






With the book you are holding you will:
➜ Gain insights into Biology and Geology employing the 5-stage methodology, mirroring the Spanish version: Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate.
➜ Enhance and expand your English skills through activities designed for practicing written and oral comprehension and expression.
A learning experience related to Andalusia is explored through the following steps:
Engage. A motivational video related to the unit’s content.
Explore. Activities to investigate the situation. Elaborate. Activities to apply the concepts.

The left-hand pages focus on presenting content in the Explain phase.
On the right-hand pages, you’ll find a variety of activities designed to reinforce the content.
The final step of the 5-stage model, Evaluate, is completed with an assessment at the end of each section.
The term closes with a double-page spread that includes texts and activities related to some of the topics covered during the term.

Researchers from the University of Granada’s Department of Histology, the Tissue Bank of Granada and Almería, and the Virgen de las Nieves and San Cecilio University Hospitals in Granada have recently improved the method used to cultivate human tissues from the cornea, oral mucosa (the gums), the cartilage and the urinary system for subsequent clinical use.
From biopsies, they have isolated adult stem cells that are capable of generating new cells. They have also developed optimal culture matrices for growing new cells. These new findings will increase the success of regenerative medicine in recovering and replacing lost or damaged organs and tissues. In addition, they have designed a matrix based on a mixture of fibrin (an abundant protein in the body) and agarose (an abundant natural element in some living things, such as algae). In this matrix, cells can grow and faithfully reproduce the properties of tissues.
1 Work in groups and investigate this advanced tissue engineering method in Andalusia.
2 In 2014, the San Cecilio University Hospital of Granada performed an artificial cornea transplant. Investigate the disease this patient suffered from: severe corneal fibrosis, resulting in an ulcer that caused vision loss and severe pain. Was the operation a success? What effects did it have on the patient’s quality of life?
Elaborate
1 Select the most important aspects of the information you have obtained, organise the information and write a summary.
2 Search for pictures, illustrations, animations or videos, or create your own, to accompany the information.
3 You can also make a model using recycled materials from your home or school.
4 Create a lapbook, poster, presentation or video. Include diagrams or graphics using tools such as Word/Writer, PowerPoint/Impress, Prezi, Keynote, Canva or VideoScribe.
Communicate
1 Present your project to the class, making sure all the members of your group participate.
2 During the presentation, your classmates have to take notes, writing down any questions they have.
3 After the presentation, answer your classmates’ questions.
4 You can organise a quiz about your projects, in which all your classmates can participate. You could use Kahoot or a similar application.

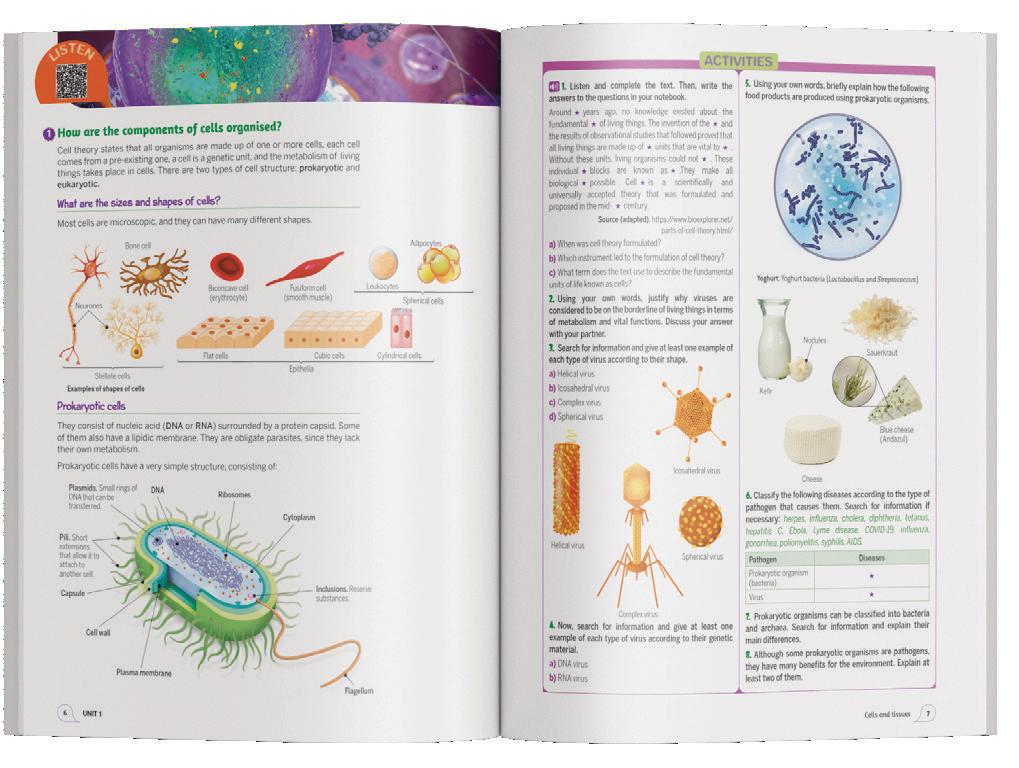
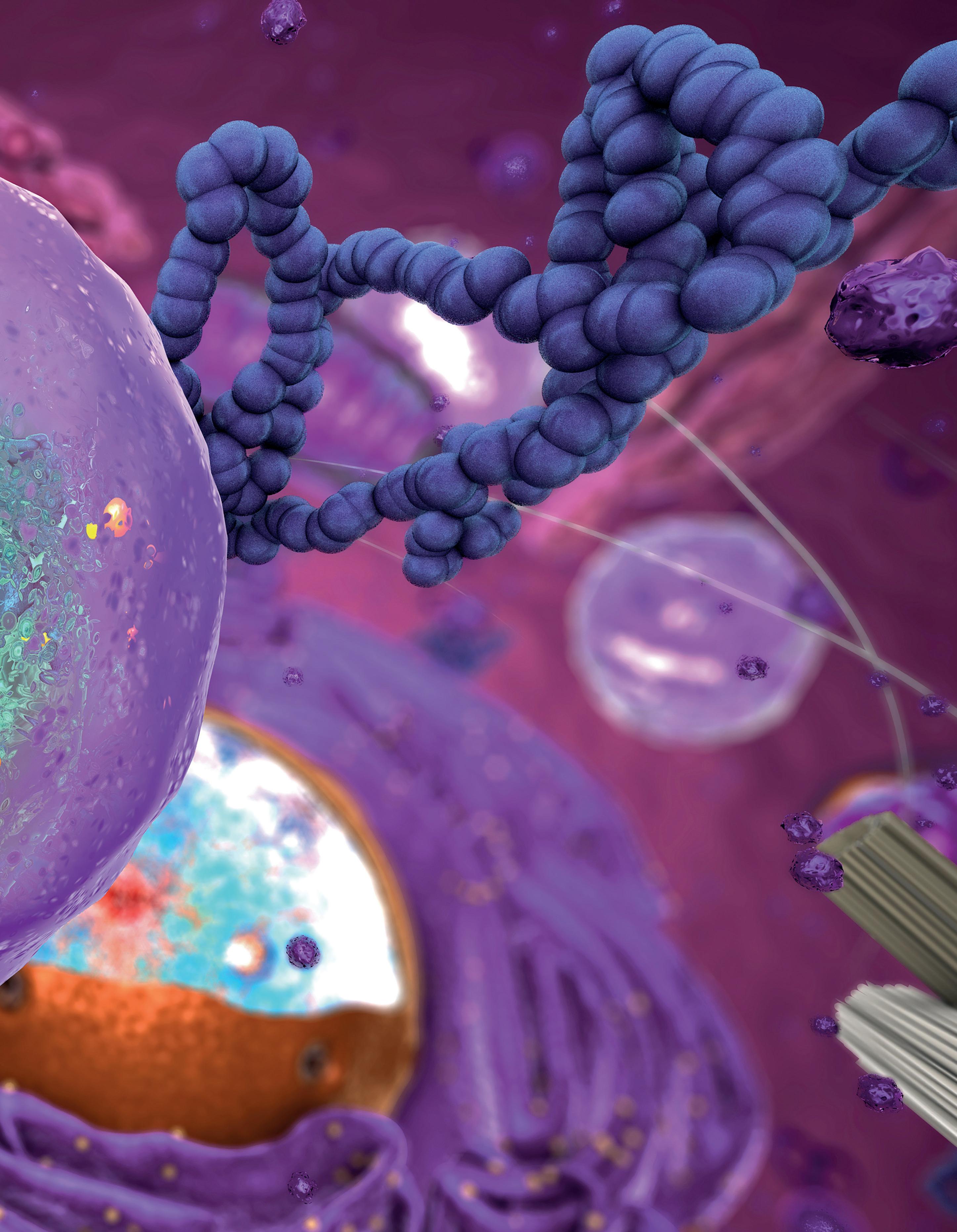
Cell theory states that all organisms are made up of one or more cells, each cell comes from a pre-existing one, a cell is a genetic unit, and the metabolism of living things takes place in cells. There are two types of cell structure: prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Most cells are microscopic, and they can have many different shapes.
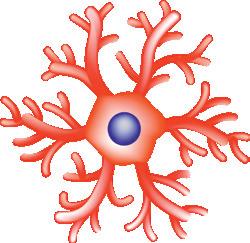
Neurones
Bone cell Adipocytes

Stellate cells




Examples of shapes of cells
Plasmids. Small rings of DNA that can be transferred.
Pili. Short extensions that allow it to attach to another cell.
Capsule
Cell wall
Plasma membrane





Flat cells
Biconcave cell (erythrocyte)



