3 minute read
The durability of the adhesive bond over time
from EstrattoVeneziani_EN
by Grupo Asís
29 28
Advertisement
30
31
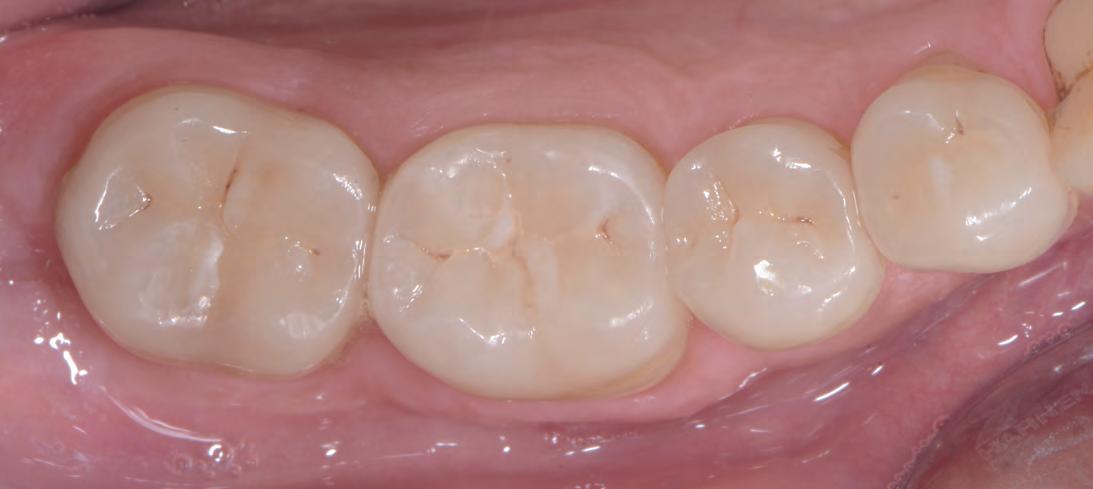
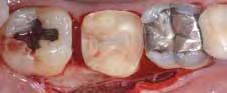
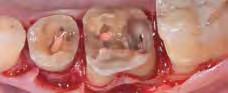
Figures 28-30 The same restorative approach – simultaneous with Q3 – involves quadrant 4 of which one can see the ultraconservative preparations (Fig. 28), a detail of the ultra-thin table top of tooth 46 (Fig. 29) and the quadrant after adhesive luting of all the restorations (Fig. 30). Figures 31 and 32 The clinical images, in the oral cavity, of quadrant 4 (Fig. 31) and quadrant 3 restorations (Fig. 27) show excellent morphological and esthetic integration with adequate interproximal contact points and excellent marginal fit.
73d 73e
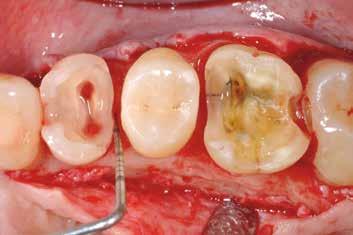
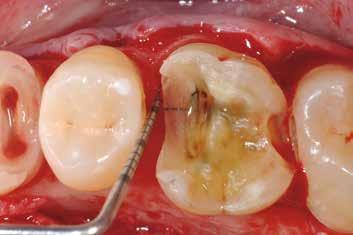
Figure 73a-f illustrates a clinical case in which the surgical exposure of the margins is necessary following clinical and radiographic assessment of distance between the cervical margins and the periodontal attachment complex.
73f

Three different clinical situations are thus identified by using the two aforementioned parameters, ranked according to their severity as grade 1, 2, and 3 (Table 16).
Table 16 - CLASSIFICATION OF RESTORATIONS WITH SUBGINGIVAL MARGINS (M Veneziani, 2010)[28]
GRADE 1 The dam correctly inverted in the sulcus is sufficient to isolate the properly prepared cervical margin of the cavity.
GRADE 2
The dam does not allow the field to be correctly isolated, but the supracrestal tissue attachment is respected (margin – attachment complex distance >2 mm, or margin-bone crest >3 mm). This situation is made possible by the fact that especially in the posterior regions, in particular in patients with thick periodontal biotype, not infrequently the gingival sulcus has a probing depth equal to or greater than 3 mm[127] .
GRADE 3
The cavity cervical margin (following carious lesion or coronal fracture) is clearly sub-gingival with violation of the supracrestal tissue attachment (margin-attachment complex distance <2 mm, or margin-bone crest <3 mm).
A differentiated therapeutic approach must be applied for the three different clinical situations mentioned above with the operational sequences illustrated in Table 17.
Table 17 - DIFFERENTIATED THERAPEUTICAL APPROACH FOR GRADE 1, 2 AND 3 (M Veneziani, 2010)[28]
GRADE 1
Deep margin elevation with flowable composite with maximum thickness 1-1.5 mm plus build-up, preparation and impression. Adhesive cementation of restoration after 7 days.
GRADE 2
Surgical exposure of the margin plus flowable composite at the level of the cervical margin with thickness 0.5 mm plus build-up, preparation and immediate impression. Adhesive cementation of restoration after 7 days at the same time as removing the sutures.
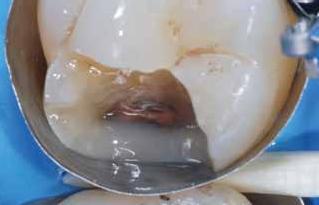
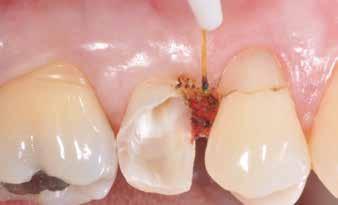
GRADE 3
Procedure for clinical crown lengthening (osseous resective surgery) with three different operational sequences according to the different clinical situations: a) immediate impression, b) early impression, c) delayed impression.
GRADE 3A
Clinical crown lengthening procedure, placement of the rubber dam, flowable composite at cervical level in controlled thickness 0.5 mm plus build-up, preparation plus immediate post-operative impression. Adhesive cementation after 7 days at the same time as suture removal. Approach generally applied to cases of single (vital or endodontically treated) teeth.
GRADE 3B
Clinical crown lengthening procedure, pre-endodontic restoration (or total build-up in composite) plus root canal plus early impression after 3 weeks (tissue re-epithelisation time)[122] after placing the dam, flowable composite at cervical level in controlled thickness 0.5 mm + build-up (or only closing the access cavity in case of total build-up), preparation for indirect restoration. Adhesive cementation after 7 days. Approach generally applied to cases of single teeth that are to be endodontically treated.
GRADE 3C
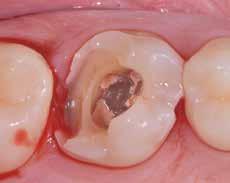
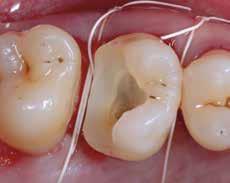
Clinical crown lengthening procedure, provisional (pre-endodontic) restorations in glass ionomer cement or total adhesive build-up in composite + delayed impression from 8 to 12 weeks (tissue maturation time) after placing the dam, cervical flowable composite in controlled thickness of 0.5 mm plus build-up (or only closing the access cavity in case of total buildup), preparation for indirect restoration. Adhesive cementation after 7-12 days. Approach generally applied to cases of multiple restorations, quadrant rehabilitations, complex cases with possible prosthetic treatment of some teeth.