AQA Chemistry A-level Year 2
Example
Notes The units of R are J K−1 mol−1 so, in this equation, after multiplying by temperature the units of Ea are J mol−1.
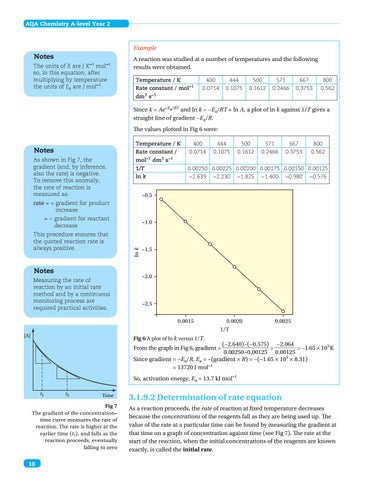
A reaction was studied at a number of temperatures and the following results were obtained. Temperature / K Rate constant / mol−1 dm3 s−1
400 444 500 571 667 800 0.0714 0.1075 0.1612 0.2466 0.3753 0.562
Since k = Ae−Ea/RT and ln k = −Ea/RT + ln A, a plot of ln k against 1/T gives a straight line of gradient −Ea/R. The values plotted in Fig 6 were: Temperature / K 400 444 500 571 667 800 Rate constant / 0.0714 0.1075 0.1612 0.2466 0.3753 0.562
Notes As shown in Fig 7, the gradient (and, by inference, also the rate) is negative. To remove this anomaly, the rate of reaction is measured as:
mol−1 dm3 s−1 1/T ln k
0.00250 0.00225 0.00200 0.00175 0.00150 0.00125 −2.639 −2.230 −1.825 −1.400 −0.980 −0.576
–0.5
rate = + g radient for product increase = − gradient for reactant decrease
This procedure ensures that the quoted reaction rate is always positive.
Notes Measuring the rate of reaction by an initial rate method and by a continuous monitoring process are required practical activities.
–1.0
In k
–1.5
–2.0
–2.5 0.0015
[A]
0.0020 1/T
0.0025
Fig 6 A plot of ln k versus 1/T.
(−2.640)−(−0.575) −2.064 = = −1.65 × 103 K 0.00250−0.00125 0.00125 Since gradient = −Ea/R, Ea = −(gradient × R) = −(−1.65 × 103 × 8.31) = 13720 J mol−1
From the graph in Fig 6, gradient =
So, activation energy, Ea = 13.7 kJ mol−1 t1
t2
Time
Fig 7 The gradient of the concentration– time curve measures the rate of reaction. The rate is higher at the earlier time (t1), and falls as the reaction proceeds, eventually falling to zero
3.1.9.2 Determination of rate equation As a reaction proceeds, the rate of reaction at fixed temperature decreases because the concentrations of the reagents fall as they are being used up. The value of the rate at a particular time can be found by measuring the gradient at that time on a graph of concentration against time (see Fig 7). The rate at the start of the reaction, when the initial concentrations of the reagents are known exactly, is called the initial rate.
10
89518_P006_015.indd 10
8/18/16 2:49 PM