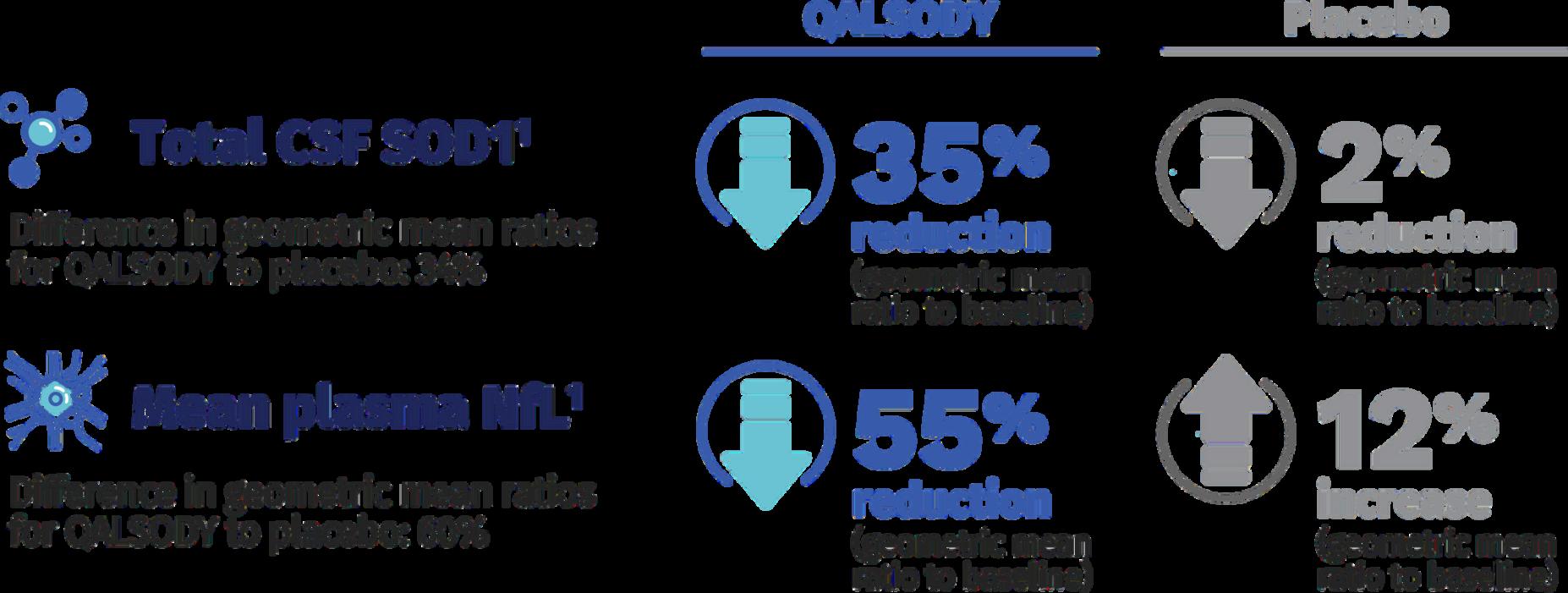
To assess the efficacy of QALSODY, two biomarkers have been used:
1) The total concentration of SOD1 protein in cerebrospinal fluid; 2) The concentration of neurofilament light (Nfl) chains in blood. Nfl is a marker of neuron degeneration.
In Figure 5, you can see that QALSODY allows a more significant reduction of the mutated protein than the placebo, 35% versus 2%.
Also, neuron degeneration seems to be reduced by QALSODY, where a 55% reduction is observed, while neuron degeneration progresses in the patient on placebo (12%).
QALSODY provides positive results with an acceptable safety profile, offering hope for these patients.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) is a rare neuroendocrine skin cancer. MCC is associated with frequent recurrences and a high mortality rate. In recent years, the number of MCC diagnoses has increased in the USA, Australia, and Europe.(7)
Factors strongly associated with the development of MCC include aging, fair skin, history of extensive sun exposure, chronic immune suppression (e.g., kidney or heart transplantation or HIV), and the Merkel cell polyomavirus.(8)
Merkel cells are found in the lower part of the skin(epidermis). Although the exact function of Merkel cells is unknown, they are thought to be touch receptors. Also known as neuroendocrine cells, they have machinery like nerve cells and to hormone-secreting (endocrine) cells.
Health Canada's recent approvals in 2025 cont'd
In February 2025, Incyte received approval for ZYNYZ (retifanlimab) as the first-line treatment for metastatic or advanced MCC. The complete indication can be found in Health Canada or the Incyte website (Figure 6).


