
10 minute read
2 Is water undervalued ?
Carmen is a Spanish girl who studies 4th Grade Primary School in a class with other classmates. They did some research on the latest UNICEF reports for their group work. The report Carmen has found most interesting is a 2019 report on inequalities of access to water around the world. This report says approximately 2.2 billion people around the world do not have access to safe drinking water facilities. Also, this problem is increasing because of the rising pollution of freshwater sources. Sadly, children are the first to suffer the consequences of this situation.
What do you think?
What would happen if we suddenly had no drinking water in our homes and had to travel several kilometres to get it? Why do you think children suffer the most from these problems?

Context
In this unit...
Target in action
Make a sign with a catchy slogan to make people conscious of the importance of saving and not polluting our available water.
Follow the thread!
UNICEF says 1.8 billion people have gained access to safe drinking water since 2000, but there are large inequalities in accessibility, availability and quality of these facilities.
The hydrosphere
1
Where is water collected on our planet?
Groundwater and surface water
2
How is water divided up on Earth?
Rivers: elements and characteristics
3
What are rivers like?
Rivers in Spain
4
What are the most important rivers in Spain?
Responsible water use

5
Are we using water properly?
Where is water collected on our planet?
If water covers more than half of the earth's surface, why is access to it so limited in some countries?
The blue planet
Our planet looks blue when you look from space. This is because almost three quarters of the Earth's surface is covered by water, almost all of it is salty.
The hydrosphere is the Earth's water. Without it, life on Earth would be impossible.
• Humans, animals and plants need water to survive. Many living things live in it.
• The water in oceans and seas absorbs heat from the sun, helping to maintain and moderate the temperature of the planet.
Water can be found in nature in three states or forms: solid, liquid and gaseous. Water will change its state depending on how much cold or heat is applied.


Water states and its changes
Solid state
Language Bank

Speaking. In pairs, try to guess what you’re thinking about using the clues from the writing.
Writing. Imagine a place or object that has got water. Write some sentences to describe what it looks like.
To find a summary of the unit, watch the video 'Let me tell you' on anayaeducacion.es
To learn more about water, watch the video "The importance of water" on anayaeducacion.es.
Melting Evaporation
Liquid state
Gaseous state
Solidification
Condensation
The water cycle
Water is always moving around the Earth. Thanks to changes in its state, the water cycle takes place.
Condensation
As the water vapour rises, because of low temperatures, it condenses into small droplets that form clouds.
Take note!
Only 0.007% of the Earth's water is drinkable, and this amount is decreasing every year due to pollution.
Precipitation
As the clouds grow larger and larger, their weight and the drop in temperature cause the droplets to precipitate in the form of rain, snow or hail.
Evaporation
The liquid water present in the large bodies of water evaporates thanks to the heat of the sun and rises into the atmosphere in the form of water vapour.
1 Ideas pool Why is the Earth known as the blue planet? What is the hydrosphere?
2 Think and share in pairs Explain the importance of the hydrosphere.
3 Investigate at what temperature water melts and solidifies.
Accumulation
Water from precipitation accumulates again, forming bodies of water. Some of it filters down, forming groundwater, some of it stays on the surface, starting the water cycle all over again.
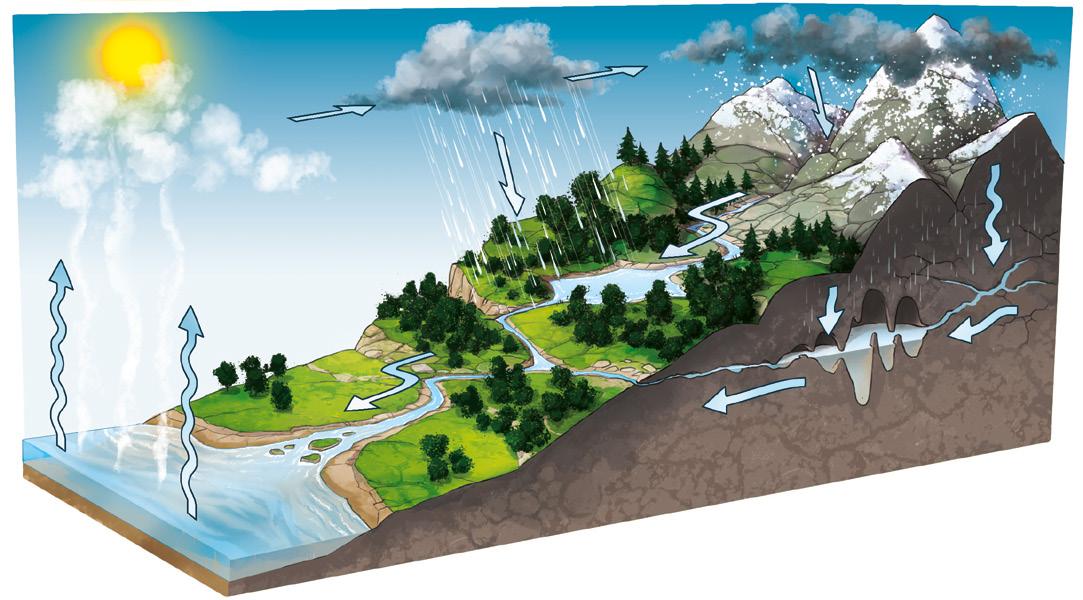
To better understand the water cycle, watch the video "The drop of water" on anayaeducacion.es.
4 Draw a diagram of the water cycle in your notebook.
5 Name the states of water and write what change is taking place in each case:
• Marina leaves the house and it starts to rain.
• Desiree and Juanlu are skating on a frozen lake.
How is water divided up on Earth?
Which bodies of water do we extract the water we use daily?
Surface water and groundwater
The waters that make up the hydrosphere can be surface water or groundwater .
Surface water
Surface waters are those found on the earth's surface, resulting from the accumulation of precipitation or from the escape of groundwater to the surface. They can be inland or marine.