Leukocytes

Epithelia




Fusiform cell (smooth muscle) Spherical cells

⎧⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎩
They consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein capsid. Some of them also have a lipidic membrane. They are obligate parasites, since they lack their own metabolism.
Prokaryotic cells have a very simple structure, consisting of:
Ribosomes DNA
Cytoplasm
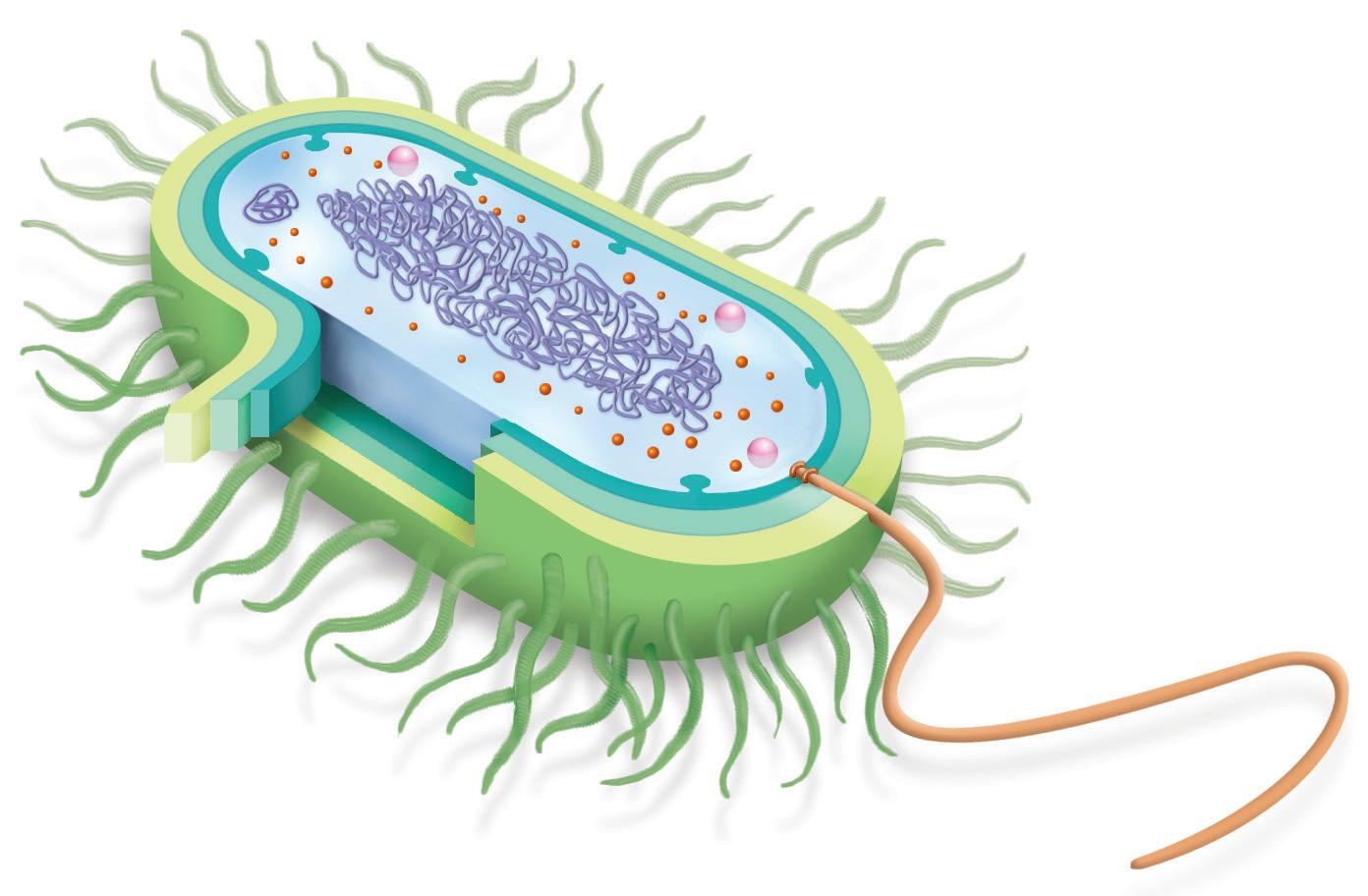
Inclusions. Reserve substances.
Flagellum
Cubic cells Cylindrical cells
⎧⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎩ ⎧⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎩
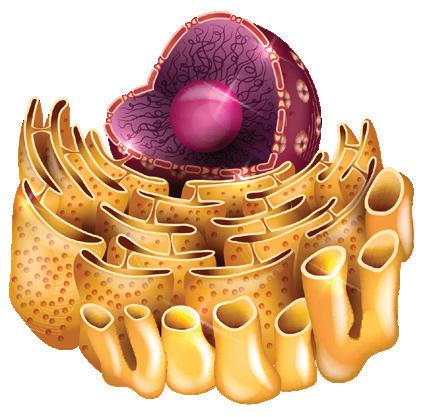
Their internal structure consists of a nucleus, and cytoplasm surrounded by a plasma membrane.
Ribosomes. Protein synthesis.
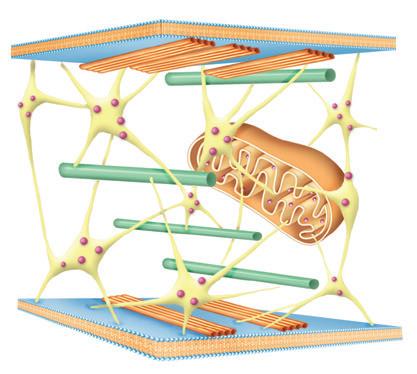
Cytoskeleton: Microfilaments (1), intermediate filaments (2) and microtubules (3). Support and movement of organelles.
Nucleus. Directs cell activity.
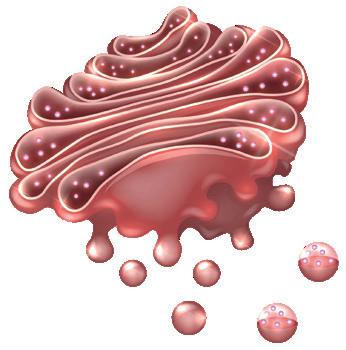
Rough endoplasmic reticulum. Protein synthesis and modification.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Synthesis of lipids and elimination of toxins. Flagellum. Movement.
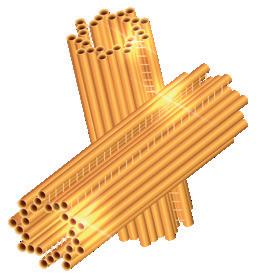
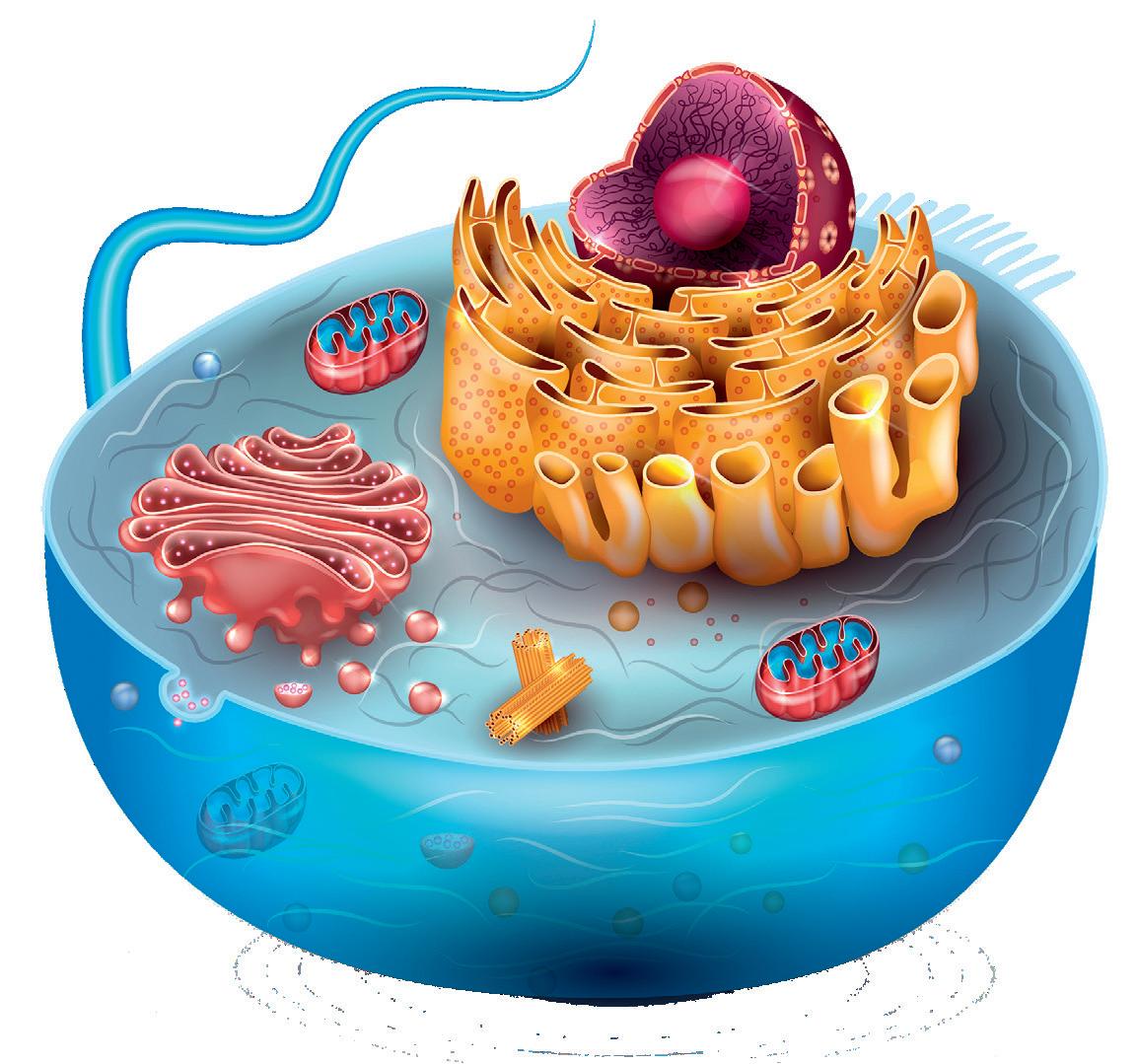
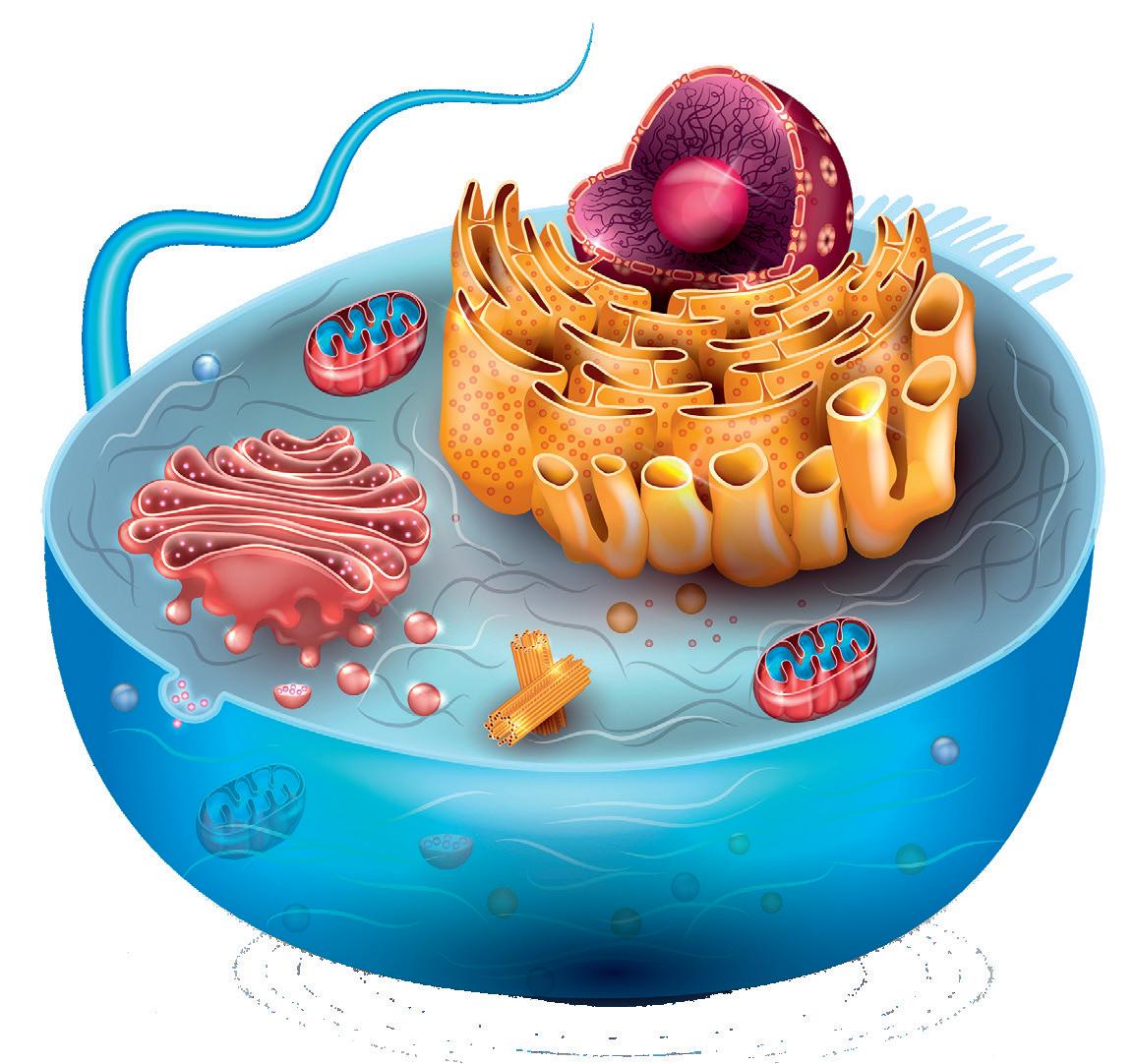
Centrioles. Made up of nine groups of three microtubules.
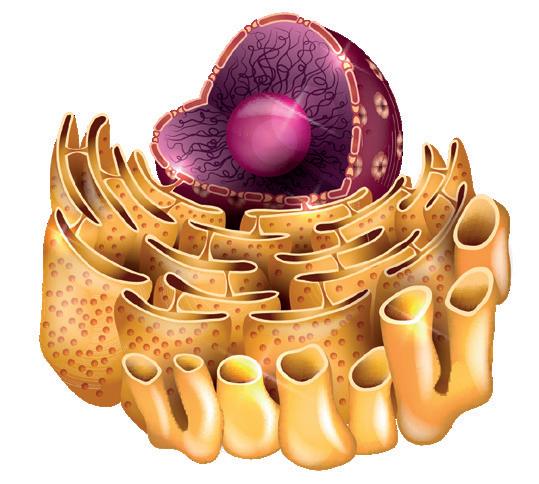
It is surrounded by a double membrane with pores, which regulates the exchange of substances. It has a nucleolus in its centre, which synthesises the ribosomes. It contains chromatin, which is made up of histones bound to DNA. During cell division, this condenses and forms chromosomes.
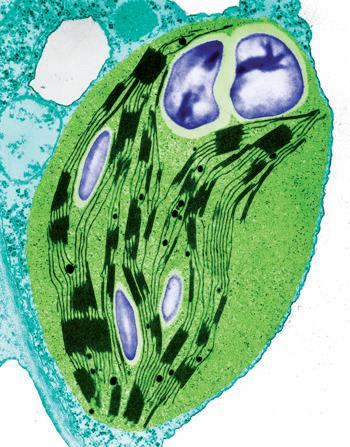
They have similar organelles to animal cells, but do not have centrioles or lysosomes. Unlike animal cells, they have a cellulose cell wall, which provides them with support; a large central vacuole, which stores nutrients and waste; and chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis.
Lysosomes. Digestion.
Mitochondria. Cellular respiration.
Cilia Golgi body. Protein modification.9. Look at this picture of a eukaryotic plant cell and compare it with the animal cell on the previous page. What differences can you find?

