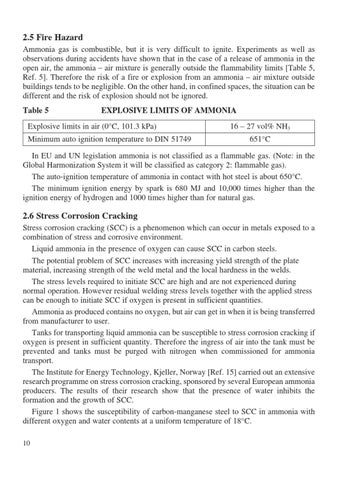
2.5 Fire Hazard Ammonia gas is combustible, but it is very difficult to ignite. Experiments as well as observations during accidents have shown that in the case of a release of ammonia in the open air, the ammonia – air mixture is generally outside the flammability limits [Table 5, Ref. 5]. Therefore the risk of a fire or explosion from an ammonia – air mixture outside buildings tends to be negligible. On the other hand, in confined spaces, the situation can be different and the risk of explosion should not be ignored. Table 5
EXPLOSIVE LIMITS OF AMMONIA
Explosive limits in air (0°C, 101.3 kPa) Minimum auto ignition temperature to DIN 51749
16 – 27 vol% NH3 651°C
In EU and UN legislation ammonia is not classified as a flammable gas. (Note: in the Global Harmonization System it will be classified as category 2: flammable gas). The auto-ignition temperature of ammonia in contact with hot steel is about 650°C. The minimum ignition energy by spark is 680 MJ and 10,000 times higher than the ignition energy of hydrogen and 1000 times higher than for natural gas.
2.6 Stress Corrosion Cracking Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is a phenomenon which can occur in metals exposed to a combination of stress and corrosive environment. Liquid ammonia in the presence of oxygen can cause SCC in carbon steels. The potential problem of SCC increases with increasing yield strength of the plate material, increasing strength of the weld metal and the local hardness in the welds. The stress levels required to initiate SCC are high and are not experienced during normal operation. However residual welding stress levels together with the applied stress can be enough to initiate SCC if oxygen is present in sufficient quantities. Ammonia as produced contains no oxygen, but air can get in when it is being transferred from manufacturer to user. Tanks for transporting liquid ammonia can be susceptible to stress corrosion cracking if oxygen is present in sufficient quantity. Therefore the ingress of air into the tank must be prevented and tanks must be purged with nitrogen when commissioned for ammonia transport. The Institute for Energy Technology, Kjeller, Norway [Ref. 15] carried out an extensive research programme on stress corrosion cracking, sponsored by several European ammonia producers. The results of their research show that the presence of water inhibits the formation and the growth of SCC. Figure 1 shows the susceptibility of carbon-manganese steel to SCC in ammonia with different oxygen and water contents at a uniform temperature of 18°C. 10