Marine waters are bodies of salt water, such as the seas and oceans. Two phenomena happen in them:
• Ocean currents. These are movements of water caused by changes in temperature and level of salt, by the wind or by the earth's rotation.
Inland waters are bodies of fresh water. They can be moving, as in rivers and streams, or still, as in lakes.
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water that cannot be seen. It is located below the surface of the earth. It filters through porous soils or cracks in rocks and accumulates in the earth's interior, forming aquifers and underground rivers.
• Tides. These are changes in sea level caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the earth.
Sometimes they are extracted artificially by digging wells
These waters form underground caves and tunnels. Occasionally, they rise to the surface, creating to natural springs or fountains.

Less and less water is available!
Look at the graph, think and answer:
• What is the trend in the evolution of available water, is it increasing or decreasing?
• In which year was the highest amount recorded? And the lowest?
• How many years are there between the two dates?
• What is the approximate difference between the two?
Water usage
Humans use water for activities such as agriculture, livestock farming, industry, etc. We also use it for our own consumption (drinking, hygiene, food, cleaning, etc.).
Stored water
Dams are built on rivers to store fresh water in reservoirs to provide water when it is not raining and to produce electricity.

1 What two types of surface water are there?
2 Write two examples of bodies of fresh water and two examples of salt water.
3 What is the difference between groundwater and surface water?
Evolution of available water in Spain
drinkable For its puri cation
Seawater treatment may be a solution to the increased lack of freshwater, but its economic and energy costs are too high for it to be a cost-effective solution.
Before it can be used for human consumption, water must be treated, which is why desalination and purification processes are carried out.
4 1-2-4 List the main activities in your daily life that require the use of water. Where do you think it comes from?