Cancer cells can express a molecule called PD ligand (PD-L1) (Figure 7). When this ligand binds to the PD-1 molecule on the T cell, it inhibits the activation of the immune system. Thus, cancer cells can escape immune surveillance. ZYNYZ interferes with this process by binding PD-1 on the T cell and preventing the interaction with the cancer cells' PD ligand.(9)
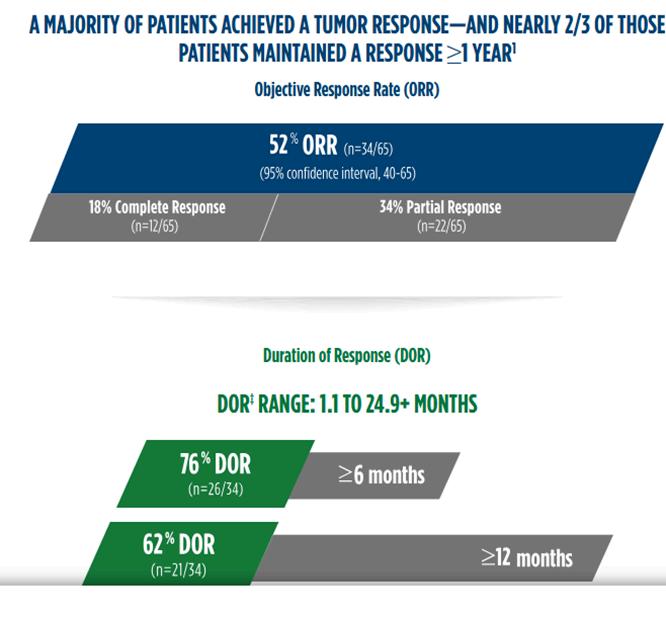
Marketing authorization was based on tumour response and the durability of response observed in the POD1UM-201 clinical trial (Figure 8). (10) This new approval offers hope for patients with MCC.
Several clinical strategies have been put in place during the last two decades to improve the survival of patients diagnosed with Breast Cancer. Preventive recommendations, early diagnosis and targeted therapies are some of these strategies. However, the war has not been won yet. Some forms of breast cancer can still be challenging.
Hormone-receptor (HR)-positive breast cancer is the most prevalent type of all breast cancers, accounting for approximately 70% of cases. A defining feature of HR-positive breast cancer is that its tumour cells have receptors that attach to one or both hormones – estrogen or progesterone – which can contribute to tumour growth. People diagnosed with HR-positive metastatic breast cancer often face the risk of disease progression and treatment side effects, creating a need for additional treatment options. The PI3K signalling pathway is commonly dysregulated in HR-positive breast cancer, due to activating mutations, which have been identified as a potential mechanism of intrinsic resistance to standard of care.
(11) (12) (13)

Health Canada's recent approvals in 2025 cont'd
In February 2025, Roche received approval for ITOVEBI® (inavolisib) to treat advanced or metastatic breast cancer (Figure 10). The complete indication can be found in Health Canada or on the Roche website. Itovebi inhibits a molecule called PI3K, which slows tumour growth and causes cancer cells to die.
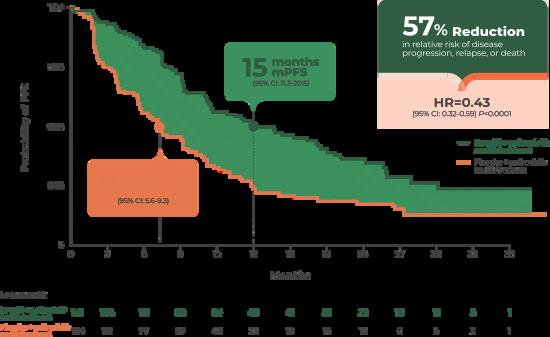
The INAVO120 study [NCT04191499] is a phase III study evaluating the efficacy and safety of Itovebi® (inavolisib) in combination with other standard treatments. Study results showed that the Itovebi-based treatment regimen more than doubled progression-free survival in the patient population (Figure 11) with an acceptable safety profile. ITOVEBI offers another chance for these women. (14)

by Brigitte Leonard, Ph.D
The Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CDA/CADTH) is an independent, not-for-profit organization that provides evidence-based assessments on drugs, medical devices, and healthcare technologies to support informed decision-making in Canada's healthcare system. CDA/CADTH collaborates with federal, provincial, and territorial governments (excluding Quebec) to evaluate the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and broader impact of new and existing healthcare interventions. By conducting Health Technology Assessments (HTAs), providing reimbursement recommendations, and developing guidance reports, CDA/CADTH plays a crucial role in shaping healthcare policies, ensuring that patients, healthcare providers, and policymakers have access to reliable, science-driven information to improve health outcomes and optimize resource allocation.

Exciting News from Heal Canada! We are thrilled to announce the launch of our new podcast series, Empowering Voices, dedicated to amplifying the stories and insights of patients, healthcare professionals, and advocates in the blood disorder and rare disease communities. Each episode will feature meaningful conversations on patient experiences, emerging research, and the evolving landscape of healthcare advocacy. Through Empowering Voices, we aim to educate, inspire, and drive change by bringing real-world perspectives to the forefront. Stay tuned for our first episode, coming soon because every voice matters!
https://www.healcanada.org/empowering-voice-podcast/

Belonging, Diversity, Inclusion and Equity
Welcome to the Belonging, Diversity, Inclusion and Equity section of E3 Advocacy Digital Magazine. In this section, we provide information on ensuring that BDEI is part of the patient conversation in our Health ecosystem. Our focus is to illuminate the pathways through which individuals grappling with health challenges can not only find their voice but also harness it to drive their own journey.
Healthcare and the patient’s experiences should not be determined by social determinants of health.
We believe that an informed and engaged patient is an empowered one. Through enlightening articles, expert insights, and inspiring stories, we aim to equip our readers with the tools and knowledge necessary to navigate the complex healthcare landscape.