Then, identify the labelled organelles and write their functions.
10. Look at the following picture. What does it show and where is it located?

12. Complete the table with the descriptions and functions of the elements that make up the nucleus.
Elements Description Function
Nuclear membrane ★
Nucleolus ★
Chromatin ★
13. Choose the correct option in each pair. Then, write the text in your notebook.
Prokaryotic/eukaryotic plant cells have similar organelles to animal cells, but they have/do not have centrioles or lysosomes. Unlike animal cells, they have a cellulose cell membrane/wall, which provides them with support/colour; a large central vacuole/mitochondrion, which stores nutrients and waste; and chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis/respiration
14. Copy the sentences in your notebook and complete with the missing words.















a) During cell ★ , chromatin condenses and forms ★






b) Each segment of a ★ that carries the information to make a ★ is called a gene.


c) Most human cells contain 23 pairs of ★ ★
d) A diploid cell contains ★ copies of each ★
e) ★ have an ★ ★
f) ★ perform cellular respiration.
g) ★ cells do not contain a large central ★ . In ★ cells, this stores substances.
h) ★ perform photosynthesis.
11. Read the following sentences. Then, copy and complete them in your notebook.
1 During cell division, ★ condenses and forms chromosomes.
2 Each segment of a chromosome that carries the information to make a protein is called a ★ .
3 Most human cells contain 23 pairs of ★ chromosomes.
4 A ★ cell contains two copies of each chromosome.
5 Gametes have are ★ cells.
i) In the ★ phase of photosynthesis, ★ captures solar energy to generate ★ energy in the form of ATP.
j) In the ★ phase of photosynthesis, the ATP obtained is used to transform ★ matter into ★ matter.
k) The plasma ★ is made up of a ★ bilayer and it regulates the flow of ★
l) Plant cells have a cellulose cell ★ , which provides them with ★
m) Both eukaryotic and ★ cells contain ★ , where ★ synthesis takes place.
15. Using your own words, answer the following questions.
a) Briefly explain why you think human gametes are haploid cells.
b) What do you think would happen if they were diploid cells?
Nutrition, interaction and reproduction.
It is the set of processes in which cells exchange matter and energy with their environment.
➜ Autotrophic. They use free energy to transform inorganic matter into organic matter.
➜ Heterotrophic. They obtain organic matter from the environment.
It is the set of reactions within the cell.
➜ Catabolism involves destructive reactions, such as cellular respiration, which release energy.
➜ Anabolism involves synthetic reactions that consume energy.
INTERACTION FUNCTION
REPRODUCTION FUNCTION
It is the ability to perceive stimuli and react. Responses can be static or dynamic.
It is the process in which stem cells produce daughter cells. This involves the division of the nucleus, followed by the division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis).
Cell differentiation allows the formation of tissues and organs and the replacement of cells. Humans have the following tissues: cartilaginous, adipose, bone, epithelial bone, muscle and nervous (neuroglia and neurons) tissue.
How can we observe cells and tissues?
We have to prepare a thin section of a sample, stain it and observe it under an optic microscope.
Humans have the following systems: the neuroendocrine, musculoskeletal, respiratory, excretory, digestive, integumentary, circulatory and reproductive system.








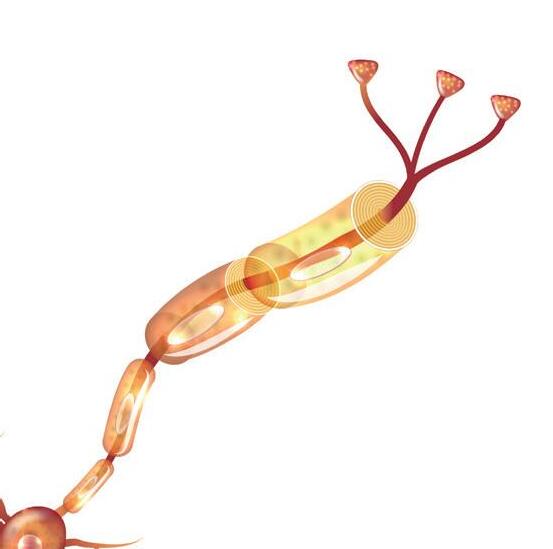

































2 Nucleus
3 Myelin sheath
5 Axon
8 Schwann cells
9 Mitochondria
10 Dendrites



4 Golgi apparatus

























6 Synaptic buttons
7 Ranvier’s nodules

1 Endoplasmic reticulum










16. Write the type of nutrition each sentence describes.
a) It takes place in most plants, algae and cyanobacteria, and some bacteria.
b) In plants and algae, photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts.
c) It is characteristic of animals, fungi and protozoa.
d) Inorganic matter is converted into organic matter.
e) Organic matter is obtained from the environment.
17. Complete the following text using these words, and write it in your notebook: biosphere, molecules, community, biotic, subatomic, matter, system, abiotic, cell, organism. The levels of organisation of ★ , in order of complexity, are:
➜
★ : ★ particles, atoms, ★ and organelles.
➜
★ : ★ , tissue, organ, ★ , ★ , population, ★ , ecosystem and ★
18. Identify the name of each type of human tissue and cell described below, and copy the sentences in your notebook.
a) ★ tissue is made up of chondrocytes.
b) ★ tissue is made up of ★ , which store lipids. Its function is to store energy and to offer protection against the cold.
c) ★ tissue contains tightly-bound cells.
d) ★ epithelia protect external and internal surfaces.
e) ★ epithelia secrete substances outside the cell. The body has ★ , exocrine and mixed glands.
f) ★ tissue is formed by ★ and a matrix of calcium and collagen. It can be spongy or compact.
g) ★ tissue is made up of ★ that contract in response to nervous stimuli. Types: ★ or striated (moves the bones), ★ (moves the viscera) and ★
h) ★ tissue is made up of ★ cells, such as Schwann cells, which support and protect the ★ . These receive stimuli, and help transmit the nervous impulse.
19. Put the letters of the words in the first column of the table in the correct order. Then, join each body system with its function.
a. Neendounerocri 1. It is the set of organs that allow gases to be exchanged.
b. Mukesculetlosal 2. It is different in men and women. Its function is to ensure the survival of the species.
c. Resatorypir 3. It includes the skin, which protects us and captures stimuli.
d. Eetoxcrry 4. It transports gases, nutrients and hormones around the body and eliminates waste.
e. Distivege 5. It eliminates metabolic waste from the body.
f. Inntateerygum 6. It provides support and allows the body to move. In addition, the bones store mineral salts, and red blood cells are formed in them.
g. Ciroryculat 7. It obtains nutrients from food.
h. Reductivproe 8. It coordinates all the systems through nerve impulses and hormone secretion.
20. Copy the text in your notebook. Then, listen and complete it with the missing words.
The musculoskeletal system is also known as the ★ system, since it allows our body to ★ . It also provides it with support and gives it ★ . It is subdivided into two ★ :
➜ The ★ , which consists of all the ★ in the body. ★ muscles pull on the joints, allowing us to move. Besides ★ , the muscular system contains ★ , which attach the muscles to the ★
➜ The ★ , whose main component is the bones. They articulate with each other, forming the ★ . The ★ structures of the skeletal system are the articular ★ and the ligaments. Besides giving the body support and ★ , the musculoskeletal system has many other functions. The skeletal system plays an important role in ★ functions. These include storing ★ like calcium, and ★ . On the other hand, the muscular system ★ the majority of the body’s carbohydrates in the form of ★ .