5 Investigate and explain what desalination and water purification are.
What are rivers like?
Do humans benefit from the features and elements of rivers?
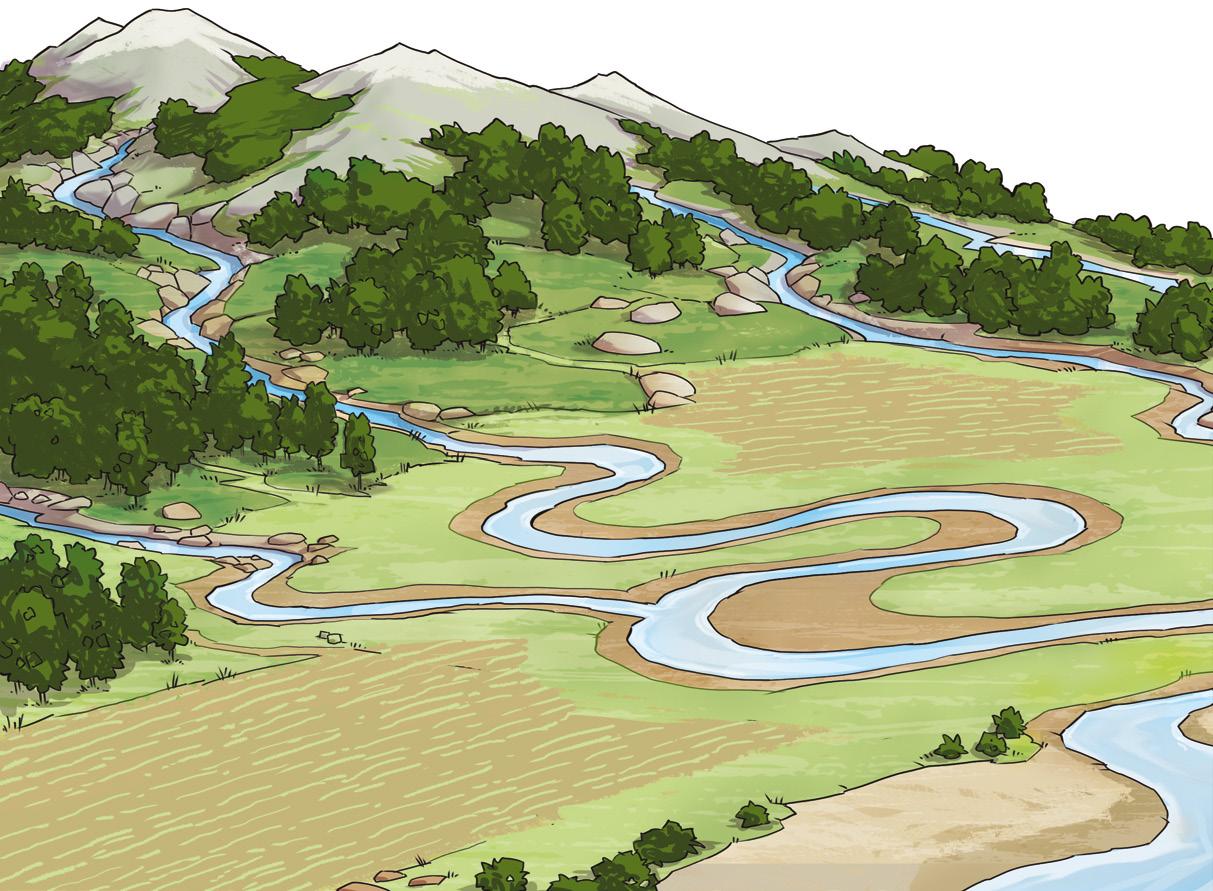
What is a river?
A river is a freshwater stream made by precipitation or snowmelt that starts in the mountains and flows into the sea, a lake or another river.
Elements of a river
We can distinguish different parts or elements of a river: source, course and mouth
Source. Place where a river starts or springs. It is normally in mountainous areas.

Upper course. The section closest to the source. The waters flow very fast because of the gradient.
Course. The course of the river from its source to its mouth. We divide it into the upper, middle and lower course.
Middle course. The central section of the course. The gradient decreases and the speed of the water decreases.
Tributary. River that flows into another river.
Lower course. The section closest to the mouth of the river. There is hardly any gradient and the water flows slowly. The river forms very sharp bends, called meanders
Characteristics of a river
The main characteristics of a river are length , flow and regime
These characteristics depend on two factors : relief , which determines the length and velocity of the water, and climate , which determines the flow and regime.
1 List the elements of a river.
2 In your notebook, define these concepts: tributary, riverbed, mouth and flow .
3 Do you know if there are any reservoirs
The waters around me
Look for information and make a list of the bodies of freshwater in your area.
It does not need to be only rivers, but also lakes, ponds, aquifers, etc.
Length. The distance from the source to the mouth of the river. Rivers can be short or long.
4 Classify these terms according to whether they are elements or characteristics of a river: regime - course - mouth - flowsource - length.
Flow. The amount of water that the river carries during a particular section and at a particular time.
Regime. Variation of the flow throughout the year. Regular regime if it varies little; irregular regime if it varies a lot, or even dries up.
Mouth. The final section of a river. Its waters flow into a sea, ocean, lake or another river.

