Clinical Evaluation Report
Rev: 1 Date: 01/10/2019
Air Ionization
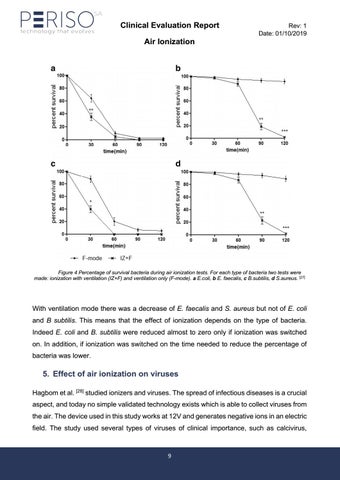
Figure 4 Percentage of survival bacteria during air ionization tests. For each type of bacteria two tests were made: ionization with ventilation (IZ+F) and ventilation only (F-mode). a E.coli, b E. faecalis, c B.subtilis, d S.aureus. [27]
With ventilation mode there was a decrease of E. faecalis and S. aureus but not of E. coli and B subtilis. This means that the effect of ionization depends on the type of bacteria. Indeed E. coli and B. subtilis were reduced almost to zero only if ionization was switched on. In addition, if ionization was switched on the time needed to reduce the percentage of bacteria was lower.
5. Effect of air ionization on viruses Hagbom et al. [28] studied ionizers and viruses. The spread of infectious diseases is a crucial aspect, and today no simple validated technology exists which is able to collect viruses from the air. The device used in this study works at 12V and generates negative ions in an electric field. The study used several types of viruses of clinical importance, such as calcivirus,
9