Source (adapted): https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/ anatomy/the-musculoskeletal-system 21. Put the words in order to make sentences. Then, write them in your notebook.
a) The system through which is the mechanism the hypothalamus maintains homeostasis neuroendocrine.







b) The respiratory that make possible breathing system is the network of organs and tissues.

c) The consists of and connective bones tissue skeletal system.



d) The skeletal, muscular system is consisting of smooth and cardiac an organ system muscles. Neuroglia



The Professional Association of Dietitians-Nutritionists of Andalusia (CODINAN) has the following objectives: for the role of these professionals to be recognised as much more than simply putting people on a diet to lose weight; to support their inclusion in the public health service of the autonomous community; and to increase awareness of the difference between these professionals and those who are not qualified to perform these roles.
1 Work in groups and investigate the roles of professional dietitians and nutritionists in nutritional education, research projects, improving the performance of athletes, and controlling the safety and quality of menus in hospitals, residences and schools in Andalusia.
2 Serious eating disorders are caused by an unhealthy attitude towards food. Investigate what these disorders are, how common they are in Andalusia, and how a nutritionist can help to prevent or treat each one.
3 Investigate the recommendations from the Professional Association of Dietitians and Nutritionists of Andalusia (CODINAN) regarding image and health. Do you have to eat well to look good?
1 Select the most important aspects of the information you have obtained, organise the information and write a summary.
2 Search for pictures, illustrations, animations or videos, or create your own, to accompany the information.
3 Create a lapbook, poster, presentation or video. Include diagrams or graphics using tools such as Word/Writer, PowerPoint/Impress, Prezi, Keynote, Canva or VideoScribe.
1 Present your project to the class, making sure all the members of your group participate.
2 During the presentation, your classmates have to take notes, writing down any questions they have.
3 After the presentation, answer your classmates’ questions.
4 You can organise a quiz about your project, in which all your classmates can participate. You could use Kahoot or a similar application.


Eating is a voluntary action, while nutrition is a set of unconscious processes. After ingesting food, we digest it to absorb its nutrients.
Nutrients are the biomolecules that make up food. They provide us with matter and energy.
➜ Carbohydrates. They provide the body with energy. Dietary fibre is a type of indigestible carbohydrate.
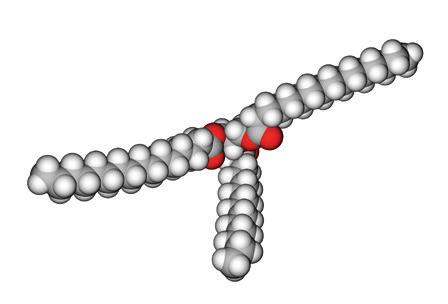
➜ Lipids. They are a group of nutrients that are insoluble in water. They perform various functions: structural support, energy storage, insulation, fat-soluble vitamin provision (A, D, E and K) and hormone (sex hormones, corticosteroids, etc.). Fats can be saturated or unsaturated.
➜ Proteins. They are combinations of amino acids. They perform various functions: structural support, catalyse metabolic reactions, defence against infection and energy provision.
➜ Water. It is the most abundant substance in our body, where most metabolic reactions take place. It transports nutrients, removes waste and regulates our temperature.



➜ Mineral salts. They perform various functions: structural support, nerve impulse transmission, pH and osmotic pressure regulation (sodium, potassium, etc.).
➜ Vitamins. Water-soluble vitamins, such as C and B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9 and B12, and fatsoluble vitamins, such as A, D, E and K.
The energy each person needs is the sum of these two components:
➜ The basal metabolic rate (BMR). It is the energy needed to perform the vital functions.
➜ The energy required to perform physical or mental activities. It depends on the types of activities and their duration, as well as the person’s gender, age and weight.

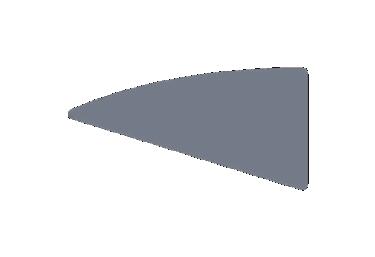
Proteins 10-15 %
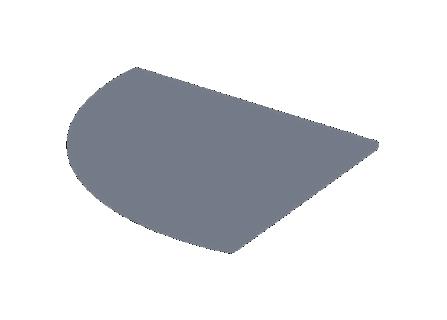
Balanced diet
Our diet needs to contain enough kilocalories to meet our needs. However, we also need to consume a sufficient amount of all the nutrients our body requires. If not, we can suffer from deficiencies. In a balanced diet, the amount of daily energy provided by each nutrient is approximately as follows:
➜ One gram of carbohydrates supplies 4 kcal.
➜ One gram of fat supplies 9 kcal.
➜ One gram of protein supplies 4 kcal.
1. Copy and complete the following text in your notebook. While ★ is a voluntary action, ★ is a set of unconscious processes. We digest food to absorb its ★ . These are the biomolecules that make up food. They provide us with matter and ★ . Some foods, such as milk, provide a great variety of ★ , and others, such as extra virgin olive oil, only provide fats or ★ , and some vitamins.
2. Read the following definitions and write the terms in your notebook.
a) They are nutrients that provide energy quickly.
b) It is a voluntary action in which we ingest food.
c) They are biomolecules that make up food.
d) They are organic substances that regulate numerous functions.
e) It is the most abundant substance in our body, where most metabolic reactions take place.
f) Nutrients like phospholipids and cholesterol belong to this group.



3. Read the following descriptions and decide which type of nutrient they refer to.
a) They are combinations of amino acids. They perform numerous functions.
b) They are a type of lipid that is usually of animal origin and can be solid.
c) They are a group of nutrients that include indigestible dietary fibre.
d) They provide unsaturated fatty acids, such as omega 3, which improve cardiovascular health.
e) They are organic substances that regulate numerous functions. There are two kinds: water-soluble and fatsoluble.
f) They perform multiple functions, such as structural support, pH and osmotic pressure regulation and nerve impulse transmission.
4. In your notebook, match the following terms with their definitions:
a. Basal metabolic rate (BMR). 1. The energy needed depends on the types of activities and their duration, as well as the person’s gender, age and weight.
b. Energy required to perform physical or mental activities.
2. The energy needed to digest food and absorb and metabolise nutrients.
c. Specific dynamic action. 3. The energy needed to perform the vital functions.
5. Do some research and write the vitamin lacking for each deficiency disorder below.
a) Night blindness
b) Beri-beri
c) Delayed growth, bad skin
d) Anaemia
6. Choose the correct word in each pair. Then, write the sentences in your notebook.
a) While eating/nutrition is a voluntary action, eating/ nutrition is a set of unconscious processes.
b) Foods/Nutrients are the biomolecules that make up food/ nutrients.
c) One gram of carbohydrates/fat supplies 4 kcal.
d) One gram of protein/fat supplies 9 kcal.
e) One gram of protein supplies the same energy as one gram of carbohydrates/fat.
7. Put the letters in the correct order to form the terms. Then, write their definitions in your notebook.
a) Viminsta
b) Wetra
c) Cahydrarbotes
d) Pteroins
e) Miralne talss
8. Play this hangman game to complete the terms. Then copy the sentences in your notebook.
a) Ba ★ l M ★ t ★ o ★ c R ★ te: The energy needed to perform the vital functions.
b) En ★ gy r ★ qu ★ ed to p ★ fo ★ m a ★ i ★ ties: It partly depends on the person’s gender, age and weight.
c) Sp ★ if ★ c dy ★ m ★ c act ★ n: The energy needed to digest food and to absorb and metabolise nutrients.
Carbohydrates LipidsIt is an example of a balanced diet, as it provides the necessary nutrients in adequate amounts. It contains a high amount of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, cereals, oily fish and olive oil, which is the main fat.
What impacts does food consumption have on the environment?
➜ Diet pyramid. It shows the foods that should form part of our diet.
➜ Environmental pyramid. It shows the environmental impacts generated by the consumption of different foods. It takes into account their ecological, water and carbon footprint.
When these pyramids are placed beside each other, we can see that the foods that we should eat more frequently are those with the lowest levels of environmental impact, and vice versa.





The discovery of fire modified the behaviour of primitive humans. Cooked food is easier to digest and safer for consumption. Heat destroys many of the parasites that cause infectious diseases.
Fermentation is the biochemical reaction carried out by certain bacteria, yeasts and moulds.
Microorganisms involved in food and beverage production
➜ Alcoholic drinks. They are produced by the fermentation of carbohydrates from fruits or cereals, which is carried out by yeasts.
➜ Fermented foods. Yeasts, bacteria and moulds are used in the production of yogurt, kefir, cheese, etc. These fermented foods provide us with probiotics. These are live microorganisms, such as lactobacilli and bifidobacteria, which enrich the intestinal microbiota.
After being produced, food must be subjected to certain preservation procedures to maintain its nutritional value and keep it in good condition. Conservation procedures include refrigeration, deep-freezing, sterilisation, pasteurisation, drying, dehydration, salting, sweetening, smoking and pickling.





Blue cheese (Andazul)

Examples of fermented food
9. Read and complete the text with the following words: doubled, digest, brain, study, raw, fire, size, enzymes, nutrients.
According to a new ★ , the increase in the size of the human ★ that took place about 1.8 million years ago could be directly related to advances in food preparation. Homo erectus learned to cook and the ★ of its brain ★ over a period of 600,000 years. This was not the case, however, for gorillas or chimpanzees, whose diet is based on ★ foods. When our ancestors began to use ★ to cook food, this softened the toughest fibres, reducing the time needed to chew it and making it easier to ★ . As they were able to absorb more ★ , they developed bigger brains. As they saved time, they were able to focus on other activities. However, today there are those who think that heating food to more than 40 degrees destroys plant ★ , molecular structures that help us digest proteins.
Source (adapted): Cocinar nos hizo humanos | National Geographic.
10. Discuss with your partner the importance of the Mediterranean diet. You can use some of these phrases:
I think that..., In my opinion..., From my point of view..., It seems to me that..., I agree/disagree with/that...
11. The food wheel is a guide to the types and proportions of food we should consume daily to obtain the nutrients we need. It is divided into six groups of different sizes, which indicate the recommended amount of each type of food.
Group I: Cereals, potatoes, confectionery
Group II: fat and oils
Group III: Milk and dairy products
Group IV: meat, eggs, fish, legumes
Group V: Vegetables
Look at the food wheel above. Then, write the types of food, the nutrients they contain and their main functions next to the groups below.
➜ Groups I and II: ★
➜ Groups III and IV: ★
➜ Groups V and VI: fruits and ★
12. Write the following text in your notebook. Then, listen and complete it with the missing words.
The environmental ★ was created to show the environmental ★ associated with each type of ★ . It is an upside–down ★ . The top level shows the foods that generate the ★ impact, while the bottom level shows those that have ★ consequences. The impact associated with each food was estimated using the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). This is a more objective and innovative method than the traditional criteria used to assess a given process. It ★ the environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product’s ★ , such as ★ consumption.
The ★ footprint is an indicator that measures the ★ gas emissions generated by human activities. It is expressed in tonnes of CO2 or CO2 equivalent.
The ★ footprint measures the volume of ★ that is consumed and/or ★ throughout the supply chain per unit of time. The ★ footprint measures the amount of ★ needed by people to produce the resources they consume and absorb the ★ they produce.
The ★ pyramid produced by the Barilla Centre for Food and Nutrition (BCFN) effectively shows that foods at the ★ recommended ★ levels are also those with the ★ levels of environmental ★
The ★ diet is the one that most closely follows the ★ guidelines and is the most sustainable.
Source (adapted): Microsoft PowerPoint - Barilla.ENG.ppt (fao.org)
13. Indicate whether the following statements are true or false and correct the false ones in your notebook.
a) The greater the variety of nutrients in a food, the higher its nutritional value.
b) Water is an organic nutrient.
c) Lipids and carbohydrates are inorganic nutrients.
d) Mineral salts should be consumed in huge quantities.
e) We must drink at least 2 litres of water a day.
f) Proteins help to build and repair cells.