What are the most important rivers in Spain?
How well preserved are Spanish rivers?
The three watersheds
Spain is divided into three hydrographic watersheds : the Cantabrian watershed, the Atlantic watershed and the Mediterranean watershed.

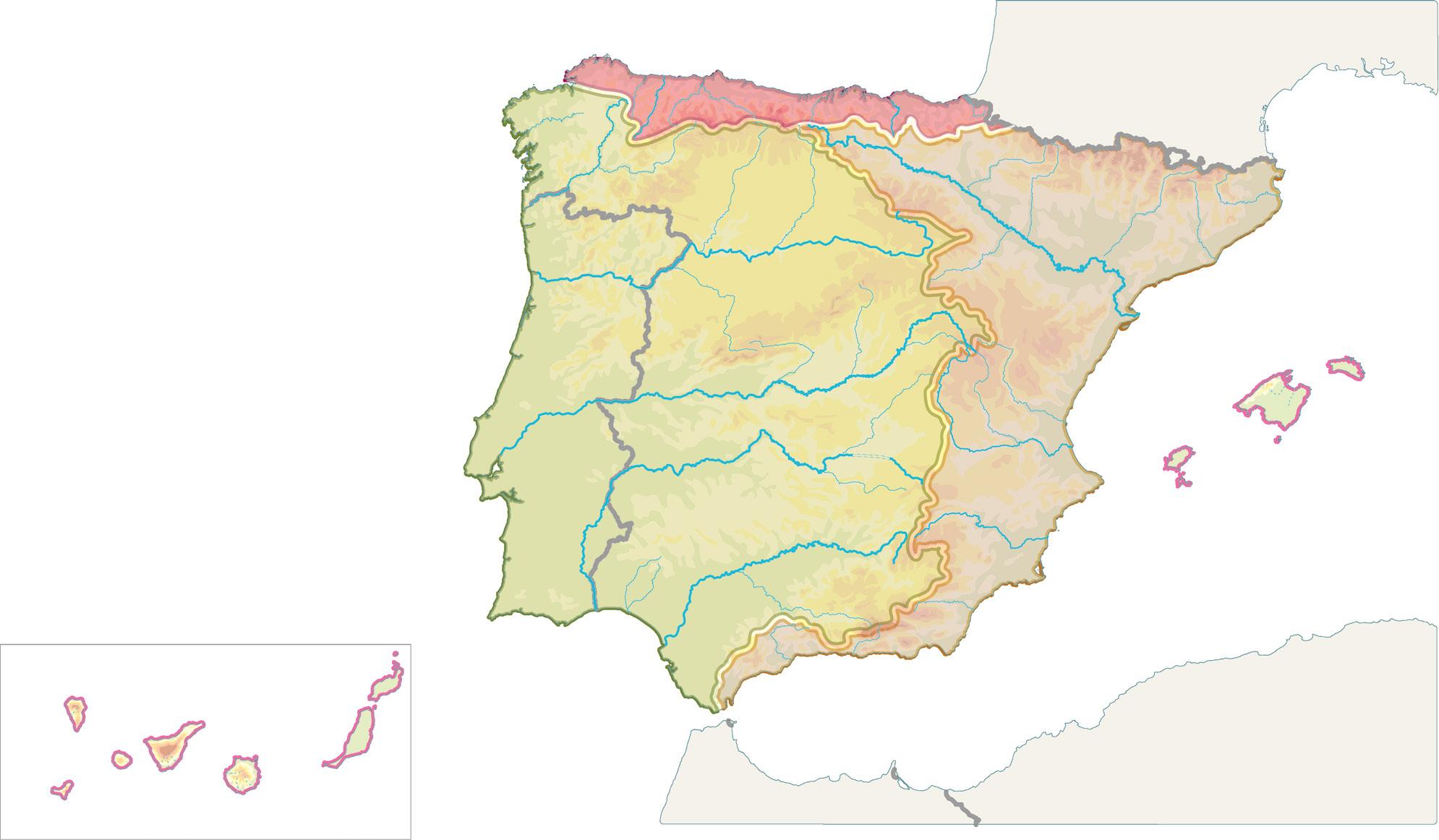
These are rivers that flow into the Atlantic Ocean, which are the majority because of the gentle westward slope of the Central Plateau. We have two groups:
- Galician rivers They are short and regular. The most important are the Tambre, the Miño and its tributary, the Sil
- Rivers of the Meseta and the Guadalquivir depression. These are long and irregular rivers. The main ones are the Duero and the Tajo , the Guadiana and the Guadalquivir
There are no permanent rivers in the Canary archipelago. When it rains in storms, the water flows in channels known as ravines
To better understand landforms, watch the video "The rivers of Spain” on anayaeducacion.es.
Rivers in Spain
River that ows into the Cantabrian Sea River that ows into the Atlantic Ocean River that ows into the Mediterranean Sea Archipelagos
River
Tributary
Torrents and ravines
Country boundaries
Rivers that flow into the Cantabrian Sea They are short rivers, as they start very close to the sea, in the Cantabrian mountain range. Thanks to the rainy climate, they are regular rivers. The main ones, from east to west, are the Bidasoa, the Nervión, the Besaya, the Nalón, the Navia and the Eo
1 How many watersheds are there in Spain? Draw a map of Spain and point out the main rivers in each one.
2 In pairs, play a game where you say the name of a river out loud. Your partner has to guess which watershed it belongs to.
3 Look at the map and write down: two tributaries of the Duero, one of the Tajo, one of the Guadiana, one of the Guadalquivir and two of the Ebro.
4 Draw up a diagram or conceptual map with the basic information about the rivers of Spain.

