section one introduction
The toxic trail of clothes
1
2
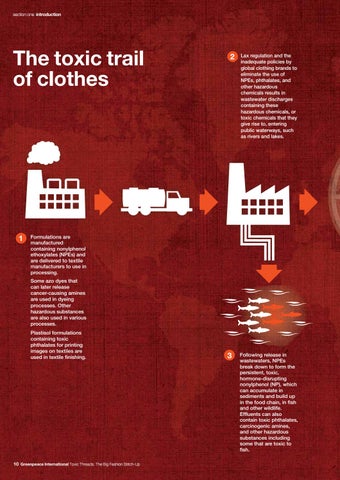
Lax regulation and the inadequate policies by global clothing brands to eliminate the use of NPEs, phthalates, and other hazardous chemicals results in wastewater discharges containing these hazardous chemicals, or toxic chemicals that they give rise to, entering public waterways, such as rivers and lakes.
Formulations are manufactured containing nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPEs) and are delivered to textile manufacturers to use in processing. Some azo dyes that can later release cancer-causing amines are used in dyeing processes. Other hazardous substances are also used in various processes. Plastisol formulations containing toxic phthalates for printing images on textiles are used in textile finishing.
10 Greenpeace International Toxic Threads: The Big Fashion Stitch-Up
3
Following release in wastewaters, NPEs break down to form the persistent, toxic, hormone-disrupting nonylphenol (NP), which can accumulate in sediments and build up in the food chain, in fish and other wildlife. Effluents can also contain toxic phthalates, carcinogenic amines, and other hazardous substances including some that are toxic to fish.