1/2 vegetables


1/4 proteins
Group VI: Fruits➜ Pesticides remove pathogens from plants, but they contaminate food and the environment.
➜ Organic farming produces food without using toxic substances, so this is the healthiest type of food. It causes minimal pollution and environmental impacts. It must carry a special label that guarantees it is organic.
Organic farming does not contribute to the desertification of soils, but increases their long-term fertility. It also conserves plant and animal biodiversity.
➜ In developed countries, malnutrition can be caused by an unbalanced diet, which may contain a lack or excess of nutrients.
➜ In developing countries, malnutrition results from a lack of access to essential foods. What should we eat?
Healthy habits include:
➜ Doing sufficient exercise.
➜ Limiting our consumption of foods rich in saturated fat or sugars.
➜ Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, whole grains and oily fish.
➜ Drinking plenty of water.
➜ Avoiding burnt meat and limiting our consumption of cured meats.


14. Define the following methods of food preservation in your notebook. Search for information if necessary.
a) Refrigeration
b) Deep-freezing
c) Pasteurisation
d) Pickling
15. Search for information and write how to make your own yoghurt. What is the microbiological explanation for this process?
16. Think about the activities you do in your daily life and discuss them with your partner. Do you have a sedentary, active or very active lifestyle? You can use some of these phrases:
I often.../I never.../Usually, I.../I hardly ever.../Sometimes, I.../...times a week, I...
17. Do you think that a person who does a lot of sport should eat the same food as someone who stays at home watching TV all day? Justify your answer. Can you design a balanced meal for each of them?
18. In your notebook, complete the sentences using the following words:
obesity, fibre, anorexia, salt, diets, transit, hypertension, thin.
People who are extremely ★ should have a diet rich in energy foods.
★ is associated with hypercaloric ★ , which contain a lot of fats and junk food.
To avoid constipation, a diet that is rich in ★ is recommended.
When someone suffers from ★ , they eat an insufficient amount of food to avoid gaining weight.
For ★ , a diet that is low in ★ is recommended.
Intestinal ★ can be improved with either a low-residue or high-fibre diet.
19. Indicate whether the following statements are true or false and correct the false ones in your notebook.
a) Cakes and red meat can be eaten on a daily basis.
b) We should eat meat and fish every day of the week.
c) Olive oil and dairy products can be consumed daily.
d) We should eat eggs daily.
e) Vegetables and fruits should be eaten as often as eggs.
f) We must eat a variety of foods to cover our daily energy needs.
20. Search for information and answer this question: What is the difference between anorexia and bulimia, and why do you think that more women than men usually suffer from these disorders?
21. In your notebook, record what you eat in a week. Then complete the sentences below and write a paragraph to answer the question: Does your diet cover your daily energy needs?
I eat ★ every evening.
I usually/often have ★ I eat ★ 3-5 times a week.
Sometimes, I eat high-calorie foods like ★ and ★ I hardly ever/never/always/usually eat organic ★ . Considering my diet, I am/am not covering my daily energy needs.
I should include more ★ in my diet.
I shouldn’t eat so many/much ★ . I should eat more organic/less processed food.
22. Put the words in the right order to make sentences. Then, write them in your notebook.
a) farming and conserves Organic animal biodiversity plant.
b) guarantees Organic label must carry a food special that it organic is.
c) remove pathogens environment they from Pesticides contaminate plants, but the.
d) without farming using toxic produces substances Organic food.
e) and is the healthiest food also minimises type pollution Organic.
23. Choose the correct word in each pair. Then, write the sentences in your notebook.
a) In developed/developing countries, malnutrition can be caused by an unbalanced/a balanced diet, which may contain a lack or excess of nutrients.
b) In developed/developing countries, malnutrition results from a lack/excess of essential foods.
Healthier Less healthy
Nutri-Score: 5-colour nutrition label for food and beverages
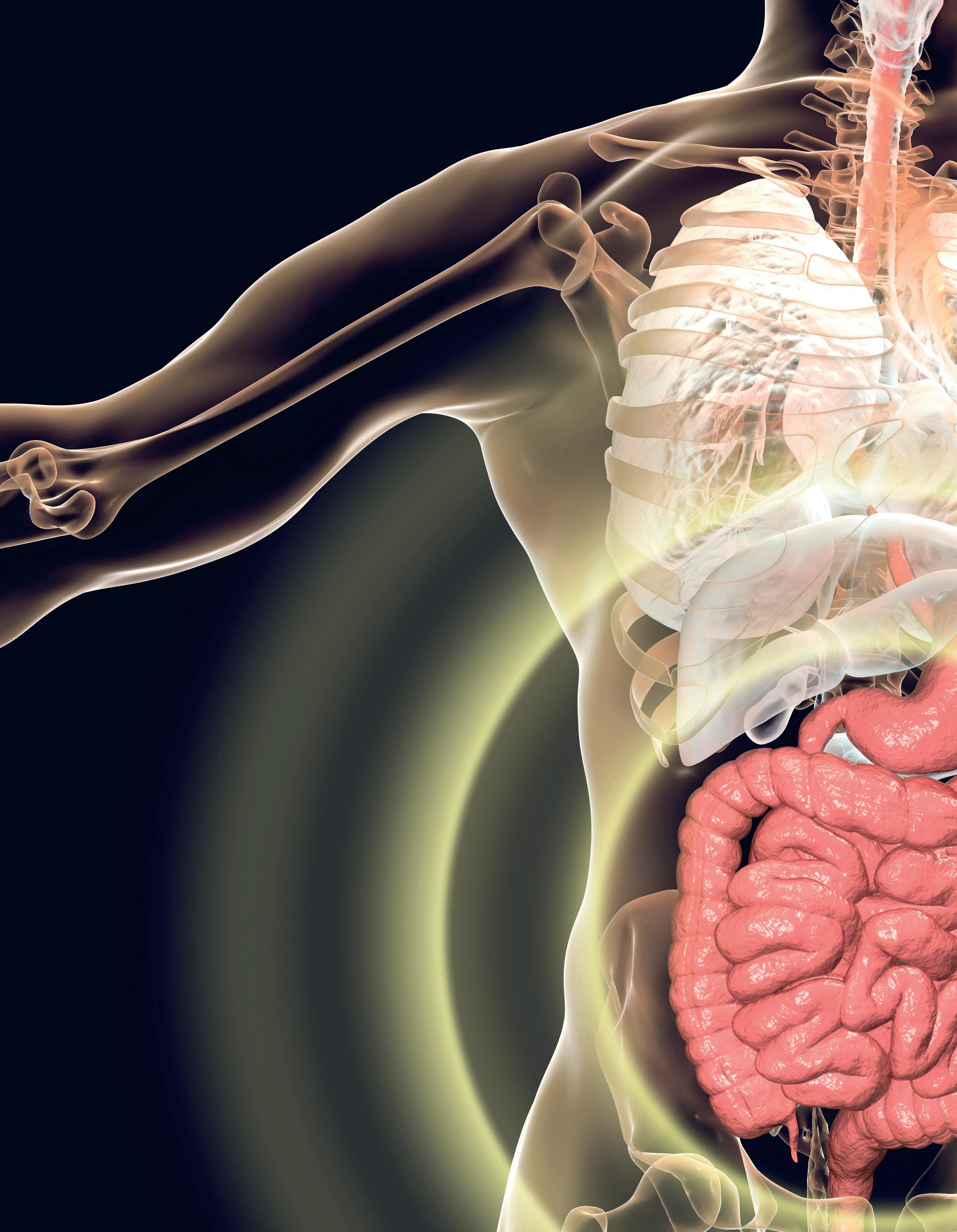

In February 2023, the Virgen de las Nieves Hospital in Granada began to use a new technique to treat patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who suffer damage from emphysema. The parts of the lung that are damaged and cannot carry out gas exchange hyperinflate, generating dyspnea. This treatment involves placing a one-way valve in the lung, allowing air to leave, but not to flow back in. This deflates the diseased parts of the lung, considerably decreasing dyspnea.
1 Work in groups and investigate this advanced treatment in Andalusia.
2 COPD is a group of diseases that cause breathing problems. Investigate what these diseases are, how common they are in Andalusia, and why this new technique can only be used to treat some COPD patients.
3 Investigate the cost of COPD treatments in Andalusia.
4 Research the best climatic conditions for people that suffer from COPD, and locate the best places for these patients to live in the region of Andalusia.
1 Select the most important aspects of the information you have obtained, organise the information and write a summary.
2 Search for pictures, illustrations, animations or videos, or create your own, to accompany the information.
3 Create a lapbook, poster, presentation or video. Include diagrams or graphics using tools such as Word/Writer, PowerPoint/Impress, Prezi, Keynote, Canva or VideoScribe.
1 Present your project to the class, making sure all the members of your group participate.
2 During the presentation, your classmates have to take notes, writing down any questions they have.
3 After the presentation, answer your classmates’ questions.
4 You can organise a quiz about your project, in which all your classmates can participate. You could use Kahoot or a similar application.