They are rivers with different lengths and regimes. There are two groups:
- Eastern rivers. From north to south, the main ones are the Ter; the Llobregat; the Ebro , which is the largest in Spain; the Turia ; the Júcar and the Segura
- Southern rivers. These are short, as they start near the coast, in the Penibetic mountain range. The most important are found in Andalucía and are, from east to west, the Almanzora, the Guadalfeo and the Guadalhorce
There are no permanent rivers in the Balearic archipelago either. When there are strong storms, streams called torrents are formed.
Take note!
Are we taking care of our rivers?
Think with a partner 3 eveyday actions we can take to prevent river pollution.
More than half of Spain's rivers are polluted, because of toxic fertilisers or chemicals. There are also other more common pollutants, such as household appliances, masks, furniture or debris.
Are we using water correctly?
Is it the responsibility of all citizens to care for water and use it correctly?
Water is essential for the life of all living things on the planet. Apart from drinking, people use water for many other activities.
This natural resource may seem unlimited to us, but not using it correctly or over-consumption could lead to its drying up and have very negative consequences. So, it is very important that we use water intelligently.
Uses of water
When we use water to clean streets, fill public fountains, water parks and gardens or put out fires, we are making a public use of it, as it is used for the benefit of all citizens in general.

Who consumes less water?
Look at the graph and answer:
• Which autonomous community spent the most water in 2020?
• Which autonomous community had the lowest consumption in 2020? Why do you think this is?
• Which number is closest to your region's consumption in 2020?
Language Bank
Speaking. Go over the tips for saving water with a friend and say which ones you like.

Writing. Organise the tips into two groups: the ones you like and the ones you don’t. Write a sentence explaining why.
When we use water at home, we are using it for domestic purposes, for example, when we drink, take a shower, brush our teeth, wash dishes and clothes, etc.
Water saving tips
Instead of taking a bath, take a shower. Remember to turn off the tap while applying soap.
Run the washing machine and dishwasher only when they are completely full.

Don't leave the tap running while soaping the dishes. Use less detergent to pollute less.
Turn off the tap when brushing your teeth.

1 What two uses do people make of water?
2
Before I thought, now I think Your local environmental council has asked all local schools to submit ideas on how to improve the public's use of water. Write a letter to the councillor explaining four ideas and why they would be beneficial to your local area.
3 Think about the water saving tips and complete this table in your notebook. What aspects of your daily life do you think you could improve? Could you help your family to follow these tips too?
Tips I always do it
I sometimes do it I never do it ? ? ? ?
Use glasses or bottles for drinking. Do not pour directly from the tap.
To better understand how to save water, watch the video "Domestic uses of water" on anayaeducacion. es.

Take note!
Women and girls are responsible for collecting water in 8 out of 10 households without access to piped water.