What is the nutrition function?
It is the oxidation of nutrients to obtain energy. The systems that are involved in the nutrition function are: the digestive, circulatory, respiratory and excretory systems.
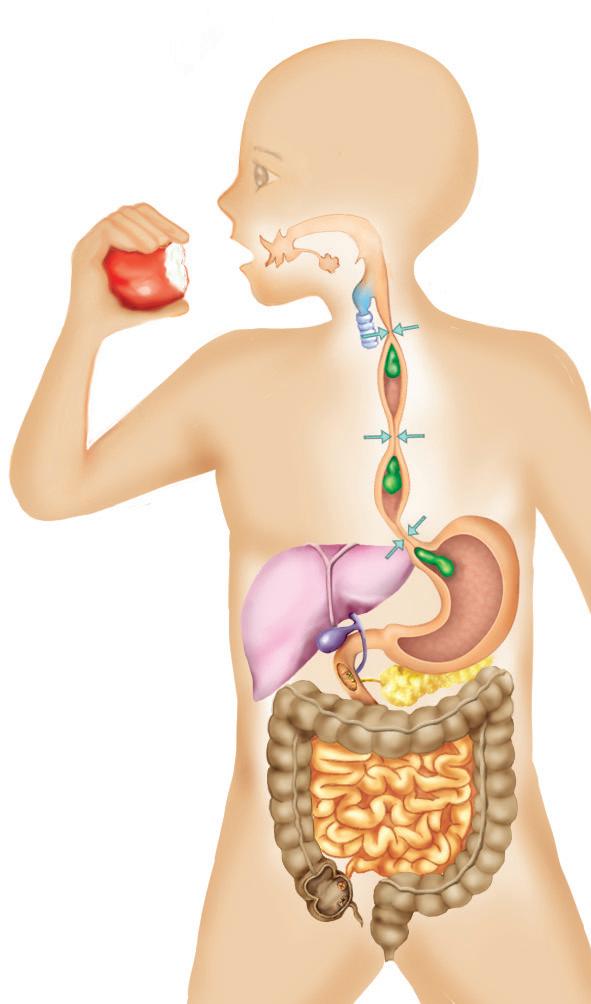
What is the function of the digestive system?
Digestion is the process of transforming food into molecules that can be used by the cells of the body. This transformation is mechanical (through the teeth) and chemical (through glandular secretions).
How is food digested in the mouth?
The tongue mixes the chewed food with saliva to form a bolus. The adult dentition in each jaw consists of: 4 incisors, 2 canines, 4 premolars and 6 molars. Saliva lubricates the bolus and contains amylase.
How does the pharynx function?
In this organ, the digestive and respiratory tracts intersect. It connects on either side with the middle ear. When air enters the pharynx, the epiglottis stays open in. When the bolus passes into the pharynx, the epiglottis folds to prevent the bolus from entering the respiratory system.
How does the oesophagus function?
It connects the pharynx with the stomach through the cardiac sphincter.
How does the stomach digest food?
Here, mechanical digestion is completed and chemical digestion continues in the the gastric juices, resulting in chyme. Contractions push the chyme towards the duodenum through the pyloric sphincter.
The small intestine and its functions
It performs chemical digestion and absorbs nutrients. The duodenum carries out chemical digestion with the bile from the liver and the enzymes from the pancreas. The jejunum absorbs the nutrients and the ileum completes the processes of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption. The small intestine connects with the large intestine through the ileocecal valve.
The large intestine and its functions
It absorbs water and mineral ions, and removes faeces. The cecum has a vermiform appendix, with lymphoid tissue, and the colon absorbs water and forms faeces. The rectum is at the end of the digestive tract, which terminates in the anus.
What are intestinal microbiota?
They act as external barriers against infection, carry out fermentation and synthesise vitamin K and some group B vitamins.
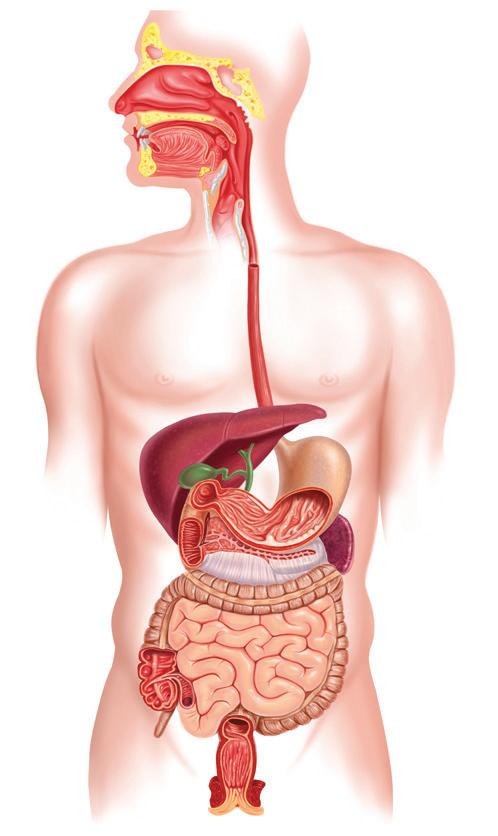
Mouth
Salivary glands
Oesophagus
Intestinal microbiota
Liver
Gallbladder
Stomach
Pancreas
Small intestine
Large intestine Anus
Digestive system
Transverse colon
Undigested waste
Cecum
Vermiform appendix Anus
Ileum
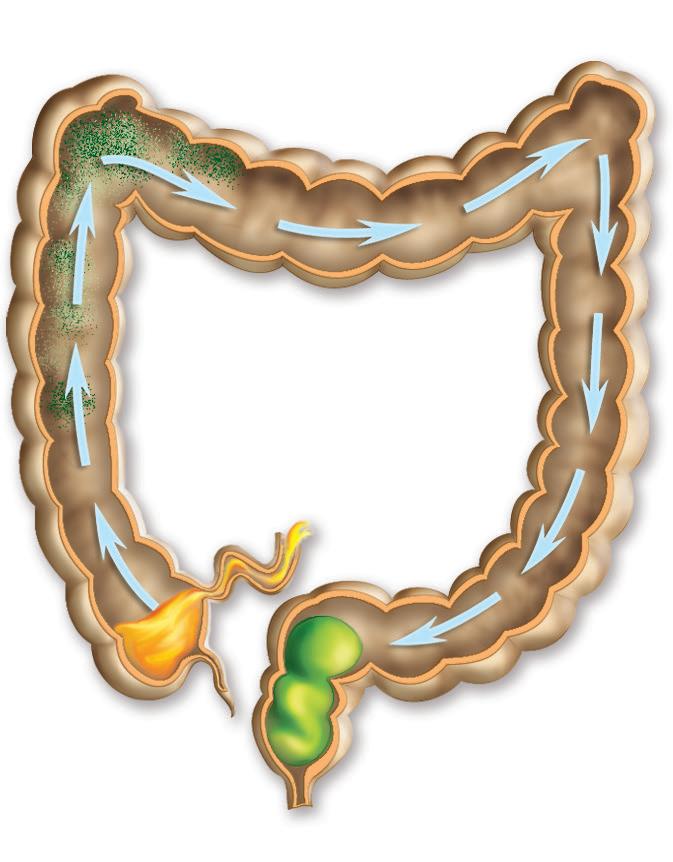
Faeces
Rectum
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Large intestine
1. Copy the text about the nutrition function in your notebook. Then, complete it using the following words: energy, nutrients, metabolism, life, chemical, oxygen. The nutrition function allows the body to obtain the nutrients and energy it requires from food.
Each cell uses oxygen and ★ to carry out a series of ★ reactions. This process is called cellular ★ ★ oxidises the nutrients, and the cells obtain ★ in the form of ATP. This is used to generate new substances and maintain ★
2. Put the letters of the names of the systems involved in nutrition in order. Then, copy the terms and their definitions in your notebook.
a) Ciruyto mesyst: it is responsible for taking in atmospheric oxygen and eliminating carbon dioxide.
b) Disegveti tysesm: it eliminates waste from cellular metabolism.
c) Ratoserpiyr mysest: it is responsible for the digestion of food and its transformation into simple molecules. They can then be absorbed and pass into the circulatory system.
d) Eryrot ysmets: it transports oxygen and nutrients to the cells and collects waste products.
3. Choose the correct word in each pair. Then, copy the text in your notebook.
Digestion/nutrition is the process of transforming food into molecules that can be digested/absorbed in the stomach/ intestine, transported by the intestine/blood and used by the cells of the body. This transformation is mechanical (through the intestine/teeth) and chemical (through glandular secretions). Food travels through the digestive/nutrition tract in the following order: through the mouth, oesophagus/ pharynx, stomach, large/small intestine, large/small intestine and out of the anus.
4. Match each part of the mouth with its function.
Parts of the mouth Functions
1. Tongue a. They perform mechanical digestion by crushing the food.
2. Teeth b. They secrete saliva, which lubricates the bolus. It contains an enzyme called amylase, which initiates the digestion of complex carbohydrates (starch and glycogen).
3. Salivary glands c. There are 16 in each jaw: 4 incisors to cut, 2 canines to tear, and 4 premolars and 6 molars to grind.
4. Adult dentition d. It mixes the chewed food with saliva to form a bolus, which is pushed into the pharynx to be swallowed. It is covered with taste receptors, which allow us to perceive flavours.
5. The images below show how a particular organ functions. In your notebook, identify and describe the organ. Then, describe what is happening in each image.
6. Each of the following sentences contains one mistake. It can either be a conceptual, grammatical or spelling mistake. Correct them in your notebook.
a) The oesophagus is a narrow, muscullar tube.
b) The mouth connects the pharynx with the stomach.
c) After swallowing, the food bolus descend from the oesophagus to the stomach.
d) The food bolus is pushed by muscle tracktion (peristaltic waves).
e) The food bolus enters the oesophagus through the cardiac sphincter.
f) The food bolus enters the stomach through the pyloric sphincter.
g) After digestion is completed in the stomach, the chyme leaves the stomach through the cardiac sphincter.
7. Put the sentences in order to describe the digestion process in the stomach. Then, copy the text in your notebook.
a) Contractions in the stomach push the chyme towards the duodenum through the pyloric sphincter.
b) In the stomach, the hydrochloric acid in the gastric juices acts on the food.
c) The resulting substance is called chyme.
A B Stomach
Gastric glands Oesophagus Food bolus Gastric juices Small intestine Gastric emptying Digestive process
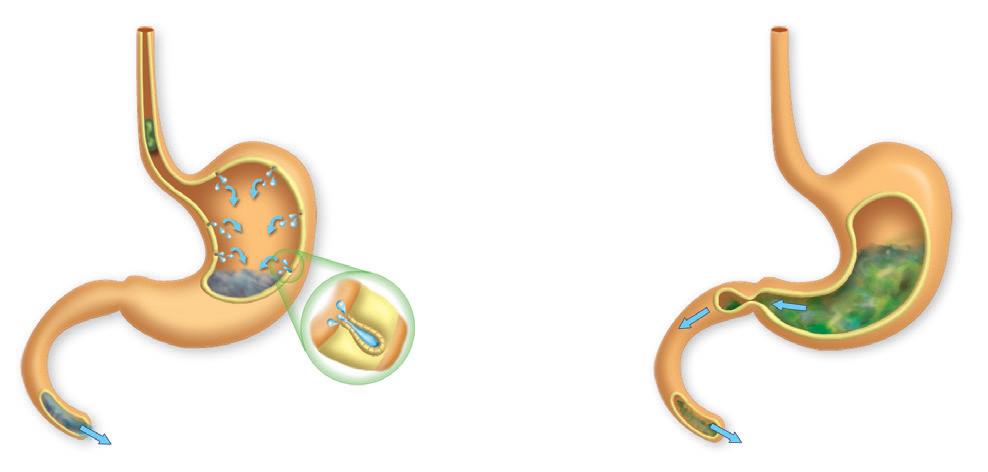
Chyme from the stomach enters the duodenum.
Bile from the liver (stored in the gallbladder):
➜ Emulsifies fats into micelles.
➜ Facilitates the absorption of fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins.
In the glands of the duodenum, the intestinal juices:
➜ Contain mucus, which protects the small intestine.
In the pancreas, the pancreatic juices:
➜ Together with bile, neutralises the acidic chyme.
➜ Contain enzymes.
How are nutrients absorbed in the small intestine?
Intestinal chemical digestion results in chyle. The small intestine also absorbs nutrients, which pass into the bloodstream. To increase the surface area for absorption, its lining has folds called villi, containing cells called microvilli.
➜ Stores surplus A, B, D, E and K vitamins and releases them when they are needed.
➜ Transforms some carbohydrates into fatty acids and transports them to the tissues.
➜ Converts glucose into glycogen and stores it.
➜ Converts toxic molecules into derivatives, facilitating their excretion in urine, bile, or along other pathways, through a process called «biotransformation».
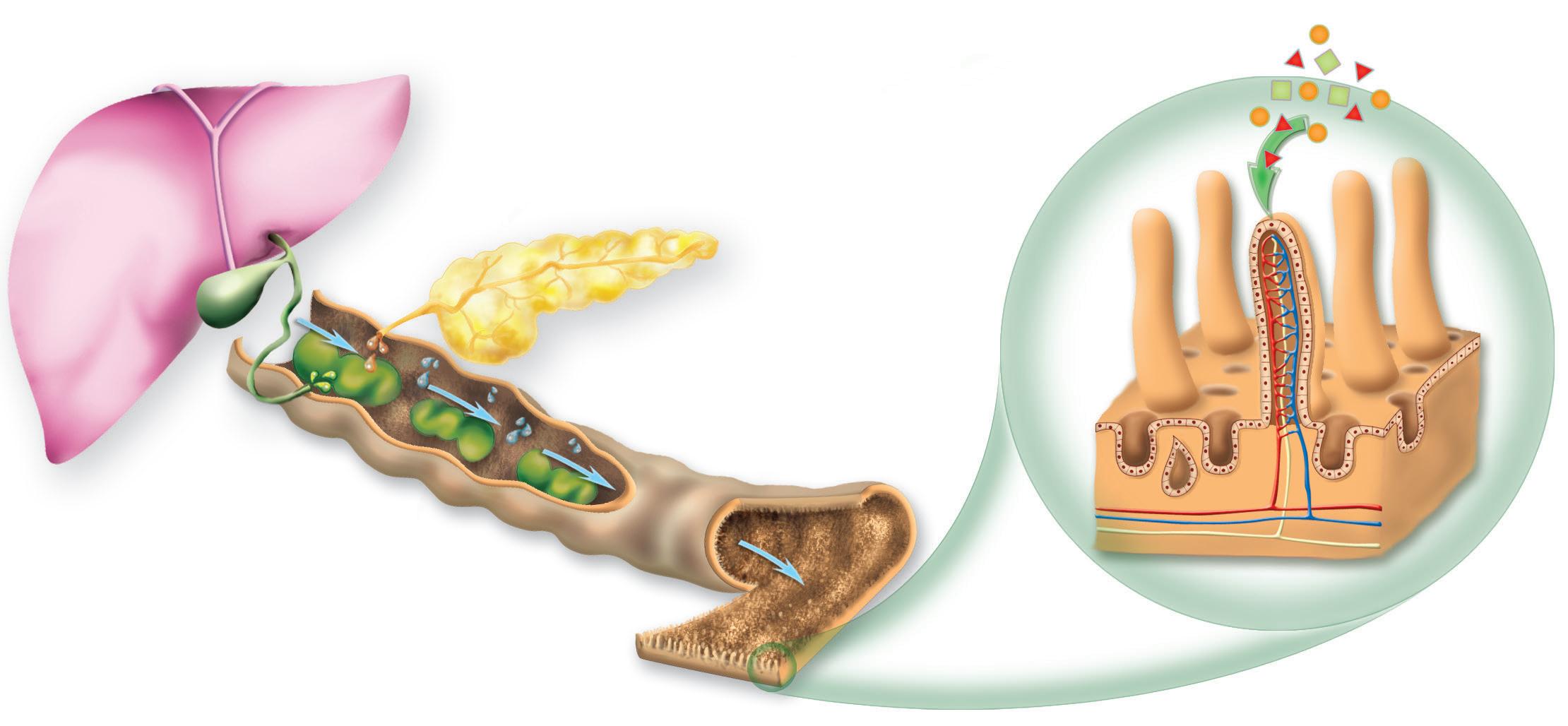
8. Copy the table in your notebook. Then, write the following terms in the correct box.
decomposition of nutrients, swallowing, bolus formation, formation of faeces, peristaltic movements.
Digestive process Organs Related terms
Mechanical digestion. Mouth. ★
Chemical digestion. Stomach, liver, pancreas and duodenum.
Assimilation and absorption of nutrients.
Small intestine.
Egestion. Large intestine. ★
9. Write the sentences in your notebook. Then, complete them with the correct words.
a) The ★ is a muscular organ in the mouth that moves the food around.
b) The ★ is the organ shared by the digestive and ★ systems. It connects the mouth with the oesophagus and the ★
c) In the ★ intestine, most of the water is ★ and faeces are stored until they are removed through the ★
d) There are three ★ in our digestive system:
➜ Salivary ★ , which produce ★ .
➜ The ★ , whose main function is to secrete bile.
➜ The pancreas, which produces pancreatic juices and two ★ to control the amount of sugar in the blood.
10. Copy the text in your notebook. Then, listen and complete it with the missing words.
When you eat, ★ begins to break down the chemicals in the food, which helps make it mushy and easy to ★ . Your tongue helps out, ★ the food around while you ★ with your teeth. When you’re ready to swallow, the tongue pushes a tiny bit of mushed-up food called a ★ towards the back of your ★ and into the opening of your ★ , the second part of the digestive tract.
The oesophagus is like a stretchy ★ , which is about 10 inches (25 centimetres) long. It moves food from the back of your throat to your ★ . Your ★ is also at the back of your throat , allowing air to enter and leave your body. When you swallow a small ball of mushed-up food or liquids, a special flap called the ★ covers the opening of your windpipe. This makes sure the food enters the oesophagus and not the windpipe.
Source (adapted): Kids Health from Nemours, by Larissa Hirsch.
11. Put the letters of the words in green in order. Then, copy the sentences about the digestive system in your notebook.
a) Some kinds of fodo spend more time in the machsto because their tionesdig takes longer.
b) Before doing icphysal exercise, we shouldn’t comensu food that takes longer than two hurso to digest because it will make us feel heierav and will make exercising more iffidcult
c) If you have teean a plate of pasta, you should wait betenwe one and two hours before rcisiexeng
12. Decide whether these sentences are true or false and correct the false ones in your notebook.
a) The larynx belongs to both the digestive and respiratory systems.
b) We should always consume fruits, vegetables and food rich in fibre to prevent us from developing caries.
c) We should always brush our teeth after every meal and shouldn’t eat many sweets to prevent us from developing caries.
d) The formation of gallstones in the stomach is known as cholelithiasis.
13. Complete the following sentences in your notebook.
a) When you eat, the ★ enzyme in saliva breaks down some of the glucides in the food.
b) Saliva helps make the food mushy and easy to ★
c) The ★ pushes the food towards the back of the throat.
d) Mechanical digestion in the mouth results in the formation of a ★
e) The ★ is like a stretchy pipe and moves food from the back of the throat to the stomach.
f) The trachea is commonly known as the ★ .
g) When the ★ folds, it prevents the food bolus from entering the respiratory system.

Oxygen is used by the cells to extract energy from nutrients, and carbon dioxide is released as a product. This process is carried out by the respiratory system.
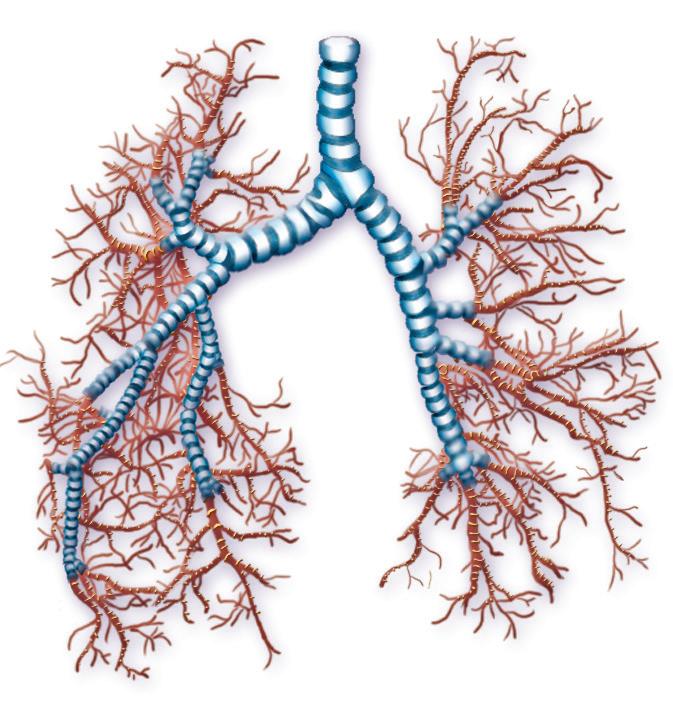
1 Nostrils. They are two cavities through which air enters. They are lined with a mucous membrane which moistens and warms the inspired air. It also destroys certain germs.
6 Larynx. Cartilaginous duct, whose anterior opening, the glottis, is regulated by the epiglottis. The larynx contains the vocal cords, which vibrate and emit sounds when air is expelled, through the process of phonation.
Open vocal cords
Closed vocal cords
5 Bronchi and Bronchioles. Each bronchus branches into bronchioles. They are lined with ciliated cells and secretory cells, which release mucus.
Respiratory system
2 Pharynx. Organ shared by the digestive and respiratory systems. It contains the tonsils, structures in the lymphatic system that have a defensive function.
3 Trachea or windpipe. Tube that divides into two bronchi. It is lined with a mucous membrane containing ciliated cells, with hair-like structures, and secretory cells, which release mucus. This layer traps inhaled particles, preventing them from reaching the lungs.
Rib cage Lungs
Diaphragm
The lungs are two elastic, spongy organs covered by a thin membrane called the pleura. They are located in the rib cage. Below them is a muscle called the diaphragm, which separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
The right lung has three lobes and the left has two, with a cavity containing the heart.
It is the renewal of the air in the alveoli through inspiration (the diaphragm contracts and the ribs rise) and expiration (the lungs retract, expelling air rich in CO2, and the volume of the rib cage decreases).
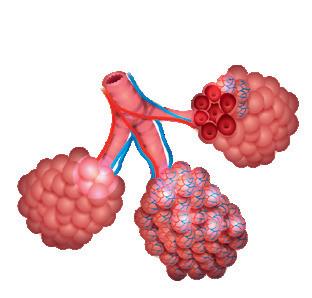
The air from the airways reaches the clusters of pulmonary alveoli. Each alveoli is covered by a network of blood capillaries, where gas exchange takes place. During gas exchange, oxygen passes from the alveoli to the blood of the capillaries. The hemoglobin in the red blood cells then transports the oxygen to the cells in the tissues. Carbon dioxide travels in the opposite direction: it goes from the cells to the blood and from there, to the alveoli to be removed.
4 Pulmonary alveoli. They are covered with blood capillaries, where gas exchange takes place.
14. Decide whether these sentences are true or false and correct the false ones in your notebook.
a) The pharynx belongs to both the digestive and respiratory systems.
b) Gas exchange occurs in the bronchi.
c) Most diseases of the respiratory system are caused by viruses or bacteria.
d) The cilia and mucus in the trachea do not participate in cleaning inhaled air.
e) When we breathe in, the diaphragm contracts and the lungs expand.
15. Put the words in order to make sentences and write them in your notebook.
a) voice suffer When our from sounds hoarseness, different we.
b) nostrils reaches our lungs The air that enters through our.
c) we are exposed to quick temperature changes We can get sick when.
d) happens the process exchange through of diffusion Gas.
e) cilia is air to in through the nostrils breathe so better can clean It the the.
f) by the rib cage the lungs and the heart are protected.
16. Match each part of the respiratory system with its function:
a. Nostrils 1. They are lined with ciliated cells and secretory cells, which release mucus. They are ramifications at the end of the windpipe. Each bronchus branches into bronchioles.
b. Pharynx 2. Cartilaginous duct, whose anterior opening, the glottis, is regulated by the epiglottis. It contains the vocal cords, which vibrate and emit sounds when air is expelled, through the process of phonation.
c. Larynx 3. Small sacs that are irrigated by blood capillaries for gas exchange.
d. Trachea or windpipe 4. Two cavities through which air enters. They are lined with a mucous membrane which moistens and warms the inspired air. It also destroys certain germs.
e. Bronchi and bronchioles
f. Pulmonary alveoli
5. Tube that divides into two bronchi. It is lined with a mucous membrane containing ciliated cells and secretory cells, which release mucus. This layer traps inhaled particles.
6. Organ shared by the digestive and respiratory systems. It contains the tonsils, structures in the lymphatic system that have a defensive function.
17. Complete the text in your notebook using the following words: hygiene, smoke, exercise, avoid, ventilation, nose, infections, cancer, removal, temperature, regularly, gases, breathe, flu.
We should follow these recommendations to prevent respiratory diseases:
a) ★ through the ★ : this facilitates the ★ of airborne microbes.
b) ★ sudden changes in ★ : this helps prevent the ★ and hoarseness.
c) Stay away from areas with irritant or toxic ★
d) Don’t ★ ! Giving up improves gas exchange and prevents ★ .
e) Do regular ★ : this increases pulmonary ★
f) Maintain good body ★ : washing your hands ★ helps prevent many ★
18. Using your own words, explain in your notebook what pulmonary ventilation is.
19. Choose the correct word in each pair. Then copy the sentences in your notebook.
a) The lungs are covered by a thin membrane called the mucus/plura, and they are located in the rib/vertebral cage.
b) Below/Above the lungs, there is a muscle called the heart/ diaphragm.
c) The right/left lung has three lobes and the right/left one has two, with a cavity containing the heart.
20. Write the terms for the following definitions in your notebook.
a) They are tubes at the end of the windpipe.
b) Each bronchus branches into these.
c) A cartilaginous duct that contains the vocal cords.
d) Small sacs that are covered with blood capillaries, where gas exchange takes place.
e) Tube that divides into two bronchi.
f) Organ that is shared by the digestive and respiratory systems.
g) Two cavities through which air enters.
Write the answers in your notebook.
1. Write the names of the organelles and cell structures in the images. Indicate if they are found in animal or plant cells and explain their function. Organise the information in a table.
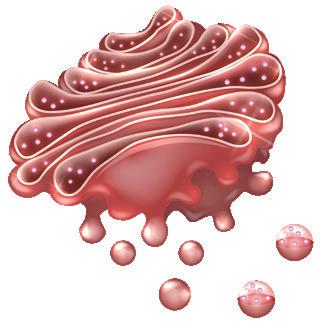
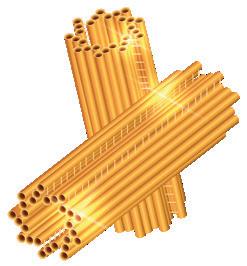
1) Plasma membrane
2) Lysosomes
3) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
4) Nucleolus
5) Golgi apparatus
6) Cytoskeleton
7) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
8) Centrioles
9) Ribosomes
3. Match the organs with the corresponding tissues.
Organs
1) Diaphysis of a long bone
2) Epidermis
Tissues
a) Elastic cartilage
b) Dense connective tissue
3) Meniscus
4) Myocardium
c) Spongy bone tissue
d) Compact bone tissue
e) Smooth muscle tissue

5) Epiphysis of a long bone
6) Epiglottis
7) Tendon
8) Stomach
9) Encephalon
f) Fibrous cartilage
g) Stratified epithelium
h) Cardiac striated muscle
i) Nerve tissue
4. In each group, find the odd one out and explain why.
a) Myofibrils, mitosis, meiosis, cytokinesis.
b) Dendrite, axon, chondrocyte, neuronal body.
2. Indicate if the following statements are true or false and correct the false ones.
a) Protein synthesis takes place in lysosomes.
b) Chromatin is made up of DNA and special proteins called histones.
c) Lysosomes, plasma, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus.
d) Nucleolus, chromatin, nuclear envelope, periosteum.
5. To which tissues do the following cells correspond?
a) Chondrocyte
b) Schwann cell
c) Fibroblast
d) Adipocyte
e) Oligodendrocyte
f) Osteocyte
g) Astrocyte














6. Indicate if the following statements are true or false and correct the false ones.
a) To increase the surface area for absorption, the inner wall of the small intestine is lined with millions of alveoli.
b) During gas exchange, carbon dioxide passes from the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries.
7. Write the terms that correspond to the following definitions.
a) Biochemical reaction produced by certain bacteria and yeasts that is used in the food industry.
b) Eating disorder in which a person compulsively eats food in secret and then induces vomiting.
c) A disease caused by insulin resistance, preventing glucose from entering cells.
d) Quotient between the mass of an individual in kg and their height in m2
e) Caloric consumption of an individual fasting and in a state of physical and mental rest.
8. Indicate if the following statements are true or false and correct the false ones.
a) Each gram of fat supplies 9 kcal.
b) Cellulose is a protein.
c) Carbohydrates provide energy quickly.
9. Identify the missing foods in the food wheel. Write the group they belong to and their main functions. ?
10. In each group, find the odd one out and explain why.
a) Hemoglobin, pepsin, lipase.
b) Trachea, cardia, larynx, bronchiole.
c) Colon, duodenum, jejunum, ileum.
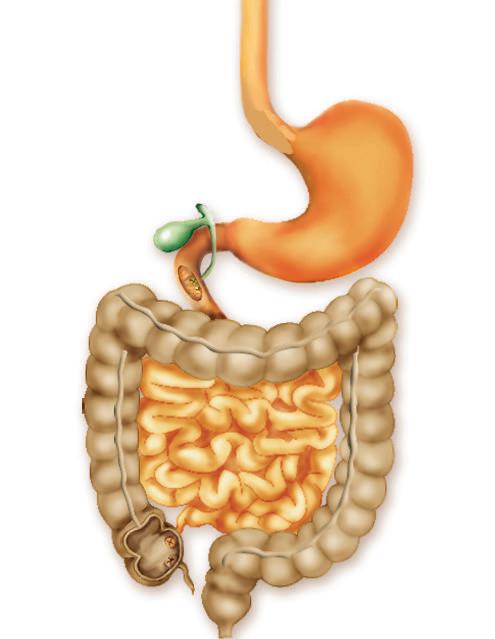
11. Write the order in which food passes through the following organs. You can refer to the image below if necessary.
Small intestine, stomach, mouth, oesophagus, pharynx, anus, large intestine.
12. Write two sentences, one with the concepts in a) and another with those in b).
a) Epiglottis, bolus, pharynx, oesophagus.
b) Alveoli, red blood cells, hemoglobin, oxygen.
13. Match the elements in the first series with those in the second.
1) Alveoli
2) IIeum
3) Bile
4) Parotid glands
5) Pepsin
6) Larynx
7) Diaphragm
a) Respiratory muscle
b) Saliva
c) Stomach
d) Liver
e) Lung
f) Small intestine
g) Phonation
14. Identify the two missing elements in the following image.
Divide the class into mixed teams (A, B, C, D, etc.) of four students. Each team member will be given a number (1 to 4). The teams must answer the questions below on human beings as multicellular organisms, the immune system, health and disease.
Your teacher will give you a time limit to answer the questions. When they call out a number, all the team members with that number will go to the front of the class and read and answer Question 1. When they call out the next number, those team members will read and answer Question 2, and so on. Each question is worth a total of 20 points (5 points for each section). The team, or teams, with the most points wins the game.
1 Match each organelle to one of the functions indicated below.
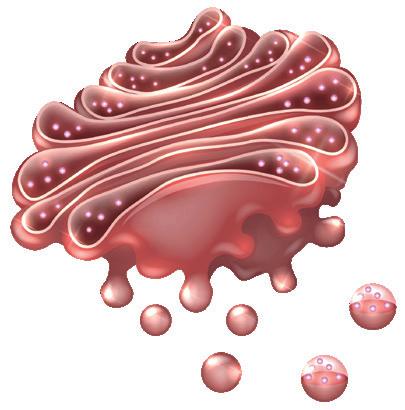
1) Golgi apparatus
2) Plasma membrane
a) It regulates the entry and exit of substances.
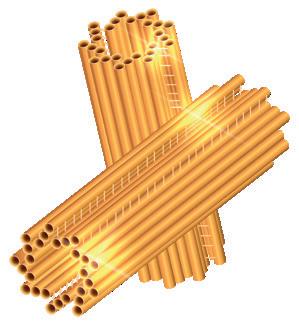
3) Centrioles
b) It produces the energy needed for all the different cellular functions.
c) It is involved in organising a cell’s microtubules.
4) Mitochondria
d) It modifies synthesised proteins in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into vesicles that are sent to other parts of the cell or outside the cell.
When answering the questions in front of the class, point to the right answer and say something like ‘The function of mitochondria is to ★ .’


















2 Each of these blood groups has one of the following antibodies (agglutinins) in its blood plasma. Match each blood group to the correct antibody.




Plasma A


4
group 2 C






anti-B) 1 B












3 D


















© GRUPO EDITORIAL BRUÑO, S. L., 2024 - C/ Valentín Beato, 21 - 28037 Madrid.
Reservados todos los derechos. El contenido de esta obra está protegido por la Ley, que establece penas de prisión y/o multas, además de las correspondientes indemnizaciones por daños y perjuicios, para quienes reprodujeren, plagiaren, distribuyeren o comunicaren públicamente, en todo o en parte, una obra literaria, artística o científica, o su transformación, interpretación o ejecución artística fijada en cualquier tipo de soporte o comunicada a través de cualquier medio, sin la preceptiva autorización.